尚学堂JAVA基础学习笔记_2/2
文章目录
写在前面
学习链接:Java 视频教程全集
课件链接:Java课件
第10章 IO技术
1. IO入门
-
对于任何程序设计语言而言,输入输出(Input/Output)系统都是非常核心的功能。程序运行需要数据,数据的获取往往需要跟外部系统进行通信,外部系统可能是文件、数据库、其他程序、网络、IO设备等等。外部系统比较复杂多变,那么我们有必要通过某种手段进行抽象、屏蔽外部的差异,从而实现更加便捷的编程。
-
数据源:数据源data source,提供数据的原始媒介。常见的数据源有:数据库、文件、其他程序、内存、网络连接、IO设备。
-
数据源分为:源设备、目标设备。
-
源设备:为程序提供数据,一般对应输入流。
-
目标设备:程序数据的目的地,一般对应输出流。
-
-
-
流的概念
-
流是一个抽象、动态的概念,是一连串连续动态的数据集合。
-
对于输入流而言,数据源就像水箱,流(stream)就像水管中流动着的水流,程序就是我们最终的用户。我们通过流(A Stream)将数据源(Source)中的数据(information)输送到程序(Program)中。
-
对于输出流而言,目标数据源就是目的地(dest),我们通过流(A Stream)将程序(Program)中的数据(information)输送到目的数据源(dest)中。
-
-
第一个简单的IO流程序及深入理解
-
当程序需要读取数据源的数据时,就会通过IO流对象开启一个通向数据源的流,通过这个IO流对象的相关方法可以顺序读取数据源中的数据。
import java.io.*; public class TestIO1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { //创建输入流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:/a.txt"); // 文件内容是:abc //一个字节一个字节的读取数据 int s1 = fis.read(); // 打印输入字符a对应的ascii码值97 int s2 = fis.read(); // 打印输入字符b对应的ascii码值98 int s3 = fis.read(); // 打印输入字符c 对应的ascii码值99 int s4 = fis.read(); // 由于文件内容已经读取完毕,返回-1 System.out.println(s1); System.out.println(s2); System.out.println(s3); System.out.println(s4); // 流对象使用完,必须关闭!不然,总占用系统资源,最终会造成系统崩溃! fis.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
注意:
-
在示例10-1中我们读取的文件内容是已知的,因此可以使用固定次数的“int s= fis.read();”语句读取内容,但是在实际开发中通常我们根本不知道文件的内容,因此我们在读取的时候需要配合while循环使用。
-
为了保证出现异常后流的正常关闭,通常要将流的关闭语句要放到finally语句块中,并且要判断流是不是null。
-
-
使用流读取文件内容(经典代码,一定要掌握)
import java.io.*; public class TestIO2 { public static void main(String[] args) { FileInputStream fis = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream("d:/a.txt"); // 内容是:abc StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); int temp = 0; //当temp等于-1时,表示已经到了文件结尾,停止读取 while ((temp = fis.read()) != -1) { sb.append((char) temp); } System.out.println(sb); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { //这种写法,保证了即使遇到异常情况,也会关闭流对象。 if (fis != null) { fis.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
-
-
Java中流的概念细分
-
按流的方向分类:
-
输入流:数据流向是数据源到程序(以InputStream、Reader结尾的流)。
-
输出流:数据流向是程序到目的地(以OutPutStream、Writer结尾的流)。
-
-
按处理的数据单元分类:
-
字节流:以字节为单位获取数据,命名上以Stream结尾的流一般是字节流,如FileInputStream、FileOutputStream。
-
字符流:以字符为单位获取数据,命名上以Reader/Writer结尾的流一般是字符流,如FileReader、FileWriter。
-
-
按处理对象不同分类:
-
节点流:可以直接从数据源或目的地读写数据,如FileInputStream、FileReader、DataInputStream等。
-
处理流:不直接连接到数据源或目的地,是”处理流的流”。通过对其他流的处理提高程序的性能,如BufferedInputStream、BufferedReader等。处理流也叫包装流。
节点流处于IO操作的第一线,所有操作必须通过它们进行;处理流可以对节点流进行包装,提高性能或提高程序的灵活性。
-
-
-
Java中IO流类的体系
-
InputStream/OutputStream:字节流的抽象类。
-
Reader/Writer:字符流的抽象类。
-
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream:节点流:以字节为单位直接操作“文件”。
-
ByteArrayInputStream/ByteArrayOutputStream:节点流:以字节为单位直接操作“字节数组对象”。
-
ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream:处理流:以字节为单位直接操作“对象”。
-
DataInputStream/DataOutputStream:处理流:以字节为单位直接操作“基本数据类型与字符串类型”。
-
FileReader/FileWriter:节点流:以字符为单位直接操作“文本文件”(注意:只能读写文本文件)。
-
BufferedReader/BufferedWriter:处理流:将Reader/Writer对象进行包装,增加缓存功能,提高读写效率。
-
BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream:处理流:将InputStream/OutputStream对象进行包装,增加缓存功能,提高 读写效率。
-
InputStreamReader/OutputStreamWriter:处理流:将字节流对象转化成字符流对象。
-
PrintStream:处理流:将OutputStream进行包装,可以方便地输出字符,更加灵活。
-
-
四大IO抽象类
-
InputStream/OutputStream和Reader/writer类是所有IO流类的抽象父类,我们有必要简单了解一下这个四个抽象类的作用。然后,通过它们具体的子类熟悉相关的用法。
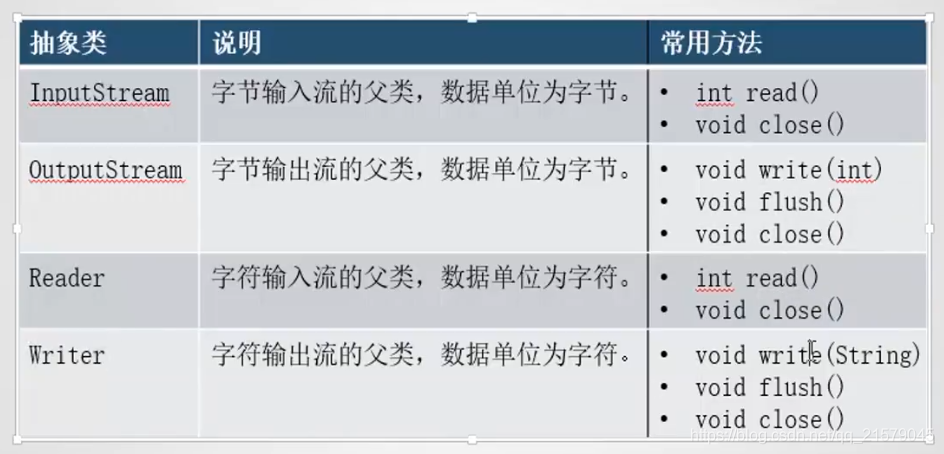
-
IO文件字节输入流操作标准步骤
- 创建源
- 选择流
- 操作
- 释放
-
字节输入流测试:
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO05.java * @time: 2019/10/17 16:39 * @desc: 理解操作步骤 */ public class TestIO05 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); // 2. 选择流 try{ InputStream is = new FileInputStream(src); System.out.println(src.getAbsolutePath()); // 3. 操作(读取) int data1 = is.read(); // 第1个数据 int data2 = is.read(); // 第2个数据 int data3 = is.read(); // 第3个数据 System.out.println((char)data1); System.out.println((char)data2); System.out.println((char)data3); // 4. 释放资源 is.close(); }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
字节输入流标准操作
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO06.java * @time: 2019/10/17 16:39 * @desc: 理解操作步骤 标准 */ public class TestIO06 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); // 2. 选择流 InputStream is = null; try{ is = new FileInputStream(src); // 3. 操作(读取) int temp; while((temp=is.read()) != -1){ System.out.println((char)temp); } }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 4. 释放资源 if (null != is) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
字节输出流标准操作
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO07.java * @time: 2019/10/17 16:39 * @desc: 读入字符数组 */ public class TestIO07 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); // 2. 选择流 InputStream is = null; try{ is = new FileInputStream(src); // 3. 操作(读取) // 缓冲容器,这里设为3个字节 byte[] car = new byte[3]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len=is.read(car)) != -1){ // 字节数组 --> 字符串(解码) String str = new String(car, 0, len); System.out.println(str); } }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 4. 释放资源 if (null != is) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
IO文件字节输出流操作标准步骤
- 创建源
- 选择流
- 操作(写出内容)
- 释放资源
-
输出流实战
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO08.java * @time: 2019/10/17 18:10 * @desc: 文件字节输出流 */ public class TestIO08 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 File dest = new File("dest.txt"); // 2. 选择流 OutputStream os = null; try{ // true则是增加,false则是不增加 os = new FileOutputStream(dest, true); // 3. 操作(写出) String temp = "IO is so easy!"; byte[] datas = temp.getBytes(); os.write(datas, 0, datas.length); os.flush(); }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 释放资源 if(null != os){ try { os.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
文件的拷贝
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestFileCopy.java * @time: 2019/10/17 18:22 * @desc: 文件的拷贝 */ public class TestFileCopy { public static void main(String[] args) { copy("test.png", "copy_test.png"); } public static void copy(String srcPath, String destPath){ // 1. 创建源 // 源头 File src = new File(srcPath); File dest = new File(destPath); // 2. 选择流 InputStream is = null; OutputStream os = null; try{ is = new FileInputStream(src); os = new FileOutputStream(dest, true); // 3. 操作(分段读取) // 缓冲容器 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len=is.read(flush)) != -1){ // 字节数组 --> 字符串(解码) String str = new String(flush, 0, len); os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 释放资源 先打开的后关闭 try{ if(null != os){ os.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try{ if(null != is){ is.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } -
字符输入流
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO07.java * @time: 2019/10/17 16:39 * @desc: 文件字符输入流 */ public class TestIO09 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); // 2. 选择流 Reader reader = null; try{ reader = new FileReader(src); // 3. 操作(读取) char[] flush = new char[1024]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len=reader.read(flush)) != -1){ String str = new String(flush, 0, len); System.out.println(str); } }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 4. 释放资源 if (null != reader) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
字符输出流
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO08.java * @time: 2019/10/17 18:10 * @desc: 文件字符输出流 */ public class TestIO10 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 File dest = new File("dest.txt"); // 2. 选择流 Writer writer = null; try{ // true则是增加,false则是不增加 writer = new FileWriter(dest, false); // 3. 操作(写出) // 写法1 String temp = "IO is so easy!我是你大爷"; char[] datas = temp.toCharArray(); writer.write(datas, 0, datas.length); writer.flush(); // 写法2 String temp = "IO is so easy!我是你大爷"; writer.write(temp); writer.flush(); // 写法3 writer.append("IO is so easy!").append("我是你大爷"); writer.flush(); }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 释放资源 if(null != writer){ try { writer.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
字节数组输入流
- 创建源:字节数组不要太大
- 选择流
- 操作
- 释放资源:可以不做处理
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO07.java * @time: 2019/10/17 16:39 * @desc: 字节数组输入流 */ public class TestIO11 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 byte[] src = "talk is cheap show me the code. ".getBytes(); // 2. 选择流 InputStream is = null; try{ is = new ByteArrayInputStream(src); // 3. 操作(读取) // 缓冲容器,这里设为5个字节 byte[] car = new byte[5]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len=is.read(car)) != -1){ // 字节数组 --> 字符串(解码) String str = new String(car, 0, len); System.out.println(str); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 4. 释放资源 if (null != is) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
字节数组输出流:
- 创建源:内部维护
- 选择流:不关联源
- 操作:写出内容
- 获取数据:toByteArray()
- 释放资源:可以不用处理
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO08.java * @time: 2019/10/17 18:10 * @desc: 字节数组输出流 */ public class TestIO12 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源:不用创建源 byte[] dest = null; // 2. 选择流:新增方法 ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null; try{ // true则是增加,false则是不增加 baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 3. 操作(写出) String temp = "show me the code bie bibi"; byte[] datas = temp.getBytes(); baos.write(datas, 0, datas.length); baos.flush(); // 获取数据 dest = baos.toByteArray(); System.out.println(dest.length + "-->" + new String(dest, 0, baos.size())); } catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally{ // 释放资源 if(null != baos){ try { baos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
从文件拷贝到字节数组,再从字节数组输出到文件。
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO08.java * @time: 2019/10/17 18:10 * @desc: 图片读取到字节数组,字节数组写出到文件 */ public class TestIO13 { public static void main(String[] args){ byte[] datas = fileToByteArray("test.png"); System.out.println(datas.length); byteArrayToFile(datas, "p-byte.png"); } public static byte[] fileToByteArray(String filePath){ /* 1. 图片读取到字节数组中 1). 图片到程序:FileInputStream 2). 程序到字节数组:ByteArrayOutputStream */ // 1. 创建源与目的地 File src = new File(filePath); byte[] dest = null; // 2. 选择流 InputStream is = null; ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null; try{ is = new FileInputStream(src); baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 3. 操作:分段读取 byte[] flush = new byte[1024*10]; int len = -1; while((len = is.read(flush)) != -1){ baos.write(flush, 0, len); // 写出到字节数组中 } baos.flush(); return baos.toByteArray(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { // 4. 释放资源 try{ if(null != is){ is.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return null; } public static void byteArrayToFile(byte[] src, String filePath){ /* 2. 字节数组写出到文件 1). 字节数组到程序:ByteArrayInputStream 2). 程序写出到文件:FileOutputStream */ // 1. 创建源 File dest = new File(filePath); // 2. 选择流 InputStream is = null; OutputStream os = null; try{ is = new ByteArrayInputStream(src); os = new FileOutputStream(dest, false); // 3. 操作:分段读取 byte[] flush = new byte[5]; // 缓冲容器 int len = -1; while((len = is.read(flush)) != 1){ os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 4. 释放资源 try { if (null != os) { os.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } -
java1.7之后可以用try…with…resource自动释放
try(is;os){} try(InputStream is = new FileInputStream(src); OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(dest);){}
-
2. IO的API
-
IO基础操作
import java.io.File; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO1.java * @time: 2019/10/9 17:19 * @desc: IO学习1 */ public class TestIO1 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 输出文件分隔符 System.out.println(File.separator); // 1. 构建File对象 String path = "F:/BookStudy/else/Java知识点思维导图.png"; File src = new File(path); // 输出文件大小 System.out.println(src.length()); // 2. 第二种构建File对象的方法 File src2 = new File("F:/BookStudy/else", "Java知识点思维导图.png"); System.out.println(src2.length()); // 3. 第三种构建File对象的方法 File src3 = new File(new File("F:/BookStudy/else"), "Java知识点思维导图.png"); System.out.println(src3.length()); // 相对路径的源路径 System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.dir")); // 绝对路径 System.out.println(src3.getAbsolutePath()); // 构建一个不存在的对象 File src4 = new File("aaa/asdf.jpg"); System.out.println(src4.getAbsolutePath()); } } -
文件操作
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO2.java * @time: 2019/10/11 17:31 * @desc: IO操作api */ public class TestIO2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File src = new File("F:/BookStudy/else/Java知识点思维导图.png"); // 基本信息 System.out.println("名称:" + src.getName()); System.out.println("路径:" + src.getPath()); System.out.println("绝对路径:" + src.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println("父路径:" + src.getParent()); System.out.println("父对象:" + src.getParentFile().getName()); // 文件状态 System.out.println("是否存在:" + src.exists()); System.out.println("是否文件:" + src.isFile()); System.out.println("是否文件夹:" + src.isDirectory()); // 获取文件的字节数,如果是文件夹,则为0。 System.out.println("长度:" + src.length()); // 创建文件:不存在才创建,返回true,不然返回false;不带后缀只是文件名,不是文件夹 boolean flag = src.createNewFile(); System.out.println(flag); // 文件的删除:删除已经存在的文件 flag = src.delete(); System.out.println(flag); } } -
文件夹的创建和遍历
import java.io.File; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO3.java * @time: 2019/10/11 17:50 * @desc: 文件夹创建和遍历 */ public class TestIO3 { public static void main(String[] args){ // mkdir():确保上级目录存在,不存在则创建失败 // mkdirs():上级目录可以不存在,不存在则一同创建 File dir = new File("D:/"); boolean flag1 = dir.mkdir(); boolean flag2 = dir.mkdirs(); System.out.println(flag1); System.out.println(flag2); // list():列出下级名称 // listFiles():列出下级File对象 String[] subNames = dir.list(); for(String s: subNames){ System.out.println(s); } File[] subFiles = dir.listFiles(); for(File s: subFiles){ System.out.println(s.getAbsolutePath()); } // listRoots():列出所有盘符 File[] roots = dir.listRoots(); for(File r: roots){ System.out.println(r.getAbsolutePath()); } // 递归:方法自己调用自己 // 递归头:何时结束递归 // 递归体:重复调用 printName(dir, 0); } public static void printName(File src, int deep){ /* 打印子孙级目录和文件的名称 */ for(int i=0; i<deep; i++){ System.out.print("-"); } System.out.println(src.getName()); if(null == src || !src.exists()){ return; } else if(src.isDirectory()){ for(File s: src.listFiles()){ printName(s, deep + 1); } } } } -
统计文件夹的大小
import java.io.File; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO4.java * @time: 2019/10/15 15:20 * @desc: 统计文件夹的大小 */ public class TestIO4 { public static void main(String[] args){ File src = new File("F:\\BookStudy"); count(src); System.out.println(LEN); } private static long LEN = 0; public static void count(File src){ // 获取大小 if(null != src && src.exists()){ if(src.isFile()){ LEN += src.length(); }else{ for(File s: src.listFiles()){ count(s); } } } } } -
使用面向对象:统计文件夹大小
