看了 Loiane Groner 著的《学习JavaScript数据结构与算法》一书,自己写篇博客对着敲敲代码:
全文包含十个部分,分别是:数组、栈、队列、链表、集合、字典与散列表、树、图、排序和搜索算法、算法补充知识。
知识点其他部分参考:
学习JavaScript数据结构和算法(部分一)
学习JavaScript数据结构和算法(部分二)
学习JavaScript数据结构和算法(部分三)
学习JavaScript数据结构和算法(部分四)
6、字典和散列表
集合、字典和散列表可以存储不重复的值。在集合中,以[值,值]的形式存储元素,我们感兴趣的是每个值的本身,并把它们当做主要元素。在字典和散列表中,我们使用 [键 , 值] 的形式来存储数据。
6.1 字典(Map类,它和Set类很相似)
实现代码:
/*
字典所能使用的方法:
set(key,value):向字典中添加新元素。
remove(key):通过使用键值来从字典中移除键值对应的数据值。
has(key):如果某个键值存在于这个字典中,则返回true,反之则返回false。
get(key):通过键值查找特定的数值并返回。
clear():将这个字典中的所有元素全部删除。
size():返回字典所包含元素的数量。与数组的length属性类似。
keys():将字典所包含的所有键名以数组形式返回。
values():将字典所包含的所有数值以数组形式返回。
*/
function Dictionary(){
let items = {};
//声明方法
//1、has方法
this.has = function(key){
return items.hasOwnProperty(key);
};
//2、set方法
this.set = function(key, value){
items[key] = value; //添加新值,或更新已有的值
};
//3、remove方法
this.remove = function(key){
if(this.has(key)){
delete items[key];
return true;
}
return false;
};
//4、get方法
this.get = function(key){
return this.has(key) ? items[key] : undefined ;
};
//5、values方法
this.values = function(){
let values = [];
for(let key in items){
if(this.has(key)){
values.push(items[key]);
}
}
return values ;
};
//6、clear方法
this.clear = function(){
items = {};
};
//7、size方法
this.size = function(){
let count = 0;
for(let key in items){
if(this.has(key)){
count++;
}
}
return count;
};
//8、keys方法
this.keys = function(){
let keys= [];
for(let key in items){
if(this.has(key)){
keys.push(key);
}
}
return keys;
}
//9、getItems方法
this.getItems = function(){
return items;
}
}
//使用Dictionary类
var dictionary = new Dictionary();
dictionary.set('Gandalf', 'gandalf@email.com');
dictionary.set('John', 'johnsnow@email.com');
dictionary.set('Tyrion', 'tyrion@email.com');
console.log(dictionary.has('Gandalf')); //true
console.log(dictionary.size()); //3
console.log(dictionary.keys()); //["Gandalf", "John", "Tyrion"]
console.log(dictionary.values()); //["gandalf@email.com","johnsnow@email.com","tyrion@email.com"]
console.log(dictionary.get('Tyrion')); //tyrion@email.com
dictionary.remove('John');
console.log(dictionary.keys()); //["Gandalf", "Tyrion"]
console.log(dictionary.values()); //["gandalf@email.com", "tyrion@email.com"]
console.log(dictionary.getItems()); //Object {Gandalf: "gandalf@email.com", Tyrion: "tyrion@email.com"} 6.2 散列表
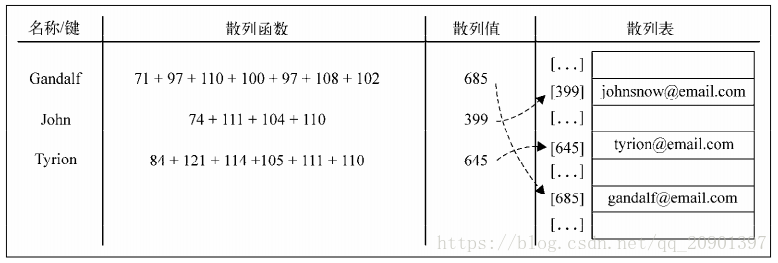
HashTable类是Dictionary类的一种散列表实现方式。散列算法的作用是尽可能快地在数据结构中找到一个值。散列函数的作用是给定一个键值,然后返回值在表中的地址。在散列表上插入、 删除和取用数据都非常快, 但是对于查找操作来说却效率低下, 比如查找最大最小值。 得求助于其他数据结构, 二叉查找树是一个很好的选择。
举例:使用在6.1中的电子邮件地址簿。我们将要使用最常见的散列函数——“lose lose”散列函数,方法是简单地将每个键值中的每个字母的ASCII值相加。
6.2.1 创建一个散列表:HashTable类
