一、什么是 platform总线
根据Linux设备模型可知,一个现实的Linux设备和驱动通常都需要挂接在一种总线上,对于本身依附于PCI、USB等的设备而言,这自然不是问题,但是在嵌入式系统里面,SoC系统中集成的独立的外设控制器、挂接在 SoC 内存空间的外设等却不依附于此类总线。
基于这一背景,Linux设计了一种虚拟的总线,称为platform总线,相应的设备称为platform_device,而驱动称为platform_drive
- 平台(platform)总线是一种虚拟的总线,在 /sys/bus/platform 目录可以看到。
- 平台总线三要素:平台总线、平台设备、平台驱动
- 平台总线原则:先分离,后合并
二、为什么需要platform总线
1、PCI/PCIE 总线是x86架构的脊椎,且拥有探测pci/pcie 设备的能力。PC上的usb总线控制器,对上是一个pcie设备,对下则是usb总线的控制器。等于pcie总线下扩展出了新的usb总线。usb总线也是有硬件探测能力的。个人电脑几乎所有重要的外设:硬盘、u盘、键盘、鼠标、声卡、显卡,都是pcie或者usb设备。再加上BIOS的帮助,普通pc的内核几乎不需要程序员手动注册一个设备信息,自己就能探测就出来当前计算机插了哪些设备。
2、手机、平板等大量使用SOC的非X86架构的嵌入式系统,它自己的usb控制器、i2c控制器、声卡控制器、lcd驱动器、存储控制器(一般是flash控制器,个别SOC也有sata控制器)等,都不再是X86架构下的pci设备了,靠硬件自己是无法探测的。此时就需要程序员自己手动写代码或者配置文件,来注册这些device的信息。
假如是i2c 设备、spi设备,硬件也没有探测设备属性的能力,程序员手动注册device就注册了吧,起码知道是要注册到那条bus上去。可偏偏这些SOC外设并没有一个统一的总线名称,ARM上叫AHB、 APB ,powerpc上叫CCB,甚至隔个几年又会发明新的叫法。platform 这条虚拟的bus,就是用来统一维护此类device的bus。3、另一方面,随着设备SOC的升级换代,按照原始的非platform 总线方法的驱动就得重新写一遍,做着大量的重复工作。所以为了提高效率,因为升级的SOC芯片只有寄存器地址不一样,如果将与硬件有关的代码(platform_device)和驱动代码(platform_driver)分开,升级soc后,因为驱动方式一样,只需要修改与硬件有关的代码就可以,实现一个驱动控制多个设备。
总结:platform 总线 是一种虚拟、抽象出来的总线,实际中并不存在这样的总线,主要作用就是 解耦
三、platform总线工作流程
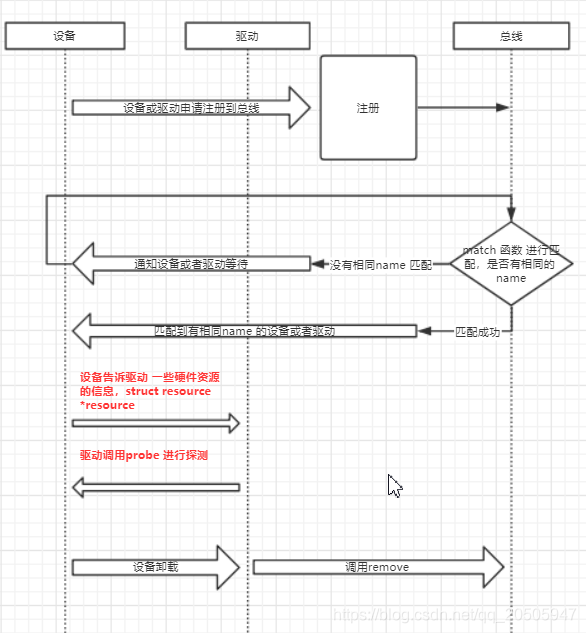
设备(或驱动)注册的时候,都会引发总线调用自己的match函数来寻找目前platform总线是否挂载有与该设备(或驱动)名字匹配的驱动(或设备),如果存在则将双方绑定;
如果先注册设备,驱动还没有注册,那么设备在被注册到总线上时,将不会匹配到与自己同名的驱动,然后在驱动注册到总线上时,因为设备已注册,那么总线会立即匹配与绑定这时的同名的设备与驱动,再调用驱动中的probe函数等;
如果是驱动先注册,同设备驱动一样先会匹配失败,匹配失败将导致它的probe函数暂不调用,而是要等到设备注册成功并与自己匹配绑定后才会调用。
3.1、平台总线下重要的两个结构体
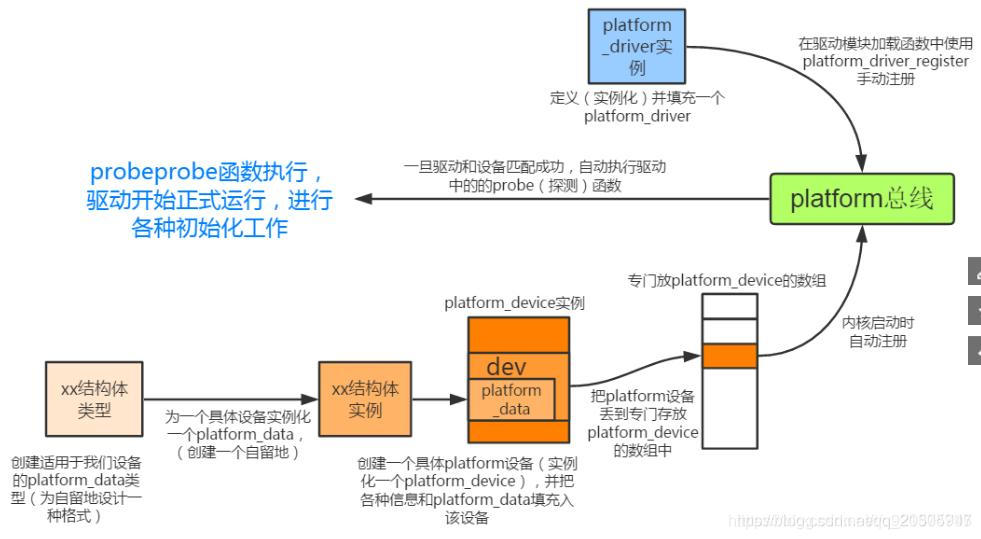
platform_device(设备)
platform_driver (驱动)
//include\linux\platform_device.h
struct platform_device { // platform总线设备
const char * name; // 平台设备的名字
int id; // ID 是用来区分如果设备名字相同的时候(通过在后面添加一个数字来代表不同的设备,因为有时候有这种需求)
struct device dev; // 内置的device结构体
u32 num_resources; // 资源结构体数量
struct resource * resource; // 指向一个资源结构体数组
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry; // 用来进行与设备驱动匹配用的id_table表
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata; // 自留地 添加自己的东西
};
struct resource { // 资源结构体
resource_size_t start; // 资源的起始值,物理地址
resource_size_t end; // 资源的结束值,物理地址
const char *name; // 资源名
//a -- flags为IORESOURCE_MEM 时,start 、end 分别表示该platform_device占据的内存的开始地址和结束值;
//b -- flags为 IORESOURCE_IRQ 时,start 、end 分别表示该platform_device使用的中断号的开始地址和结束值;
unsigned long flags; // 资源的标示,用来识别不同的资源
struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child; // 资源指针,可以构成链表
};// include\linux\platform_device.h
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *); // 这个probe函数其实和 device_driver中的是一样的功能,但是一般是使用device_driver中的那个
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *); // 卸载平台设备驱动的时候会调用这个函数,但是device_driver下面也有,具体调用的是谁这个就得分析了
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver; // 内置的device_driver 结构体
const struct platform_device_id *id_table; // 该设备驱动支持的设备的列表 他是通过这个指针去指向 platform_device_id 类型的数组
};3.2.platform_device与platform_driver的匹配方式
- 基于ACPI风格的匹配;
- 基于设备树
- 匹配ID表(即platform_device设备名是否出现在platform_driver的ID表内);