import java.io.File; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DirCount.java * @time: 2019/10/15 15:58 * @desc: 使用面向对象:统计文件夹大小 */ public class DirCount { // 大小 private long len; // 文件夹路径 private String path; // 源 private File src; // 文件的个数 private int fileSize; // 文件夹的个数 private int dirSize; public DirCount(String path){ this.path = path; this.src = new File(path); count(this.src); } private void count(File src){ // 获取大小 if(null != src && src.exists()){ if(src.isFile()){ this.len += src.length(); this.fileSize++; }else{ this.dirSize++; for(File s: src.listFiles()){ count(s); } } } } public long getLen() { return len; } public int getFileSize() { return fileSize; } public int getDirSize() { return dirSize; } public static void main(String[] args){ DirCount dir = new DirCount("F:\\BookStudy"); System.out.println(dir.getLen()); System.out.println("文件的数量" + "--->" + dir.getFileSize()); System.out.println("文件夹的数量" + "--->" + dir.getDirSize()); DirCount dir2 = new DirCount("F:\\BookStudy\\else"); System.out.println(dir2.getLen()); System.out.println("文件的数量" + "--->" + dir2.getFileSize()); System.out.println("文件夹的数量" + "--->" + dir2.getDirSize()); } } -
编码和解码
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ContentEncode.java * @time: 2019/10/15 16:26 * @desc: 编码:字符串-->字节;解码:字节-->字符串 */ public class ContentEncode { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { String msg = "你怕不是个铁憨憨"; // 编码:字节数组 byte[] datas = msg.getBytes(); System.out.println(datas); // 中文utf-8:一个字符占3个字节;默认使用工程的字符集 System.out.println(datas.length); // 编码:其他字符集 datas = msg.getBytes("UTF-16LE"); System.out.println(datas.length); datas = msg.getBytes("GBK"); System.out.println(datas.length); // 解码 msg = new String(datas, 0, datas.length, "gbk"); System.out.println(msg); } } -
乱码的原因:
- 字节数不够
- 字符集不统一
3. 装饰流
-
装饰器模式原理剖析
- 抽象组件:需要装饰的抽象对象(接口或抽象父类)
- 具体组件:需要装饰的对象
- 抽象装饰类:包含了对抽象组件的引用以及装饰者共有的方法
- 具体装饰类:被装饰的对象
-
模拟声音
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DecorateTest01.java * @time: 2019/10/18 15:53 * @desc: 实现放大器对声音放大的功能 */ public class DecorateTest01 { public static void main(String[] args){ Person p = new Person(); p.say(); // 装饰 Amplifier am = new Amplifier(p); am.say(); } } interface Say{ void say(); } class Person implements Say{ // 属性 private int voice = 10; @Override public void say() { System.out.println("人的声音为:" + this.getVoice()); } public int getVoice() { return voice; } public void setVoice(int voice) { this.voice = voice; } } class Amplifier implements Say{ private Person p; Amplifier(Person p){ this.p = p; } @Override public void say() { System.out.println("人的声音为:" + p.getVoice()*100); System.out.println("噪音..."); } } -
模拟咖啡
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DecorateTest02.java * @time: 2019/10/18 15:53 * @desc: 模拟咖啡 */ public class DecorateTest02 { public static void main(String[] args){ Drink coffee = new Coffee(); Drink suger = new Suger(coffee); // 装饰 System.out.println(suger.info() + "-->" + suger.cost()); Drink milk = new Milk(coffee); // 装饰 System.out.println(milk.info() + "-->" + milk.cost()); Drink mixed = new Milk(suger); // 装饰 System.out.println(mixed.info() + "-->" + mixed.cost()); } } // 抽象组件 interface Drink{ double cost(); // 费用 String info(); // 说明 } // 具体组件 class Coffee implements Drink{ private String name = "原味咖啡"; @Override public double cost() { return 10; } @Override public String info() { return name; } } // 抽象装饰类 abstract class Decorate implements Drink{ // 对抽象组件的引用 private Drink drink; public Decorate(Drink drink){ this.drink = drink; } @Override public double cost() { return this.drink.cost(); } @Override public String info() { return this.drink.info(); } } // 具体装饰类 class Milk extends Decorate{ public Milk(Drink drink) { super(drink); } @Override public double cost() { return super.cost()*4; } @Override public String info() { return super.info() + "加入了牛奶"; } } class Suger extends Decorate{ public Suger(Drink drink) { super(drink); } @Override public double cost() { return super.cost()*2; } @Override public String info() { return super.info() + "加入了糖"; } }
-
字节缓冲流(输入输出同理)
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO07.java * @time: 2019/10/17 16:39 * @desc: 加入缓冲流(只需要释放底层的is) */ public class BufferedTest02 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); // 2. 选择流 InputStream is = null; try{ is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); // 3. 操作(读取) byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len=is.read(flush)) != -1){ // 字节数组 --> 字符串(解码) String str = new String(flush, 0, len); System.out.println(str); } }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 4. 释放资源 if (null != is) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
字符缓冲流(输入输出同理)
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TestIO07.java * @time: 2019/10/17 16:39 * @desc: 文件字符输入流 加入缓冲流 */ public class BufferedTest03 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 1. 创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); // 2. 选择流 BufferedReader reader = null; try{ reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); // 3. 操作(读取) String line = null; while((line = reader.readLine()) != null){ System.out.println(line); } }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 4. 释放资源 if (null != reader) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } -
转换流:InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter
- 以字符流的形式操作字节流(纯文本的)
- 指定字符集
- 循环读取键盘输入
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ConvertTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/19 14:48 * @desc: 转换流:InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter */ public class ConvertTest1 { public static void main(String[] args){ // 操作System.in和System.out try(BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));){ // 循环获取键盘的输入(exit退出),输入此内容 String msg = ""; while(!msg.equals("exit")){ msg = reader.readLine(); // 循环读取 writer.write(msg); // 循环写出 writer.newLine(); writer.flush(); // 强制刷新 } } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("操作异常"); } } }- 读取网站的内容并保存
import java.io.*; import java.net.URL; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ConvertTest2.java * @time: 2019/10/19 14:48 * @desc: 转换流:InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter */ public class ConvertTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 中文乱码 test1(); // 中文不是乱码 test2(); // 效率更高 test3(); } public static void test1(){ // 操作网络流,下载百度的源代码 try(InputStream is = new URL("http://www.baidu.com").openStream();){ int temp; while((temp=is.read()) != -1){ System.out.print((char)temp); } } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("操作异常"); } } public static void test2(){ // 操作网络流,下载百度的源代码 try(InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader(new URL("http://www.baidu.com").openStream(), "UTF-8")){ int temp; while((temp=is.read()) != -1){ System.out.print((char)temp); } } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("操作异常"); } } public static void test3(){ // 操作网络流,下载百度的源代码 try(BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader( new URL("http://www.baidu.com").openStream(), "UTF-8" ) ); BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter( new OutputStreamWriter( new FileOutputStream("baidu.html"), "UTF-8" ) ) ){ String msg; while((msg = reader.readLine()) != null){ writer.write(msg); // 字符集不统一,字节数不够出现乱码 writer.newLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("操作异常"); } } } -
数据流
- 先写出后读取
- 读取的顺序与写出保持一致
import com.sun.xml.internal.messaging.saaj.util.ByteInputStream; import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DataTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/19 15:57 * @desc: 数据流 */ public class DataTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 写出 ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream( new BufferedOutputStream(baos) ); // 操作数据类型 + 数据 dos.writeUTF("编码辛酸泪啊"); dos.writeInt(18); dos.writeBoolean(false); dos.writeChar('a'); dos.flush(); byte[] datas = baos.toByteArray(); System.out.println(datas.length); // 读取 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new ByteArrayInputStream(datas) ) ); // 顺序与写出一致 String msg = dis.readUTF(); int age = dis.readInt(); boolean flag = dis.readBoolean(); char ch = dis.readChar(); System.out.println(flag); } } -
对象流
- 先写出后读取
- 读取的顺序与写出保持一致
- 不是所有的对象都可以序列化,必须要实现接口Serializable
-
将对象数据序列化并反序列化
import java.io.*; import java.util.Date; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DataTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/19 15:57 * @desc: 对象流 */ public class ObjectTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // 写出:序列化 ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream dos = new ObjectOutputStream( new BufferedOutputStream(baos) ); // 操作数据类型 + 数据 dos.writeUTF("编码辛酸泪"); dos.writeInt(18); dos.writeBoolean(false); dos.writeChar('a'); // 对象 dos.writeObject("谁解其中味"); dos.writeObject(new Date()); Employee emp = new Employee("马云", 400); dos.writeObject(emp); dos.flush(); byte[] datas = baos.toByteArray(); System.out.println(datas.length); // 读取:反序列化 ObjectInputStream dis = new ObjectInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new ByteArrayInputStream(datas) ) ); // 顺序与写出一致 String msg = dis.readUTF(); int age = dis.readInt(); boolean flag = dis.readBoolean(); char ch = dis.readChar(); System.out.println(flag); // 对象的数据还原 Object str = dis.readObject(); Object date = dis.readObject(); Object employee = dis.readObject(); if (str instanceof String){ String strObj = (String) str; System.out.println(strObj); } if (date instanceof Date){ Date strObj = (Date) date; System.out.println(strObj); } if (employee instanceof Employee){ Employee strObj = (Employee) employee; System.out.println(strObj.getName() + "-->" + strObj.getSalary()); } } } // javabean 封装数据 class Employee implements java.io.Serializable{ private transient String name; // 该数据不需要序列化 private double salary; public Employee() { } public Employee(String name, double salary) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public void setSalary(double salary) { this.salary = salary; } } -
在上面的基础上,序列化成文件并反序列化
import java.io.*; import java.util.Date; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DataTest2.java * @time: 2019/10/19 15:57 * @desc: 对象流 */ public class ObjectTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // 写出:序列化 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream( new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("obj.txt") ) ); // 操作数据类型 + 数据 oos.writeUTF("编码辛酸泪"); oos.writeInt(18); oos.writeBoolean(false); oos.writeChar('a'); // 对象 oos.writeObject("谁解其中味"); oos.writeObject(new Date()); Employee emp = new Employee("马云", 400); oos.writeObject(emp); oos.flush(); oos.close(); // 读取:反序列化 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream("obj.txt") ) ); // 顺序与写出一致 String msg = ois.readUTF(); int age = ois.readInt(); boolean flag = ois.readBoolean(); char ch = ois.readChar(); System.out.println(flag); // 对象的数据还原 Object str = ois.readObject(); Object date = ois.readObject(); Object employee = ois.readObject(); if (str instanceof String){ String strObj = (String) str; System.out.println(strObj); } if (date instanceof Date){ Date strObj = (Date) date; System.out.println(strObj); } if (employee instanceof Employee){ Employee strObj = (Employee) employee; System.out.println(strObj.getName() + "-->" + strObj.getSalary()); } } }
-
打印流
-
PrintStream
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: PrintTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/20 15:43 * @desc: 打印流 */ public class PrintTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { // 打印流System.out PrintStream ps = System.out; ps.println("打印流"); ps.println(true); ps = new PrintStream( new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("print.txt") ), true ); ps.println("打印流"); ps.println(true); ps.close(); // 重定向输出端 System.setOut(ps); System.out.println("change"); // 重定向回控制台 System.setOut( new PrintStream( new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out) ), true ) ); System.out.println("i am backing..."); } } -
PrintWriter
import java.io.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: PrintTest2.java * @time: 2019/10/20 15:43 * @desc: 打印流 */ public class PrintTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter( new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("print.txt") ), true ); pw.println("打印流"); pw.println(true); pw.close(); } }
-
4. IO实战
-
文件分割
-
随机读取和写入流
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.util.Random; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: RanTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/21 9:01 * @desc: 随机读取和写入流 RandomAccessFile */ public class RanTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 分多少块 File src = new File("D:\\李添的数据哦!!!\\BookStudy\\else\\JAVAPro\\src\\PrintTest2.java"); // 总长度 long len = src.length(); // 每块大小 int blockSize = 240; // 块数:多少块 int size = (int)Math.ceil(len*1.0/blockSize); System.out.println(size); int beginPos = 0; int actualSize = (int)(blockSize>len?len:blockSize); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ beginPos = i*blockSize; if(i == size-1){ // 最后一块 actualSize = (int)len; }else{ actualSize = blockSize; // 剩余量 len -= actualSize; } System.out.println(i + "-->" + beginPos + "-->" + actualSize); test1(i, beginPos, actualSize); } } // 指定起始位置,读取剩余指定长度内容 public static void test1(int i, int beginPos, int actualSize) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("D:\\李添的数据哦!!!\\BookStudy\\else\\JAVAPro\\src\\PrintTest2.java"), "r"); // 指定起始位置 // int beginPos = 2; // 实际大小 // int actualSize = 128; // 随机读取 raf.seek(beginPos); byte[] flush = new byte[124]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len = raf.read(flush)) != -1){ if (actualSize > len){ // 实际大小大于接受长度,则获取本次读取的所有内容 System.out.println(new String(flush, 0, len)); actualSize -= len; }else{ System.out.println(new String(flush, 0, actualSize)); break; } } raf.close(); } } -
增加输出流
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: RanTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/21 9:01 * @desc: 随机读取和写入流 RandomAccessFile 并增加输出流 */ public class RanTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 分多少块 File src = new File("D:\\李添的数据哦!!!\\BookStudy\\else\\JAVAPro\\src\\PrintTest2.java"); // 总长度 long len = src.length(); // 每块大小 int blockSize = 240; // 块数:多少块 int size = (int)Math.ceil(len*1.0/blockSize); System.out.println(size); int beginPos = 0; int actualSize = (int)(blockSize>len?len:blockSize); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ beginPos = i*blockSize; if(i == size-1){ // 最后一块 actualSize = (int)len; }else{ actualSize = blockSize; // 剩余量 len -= actualSize; } System.out.println(i + "-->" + beginPos + "-->" + actualSize); test1(i, beginPos, actualSize); } } // 指定起始位置,读取剩余指定长度内容 public static void test1(int i, int beginPos, int actualSize) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(new File("D:\\李添的数据哦!!!\\BookStudy\\else\\JAVAPro\\src\\PrintTest2.java"), "r"); RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("Print_Copy_" + i + ".java"), "rw"); // 指定起始位置 // int beginPos = 2; // 实际大小 // int actualSize = 128; // 随机读取 raf.seek(beginPos); byte[] flush = new byte[124]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len = raf.read(flush)) != -1){ if (actualSize > len){ // 实际大小大于接受长度,则获取本次读取的所有内容 raf2.write(flush, 0, len); actualSize -= len; }else{ raf2.write(flush, 0, actualSize); break; } } raf2.close(); raf.close(); } } -
对RanTest进行封装,功能是拆分文件,面向对象思想封装