//基于数组进行设计
function HashTable(){
this.table = [];
//散列函数,HashTable类中的一个私有方法
this.loseloseHashCode = loseloseHashCode; //散列函数
this.put = put; //put(key,value),向散列表增加一个新的项,也能更新散列表
this.remove = remove; //remove(key),根据键值从散列表中移除值
this.get = get; //get(key), 返回根据键值检索到的特定的值
}
function loseloseHashCode(key){
let hash = 0;
for(let i=0; i<key.length; i++){
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37; //37为一般定义为table的长度,余数结果就是0-36
}
function put(key, value){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
console.log(position + ' - ' + key);
this.table[position] = value;
}
function get(key){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
return this.table[position];
}
/*
对于HashTable类来说,不需要像ArrayList类一样从table数组中将位置也移除,赋值undefined即可。
*/
function remove(key){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
this.table[position] = undefined;
}
//测试
let hash = new HashTable();
hash.put('Gandalf', 'gandalf@email.com'); //19 - Gandalf
hash.put('John', 'johnsnow@email.com'); //29 - John
hash.put('Tyrion', 'tyrion@email.com'); //16 - Tyrion
console.log(hash.get('Gandalf')); //gandalf@email.com
console.log(hash.get('Loiane')); //undefined
hash.remove('Gandalf');
console.log(hash.get('Gandalf')); //undefined6.2.2 散列碰撞: 不同的值在散列表中对应相同位置的时候,我们称这种情况为散列碰撞。若是不做处理,则后面的值会覆盖前面的值。解决散列碰撞的常用方法有:线性探测法(寻址法)、再哈希法、拉链法、建立一个公共溢出区。
//举例
let hash = new HashTable();
hash.put('Tyrion', 'tyrion@email.com');
hash.put('Aaron', 'aaron@email.com');
hash.put('Donnie', 'donnie@email.com');
hash.put('Ana', 'ana@email.com');
hash.put('Jonathan', 'jonathan@email.com');
hash.put('Jamie', 'jamie@email.com');
hash.put('Sue', 'sue@email.com');
hash.put('Mindy', 'mindy@email.com');
hash.put('Paul', 'paul@email.com');
/* 输出
16 - Tyrion
16 - Aaron
13 - Donnie
13 - Ana
5 - Jonathan
5 - Jamie
5 - Sue
32 - Mindy
32 - Paul
*/
//hash中table实际的值:
/*
5: sue@email.com
13: ana@email.com
16: aaron@email.com
32: paul@email.com
*/- 线性探测法: 当发生碰撞时,检测下一个位置是否为空。如果为空,就将此数据存入该位置;如果不为空,则会继续检查下一个位置,直到找到下一个空的位置为止。
//线性探测法解决散列碰撞
function XZHashTable(){
this.dataStore = []; //在对应的实际位置存储键
this.table = [];
//散列函数,HashTable类中的一个私有方法
this.loseloseHashCode = loseloseHashCode; //散列函数
this.putXZ = putXZ; //put(key,value),向散列表增加一个新的项,也能更新散列表
this.removeXZ = removeXZ; //remove(key),根据键值从散列表中移除值
this.getXZ = getXZ; //get(key), 返回根据键值检索到的特定的值
}
function loseloseHashCode(key){
let hash = 0;
for(let i=0; i<key.length; i++){
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37; //37为一般定义为table的长度,余数结果就是0-36
}
function putXZ(key, value){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