- 匹配platform_device设备名和驱动的名字。
3.3.匹配过程按优先顺序如下:
- 比较 platform_dev.driver_override 和 platform_driver.drv->name
- 比较 platform_dev.dev.of_node的compatible属性 和 platform_driver.drv->of_match_table
- 比较 platform_dev.name 和 platform_driver.id_table->name
- 比较 platform_dev.name 和 platform_driver.drv->name
- 有一个成功, 即匹配成功
platform_bus_type
在设备总线驱动模型的中,BUS通过它的match函数,将注册到bus中的device与driver进行配对,那么每一个不同的bus 都有自己的match函数
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = { .name = "platform", .dev_attrs = platform_dev_attrs, .match = platform_match, .uevent = platform_uevent, .pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops, };platform_match
platform_device与platform_driver的匹配 的重要函数 platform_match
/** * platform_match - bind platform device to platform driver. * @dev: device. * @drv: driver. * * Platform device IDs are assumed to be encoded like this: * "<name><instance>", where <name> is a short description of the type of * device, like "pci" or "floppy", and <instance> is the enumerated * instance of the device, like '0' or '42'. Driver IDs are simply * "<name>". So, extract the <name> from the platform_device structure, * and compare it against the name of the driver. Return whether they match * or not. */ static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv) { struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev); struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv); /* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */ if (pdev->driver_override) return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name); /* Attempt an OF style match first */ if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))//第一种匹配方式,OF类型匹配,设备树采用的匹配方式 return 1; /* Then try ACPI style match */ if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))//第二种匹配方式,ACPI匹配 return 1; /* Then try to match against the id table */ if (pdrv->id_table) return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;//第三种匹配方式,id_table匹配 /* fall-back to driver name match */ return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);//第四种匹配方式,直接比较驱动和设备的name字段 }
3.4.从内核态分析platform配对流程 (参考链接 https://www.pianshen.com/article/1414317470/)
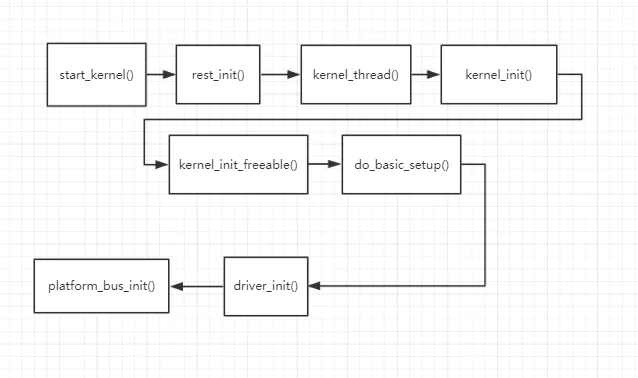
初始化platform总线
platform_bus_init()
--> device_register(&platform_bus)
--> bus_register(&platform_bus_type)
--> platform_bus_type ==> platform_match(dev和drv的配对原则)
注册device
platform_device_register(struct platform_device *dev)
--> platform_device_add(pdev)
--> device_add(&pdev->dev)
--> bus_probe_device(dev)
--> device_initial_probe(dev)
--> __device_attach(dev, true)
--> bus_for_each_drv(dev->bus, NULL, &data, __device_attach_driver)
--> __device_attach_driver
--> driver_match_device(drv, dev) ==> 匹配driver,匹配成功才能往下走
--> driver_probe_device(drv, dev)
--> really_probe(dev, drv)
--> dev->bus->probe(dev) / drv->probe(dev)
注册driver
platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv)
--> __platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE)