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: SplitFile.java * @time: 2019/10/21 9:35 * @desc: 对RanTest进行封装,功能是拆分文件,面向对象思想封装 */ public class SplitFile { // 源头 private File src; // 目的地(文件夹) private String destDir; // 所有分割后的文件存储路径 private List<String> destPaths; // 每块大小 private int blockSize; // 块数:多少块 private int size; public SplitFile(String srcPath, String destDir, int blockSize){ this.src = new File(srcPath); this.destDir = destDir; this.blockSize = blockSize; this.destPaths = new ArrayList<>(); // 初始化 init(); } // 初始化 private void init(){ // 总长度 long len = this.src.length(); // 块数:多少块 this.size = (int)Math.ceil(len*1.0/blockSize); // 路径 for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ this.destPaths.add(this.destDir + "/" + i + "-" + this.src.getName()); } } // 分割 public void split() throws IOException { /* 1. 计算每一块起始位置及大小 2. 分割 */ // 总长度 long len = this.src.length(); // 每块大小 int size = (int)Math.ceil(len*1.0/blockSize); System.out.println(size); int beginPos = 0; int actualSize = (int)(this.blockSize>len?len:this.blockSize); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ beginPos = i*blockSize; if(i == size-1){ // 最后一块 actualSize = (int)len; }else{ actualSize = blockSize; // 剩余量 len -= actualSize; } splitDetail(i, beginPos, actualSize); } } // 指定起始位置,读取剩余指定长度内容 private void splitDetail(int i, int beginPos, int actualSize) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile((this.src), "r"); RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile((this.destPaths.get(i)), "rw"); raf.seek(beginPos); byte[] flush = new byte[124]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len = raf.read(flush)) != -1){ if (actualSize > len){ // 实际大小大于接受长度,则获取本次读取的所有内容 raf2.write(flush, 0, len); actualSize -= len; }else{ raf2.write(flush, 0, actualSize); break; } } raf2.close(); raf.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { SplitFile sf = new SplitFile("test.png", "dest", 1024*10); sf.split(); } }
-
-
增加文件的合并功能
import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: SplitFile.java * @time: 2019/10/21 9:35 * @desc: 对RanTest进行封装,功能是拆分文件,面向对象思想封装 */ public class SplitFile { // 源头 private File src; // 目的地(文件夹) private String destDir; // 所有分割后的文件存储路径 private List<String> destPaths; // 每块大小 private int blockSize; // 块数:多少块 private int size; public SplitFile(String srcPath, String destDir, int blockSize){ this.src = new File(srcPath); this.destDir = destDir; this.blockSize = blockSize; this.destPaths = new ArrayList<>(); // 初始化 init(); } // 初始化 private void init(){ // 总长度 long len = this.src.length(); // 块数:多少块 this.size = (int)Math.ceil(len*1.0/blockSize); // 路径 for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ this.destPaths.add(this.destDir + "/" + i + "-" + this.src.getName()); } } // 分割 public void split() throws IOException { /* 1. 计算每一块起始位置及大小 2. 分割 */ // 总长度 long len = this.src.length(); // 每块大小 int size = (int)Math.ceil(len*1.0/blockSize); System.out.println(size); int beginPos = 0; int actualSize = (int)(this.blockSize>len?len:this.blockSize); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ beginPos = i*blockSize; if(i == size-1){ // 最后一块 actualSize = (int)len; }else{ actualSize = blockSize; // 剩余量 len -= actualSize; } splitDetail(i, beginPos, actualSize); } } // 指定起始位置,读取剩余指定长度内容 private void splitDetail(int i, int beginPos, int actualSize) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile((this.src), "r"); RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile((this.destPaths.get(i)), "rw"); raf.seek(beginPos); byte[] flush = new byte[124]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len = raf.read(flush)) != -1){ if (actualSize > len){ // 实际大小大于接受长度,则获取本次读取的所有内容 raf2.write(flush, 0, len); actualSize -= len; }else{ raf2.write(flush, 0, actualSize); break; } } raf2.close(); raf.close(); } // 文件的合并 private void merge(String destPath) throws IOException { // 输出流 OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(destPath, true) ); // 输入流 for (int i = 0; i < destPaths.size(); i++) { InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream((new FileInputStream(destPaths.get(i)))); // 拷贝 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; while((len = is.read(flush)) != -1){ os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); is.close(); } os.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { SplitFile sf = new SplitFile("test.png", "dest", 1024*10); sf.split(); sf.merge("merge.png"); } } -
利用SequenceInputStream增加文件合并功能
import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Vector; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: SplitFile.java * @time: 2019/10/21 9:35 * @desc: 对RanTest进行封装,功能是拆分文件,面向对象思想封装 */ public class SplitFile { // 源头 private File src; // 目的地(文件夹) private String destDir; // 所有分割后的文件存储路径 private List<String> destPaths; // 每块大小 private int blockSize; // 块数:多少块 private int size; public SplitFile(String srcPath, String destDir, int blockSize){ this.src = new File(srcPath); this.destDir = destDir; this.blockSize = blockSize; this.destPaths = new ArrayList<>(); // 初始化 init(); } // 初始化 private void init(){ // 总长度 long len = this.src.length(); // 块数:多少块 this.size = (int)Math.ceil(len*1.0/blockSize); // 路径 for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ this.destPaths.add(this.destDir + "/" + i + "-" + this.src.getName()); } } // 分割 public void split() throws IOException { /* 1. 计算每一块起始位置及大小 2. 分割 */ // 总长度 long len = this.src.length(); // 每块大小 int size = (int)Math.ceil(len*1.0/blockSize); System.out.println(size); int beginPos = 0; int actualSize = (int)(this.blockSize>len?len:this.blockSize); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ beginPos = i*blockSize; if(i == size-1){ // 最后一块 actualSize = (int)len; }else{ actualSize = blockSize; // 剩余量 len -= actualSize; } splitDetail(i, beginPos, actualSize); } } // 指定起始位置,读取剩余指定长度内容 private void splitDetail(int i, int beginPos, int actualSize) throws IOException { RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile((this.src), "r"); RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile((this.destPaths.get(i)), "rw"); raf.seek(beginPos); byte[] flush = new byte[124]; // 接受长度 int len = -1; while((len = raf.read(flush)) != -1){ if (actualSize > len){ // 实际大小大于接受长度,则获取本次读取的所有内容 raf2.write(flush, 0, len); actualSize -= len; }else{ raf2.write(flush, 0, actualSize); break; } } raf2.close(); raf.close(); } // 文件的合并 private void merge(String destPath) throws IOException { // 输出流 OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(destPath, true) ); // 输入流 for (int i = 0; i < destPaths.size(); i++) { InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream((new FileInputStream(destPaths.get(i)))); // 拷贝 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; while((len = is.read(flush)) != -1){ os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); is.close(); } os.close(); } // 利用合并流来进行文件的合并 private void seq_merge(String destPath) throws IOException { // 输出流 OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(destPath, true) ); Vector<InputStream> vi = new Vector<InputStream>(); SequenceInputStream sis = null; // 输入流 for (int i = 0; i < destPaths.size(); i++) { InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream((new FileInputStream(destPaths.get(i)))); } sis = new SequenceInputStream(vi.elements()); // 拷贝 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; while((len = sis.read(flush)) != -1){ os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); sis.close(); os.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { SplitFile sf = new SplitFile("test.png", "dest", 1024*10); sf.split(); sf.seq_merge("merge-seq.png"); } }
5. CommonsIO
-
常用核心操作和拷贝核心操作
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.commons.io.LineIterator; import org.apache.commons.io.filefilter.DirectoryFileFilter; import org.apache.commons.io.filefilter.EmptyFileFilter; import org.apache.commons.io.filefilter.FileFilterUtils; import org.apache.commons.io.filefilter.SuffixFileFilter; import javax.imageio.stream.FileCacheImageInputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URL; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: CIOTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/22 16:00 * @desc: */ public class CIOTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 文件大小 long len = FileUtils.sizeOf(new File("D:\\李添的数据哦!!!\\BookStudy\\else\\JAVAPro\\src\\CIOTest1.java")); System.out.println(len); // 目录大小 len = FileUtils.sizeOf(new File("D:\\李添的数据哦!!!\\BookStudy")); System.out.println(len); // 列出子孙集 /* 第一个参数:目标路径 第二个参数:过滤文件: NOT_EMPTY,即只要非空文件 SuffixFileFilter,即只要该后缀名的文件 第三个参数:过滤目录: INSTANCE,即只看子孙集 */ Collection<File> files = FileUtils.listFiles( new File("D:\\李添的数据哦!!!\\BookStudy\\else\\JAVAPro"), FileFilterUtils.or(EmptyFileFilter.NOT_EMPTY, new SuffixFileFilter("java"), new SuffixFileFilter("class")), DirectoryFileFilter.INSTANCE ); for (File file : files) { System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); } // 读取文件内容 String path = "D:\\李添的数据哦!!!\\BookStudy\\else\\【参考】3. 代码快捷键操作.md"; String msg = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File(path), "UTF-8"); System.out.println(msg); byte[] datas = FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(new File(path)); System.out.println(datas.length); // 逐行读取 List<String> msgs = FileUtils.readLines(new File((path)), "UTF-8"); for (String str : msgs) { System.out.println(str); } // 逐行读取2 LineIterator it = FileUtils.lineIterator(new File(path), "UTF-8"); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.nextLine()); } // 写出内容到文件 FileUtils.write(new File("happy.txt"), "学习是一件伟大的事业\n", "UTF-8"); FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("happy.txt"), "学习是一件辛苦的事业\n", "UTF-8", true); FileUtils.writeByteArrayToFile(new File("happy.txt"), "学习是一件快乐的事业\n".getBytes("UTF-8"), true); // 写出列表 List<String> dd = new ArrayList<>(); dd.add("马云"); dd.add("马化腾"); dd.add("礼拜"); FileUtils.writeLines(new File("happy.txt"), dd, "-", true); // 拷贝 FileUtils.copyFile(new File("test.png"), new File("p-copy.png")); // 复制文件到目录 FileUtils.copyFileToDirectory(new File("test.png"), new File("lib")); // 复制目录到目录下 FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(new File("lib"), new File("lib2")); // 复制当前路径的某个目录到当前目录的新目录 FileUtils.copyDirectory(new File("lib"), new File("lib2")); // 拷贝URL内容 // 方法1:保存网上的图片到本地文件 String url = "https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2019062009044675.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3FxXzIxNTc5MDQ1,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70"; FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File("what.jpg")); // 方法2:获取网页的源码 String dat = IOUtils.toString(new URL("http://www.baidu.com"), "UTF-8"); System.out.println(dat); } }
第11章 多线程技术
1. 概念
-
Process与Thread
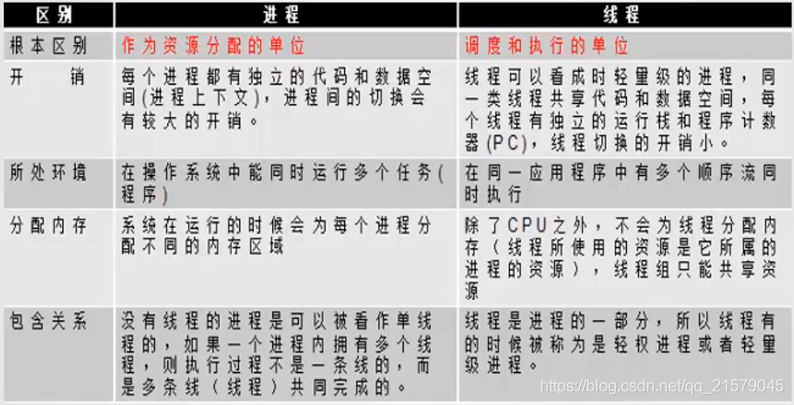
-
核心概念
- 线程就是独立的执行路径。
- 在程序运行时,即使没有自己创建线程,后台也会存在多个线程,如gc线程、主线程。
- main()称之为主线程,为系统的入口点,用于执行整个程序。
- 在一个进程中,如果开辟了多个线程,线程的运行由调度器安排调度,调度器是与操作系统紧密相关的,先后顺序是不能认为干预的。
- 对同一份资源操作时,会存在资源抢夺的问题,需要加入并发控制。
- 线程会带来额外的开销,如cpu调度时间,并发控制开销。
- 每个线程在自己的工作内存交互,加载和存储主内存控制不当会造成数据不一致。
-
少用继承多用实现,因为java里面只能单继承
-
线程Thread的使用方式
- 继承Thread,重写run()方法,通过start()方法去启动线程
- 实现Runnable接口,重写run()方法,通过new一个Thead对象调start()方法。
-
start方法不保证立即运行,由cpu调用
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ThreadStudy01.java * @time: 2019/10/25 12:37 * @desc: 进程学习1 */ public class StartThread1 extends Thread{ public void run(){ for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("一边听歌一边敲代码。"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 创建子类对象 StartThread1 st = new StartThread1(); // 启动 st.start(); // run是普通方法的调用 // st.run(); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("coding。"); Thread.sleep(1); } } } -
创建线程方式1:利用线程下载图片案例
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TDownloader.java * @time: 2019/10/28 15:58 * @desc: 进程学习2:下载图片 */ public class TDownloader extends Thread{ // 远程路径 private String url; // 存储名字 private String name; public TDownloader(String url, String name) { this.url = url; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { WebDownloader wd = new WebDownloader(); wd.download(url, name); System.out.println(name); } public static void main(String[] args){ TDownloader td1 = new TDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107085145510.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "lstm.png"); TDownloader td2 = new TDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107095455442.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "peephole_connection.png"); TDownloader td3 = new TDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107101049389.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "gru.png"); // 启动三个线程 td1.start(); td2.start(); td3.start(); } } -
利用线程方式2:(推荐使用这种方式)
- 避免单继承的局限性,优先使用接口
- 方便共享资源
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ThreadStudy01.java * @time: 2019/10/25 12:37 * @desc: 进程学习3 */ public class StartRun1 implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("一边听歌一边敲代码。"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { /* // 创建实现类对象 StartRun1 sr = new StartRun1(); // 创建代理类对象 Thread t = new Thread(sr); // 启动 t.start(); // run是普通方法的调用 // st.run(); */ // 利用匿名对象 new Thread(new StartRun1()).start(); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("coding。"); Thread.sleep(1); } } }/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TDownloader.java * @time: 2019/10/28 15:58 * @desc: 进程学习2:下载图片 */ public class IDownloader implements Runnable { // 远程路径 private String url; // 存储名字 private String name; public IDownloader(String url, String name) { this.url = url; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { WebDownloader wd = new WebDownloader(); wd.download(url, name); System.out.println(name); } public static void main(String[] args) { IDownloader td1 = new IDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107085145510.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "lstm.png"); IDownloader td2 = new IDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107095455442.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "peephole_connection.png"); IDownloader td3 = new IDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107101049389.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "gru.png"); // 启动三个线程 new Thread(td1).start(); new Thread(td2).start(); new Thread(td3).start(); } } -
共享资源:模拟买票
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Web12306.java * @time: 2019/10/30 12:36 * @desc: 共享资源:模拟买票 */ public class Web12306 implements Runnable { // 票数 private int ticketNums = 99; @Override public void run() { while(true){ if(ticketNums<0){ break; } try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + ticketNums--); } } public static void main(String[] args){ // 一份资源 Web12306 web = new Web12306(); // 多个代理 new Thread(web, "张三").start(); new Thread(web, "李四").start(); new Thread(web, "王五").start(); } } -
共享资源:模拟龟兔赛跑