while(this.dataStore[position] !== undefined){
position++;
}
console.log(position + ' - ' + key);
this.dataStore [position] = key;
this.table[position] = value;
}
function getXZ(key){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
while(this.dataStore[position] !== undefined && this.dataStore[position] !== key){
position++;
}
return this.table[position];
}
function removeXZ(key){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
while(this.dataStore[position] !== undefined && this.dataStore[position] !== key){
position++;
}
this.table[position] = undefined;
}
//测试
let hash = new XZHashTable();
hash.putXZ('Tyrion', 'tyrion@email.com');
hash.putXZ('Aaron', 'aaron@email.com');
hash.putXZ('Donnie', 'donnie@email.com');
hash.putXZ('Ana', 'ana@email.com');
hash.putXZ('Jonathan', 'jonathan@email.com');
hash.putXZ('Jamie', 'jamie@email.com');
hash.putXZ('Sue', 'sue@email.com');
hash.putXZ('Mindy', 'mindy@email.com');
hash.putXZ('Paul', 'paul@email.com');
/* 输出
16 - Tyrion
17 - Aaron
13 - Donnie
14 - Ana
5 - Jonathan
6 - Jamie
7 - Sue
32 - Mindy
33 - Paul
*/
console.log(hash.getXZ('Mindy')); //mindy@email.com,碰撞得到解决
console.log(hash.getXZ('Loiane')); //undefined
hash.removeXZ('Donnie');
console.log(hash.getXZ('Donnie')); //undefined再哈希法: 当发生冲突时,使用第二个、第三个哈希函数计算地址,直到无冲突为止。缺点:计算时间增加。
建立一个公共溢出区: 假设哈希函数的值域为 [0, m-1] ,则设向量HashTable[0, m-1]为基本表,另外设立存储空间向量OverTable[0…v]用以存储发生冲突的记录。
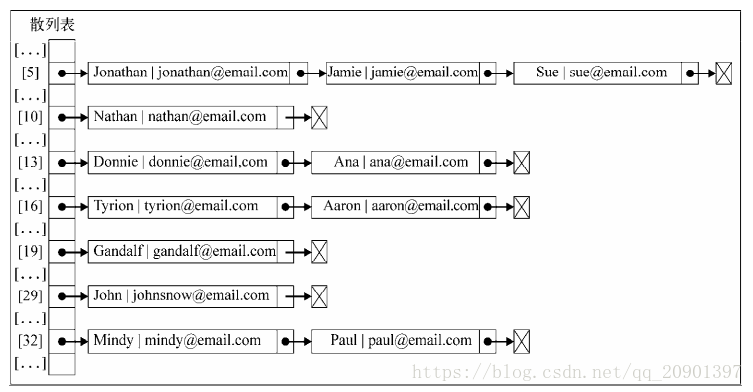
拉链法: 将所有关键字的哈希值相等的记录存储在同一线性链表中,如下:
在位置13、16和32上,将会包含多个元素的LinkedList实例;在没发生哈希碰撞的位置上,只包含单个元素的LinkedList实例。代码实现线性链表的功能,可以考虑两种方式,第一种数组,第二种使用单向链表。数组查找快,删除麻烦;链表查找慢,删除快。下面使用链表解决:
//拉链法解决散列碰撞
function LLHashTable(){
this.table = [];
//定义一个新的辅助类来表示将要加入LinkedList实例的元素。
this.ValuePair = ValuePair;
//散列函数,HashTable类中的一个私有方法
this.loseloseHashCode = loseloseHashCode; //散列函数
this.putLL = putLL; //put(key,value),向散列表增加一个新的项,也能更新散列表
this.removeLL = removeLL; //remove(key),根据键值从散列表中移除值
this.getLL = getLL; //get(key), 返回根据键值检索到的特定的值
}
function ValuePair(key, value){ //加入LinkedList实例的元素
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.toString = function(){
return '['+ this.key + ' - ' + this.value +']';
}
}
function loseloseHashCode(key){
let hash = 0;
for(let i=0; i<key.length; i++){
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37; //37为一般定义为table的长度,余数结果就是0-36
}
function putLL(key, value){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
if(this.table[position] == undefined){
this.table[position] = new LinkedList();
}
this.table[position].append(new this.ValuePair(key, value));
}
function getLL(key){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