--> driver_register(&drv->driver)
--> bus_add_driver(drv)
--> driver_attach(drv)
--> bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach)
--> __driver_attach
--> driver_match_device(drv, dev) ==> 匹配driver,匹配成功才能往下走
--> driver_probe_device(drv, dev)
--> really_probe(dev, drv)
--> dev->bus->probe(dev) / drv->probe(dev)
四、实例
device.c
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <linux/ioport.h> // 设备资源 static struct resource hello_resource[] = { [0] ={ .start = 0x100000, // 设备的 起始地址 .end = 0x100000 + 0x4, // 结束地址 .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM, }, [1] ={ .start = 0x2000000, .end = 0x2000000 + 0x14, .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM, } }; static void hello_release(struct device *dev) { printk("hello_release\n"); return ; } static struct platform_device hello_device= { .name = "hwlloworld", /* if (pdev->id != -1) // 如果不是-1 对name编号 dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d", pdev->name, pdev->id); else // -1时直接是名字 dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, pdev->name); */ .id = -1, // 一般设置为-1 .dev.release = hello_release, .num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(hello_resource), //是求设备结构体中设备的个数 .resource = hello_resource, }; static int hello_init(void) { printk("hello_init"); return platform_device_register(&hello_device); } static void hello_exit(void) { printk("hello_exit"); platform_device_unregister(&hello_device); return; } MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);
driver.c
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/platform_device.h> #include <asm/io.h> static int major = 250; static int minor=0; static dev_t devno; static struct class *cls; static struct device *test_device; #define TCFG0 0x0000 #define TCFG1 0x0004 #define TCON 0x0008 #define TCNTB0 0x000C #define TCMPB0 0x0010 static unsigned int *gpd0con; static void *timer_base; #define MAGIC_NUMBER 'k' #define TEST_ON _IO(MAGIC_NUMBER ,0) #define TEST_OFF _IO(MAGIC_NUMBER ,1) #define TEST_FREQ _IO(MAGIC_NUMBER ,2) static void hello_world_init(void) { writel ((readl(gpd0con)&~(0xf<<0)) | (0x2<<0),gpd0con); writel ((readl(timer_base +TCFG0 )&~(0xff<<0)) | (0xff <<0),timer_base +TCFG0); writel ((readl(timer_base +TCFG1 )&~(0xf<<0)) | (0x2 <<0),timer_base +TCFG1 ); writel (500, timer_base +TCNTB0 ); writel (250, timer_base +TCMPB0 ); writel ((readl(timer_base +TCON )&~(0xf<<0)) | (0x2 <<0),timer_base +TCON ); } void hello_world_on(void) { writel ((readl(timer_base +TCON )&~(0xf<<0)) | (0x9 <<0),timer_base +TCON ); } void hello_world_off(void) { writel ((readl(timer_base +TCON )&~(0xf<<0)) | (0x0 <<0),timer_base +TCON ); } static void hello_world_unmap(void) { iounmap(gpd0con); iounmap(timer_base); } static int hello_world_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filep) { hello_world_on(); return 0; } static int hello_world_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filep) { hello_world_off(); return 