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Racer.java * @time: 2019/10/30 14:55 * @desc: 共享资源:模拟龟兔赛跑 */ public class Racer implements Runnable { private String winner; // 胜利者 @Override public void run() { for (int steps = 1; steps <= 100; steps++) { // 模拟休息 if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("rabit") && steps % 10 == 0){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + steps); // 比赛是否结束 boolean flag = gameOver(steps); if (flag) { break; } } } private boolean gameOver(int steps) { if (winner != null) { // 存在胜利者 return true; } else { if (steps == 100) { winner = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println("winner==>" + winner); return true; } } return false; } public static void main(String[] args) { Racer racer = new Racer(); new Thread(racer, "tortoise").start(); new Thread(racer, "rabbit").start(); } } -
Callable:能抛出异常,有返回值(了解)
import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.operations.Bool; import jdk.nashorn.internal.codegen.CompilerConstants; import java.util.concurrent.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TDownloader.java * @time: 2019/10/28 15:58 * @desc: Callable了解学习 */ public class CDownloader implements Callable<Boolean> { // 远程路径 private String url; // 存储名字 private String name; public CDownloader(String url, String name) { this.url = url; this.name = name; } @Override public Boolean call() throws Exception { WebDownloader wd = new WebDownloader(); wd.download(url, name); System.out.println(name); return true; } public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CDownloader cd1 = new CDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107085145510.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "lstm.png"); CDownloader cd2 = new CDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107095455442.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "peephole_connection.png"); CDownloader cd3 = new CDownloader("https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20181107101049389.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L0hhcHB5Um9ja2luZw==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70", "gru.png"); // 创建执行服务 ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); // 提交执行 Future<Boolean> result1 = ser.submit(cd1); Future<Boolean> result2 = ser.submit(cd2); Future<Boolean> result3 = ser.submit(cd3); // 获取结果 boolean r1 = result1.get(); boolean r2 = result1.get(); boolean r3 = result1.get(); // 关闭服务 ser.shutdownNow(); } } -
创建线程有几种方式:常用的有两种,继承Thread类,重写Runnable接口。还有一种方式,JUC并发包下,实现Callable接口。
-
静态代理设计模式
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: StaticProxy.java * @time: 2019/10/30 15:29 * @desc: 静态代理设计模式学习 */ public class StaticProxy { public static void main(String[] args) { new WeddingCompany(new You()).happyMarry(); } } interface Marry { void happyMarry(); } // 真实角色 class You implements Marry { @Override public void happyMarry() { System.out.println("你和你的广寒仙子本月了..."); } } //代理角色,婚庆公司 class WeddingCompany implements Marry { // 真实角色 private Marry target; public WeddingCompany(Marry target) { this.target = target; } @Override public void happyMarry() { ready(); this.target.happyMarry(); after(); } private void ready() { System.out.println("布置猪窝..."); } private void after() { System.out.println("闹玉兔..."); } } -
Lambda表达式 简化线程(用一次)的使用
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LambdaThread.java * @time: 2019/10/30 16:00 * @desc: Lambda表达式 简化线程(用一次)的使用 */ public class LambdaThread { // 类中类:静态内部类 static class Test implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("一边听歌"); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new Test()).start(); // 方法中类:局部内部类 class Test2 implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("一边听歌"); } } } new Thread(new Test2()).start(); // 参数中类:匿名内部类 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("一边听歌"); } } }).start(); // jdk8简化匿名内部类,lambda new Thread( () -> { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("一边听歌"); } } ).start(); } } -
lambda推导:必须存在类型
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LambdaTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/31 15:18 * @desc: lambda推导 */ public class LambdaTest1 { static class Like2 implements ILike { public void lambda() { System.out.println("2. 我喜欢你大爷!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { class Like3 implements ILike { public void lambda() { System.out.println("3. 我喜欢你大爷!"); } } // 外部类 ILike like = new Like(); like.lambda(); // 静态内部类 like = new Like2(); like.lambda(); // 方法内部类 like = new Like3(); like.lambda(); // 匿名类 like = new ILike() { @Override public void lambda() { System.out.println("4. 我喜欢你大爷!"); } }; like.lambda(); // lambda like = () -> { System.out.println("5. 我喜欢你大爷!"); }; like.lambda(); } } interface ILike { void lambda(); } class Like implements ILike { @Override public void lambda() { System.out.println("1. 我喜欢你大爷!"); } } -
lambda推导 + 参数
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LambdaTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/31 15:18 * @desc: lambda推导 + 参数 */ public class LambdaTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ILove love = (int a) -> { System.out.println("偶买噶!-->" + a); }; love.lambda(100); // 参数类型可以省略 ILove love2 = s -> { System.out.println("偶买噶!-->" + s); }; love2.lambda(10); // 花括号也可以省略 ILove love3 = s -> System.out.println("偶买噶!-->" + s); love3.lambda(1); } } interface ILove { void lambda(int a); } class Love implements ILove { @Override public void lambda(int a) { System.out.println("偶买噶!-->" + a); } } /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LambdaTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/31 15:18 * @desc: lambda推导 + 参数 */ public class LambdaTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ILove love = (int a) -> { System.out.println("偶买噶!-->" + a); }; love.lambda(100); // 参数类型可以省略 ILove love2 = s -> { System.out.println("偶买噶!-->" + s); }; love2.lambda(10); // 花括号也可以省略 ILove love3 = s -> System.out.println("偶买噶!-->" + s); love3.lambda(1); } } interface ILove { void lambda(int a); } class Love implements ILove { @Override public void lambda(int a) { System.out.println("偶买噶!-->" + a); } } -
lambda推导 + 参数 + 返回值
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LambdaTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/31 15:18 * @desc: lambda推导 + 参数 + 返回值 */ public class LambdaTest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { IInterest in = (int q, int p) -> { System.out.println(q + p); return q + p; }; in.lambda(100, 50); // 简化版本 IInterest in2 = (q, p) -> q + p / 2; System.out.println(in2.lambda(10, 20)); } } interface IInterest { int lambda(int a, int b); } // 参考,下面内容可以不要 class Interest implements IInterest { @Override public int lambda(int aa, int bb) { System.out.println(aa + bb); return aa + bb; } } -
lambda推导实现线程
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LambdaTest1.java * @time: 2019/10/31 15:18 * @desc: lambda推导实现线程 */ public class LambdaTest4 { public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("一边学习lambda"); }).start(); // 简化:花括号可以不要 new Thread(() -> System.out.println("一边泪流满面")).start(); // 如果是多个语句,就不能省略 new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我疯了,你呢?"); } }).start(); } }
2. 线程状态
-
一个线程对象在它的生命周期内,需要经历5个状态。
-
新生状态(New)
用new关键字建立一个线程对象后,该线程对象就处于新生状态。处于新生状态的线程有自己的内存空间,通过调用start方法进入就绪状态。
-
就绪状态(Runnable)
处于就绪状态的线程已经具备了运行条件,但是还没有被分配到CPU,处于“线程就绪队列”,等待系统为其分配CPU。就绪状态并不是执行状态,当系统选定一个等待执行的Thread对象后,它就会进入执行状态。一旦获得CPU,线程就进入运行状态并自动调用自己的run方法。有4中原因会导致线程进入就绪状态:
-
新建线程:调用start()方法,进入就绪状态;
-
阻塞线程:阻塞解除,进入就绪状态;
-
运行线程:调用yield()方法,直接进入就绪状态;
-
运行线程:JVM将CPU资源从本线程切换到其他线程。
-
-
运行状态(Running)
在运行状态的线程执行自己run方法中的代码,直到调用其他方法而终止或等待某资源而阻塞或完成任务而死亡。如果在给定的时间片内没有执行结束,就会被系统给换下来回到就绪状态。也可能由于某些“导致阻塞的事件”而进入阻塞状态。
-
阻塞状态(Blocked)
阻塞指的是暂停一个线程的执行以等待某个条件发生(如某资源就绪)。有4种原因会导致阻塞:
-
执行sleep(int millsecond)方法,使当前线程休眠,进入阻塞状态。当指定的时间到了后,线程进入就绪状态。
-
执行wait()方法,使当前线程进入阻塞状态。当使用nofity()方法唤醒这个线程后,它进入就绪状态。
-
线程运行时,某个操作进入阻塞状态,比如执行IO流操作(read()/write()方法本身就是阻塞的方法)。只有当引起该操作阻塞的原因消失后,线程进入就绪状态。
-
join()线程联合: 当某个线程等待另一个线程执行结束后,才能继续执行时,使用join()方法。
-
-
死亡状态(Terminated)
死亡状态是线程生命周期中的最后一个阶段。线程死亡的原因有两个。一个是正常运行的线程完成了它run()方法内的全部工作; 另一个是线程被强制终止,如通过执行stop()或destroy()方法来终止一个线程(注:stop()/destroy()方法已经被JDK废弃,不推荐使用)。
当一个线程进入死亡状态以后,就不能再回到其它状态了。
-
线程的终止
- 线程正常执行完毕–>次数
- 外部干涉–>加入标识
不要使用stop和destroy
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TerminateThread.java * @time: 2019/11/1 14:32 * @desc: 终止线程 */ public class TerminateThread implements Runnable { // 1. 设置标识,标记线程体是否可以运行 private boolean flag = true; private String name; public TerminateThread(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { int i = 0; // 2. 关联标识,true-->运行,False-->停止 while (flag) { System.out.println(name + "-->" + i++); } } // 3. 对外提供方法改变标识 public void terminate() { this.flag = false; } public static void main(String[] args) { TerminateThread tt = new TerminateThread("你大爷"); new Thread(tt).start(); for (int i = 0; i < 99; i++) { if (i == 88){ tt.terminate(); // 线程终止 System.out.println("tt game over!"); } System.out.println("main-->" + i); } } } -
线程的暂停-sleep: 可以让正在运行的线程进入阻塞状态,直到休眠时间满了,进入就绪状态。
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: BlockedSleep1.java * @time: 2019/11/1 14:46 * @desc: sleep模拟倒计时 */ public class BlockedSleep1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 倒计时 Date endTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + 1000 * 10); long end = endTime.getTime(); while (true) { System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss").format(endTime)); Thread.sleep(1000); endTime = new Date(endTime.getTime()-1000); if(end-10000 > endTime.getTime()){ break; } } } public static void test() throws InterruptedException { // 倒数10个数,1秒一个 int num = 10; while (true) { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(num--); } } } -
线程的暂停-yield: 可以让正在运行的线程直接进入就绪状态,让出CPU的使用权。
import org.omg.PortableServer.THREAD_POLICY_ID; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: YieldDemo1.java * @time: 2019/11/1 14:55 * @desc: yield礼让线程,暂停线程,直接进入就绪状态不是阻塞状态 */ public class YieldDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { MyYield my = new MyYield(); new Thread(my, "a").start(); new Thread(my, "b").start(); // lambda实现 new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println("lambda..." + i); } }).start(); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { if (i % 20 == 0) { Thread.yield(); // main礼让 } System.out.println("main..." + i); } } } class MyYield implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->start"); Thread.yield(); // 礼让 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->end"); } } -
线程的联合-join:合并线程,插队线程。
import sun.java2d.loops.TransformHelper; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: BlockedJoin1.java * @time: 2019/11/1 15:05 * @desc: 爸爸和儿子买烟的故事 */ public class BlockedJoin1 { public static void main(String[] args){ new Father().start(); } } class Father extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("想抽烟,发现没了"); System.out.println("让儿子去买中华"); Thread t = new Son(); t.start(); try { t.join(); // father被阻塞 System.out.println("老爸接过烟,把零钱给了儿子"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("孩子走丢了,老爸出去找孩子去了..."); } } } class Son extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("接过老爸的钱出去了..."); System.out.println("路边有个游戏厅,玩了10秒"); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println(i+"秒过去了..."); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("赶紧买烟去..."); System.out.println("手拿一包中华回家了..."); } } -
观察线程的各个状态
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: AllState.java * @time: 2019/11/1 15:22 * @desc: 观察线程的各个状态 */ public class AllState { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("..."); }); // 观察状态 Thread.State state = t.getState(); System.out.println(state); // NEW t.start(); state = t.getState(); System.out.println(state); // RUNNABLE while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) { try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } state = t.getState(); // TIMED_WAITING System.out.println(state); } state = t.getState(); // TERMINATED System.out.println(state); } }
3. 线程的优先级
-
NORM_PRIORITY 5
-
MIN_PRIORITY 1
-
MAX_PRIORITY 10
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: PriorityTest1.java * @time: 2019/11/4 12:38 * @desc: 多线程优先级 */ public class PriorityTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { MyPriority mp = new MyPriority(); Thread t1 = new Thread(mp); Thread t2 = new Thread(mp); Thread t3 = new Thread(mp); Thread t4 = new Thread(mp); Thread t5 = new Thread(mp); Thread t6 = new Thread(mp); t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); t3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); t4.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); t5.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); t6.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); t4.start(); t5.start(); t6.start(); } } class MyPriority implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); Thread.yield(); } }
4. 守护线程
-
是为用户线程服务的;JVM停止不用等待守护线程执行完毕
-
默认:用户线程,JVM等待用户线程执行完毕才会停止
import org.omg.PortableServer.THREAD_POLICY_ID; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DaemonTest.java * @time: 2019/11/4 13:35 * @desc: 守护线程学习 */ public class DaemonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(new You1()); t1.run(); Thread t2 = new Thread(new God1()); // 将用户线程调整为守护线程 t2.setDaemon(true); t2.start(); } } class You1 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 365 * 100; i++) { System.out.println("happy life!"); } System.out.println("ooo..."); } } class God1 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { for (;true;) { System.out.println("bless you!"); } } }
5. 获取线程基本信息的方法
-
常用方法
-
案例
/** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: InfoTest.java * @time: 2019/11/4 13:46 * @desc: 获取线程基本信息的方法 */ public class InfoTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 线程是否活着 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isAlive()); // 设置名称:真是角色+代理角色 MyInfo info = new MyInfo("战斗机"); Thread t = new Thread(info); t.setName("公鸡"); t.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(t.isAlive()); } } class MyInfo implements Runnable{ private String name; public MyInfo(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + name); } }
6. 并发控制
- 并发:同一个对象多个线程同时操作
1. 同步
-
线程不安全案例1
package com.sxt.thread; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UnsafeTest.java * @time: 2019/11/4 13:57 * @desc: 线程同步 */ public class UnsafeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 账户 Account account = new Account(100, "结婚礼金"); Drawing you = new Drawing(account, 80, "可悲的你"); Drawing wife = new Drawing(account, 90, "happy的她"); you.start(); wife.start(); } } // 账户 class Account { int money; String name; public Account(int money, String name) { this.money = money; this.name = name; } } // 模拟取款 class Drawing extends Thread { // 取钱的账户 Account accout; // 取多少钱 int drawingMoney; // 口袋里的总数 int packetTotal; public Drawing(Account accout, int drawingMoney, String name) { super(name); this.accout = accout; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } @Override public void run() { if(accout.money - drawingMoney < 0){ return; } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } accout.money -= drawingMoney; packetTotal += drawingMoney; System.out.println(this.getName() + "-->账户余额为:" + accout.money); System.out.println(this.getName() + "-->口袋里的钱为:" + packetTotal); } } -