if(this.table[position] !== undefined){
//遍历链表寻找键值
let current = this.table[position].getHead();
while(current){
if(current.element.key == key){
return current.element.value;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
return undefined;
}
function removeLL(key){
let position = this.loseloseHashCode(key);
if(this.table[position] !== undefined){
//遍历链表寻找键值
let current = this.table[position].getHead();
while(current){
if(current.element.key == key){
this.table[position].remove(current.element);
if(this.table[position] == undefined){
this.table[position] = undefined;
}
return true; //成功删除
}
current = current.next;
}
}
return false;
}
//测试
let hash = new LLHashTable();
hash.putLL('Tyrion', 'tyrion@email.com');
hash.putLL('Aaron', 'aaron@email.com');
hash.putLL('Donnie', 'donnie@email.com');
hash.putLL('Ana', 'ana@email.com');
hash.putLL('Jonathan', 'jonathan@email.com');
hash.putLL('Jamie', 'jamie@email.com');
hash.putLL('Sue', 'sue@email.com');
hash.putLL('Mindy', 'mindy@email.com');
hash.putLL('Paul', 'paul@email.com');
console.log(hash.getLL('Mindy')); //mindy@email.com,碰撞得到解决
console.log(hash.getLL('Loiane')); //undefined
console.log(hash.getLL('Aaron')); //aaron@email.com
console.log(hash.getLL('Sue')); //sue@email.com
hash.removeLL('Tyrion');
console.log(hash.getLL('Tyrion')); //undefined
hash.removeLL('Donnie');
console.log(hash.getLL('Donnie')); //undefined6.2.3 性能: 散列表性能受以下因素影响:
- 装填因子: 已装填的数据/总容量,也就是空余位置越多,发生冲突可能性越小,性能越好;一般设置为0.75,是性能和空间的一个折中,当达到0.75时,哈希表容量自动扩容。
- 良好的散列函数: 让数据中的值成均匀分布,尽量不要扎堆,使数据查找和删除时间复杂度为O(1)和O(n)。
6.2.4 HashTable类与HashMap的区别:
继承的父类不同: Hashtable继承自Dictionary类,而HashMap继承自AbstractMap类。但二者都实现了Map接口。
内部实现使用的数组初始化和扩容方式不同: Hashtable和HashMap它们两个内部实现方式的数组的初始大小和扩容(数组内容达到装载因子就会扩容)的方式。HashTable中hash数组默认大小是素数(让数据尽可能均匀分布,),增加的方式是 old*2+1。HashMap中hash数组的默认大小是2的指数,因为(number % (2^n))== (number & (2^n-1)),位运算快于求余运算,两种结构分别选择了空间为先和效率为先。
是否提供contains方法:
HashMap把Hashtable的contains方法去掉了,改成containsValue和containsKey,因为contains方法容易让人引起误解。
Hashtable则保留了contains,containsValue和containsKey三个方法,其中contains和containsValue功能相同。key和value是否允许null值: 其中key和value都是对象,并且不能包含重复key,但可以包含重复的value。
Hashtable中,key和value都不允许出现null值。
HashMap中,null可以作为键,这样的键只有一个;可以有一个或多个键所对应 的值为null。当get()方法返回null值时,可能是 HashMap中没有该键,也可能使该键所对应的值为null。因此,在HashMap中不能由get()方法来判断HashMap中是否存在某个键, 而应该用containsKey()方法来判断。线程安全性不同: Hashtable 中的方法是Synchronize的,而HashMap中的方法在缺省情况下是非Synchronize的。在多线程并发的环境下,可以直接使用Hashtable,不需要自己为它的方法实现同步,但使用HashMap时就必须要自己增加同步处理。
上述内容参考:HashTable与HashMap使用总结





















 363
363











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