0; } #define BEPP_IN_FREQ 100000 static void hello_world_freq(unsigned long arg) { writel(BEPP_IN_FREQ/arg, timer_base +TCNTB0 ); writel(BEPP_IN_FREQ/(2*arg), timer_base +TCMPB0 ); } static long hello_world_ioctl(struct file *filep, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) { switch(cmd) { case TEST_ON: hello_world_on(); break; case TEST_OFF: fhello_world_off(); break; case TEST_FREQ: hello_world_freq( arg ); break; default : return -EINVAL; } return 0; } static struct file_operations hello_world_ops= { .open = hello_world_open, .release = hello_world_release, .unlocked_ioctl = hello_world_ioctl, }; static int bhello_world_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) { int ret; printk("match ok!"); gpd0con = ioremap(pdev->resource[0].start,pdev->resource[0].end - pdev->resource[0].start); timer_base = ioremap(pdev->resource[1].start, pdev->resource[1].end - pdev->resource[1].start); devno = MKDEV(major,minor); ret = register_chrdev(major,"hello_world",&hello_world_ops); cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "myclass"); if(IS_ERR(cls)) { unregister_chrdev(major,"hello_world"); return -EBUSY; } test_device = device_create(cls,NULL,devno,NULL,"hello_world");//mknod /dev/hello if(IS_ERR(test_device)) { class_destroy(cls); unregister_chrdev(major,"hello_world"); return -EBUSY; } fhello_world_init(); return 0; } static int hello_world_remove(struct platform_device *pdev) { hello_world_unmap(); device_destroy(cls,devno); class_destroy(cls); unregister_chrdev(major,"hello_world"); return 0; } static struct platform_driver hello_world_driver= { .driver.name = "hello_world", .probe = hello_world_probe, .remove = hello_world_remove, }; static int hello_world_init(void) { printk("hello_worldp_init"); return platform_driver_register(&hello_world_driver); } static void hello_world_exit(void) { printk("hello_world_exit"); platform_driver_unregister(&hello_world_driver); return; } MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); module_init(hello_worldp_init); module_exit(hello_world_exit);
编译驱动比较常用的 Makefile 格式
# 编译arm 版本驱动时 编译工具需要设置为 arm编译工具 CROSS_COMPILE:= arm-linux- ARCH:= arm CC:= $(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc LD:= $(CROSS_COMPILE)ld ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) obj-m:=device.o driver.o $(info "hello") else # 内核所在的位置,需要编译arm 版本的驱动时,需要将文件位置设置为需要的内核源文件 KDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build PWD:=$(shell pwd) all: $(info "1st") make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean: rm -f *.ko *.o *.symvers *.mod.c *.mod.o *.order endif
引入platform模型符合Linux 设备模型 —— 总线、设备、驱动,设备模型中配套的sysfs节点都可以用,方便我们的开发;当然你也可以选择不用,不过就失去了一些platform带来的便利;
设备驱动中引入platform 概念,隔离BSP和驱动。在BSP中定义platform设备和设备使用的资源、设备的具体匹配信息,而在驱动中,只需要通过API去获取资源和数据,做到了板相关代码和驱动代码的分离,使得驱动具有更好的可扩展性和跨平台性。






















 603
603











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