线程不安全案例2
package com.sxt.thread; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UnsafeTest.java * @time: 2019/11/4 13:57 * @desc: 线程同步 */ public class UnsafeTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { new Thread(()->{ list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }).start(); } System.out.println(list.size()); } } -
锁机制
-
为了保证数据在方法中被访问时的正确性,在访问时加入锁机制(synchronized),当一个线程获得对象的排它锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用后释放锁即可。存在以下问题:
- 一个线程持有锁会导致其它所有需要此锁的线程挂起;
- 在多线程竞争下,加锁、释放锁会导致比较多的上下文切换和调度延时,引起性能问题;
- 如果一个优先级高的线程等待一个优先级低的线程释放锁会导致优先级倒置,引起性能问题。
-
线程安全:在并发时保证数据的正确性、效率尽可能高(synchronized)
- 同步方法
- 同步块(java有四种块,普通块局部块,构造块,静态块,同步块)
-
样例1:
package com.sxt.thread; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UnsafeTest.java * @time: 2019/11/4 13:57 * @desc: 线程同步 */ public class SafeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 账户 Account account = new Account(100, "结婚礼金"); SafeDrawing you = new SafeDrawing(account, 80, "可悲的你"); SafeDrawing wife = new SafeDrawing(account, 90, "happy的她"); you.start(); wife.start(); } } // 模拟取款 class SafeDrawing extends Thread { // 取钱的账户 Account accout; // 取多少钱 int drawingMoney; // 口袋里的总数 int packetTotal; public SafeDrawing(Account accout, int drawingMoney, String name) { super(name); this.accout = accout; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } @Override public void run() { test(); } public void test() { if (accout.money <= 0) { return; } synchronized (accout) { if (accout.money - drawingMoney < 0) { return; } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } accout.money -= drawingMoney; packetTotal += drawingMoney; System.out.println(this.getName() + "-->账户余额为:" + accout.money); System.out.println(this.getName() + "-->口袋里的钱为:" + packetTotal); } } } -
样例2
package com.sxt.thread; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UnsafeTest.java * @time: 2019/11/4 13:57 * @desc: 线程同步 */ public class SafeTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { new Thread(() -> { // 同步块 synchronized (list) { list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }).start(); } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(list.size()); } }
-
-
双重检测:考虑临界值的问题
package com.sxt.thread;
/**
* @author: Li Tian
* @contact: litian_cup@163.com
* @software: IntelliJ IDEA
* @file: Web12306.java
* @time: 2019/10/30 12:36
* @desc: 线程安全买票
*/
public class Safe12306 implements Runnable {
// 票数
private int ticketNums = 10;
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
test();
}
}
private void test() {
if (ticketNums <= 0) { // 考虑的是没有票的情况
flag = false;
return;
}
synchronized (this) {
if (ticketNums <= 0) { // 考虑的是最后一张票的情况
flag = false;
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + ticketNums--);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 一份资源
Safe12306 web = new Safe12306();
// 多个代理
new Thread(web, "张三").start();
new Thread(web, "李四").start();
new Thread(web, "王五").start();
}
}
-
案例1:快乐影院
package com.sxt.thread; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: HappyCinema.java * @time: 2019/11/5 12:57 * @desc: 快乐电影院抢座位案例 */ public class HappyCinema { public static void main(String[] args) { Cinema c = new Cinema(2, "happy sxt"); new Thread(new Customer(c, 2), "老高").start(); new Thread(new Customer(c, 1), "老李").start(); } } class Customer implements Runnable { Cinema cinema; int seats; public Customer(Cinema cinema, int seats) { this.cinema = cinema; this.seats = seats; } @Override public void run() { synchronized (cinema) { boolean flag = cinema.bookTickets(seats); if (flag) { System.out.println("出票成功" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-<位置为:" + seats); } else { System.out.println("出票失败" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-<位置不够!"); } } } } class Cinema { // 可用的位置 int available; // 名称 String name; public Cinema(int available, String name) { this.available = available; this.name = name; } // 购票 public boolean bookTickets(int seats) { System.out.println("可用位置为:" + available); if (seats > available) { return false; } available -= seats; return true; } } -
案例2:快乐影院真实List座位
package com.sxt.thread; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: HappyCinema.java * @time: 2019/11/5 12:57 * @desc: 快乐电影院抢座位案例 */ public class HappyCinema2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 可用位置 List<Integer> available = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++) { available.add(i); } // 顾客需要的位置 List<Integer> seats1 = new ArrayList<>(); seats1.add(1); seats1.add(2); List<Integer> seats2 = new ArrayList<>(); seats2.add(4); seats2.add(5); seats2.add(6); SxtCinema c = new SxtCinema(available, "happy sxt"); new Thread(new HappyCustomer(c, seats1), "老高").start(); new Thread(new HappyCustomer(c, seats2), "老李").start(); } } class HappyCustomer implements Runnable { SxtCinema cinema; List<Integer> seats; public HappyCustomer(SxtCinema cinema, List<Integer> seats) { this.cinema = cinema; this.seats = seats; } @Override public void run() { synchronized (cinema) { boolean flag = cinema.bookTickets(seats); if (flag) { System.out.println("出票成功" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-<位置为:" + seats); } else { System.out.println("出票失败" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-<位置不够!"); } } } } class SxtCinema { // 可用的位置 List<Integer> available; // 名称 String name; public SxtCinema(List<Integer> available, String name) { this.available = available; this.name = name; } // 购票 public boolean bookTickets(List<Integer> seats) { System.out.println("可用位置为:" + available); List<Integer> copy = new ArrayList<>(); copy.addAll(available); // 相减 copy.removeAll(seats); // 判断大小 if (available.size() - copy.size() != seats.size()) { return false; } // 成功 available = copy; return true; } } -
案例3:快乐火车票
package com.sxt.thread; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Happy12306.java * @time: 2019/11/7 19:24 * @desc: 快乐火车票 */ public class Happy12306 { public static void main(String[] args) { Web12306 c = new Web12306(2, "happy sxt"); new Passenger(c, "老高", 2).start(); new Passenger(c, "老李", 1).start(); } } // 乘客 class Passenger extends Thread { int seats; public Passenger(Runnable target, String name, int seats) { super(target, name); this.seats = seats; } } // 火车票网 class Web12306 implements Runnable { // 可用的位置 int available; // 名称 String name; public Web12306(int available, String name) { this.available = available; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { Passenger p = (Passenger) Thread.currentThread(); boolean flag = this.bookTickets(p.seats); if (flag) { System.out.println("出票成功" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-<位置为:" + p.seats); } else { System.out.println("出票失败" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-<位置不够!"); } } // 购票 public synchronized boolean bookTickets(int seats) { System.out.println("可用位置为:" + available); if (seats > available) { return false; } available -= seats; return true; } } -
并发容器:import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList
package com.sxt.thread; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: SynContainer.java * @time: 2019/11/8 14:09 * @desc: 线程同步:并发容器 */ public class SynContainer { public static void main(String[] args) { CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { new Thread(() -> { // 同步块 list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }).start(); } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(list.size()); } }
2. 死锁
-
死锁指的是:多个线程各自占有一些共享资源,并且互相等待其他线程占有的资源才能进行,而导致两个或者多个线程都在等待对方释放资源,都停止执行的情形。
-
避免方式:不要在同一个代码块中持有多个对象锁。
-
死锁案例:
package com.sxt.thread; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DeadLock.java * @time: 2019/11/8 14:16 * @desc: 死锁 */ public class DeadLock { public static void main(String[] args) { Makeup g1 = new Makeup(1, "丰光"); Makeup g2 = new Makeup(2, "师兄"); g1.start(); g2.start(); } } // 口红 class Lipstick { } // 镜子 class Mirror { } // 化妆 class Makeup extends Thread { static Lipstick lip = new Lipstick(); static Mirror mir = new Mirror(); // 选择 int choice; // 名字 String girlname; public Makeup(int choice, String girlname) { this.choice = choice; this.girlname = girlname; } @Override public void run() { // 化妆 makeup(); } private void makeup() { // 相互持有对方的对象锁,这样才有可能造成死锁 if (choice == 1) { // 获得口红的锁 synchronized (lip) { System.out.println(this.girlname + "-->涂口红"); // 1秒后想拥有镜子的锁 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (mir) { System.out.println(this.girlname + "-->照镜子"); } } } else { synchronized (mir) { System.out.println(this.girlname + "-->照镜子"); // 2秒后想拥有口红的锁 try { Thread.sleep(1100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (lip) { System.out.println(this.girlname + "-->涂口红"); } } } } } -
死锁的解决案例:
package com.sxt.thread; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DeadLock.java * @time: 2019/11/8 14:16 * @desc: 解决死锁 */ public class DeadLock2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Makeup2 g1 = new Makeup2(1, "丰光"); Makeup2 g2 = new Makeup2(2, "师兄"); g1.start(); g2.start(); } } // 化妆 class Makeup2 extends Thread { static Lipstick lip = new Lipstick(); static Mirror mir = new Mirror(); // 选择 int choice; // 名字 String girlname; public Makeup2(int choice, String girlname) { this.choice = choice; this.girlname = girlname; } @Override public void run() { // 化妆 makeup(); } private void makeup() { // 相互持有对方的对象锁,这样才有可能造成死锁 if (choice == 1) { // 获得口红的锁 synchronized (lip) { System.out.println(this.girlname + "-->涂口红"); // 1秒后想拥有镜子的锁 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } synchronized (mir) { System.out.println(this.girlname + "-->照镜子"); } } else { synchronized (mir) { System.out.println(this.girlname + "-->照镜子"); // 2秒后想拥有口红的锁 try { Thread.sleep(1100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } synchronized (lip) { System.out.println(this.girlname + "-->涂口红"); } } } }
3. 并发协作
-
生产者消费者模式
-
view简介
- pv:page view
- uv:unique view
- vv:visit view
-
在生产者消费者问题中,仅有synchronized是不够的
- synchronized可组织并发更新同一个共享资源,实现了同步
- synchronized不能用来实现不同线程之间的消息传递(通信)
-
实现生产者消费者的方法:
- 管程法
- 信号灯法
-
实现方式:用wait()等待,notify()唤醒
-
管程法:借助缓冲区
package com.sxt.cooperation; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: CoTest1.java * @time: 2019/11/8 15:36 * @desc: 协作模型:生产者消费者实现方式1:管程法 */ public class CoTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { SynContainer container = new SynContainer(); new Productor(container).start(); new Consumer(container).start(); } } // 生产者 class Productor extends Thread { SynContainer container; public Productor(SynContainer container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { // 开始生产 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println("生产-->第" + i + "个馒头"); container.push(new SteamedBun(i)); } } } // 消费者 class Consumer extends Thread { SynContainer container; public Consumer(SynContainer container) { this.container = container; } @Override public void run() { // 开始消费 for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { System.out.println("消费-->第" + container.pop().id + "个馒头"); } } } // 缓冲区 class SynContainer { SteamedBun[] buns = new SteamedBun[10]; int count = 0; // 存储:生产 public synchronized void push(SteamedBun bun) { // 何时能生产:容器存在空间 if (count == buns.length) { try { // 线程阻塞,消费者通知生产解除 this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } // 存在空间,可以生产 buns[count++] = bun; // 存在数据了,可以通知消费了 this.notifyAll(); } // 获取:消费 public synchronized SteamedBun pop() { // 何时消费:容器中是否存在数据,存在数据则可以消费,没有数据就只能等待 if (count == 0) { try { // 线程阻塞:生产者通知消费则接触阻塞 this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } SteamedBun bun = buns[--count]; // 存在空间,可以唤醒对方生产 this.notifyAll(); return bun; } } // 数据。馒头 class SteamedBun { int id; public SteamedBun(int id) { this.id = id; } } -
信号灯法:借助标志位
package com.sxt.cooperation; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: CoTest2.java * @time: 2019/11/8 16:38 * @desc: 信号灯法 */ public class CoTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Tv tv = new Tv(); new Player(tv).start(); new Watcher(tv).start(); } } // 生产者:演员 class Player extends Thread { Tv tv; public Player(Tv tv) { this.tv = tv; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { if (i % 2 == 0) { this.tv.play("奇葩说"); } else { this.tv.play("倚天屠龙记"); } } } } // 消费者:观众 class Watcher extends Thread { Tv tv; public Watcher(Tv tv) { this.tv = tv; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { tv.watch(); } } } // 同一个资源:电视 class Tv { String voice; // T:演员表演,观众等待;F:观众观看,演员等待 boolean flag = true; // 表演 public synchronized void play(String voice) { // 演员等待 if (!flag) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("表演了" + voice); this.voice = voice; // 唤醒 this.notifyAll(); this.flag = !this.flag; } // 观看 public synchronized void watch() { // 观众等待 if (flag) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("听到了" + voice); // 唤醒 this.notifyAll(); this.flag = !this.flag; } }
7. 高级主题
-
定时调度(简单):Timer和TimerTask类
package com.sxt.cooperation; import com.sun.deploy.cache.CacheEntry; import com.sun.deploy.security.MozillaMyKeyStore; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.GregorianCalendar; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TimerTest1.java * @time: 2019/11/9 18:27 * @desc: 定时调度 */ public class TimerTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Timer timer = new Timer(); // 执行安排 // 执行一次 timer.schedule(new MyTask(), 1000); // 执行多次 timer.schedule(new MyTask(), 1000, 200); // 指定时间执行 Calendar cal = new GregorianCalendar(2099, 11, 3, 11, 22, 22); timer.schedule(new MyTask(), cal.getTime(), 200); } } class MyTask extends TimerTask { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("放空大脑休息一会儿~"); } } } -
定时调度(复杂):QUARTZ
package com.sxt.others; import static org.quartz.DateBuilder.evenSecondDate; import static org.quartz.JobBuilder.newJob; import static org.quartz.TriggerBuilder.newTrigger; import static org.quartz.SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule; import org.quartz.JobDetail; import org.quartz.Scheduler; import org.quartz.SchedulerFactory; import org.quartz.Trigger; import org.quartz.impl.StdSchedulerFactory; import java.util.Date; /** * quartz学习入门 */ public class QuartzTest { public void run() throws Exception { // 1. 创建Scheduler的工厂 SchedulerFactory sf = new StdSchedulerFactory(); // 2. 从工厂中获取调度器 Scheduler sched = sf.getScheduler(); // 时间 Date runTime = evenSecondDate(new Date()); // 3. 创建JobDetail JobDetail job = newJob(HelloJob.class).withIdentity("job1", "group1").build(); // 4. 触发器 // Trigger trigger = newTrigger().withIdentity("trigger1", "group1").startAt(runTime).build(); // 4 | 2:如果想要循环多次呢,每5秒一次,循环三次 Trigger trigger = newTrigger().withIdentity("trigger1", "group1").startAt(runTime) .withSchedule(simpleSchedule().withIntervalInSeconds(5).withRepeatCount(2)).build(); // 5. 注册任务和触发条件 sched.scheduleJob(job, trigger); // 6. 启动 sched.start(); try { // 5秒后停止 Thread.sleep(30L * 1000L); // executing... } catch (Exception e) { } // shut down the scheduler sched.shutdown(true); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { QuartzTest example = new QuartzTest(); example.run(); } } -
指令重排HappenBefore
- 执行代码的顺序可能与编写代码不一致,即虚拟机优化代码顺序,则为指令重排(HappenBefore)——优化程序性能。
- 机器语言运行步骤
- 从内存中获取要执行的下一个指令
- 将指令解码翻译,从寄存器中取值
- 操作,计算结果
- 将结果写回到对应的寄存器中
-
volatile:
-
保证线程间变量的可见性,即保证数据的同步。
-
volatile是不错的机制,但是volatile不能保证原子性。
package com.sxt.others; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: VolatileTest.java * @time: 2019/11/11 9:29 * @desc: volatile测试 * 不加volatile则程序不会停,加了之后会停 */ public class VolatileTest { private volatile static int num = 0; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Thread(() -> { while(num == 0){ // 此处不要编写代码,这是为了让系统没有时间更新数据 } }).start(); Thread.sleep(1000); num = 1; } }
-
-
dcl单例模式
- 懒汉式套路的基础上加入并发控制,保证在多线程环境下,对外存在一个对象
-
构造器私有化 --> 避免外部new构造器
-
提供私有的静态属性 --> 存储对象的地址
-
提供公共的静态方法 --> 获取属性
package com.sxt.others; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: DoubleCheckedLocking.java * @time: 2019/11/11 9:34 * @desc: 单例模式 */ public class DoubleCheckedLocking { // 2. 提供私有的静态属性 // 没有volatile其他线程可能访问一个没有初始化的对象 private static volatile DoubleCheckedLocking instance; // 1. 构造器私有化 private DoubleCheckedLocking() { } // 3. 提供公共的静态方法 --> 获取属性 public static DoubleCheckedLocking getInstance() { // 再次检测,避免不必要的同步,已经存在对象 if (null != instance) { return instance; } synchronized (DoubleCheckedLocking.class) { if (null == instance) { instance = new DoubleCheckedLocking(); // new一个对象的时候,要做的三件事情 // 开辟空间;初始化对象信息;返回对象的地址给引用 // 所以这里可能出现指令重排 } return instance; } } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(DoubleCheckedLocking.getInstance()); }); t.start(); System.out.println(DoubleCheckedLocking.getInstance()); } }
-
ThreadLocal
-
表示的是每个线程自身的存储本地、局部区域
-
方法:get/set/initialValue
package com.sxt.others; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ThreadLocalTest.java * @time: 2019/11/11 9:52 * @desc: ThreadLocal */ public class ThreadLocalTest { // private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); // 更改初始值 // private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(){ // @Override // protected Integer initialValue() { // return 200; // } // }; // 简化上面代码 private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 200); public static void main(String[] args) { // 获取值,初始值为null System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + threadLocal.get()); // 设置值 threadLocal.set(99); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + threadLocal.get()); new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); } public static class MyRun implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { threadLocal.set((int)(Math.random()*99)); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + threadLocal.get()); } } } -
每个线程只使用自身的数据,更改不会影响其他线程
package com.sxt.others; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ThreadLocalTest2.java * @time: 2019/11/11 10:06 * @desc: 取数据 */ public class ThreadLocalTest2 { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 1); public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); } } public static class MyRun implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { Integer left = threadLocal.get(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "得到了-->" + left); threadLocal.set(left - 1); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "还剩下-->" + threadLocal.get()); } } } -
ThreadLocal:分析上下文环境
-
构造器:哪里调用,就属于哪里,找线程体
-
run方法:本线程自己的
package com.sxt.others; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ThreadLocalTest3.java * @time: 2019/11/11 10:11 * @desc: 分析上下文环境 */ public class ThreadLocalTest3 { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 1); public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); new Thread(new MyRun()).start(); } public static class MyRun implements Runnable { public MyRun() { // 属于main线程 threadLocal.set(-100); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + threadLocal.get()); } @Override public void run() { // 属于其他线程 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + threadLocal.get()); } } }
-
-
InheritableThreadLocal:继承上下文环境的数据,拷贝一份给子线程
package com.sxt.others; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: ThreadLocalTest4.java * @time: 2019/11/11 10:25 * @desc: InheritableThreadLocal:继承上下文环境的数据,拷贝一份给子线程。起点 */ public class ThreadLocalTest4 { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { threadLocal.set(2); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + threadLocal.get()); // 线程由main线程开辟 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + threadLocal.get()); // 但是既然是拷贝,所以想改还是互不影响的 threadLocal.set(200); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + threadLocal.get()); }).start(); } }
-
-
可重入锁:锁可以延续使用 + 计数器:ReentrantLock
-
CAS(Compare and Swap)比较并交换:
-
参考链接:CAS乐观锁
-
悲观锁:synchronized是独占锁即悲观锁,会导致其他所有需要锁的线程挂起,等待持有锁的线程释放锁。
-
乐观锁:每次不加锁而是假设没有冲突而去完成某项操作,如果因为冲突失败就重试,直到成功为止。

package com.sxt.others; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: CASTest.java * @time: 2019/11/11 10:51 * @desc: CAS */ public class CASTest { // 库存 private static AtomicInteger stock = new AtomicInteger(3); public static void main(String[] args){ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { new Thread(()->{ // 模拟网络延时 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Integer left = stock.decrementAndGet(); if(left<1){ System.out.println("抢完了..."); return; } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "抢了一个商品" + "-->还剩" + left); }).start(); } } }
-
第12章 网络编程
1. 概念
-
网络:通讯协议+通信接口
-
网络分层:OSI(Open System Interconnect)开放系统互连参考模型
-
网络分层:OSI网络通信协议模型只是一个参考模型,而TCP/IP协议是事实上的标准。TCP/IP协议参考了OSI模型,但是并没有严格按照OSI规定的七层标准去划分,而只划分了四层。
-
数据封装与解封:
-
由于用户传输的数据一般都比较大,有的可以达到MB字节,一次性发送出去十分困难,于是就需要把数据分成许多片段,再按照一定的次序发送出去。这个过程就需要对数据进行封装。
-
数据封装(Data Encapsulation)是指将协议数据单元(PDU)封装在一组协议头和协议尾中的过程。在OSI七层参考模型中,每层主要负责与其它机器上的对等层进行通信。该过程是在协议数据单元(PDU)中实现的,其中每层的PDU一般由本层的协议头、协议尾和数据封装构成。
- 数据发送处理过程
(1) 应用层将数据交给传输层,传输层添加上TCP的控制信息(称为TCP头部),这个数据单元称为段(Segment),加入控制信息的过程称为封装。然后,将段交给网络层。
(2) 网络层接收到段,再添加上IP头部,这个数据单元称为包(Packet)。然后,将包交给数据链路层。
(3) 数据链路层接收到包,再添加上MAC头部和尾部,这个数据单元称为帧(Frame)。然后,将帧交给物理层。
(4) 物理层将接收到的数据转化为比特流,然后在网线中传送。
- 数据接收处理过程
(1) 物理层接收到比特流,经过处理后将数据交给数据链路层。
(2) 数据链路层将接收到的数据转化为数据帧,再除去MAC头部和尾部,这个除去控制信息的过程称为解封,然后将包交给网络层。
(3) 网络层接收到包,再除去IP头部,然后将段交给传输层。
(4) 传输层接收到段,再除去TCP头部,然后将数据交给应用层。
从以上传输过程中,可以总结出以下规则:
(1) 发送方数据处理的方式是从高层到底层,逐层进行数据封装。
(2) 接收方数据处理的方式是从底层到高层,逐层进行数据解封装。
接收方的每一层只把对该层有意义的数据拿走,或者说每一层只能处理发送方同等层的数据,然后把其余的部分传递给上一层,这就是对等层通信的概念。
-
**IP地址:**用来标识网络中的一个通信实体的地址。通信实体可以是计算机、路由器等。 比如互联网的每个服务器都要有自己的IP地址,而每个局域网的计算机要通信也要配置IP地址。路由器是连接两个或多个网络的网络设备。
-
目前主流使用的IP地址是IPV4,但是随着网络规模的不断扩大,IPV4面临着枯竭的危险,所以推出了IPV6。
IPV4:32位地址,并以8位为一个单位,分成四部分,以点分十进制表示,如192.168.0.1。因为8位二进制的计数范围是00000000—11111111,对应十进制的0-255,所以-4.278.4.1是错误的IPV4地址。
IPV6:128位(16个字节)写成8个16位的无符号整数,每个整数用四个十六进制位表示,每个数之间用冒号(:)分开,如:3ffe:3201:1401:1280:c8ff:fe4d:db39:1984
-
注意事项
-
127.0.0.1 本机地址
-
192.168.0.0–192.168.255.255为私有地址,属于非注册地址,专门为组织机构内部使用。
-
InetAddress:
- getLocalHost:本机
- getByName:根据域名DNS | IP地址 --> IP
-
两个成员方法
- getHostAddress:返回地址
- getHostName:返回计算机名
-
-
端口:
-
IP地址用来标识一台计算机,但是一台计算机上可能提供多种网络应用程序,如何来区分这些不同的程序呢?这就要用到端口。
-
端口是虚拟的概念,并不是说在主机上真的有若干个端口。通过端口,可以在一个主机上运行多个网络应用程序。 端口的表示是一个16位的二进制整数,对应十进制的0-65535。
-
Oracle、MySQL、Tomcat、QQ、msn、迅雷、电驴、360等网络程序都有自己的端口。
-
查看命令
- 查看所有端口:netstat -aon
- 查看指定端口:netstat -aon | findstr “808”
- 查看指定进程:tasklist | findstr “808”
- 查看具体程序:使用任务管理器查看PID
-
需要掌握的知识:
- 端口是用来区分软件的
- 2个字节,0-65535,UDP和TCP一样多
- 同一个协议端口不能冲突
- 定义的端口越大越好
-
InetSocketAddress
- 构造器 new InetSocketAddress(地址|域名, 端口);
- 方法:getAddress(),getPort(), getHostName()
package com.sxt.loc; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: PortTest.java * @time: 2019/11/12 14:24 * @desc: 端口 */ public class PortTest { public static void main(String[] args){ // 包含端口 InetSocketAddress socketAddress1 = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080); InetSocketAddress socketAddress2 = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9000); System.out.println(socketAddress1.getHostName()); System.out.println(socketAddress1.getAddress()); System.out.println(socketAddress1.getPort()); System.out.println(socketAddress2.getHostName()); System.out.println(socketAddress2.getAddress()); System.out.println(socketAddress2.getPort()); } } -
URL:
-
在www上,每一信息资源都有统一且唯一的地址,该地址就叫URL(Uniform Resource Locator),它是www的统一资源定位符。URL由4部分组成:协议 、存放资源的主机域名、资源文件名和端口号。如果未指定该端口号,则使用协议默认的端口。例如http协议的默认端口为80。在浏览器中访问网页时,地址栏显示的地址就是URL。
-
网络三大基石:html、http、url
-
由4部分组成:
- 协议
- 域名、计算机
- 端口:默认80
- 请求资源
package com.sxt.loc;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* @author: Li Tian
* @contact: litian_cup@163.com
* @software: IntelliJ IDEA
* @file: URLTest.java
* @time: 2019/11/14 9:27
* @desc: URL练习
*/
public class URLTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com:80/index.html?uname=shsxt&age=18#a");
// 获取四个值
System.out.println("协议:" + url.getProtocol());
System.out.println("域名|ip:" + url.getHost());
System.out.println("端口:" + url.getPort());
System.out.println("请求资源1:" + url.getFile());
System.out.println("请求资源2:" + url.getPath());
// 参数
System.out.println("参数:" + url.getQuery());
// 锚点
System.out.println("锚点:" + url.getRef());
}
}
-
爬虫
-
简单爬虫
package com.sxt.loc; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: SpiderTest1.java * @time: 2019/11/14 10:20 * @desc: 网络爬虫 */ public class SpiderTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 获取URL URL url = new URL("https://www.jd.com"); // 下载资源 InputStream is = url.openStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, "UTF-8")); String msg = null; while(null != (msg=br.readLine())){ System.out.println(msg); } } } -
如果爬虫被拒绝,可以模拟浏览器爬虫
package com.sxt.loc; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: SpiderTest2.java * @time: 2019/11/14 10:26 * @desc: 网络爬虫,对于那些403拒绝的,模拟浏览器 */ public class SpiderTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 获取URL URL url = new URL("https://www.dianping.com"); // http协议打开 HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); // 设置请求方式 conn.setRequestMethod("GET"); conn.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.142 Safari/537.36"); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream(), "UTF-8")); String msg = null; while (null != (msg = br.readLine())) { System.out.println(msg); } } }
-
-
Socket:
-
我们开发的网络应用程序位于应用层,TCP和UDP属于传输层协议,在应用层如何使用传输层的服务呢?在应用层和传输层之间,则是使用套接Socket来进行分离。
-
套接字(Socket)就像是传输层为应用层开的一个小口,应用程序通过这个小口向远程发送数据,或者接收远程发来的数据;而这个小口以内,也就是数据进入这个口之后,或者数据从这个口出来之前,是不知道也不需要知道的,也不会关心它如何传输,这属于网络其它层次工作。
-
Socket实际是传输层供给应用层的编程接口。Socket就是应用层与传输层之间的桥梁。使用Socket编程可以开发客户机和服务器应用程序,可以在本地网络上进行通信,也可通过Internet在全球范围内通信。
-
-
TCP协议和UDP协议的联系和区别
-
TCP协议和UDP协议是传输层的两种协议。Socket是传输层供给应用层的编程接口,所以Socket编程就分为TCP编程和UDP编程两类。
-
在网络通讯中,TCP方式就类似于拨打电话,使用该种方式进行网络通讯时,需要建立专门的虚拟连接,然后进行可靠的数据传输,如果数据发送失败,则客户端会自动重发该数据。而UDP方式就类似于发送短信,使用这种方式进行网络通讯时,不需要建立专门的虚拟连接,传输也不是很可靠,如果发送失败则客户端无法获得。
-
这两种传输方式都在实际的网络编程中使用,重要的数据一般使用TCP方式进行数据传输,而大量的非核心数据则可以通过UDP方式进行传递,在一些程序中甚至结合使用这两种方式进行数据传递。
-
由于TCP需要建立专用的虚拟连接以及确认传输是否正确,所以使用TCP方式的速度稍微慢一些,而且传输时产生的数据量要比UDP稍微大一些。
-
总结
-
TCP是面向连接的,传输数据安全,稳定,效率相对较低。
-
UDP是面向无连接的,传输数据不安全,效率较高。
-
2. UDP编程
-
接收端
- 使用DatagramSocket指定端口,创建接收端
- 准备容器,封装成DatagramPacket包裹
- 阻塞式接受包裹receeive(DatagramPacket p)
- 分析数据,byte[] getData,getLength()
- 释放资源
package com.sxt.udp; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UDPServer.java * @time: 2019/11/14 14:14 * @desc: 接收端 */ public class UDPServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ System.out.println("接收方启动中..."); // 1. 使用DatagramSocket指定端口,创建接收端 DatagramSocket server = new DatagramSocket(9999); // 2. 准备容器,封装成DatagramPacket包裹 byte[] container = new byte[1024*60]; DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(container, 0, container.length); // 3. 阻塞式接受包裹receeive(DatagramPacket p) // 阻塞式 server.receive(packet); // 4. 分析数据,byte[] getData,getLength() byte[] datas = packet.getData(); int len = packet.getLength(); System.out.println(new String(datas, 0, len)); // 5. 释放资源 server.close(); } } -
发送端
- 使用DatagramSocket指定端口,创建发送端
- 准备数据,一定转成字节数组
- 封装成DatagramPacket包裹,需要指定目的地
- 发送包裹send(DatagramPacket p)
- 释放资源
package com.sxt.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.SocketException; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UDPClient.java * @time: 2019/11/14 14:14 * @desc: 发送端 */ public class UDPClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("发送方启动中..."); // 1. 使用DatagramSocket指定端口,创建发送端 DatagramSocket client = new DatagramSocket(8888); // 2. 准备数据,一定转成字节数组 String data = "上海尚学堂"; byte[] datas = data.getBytes(); // 3. 封装成DatagramPacket包裹,需要指定目的地 DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9999)); // 4. 发送包裹send(DatagramPacket p) client.send(packet); // 5. 释放资源 client.close(); } } -
注意:Address already in use: Cannot bind,同一个协议下端口不允许冲突
-
操作基本数据类型使用Data流
-
接收端
package com.sxt.udp; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UDPServer.java * @time: 2019/11/14 14:14 * @desc: 接收端 */ public class UDPTypeServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ System.out.println("接收方启动中..."); // 1. 使用DatagramSocket指定端口,创建接收端 DatagramSocket server = new DatagramSocket(9999); // 2. 准备容器,封装成DatagramPacket包裹 byte[] container = new byte[1024*60]; DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(container, 0, container.length); // 3. 阻塞式接受包裹receeive(DatagramPacket p) // 阻塞式 server.receive(packet); // 4. 分析数据,将字节数组还原为对应的类型即可 byte[] datas = packet.getData(); int len = packet.getLength(); DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(datas))); // 顺序与写出一致 String msg = dis.readUTF(); boolean flag = dis.readBoolean(); System.out.println(msg + "-->" + flag); // 5. 释放资源 server.close(); } } -
发送端
package com.sxt.udp; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UDPClient.java * @time: 2019/11/14 14:14 * @desc: 发送端 */ public class UDPTypeClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("发送方启动中..."); // 1. 使用DatagramSocket指定端口,创建发送端 DatagramSocket client = new DatagramSocket(8888); // 2. 将基本类型,转成字节数组 ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(baos)); // 操作类型+数据 dos.writeUTF("上海尚学堂"); dos.writeBoolean(false); dos.flush(); byte[] datas = baos.toByteArray(); // 3. 封装成DatagramPacket包裹,需要指定目的地 DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9999)); // 4. 发送包裹send(DatagramPacket p) client.send(packet); // 5. 释放资源 client.close(); } }
-
-
操作引用数据类型使用Object流
-
操作文件通过将文件转换成字节数组
-
实现多次交流,单方面聊天
-
发送端:
package com.sxt.udp; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UDPClient.java * @time: 2019/11/14 14:14 * @desc: 发送端 */ public class UDPTalkClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("发送方启动中..."); // 1. 使用DatagramSocket指定端口,创建发送端 DatagramSocket client = new DatagramSocket(8888); // 2. 准备数据,一定转成字节数组 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); while (true) { String data = reader.readLine(); byte[] datas = data.getBytes(); // 3. 封装成DatagramPacket包裹,需要指定目的地 DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9999)); // 4. 发送包裹send(DatagramPacket p) client.send(packet); if (data.equals("q")) { break; } } // 5. 释放资源 client.close(); } } -
接收端:
package com.sxt.udp; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: UDPServer.java * @time: 2019/11/14 14:14 * @desc: 接收端 */ public class UDPTalkServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("接收方启动中..."); // 1. 使用DatagramSocket指定端口,创建接收端 DatagramSocket server = new DatagramSocket(9999); while (true) { // 2. 准备容器,封装成DatagramPacket包裹 byte[] container = new byte[1024 * 60]; DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(container, 0, container.length); // 3. 阻塞式接受包裹receeive(DatagramPacket p) // 阻塞式 server.receive(packet); // 4. 分析数据,byte[] getData,getLength() byte[] datas = packet.getData(); int len = packet.getLength(); String data = new String(datas, 0, len); System.out.println(data); if (data.equals("q")) { break; } } // 5. 释放资源 server.close(); } }
-
-
在线咨询
-
发送端:
package com.sxt.udp; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.SocketException; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TalkSend.java * @time: 2019/11/16 20:03 * @desc: 使用面向对象封装 */ public class TalkSend implements Runnable { private DatagramSocket client; private BufferedReader reader; private String toIP; private int toPort; public TalkSend(int port, String toIP, int toPort) { this.toIP = toIP; this.toPort = toPort; try { client = new DatagramSocket(port); reader = new BufferedReader((new InputStreamReader(System.in))); } catch (SocketException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void run() { while (true) { String data = null; try { data = reader.readLine(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } byte[] datas = data.getBytes(); // 3. 封装成DatagramPacket包裹,需要指定目的地 DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length, new InetSocketAddress(this.toIP, this.toPort)); // 4. 发送包裹send(DatagramPacket p) try { client.send(packet); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (data.equals("q")) { break; } } // 5. 释放资源 client.close(); } } -
接收端
package com.sxt.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.SocketException; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TalkReceive.java * @time: 2019/11/16 20:11 * @desc: 封装接收器 */ public class TalkReceive implements Runnable { private DatagramSocket server; private String from; public TalkReceive(int port, String from) { this.from = from; try { server = new DatagramSocket(port); } catch (SocketException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void run() { while (true) { // 2. 准备容器,封装成DatagramPacket包裹 byte[] container = new byte[1024 * 60]; DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(container, 0, container.length); // 3. 阻塞式接受包裹receeive(DatagramPacket p) // 阻塞式 try { server.receive(packet); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 4. 分析数据,byte[] getData,getLength() byte[] datas = packet.getData(); int len = packet.getLength(); String data = new String(datas, 0, len); System.out.println(from + "说:" + data); if (data.equals("q")) { break; } } // 5. 释放资源 server.close(); } } -
模拟学生
package com.sxt.udp; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TalkStudent.java * @time: 2019/11/16 20:13 * @desc: 模拟学生端 */ public class TalkStudent { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("学生加入聊天室..."); new Thread(new TalkSend(7777, "localhost", 9999)).start(); new Thread(new TalkReceive(8888, "老师")).start(); } } -
模拟老师
package com.sxt.udp; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: TalkTeacher.java * @time: 2019/11/16 20:13 * @desc: 模拟老师端 */ public class TalkTeacher { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("老师加入聊天室..."); new Thread(new TalkReceive(9999, "学生")).start(); new Thread(new TalkSend(5555, "localhost", 8888)).start(); } }
-
3. TCP编程
-
创建服务器
- 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器
- 阻塞式等待连接 accept
- 操作:输入输出流操作
- 释放资源
-
创建客户端
- 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口
- 操作:输入输出流操作
- 释放资源
-
基本步骤
-
服务器
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Server.java * @time: 2019/11/18 14:45 * @desc: 熟悉流程,创建服务器 */ public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); // 3. 操作:输入输出流操作 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); String data = dis.readUTF(); System.out.println(data); // 4. 释放资源 dis.close(); client.close(); // 关闭服务器的话 server.close(); } } -
客户端
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Client.java * @time: 2019/11/18 14:50 * @desc: 创建客户端 */ public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 操作:输入输出流操作 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); String data = "Hello"; dos.writeUTF(data); dos.flush(); // 3. 释放资源 dos.close(); client.close(); } }
-
-
模拟登陆 单向
-
服务器
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LoginServer.java * @time: 2019/11/18 15:13 * @desc: 模拟登陆 单向 服务器 */ public class LoginServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); // 3. 操作:输入输出流操作 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); String datas = dis.readUTF(); // 分析 String[] dataArray = datas.split("&"); for(String info: dataArray){ String[] userInfo = info.split("="); System.out.println(userInfo[0] + "-->" + userInfo[1]); } // 4. 释放资源 dis.close(); client.close(); // 关闭服务器的话 server.close(); } } -
客户端
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LoginClient.java * @time: 2019/11/18 15:13 * @desc: 模拟登陆 单向 客户端 */ public class LoginClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); BufferedReader console = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader((System.in))); System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String uname = console.readLine(); System.out.println("请输入密码:"); String upwd = console.readLine(); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 操作:输入输出流操作 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); dos.writeUTF("uname=" + uname + "&upwd=" + upwd); dos.flush(); // 3. 释放资源 dos.close(); client.close(); } }
-
-
模拟登陆 双向
-
服务器
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LoginTwoWayServer.java * @time: 2019/11/18 15:23 * @desc: 模拟登陆 双向 服务器 */ public class LoginTwoWayServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); // 3. 操作:输入输出流操作 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); String datas = dis.readUTF(); String uname = ""; String upwd = ""; // 分析 String[] dataArray = datas.split("&"); for (String info : dataArray) { String[] userInfo = info.split("="); if (userInfo[0].equals("uname")) { System.out.println("你的用户名为:" + userInfo[1]); uname = userInfo[1]; } else if (userInfo[0].equals("upwd")) { System.out.println("你的密码为:" + userInfo[1]); upwd = userInfo[1]; } } // 输出 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); if (uname.equals("litian") && upwd.equals("123")) { dos.writeUTF("登陆成功,欢迎回来!"); } else { dos.writeUTF("登陆失败,用户名或密码错误!"); } dos.flush(); // 4. 释放资源 dis.close(); client.close(); // 关闭服务器的话 server.close(); } } -
客户端
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.*; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LoginTwoWayClient.java * @time: 2019/11/18 15:23 * @desc: 模拟登陆 双向 客户端 */ public class LoginTwoWayClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); BufferedReader console = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader((System.in))); System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String uname = console.readLine(); System.out.println("请输入密码:"); String upwd = console.readLine(); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 操作:输入输出流操作 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); dos.writeUTF("uname=" + uname + "&upwd=" + upwd); dos.flush(); // 接受 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); String result = dis.readUTF(); System.out.println(result); // 3. 释放资源 dos.close(); client.close(); } }
-
-
文件上传
-
服务器
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.*; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: FileServer.java * @time: 2019/11/18 15:32 * @desc: 服务器:存储文件 */ public class FileServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); // 3. 操作:文件拷贝 存储 InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(client.getInputStream()); OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./快乐保存.jpg")); byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; while ((len = is.read(flush)) != -1) { os.write(flush, 0, len); } // 4. 释放资源 os.close(); is.close(); client.close(); // 关闭服务器的话 server.close(); } } -
客户端
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.*; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: FileClient.java * @time: 2019/11/18 15:32 * @desc: 客户端:上传文件 */ public class FileClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 操作:文件拷贝 上传 InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("./快乐.jpg")); OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; while ((len = is.read(flush)) != -1) { os.write(flush, 0, len); } // 3. 释放资源 os.close(); is.close(); client.close(); } }
-
-
多用户登陆
-
服务器
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LoginMultiServer.java * @time: 2019/11/19 9:18 * @desc: */ public class LoginMultiServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); boolean isRunning = true; while (isRunning) { // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); new Thread(new Channel(client)).start(); } // 关闭服务器的话 server.close(); } static class Channel implements Runnable { private Socket client; // 输入流封装 private DataInputStream dis; // 输出流封装 private DataOutputStream dos; public Channel(Socket client) { this.client = client; try { dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } @Override public void run() { // 3. 操作:输入输出流操作 String uname = ""; String upwd = ""; // 分析 String datas = receive(); String[] dataArray = datas.split("&"); for (String info : dataArray) { String[] userInfo = info.split("="); if (userInfo[0].equals("uname")) { System.out.println("你的用户名为:" + userInfo[1]); uname = userInfo[1]; } else if (userInfo[0].equals("upwd")) { System.out.println("你的密码为:" + userInfo[1]); upwd = userInfo[1]; } } if (uname.equals("litian") && upwd.equals("123")) { send("登陆成功,欢迎回来!"); } else { send("登陆失败,用户名或密码错误!"); } release(); } // 接受数据 private String receive() { String datas = ""; try { datas = dis.readUTF(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return datas; } // 发送数据 private void send(String msg) { try { dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 释放资源 private void release() { // 4. 释放资源 try { if (null != dos) { dos.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (null != dis) { dis.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (null != client) { client.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } -
客户端
package com.sxt.tcp; import java.io.*; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: LoginMultiClient.java * @time: 2019/11/19 9:18 * @desc: */ public class LoginMultiClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 操作:输入输出流操作 new Send(client).send(); new Receive(client).receive(); // 3. 释放资源 client.close(); } static class Send { private Socket client; private DataOutputStream dos; private BufferedReader console; private String msg; public Send(Socket client) { console = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader((System.in))); this.client = client; this.msg = init(); try { dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private String init() { try { System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String uname = console.readLine(); System.out.println("请输入密码:"); String upwd = console.readLine(); return "uname=" + uname + "&upwd=" + upwd; } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return "???"; } } public void send() { try { dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } static class Receive { private Socket client; private DataInputStream dis; public Receive(Socket client) { this.client = client; try { dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void receive() { String result = null; try { result = dis.readUTF(); System.out.println(result); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
-
4. 在线聊天室
-
实现一个客户可以正常收发信息
-
服务端
package com.sxt.chat1; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Chat.java * @time: 2019/11/19 10:45 * @desc: 在线聊天室:服务端 * 目标:实现一个客户可以正常收发信息 */ public class Chat { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); // 3. 接收消息 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); String msg = dis.readUTF(); // 4. 返回消息 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); // 5. 释放资源 dos.close(); dis.close(); client.close(); } } -
客户端
package com.sxt.chat1; import java.io.*; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Client.java * @time: 2019/11/19 10:45 * @desc: 在线聊天室:客户端 * 目标:实现一个客户可以正常收发信息 */ public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 客户端发送消息 BufferedReader console = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader((System.in))); String msg = console.readLine(); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); // 3. 获取消息 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); msg = dis.readUTF(); System.out.println(msg); // 4. 释放资源 dos.close(); dis.close(); client.close(); } }
-
-
实现一个客户可以正常收发多人信息——基础简易版
-
服务端
package com.sxt.chat1; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: MultiChat.java * @time: 2019/11/19 14:57 * @desc: 在线聊天室:服务端 * 目标:实现一个客户可以正常收发多人信息 */ public class MultiChat { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); boolean isRunning = true; while (isRunning) { // 3. 接收消息 String msg = dis.readUTF(); // 4. 返回消息 dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); } // 5. 释放资源 dos.close(); dis.close(); client.close(); } } -
客户端
package com.sxt.chat1; import java.io.*; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: MultiClient.java * @time: 2019/11/19 14:57 * @desc: 在线聊天室:客户端 * 目标:实现一个客户可以正常收发多条信息 */ public class MultiClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 客户端发送消息 BufferedReader console = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader((System.in))); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); boolean isRunning = true; while (isRunning) { String msg = console.readLine(); dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); // 3. 获取消息 msg = dis.readUTF(); System.out.println(msg); } // 4. 释放资源 dos.close(); dis.close(); client.close(); } }
-
-
使用多线程实现多个客户可以正常收发多人信息——oop封装版
-
问题:其他客户必须等待之前的客户退出,才能继续排队
-
工具类:释放资源
package com.sxt.chat3; import java.io.Closeable; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: SxtUtils.java * @time: 2019/11/25 13:40 * @desc: 工具类:释放资源 */ public class SxtUtils { public static void close(Closeable... targets){ for (Closeable target: targets){ try{ if(null != target){ target.close(); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } } -
在线聊天室:服务端
package com.sxt.chat3; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: MultiChat.java * @time: 2019/11/19 14:57 * @desc: 在线聊天室:服务端 * 目标:封装:使用多线程实现多个客户可以正常收发多人信息 */ public class MultiChat { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept while (true) { Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); new Thread(new Channel(client)).start(); } } // 一个客户代表一个Channel static class Channel implements Runnable { private DataInputStream dis; private DataOutputStream dos; private Socket client; private boolean isRunning; public Channel(Socket client) { this.client = client; try { dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); isRunning = true; } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } // 接受消息 private String receive() { String msg = ""; try { msg = dis.readUTF(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } return msg; } // 发送消息 private void send(String msg) { try { dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } // 释放资源 private void release() { this.isRunning = false; SxtUtils.close(dis, dos, client); } @Override public void run() { while(isRunning){ String msg = receive(); if(!msg.equals("")){ send(msg); } } } } } -
使用多线程封装了发送端
package com.sxt.chat3; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Send.java * @time: 2019/11/25 14:37 * @desc: 使用多线程封装了发送端 */ public class Send implements Runnable { private BufferedReader console; private DataOutputStream dos; private Socket client; private boolean isRunning; public Send(Socket client) { this.client = client; console = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); try { dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); isRunning = true; } catch (IOException e) { this.release(); } } @Override public void run() { while (isRunning) { String msg = getStrFromConsole(); if (!msg.equals("")) { send(msg); } } } private void send(String msg) { try { dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } private String getStrFromConsole() { try { return console.readLine(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } return ""; } // 释放资源 private void release() { this.isRunning = false; SxtUtils.close(dos, client); } } -
使用多线程封装了接收端
package com.sxt.chat3; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Receive.java * @time: 2019/11/25 14:37 * @desc: 使用多线程封装了接收端 */ public class Receive implements Runnable { private Socket client; private boolean isRunning; private DataInputStream dis; public Receive(Socket client) { this.client = client; try { dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); isRunning = true; } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } // 接受消息 private String receive() { String msg = ""; try { msg = dis.readUTF(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } return msg; } @Override public void run() { while (isRunning) { String msg = receive(); if (!msg.equals("")) { System.out.println(msg); } } } // 释放资源 private void release() { this.isRunning = false; SxtUtils.close(dis, client); } } -
在线聊天室:客户端
package com.sxt.chat3; import java.io.*; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: MultiClient.java * @time: 2019/11/19 14:57 * @desc: 在线聊天室:客户端 * 目标:封装:使用多线程实现多个客户可以正常收发多条信息 */ public class MultiClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 客户端发送消息 new Thread(new Send(client)).start(); new Thread(new Receive(client)).start(); } }
-
-
手写聊天室——群聊过渡版
-
服务器
package com.sxt.chat4; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: MultiChat.java * @time: 2019/11/19 14:57 * @desc: 在线聊天室:服务端 * 目标:加入容器实现群聊 */ public class Chat { private static CopyOnWriteArrayList<Channel> all = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept while (true) { Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); Channel c = new Channel(client); // 管理所有的成员 all.add(c); new Thread(c).start(); } } // 一个客户代表一个Channel static class Channel implements Runnable { private DataInputStream dis; private DataOutputStream dos; private Socket client; private boolean isRunning; private String name; public Channel(Socket client) { this.client = client; try { dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); isRunning = true; // 获取名称 this.name = receive(); // 欢迎你的到来 this.send("欢迎你的到来"); sendOthers(this.name + "来了shsxt聊天室", true); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } // 接受消息 private String receive() { String msg = ""; try { msg = dis.readUTF(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } return msg; } // 发送消息 private void send(String msg) { try { dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } // 群聊 private void sendOthers(String msg, boolean isSys) { for(Channel other: all){ if(other == this){ // 自己 continue; } if(!isSys) { // 群聊消息 other.send(this.name + "说:" + msg); }else{ // 系统消息 other.send(msg); } } } // 释放资源 private void release() { this.isRunning = false; SxtUtils.close(dis, dos, client); // 退出 all.remove(this); sendOthers(this.name + "离开了...", true); } @Override public void run() { while (isRunning) { String msg = receive(); if (!msg.equals("")) { // send(msg); sendOthers(msg, false); } } } } } -
客户端
package com.sxt.chat4; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: MultiClient.java * @time: 2019/11/19 14:57 * @desc: 在线聊天室:客户端 * 目标:加入容器实现群聊 */ public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Client-----"); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String name = br.readLine(); // 1. 建立连接:使用Socket创建客户端 + 服务的地址和端口 Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888); // 2. 客户端发送消息 new Thread(new Send(client, name)).start(); new Thread(new Receive(client)).start(); } } -
工具类同上
-
发送端
package com.sxt.chat4; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Send.java * @time: 2019/11/25 14:37 * @desc: 使用多线程封装了发送端 */ public class Send implements Runnable { private BufferedReader console; private DataOutputStream dos; private Socket client; private boolean isRunning; private String name; public Send(Socket client, String name) { this.client = client; this.name = name; console = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); try { dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); // 发送名称 send(name); isRunning = true; } catch (IOException e) { this.release(); } } @Override public void run() { while (isRunning) { String msg = getStrFromConsole(); if (!msg.equals("")) { send(msg); } } } private void send(String msg) { try { dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } private String getStrFromConsole() { try { return console.readLine(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } return ""; } // 释放资源 private void release() { this.isRunning = false; SxtUtils.close(dos, client); } } -
接收端
package com.sxt.chat4; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Receive.java * @time: 2019/11/25 14:37 * @desc: 使用多线程封装了接收端 */ public class Receive implements Runnable { private Socket client; private boolean isRunning; private DataInputStream dis; public Receive(Socket client) { this.client = client; try { dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); isRunning = true; } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } // 接受消息 private String receive() { String msg = ""; try { msg = dis.readUTF(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } return msg; } @Override public void run() { while (isRunning) { String msg = receive(); if (!msg.equals("")) { System.out.println(msg); } } } // 释放资源 private void release() { this.isRunning = false; SxtUtils.close(dis, client); } }
-
-
实现私聊
-
修改客户端为:
package com.sxt.chat4; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: MultiChat.java * @time: 2019/11/19 14:57 * @desc: 在线聊天室:服务端 * 目标:加入容器实现群聊 */ public class Chat { private static CopyOnWriteArrayList<Channel> all = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("-----Server-----"); // 1. 指定端口,使用ServerSocket创建服务器 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888); // 2. 阻塞式等待连接 accept while (true) { Socket client = server.accept(); System.out.println("一个客户端建立了连接..."); Channel c = new Channel(client); // 管理所有的成员 all.add(c); new Thread(c).start(); } } // 一个客户代表一个Channel static class Channel implements Runnable { private DataInputStream dis; private DataOutputStream dos; private Socket client; private boolean isRunning; private String name; public Channel(Socket client) { this.client = client; try { dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); isRunning = true; // 获取名称 this.name = receive(); // 欢迎你的到来 this.send("欢迎你的到来"); sendOthers(this.name + "来了shsxt聊天室", true); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } // 接受消息 private String receive() { String msg = ""; try { msg = dis.readUTF(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } return msg; } // 发送消息 private void send(String msg) { try { dos.writeUTF(msg); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { release(); } } // 群聊 private void sendOthers(String msg, boolean isSys) { boolean isPrivate = msg.startsWith("@"); if(isPrivate){ // 私聊 int idx = msg.indexOf(":"); // 获取目标和数据 String targetName = msg.substring(1, idx); msg = msg.substring(idx+1); for(Channel other: all){ if(other.name.equals(targetName)){ other.send(this.name + "悄悄的对你说:" + msg); break; } } }else{ for(Channel other: all){ if(other == this){ // 自己 continue; } if(!isSys) { // 群聊消息 other.send(this.name + "说:" + msg); }else{ // 系统消息 other.send(msg); } } } } // 释放资源 private void release() { this.isRunning = false; SxtUtils.close(dis, dos, client); // 退出 all.remove(this); sendOthers(this.name + "离开了...", true); } @Override public void run() { while (isRunning) { String msg = receive(); if (!msg.equals("")) { // send(msg); sendOthers(msg, false); } } } } }
-
第13章 J20飞机游戏
-
一些常量
package com.sxt.planegame2; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Constant.java * @time: 2019/11/28 10:15 * @desc: 定义常量的类 */ public class Constant { public static final int GAME_WIDTH = 500; public static final int GAME_HEIGHT = 500; } -
物体父类
package com.sxt.planegame2; import java.awt.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: GameObject.java * @time: 2019/11/28 9:15 * @desc: */ public class GameObject { Image img; double x, y; int speed; int width, height; public void drawSelf(Graphics g){ g.drawImage(img, (int)x, (int)y, null); } public GameObject(Image img, double x, double y) { this.img = img; this.x = x; this.y = y; } public GameObject(){ } public Rectangle getRect(){ // 返回物体所在的矩形,便于后续的碰撞检测 return new Rectangle((int)x, (int)y, width, height); } } -
炮弹类
package com.sxt.planegame2; import java.awt.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Shell.java * @time: 2019/11/28 10:08 * @desc: 炮弹类 */ public class Shell extends GameObject { double degree; public Shell() { x = 200; y = 200; width = 10; height = 10; speed = 3; degree = Math.random() * Math.PI * 2; } public void draw(Graphics g) { Color c = g.getColor(); g.setColor(Color.yellow); g.fillOval((int) x, (int) y, width, height); // 炮弹沿着任意角度去飞 x += speed * Math.cos(degree); y += speed * Math.sin(degree); // 炮弹遇到墙壁之后反弹 if (x < 0 || x > Constant.GAME_WIDTH - width) { degree = Math.PI - degree; } if (y < 30 || y > Constant.GAME_HEIGHT - height) { degree = -degree; } g.setColor(c); } } -
飞机类
package com.sxt.planegame2; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Plane.java * @time: 2019/11/28 9:27 * @desc: */ public class Plane extends GameObject { boolean left, up, right, down; boolean live = true; public Plane(Image img, double x, double y) { super(img, x, y); speed = 10; width = img.getWidth(null); height = img.getHeight(null); } @Override public void drawSelf(Graphics g) { if(live){ g.drawImage(img, (int) x, (int) y, null); if (left) { x -= speed; } if (right) { x += speed; } if (up) { y -= speed; } if (down) { y += speed; } }else{ } } // 按下某个键增加相应的方向 public void addDirection(KeyEvent e) { switch (e.getKeyCode()) { case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT: left = true; break; case KeyEvent.VK_UP: up = true; break; case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT: right = true; break; case KeyEvent.VK_DOWN: down = true; break; } } // 抬起某个键取消相应的方向 public void minusDirection(KeyEvent e) { switch (e.getKeyCode()) { case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT: left = false; break; case KeyEvent.VK_UP: up = false; break; case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT: right = false; break; case KeyEvent.VK_DOWN: down = false; break; } } } -
爆炸类
package com.sxt.planegame2; import java.awt.*; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: Explode.java * @time: 2019/11/28 14:59 * @desc: 爆炸效果 */ public class Explode { double x, y; static Image[] imgs = new Image[16]; static { for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) { imgs[i] = GameUtil.getImage("images/explode/e" + (i + 1) + ".gif"); imgs[i].getWidth(null); } } int count; public void draw(Graphics g) { if (count <= 15) { g.drawImage(imgs[count], (int) x, (int) y, null); count++; } } public Explode(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } } -
主程序类
package com.sxt.planegame2; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter; import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter; import java.awt.event.WindowEvent; import java.util.Date; /** * @author: Li Tian * @contact: litian_cup@163.com * @software: IntelliJ IDEA * @file: MyGameFrame.java * @time: 2019/11/27 10:33 * @desc: 飞机游戏的主窗口 */ public class GameFrame extends Frame { Image planeImg = GameUtil.getImage("images/plane.png"); Image bg = GameUtil.getImage("images/bg.jpg"); Plane plane = new Plane(planeImg, 250, 250); Shell[] shells = new Shell[50]; Explode bao; Date startTime = new Date(); Date endTime; int period; // 游戏持续的时间 @Override public void paint(Graphics g) { // paint是自动调用 g.drawImage(bg, 0, 0, null); plane.drawSelf(g); // 画出所有的炮弹 for (int i = 0; i < shells.length; i++) { shells[i].draw(g); boolean peng = shells[i].getRect().intersects(plane.getRect()); if (peng) { plane.live = false; // 只需要生成一次爆炸效果就ok if (bao == null) { bao = new Explode(plane.x, plane.y); endTime = new Date(); period = (int) ((endTime.getTime() - startTime.getTime()) / 1000); } bao.draw(g); } if(!plane.live){ g.setColor(Color.red); Font f = new Font("宋体", Font.BOLD, 20); g.setFont(f); g.drawString("时间:" + period + "秒", (int) plane.x, (int) plane.y); } } } // 帮助我们反复重画窗口! class PaintThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { while (true) { // 重画 repaint(); try { Thread.sleep(40); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } // 增加键盘监听内部类 class KeyMonitor extends KeyAdapter { @Override public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) { plane.addDirection(e); } @Override public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) { plane.minusDirection(e); } } // 初始化窗口 public void launchFrame() { this.setTitle("李英俊本俊的打飞机游戏"); this.setVisible(true); this.setSize(Constant.GAME_WIDTH, Constant.GAME_HEIGHT); this.setLocation(300, 300); // 点x就关闭程序了 this.addWindowListener( new WindowAdapter() { @Override public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.exit(0); } } ); // 启动重画窗口的线程 new PaintThread().start(); // 启动重画窗口的线程 addKeyListener(new KeyMonitor()); // 给窗口增加键盘的监听 // 初始化50个炮弹 for (int i = 0; i < shells.length; i++) { shells[i] = new Shell(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { GameFrame f = new GameFrame(); f.launchFrame(); } private Image offScreenImage = null; @Override public void update(Graphics g) { if (offScreenImage == null) offScreenImage = this.createImage(Constant.GAME_WIDTH, Constant.GAME_HEIGHT);//这是游戏窗口的宽度和高度 Graphics gOff = offScreenImage.getGraphics(); paint(gOff); g.drawImage(offScreenImage, 0, 0, null); } }
我的CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21579045
我的博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/lyjun/
我的Github:https://github.com/TinyHandsome
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行~
欢迎大家过来OB~
by 李英俊小朋友























 782
782











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










