ListView 缓存机制
一、从 ListView#setAdapter() 开始:
ListView#setAdapter():
1 若 Adapter 和 AdapterDataSetObserver 都不为空,则解注册之前的观察者
2.调用 resetList() 清空集合
3.RecycleBin#clear();
4.若存在头部和尾部布局,则将传入的 adapter 进行包装
5.super.setAdapter(adapter);
6.判断传入的 adapter 是否为空
情况一:不为空
Adapter#getCount() // 更新当前适配器中包含的数据条目
Adapter#registerDataSetObserver() // 注册观察者
RecycleBin#setViewTypeCount() // 通过 RecycleBin 设置创建的视图类型的数目
若当前适配器中包含的数据条目 mItemCount 为 0,确定是否需要更新选择位置
情况二:为空
确定是否需要更新选择位置
7.请求布局
requestLayout()
二、AbsListView#requestLayout():
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
// mBlockLayoutRequests:默认为 false(为 true 表示不会向上传播到父层次结构,用于在布局过程中布局子视图。指示当前正在布局此视图)
// mInLayout:默认为 false(为 true 表示当前正在布局此视图)
if (!mBlockLayoutRequests && !mInLayout) {
// 最终调用 View#requestLayout()
super.requestLayout();
}
}
View#requestLayout():
@CallSuper
publicvoid requestLayout() {
...
if (mParent != null && !mParent.isLayoutRequested()) {
// mParent 是 ViewParent 类型,实现类是 ViewRootImpl
mParent.requestLayout();
}
...
}
ViewRootImpl#requestLayout():
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
// 检测当前修改 UI 的线程是否是 UI 线程
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
// 开始 View 的绘制流程,当前绘制的是 ListView,对于 ListView 本身只需关注 onLayout() 方法
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
ListView#onLayout() ->
AbsListView#onLayout() ->
ListView#layoutChildren():
@Override
protected void layoutChildren() {
final boolean blockLayoutRequests = mBlockLayoutRequests;
if (blockLayoutRequests) {
return;
}
mBlockLayoutRequests = true;
try {
super.layoutChildren();
invalidate();
if (mAdapter == null) {
resetList();
invokeOnItemScrollListener();
return;
}
final int childrenTop = mListPadding.top;
final int childrenBottom = mBottom - mTop - mListPadding.bottom;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
int index = 0;
int delta = 0;
View sel;
View oldSel = null;
View oldFirst = null;
View newSel = null;
// Remember stuff we will need down below
switch (mLayoutMode) {
case LAYOUT_SET_SELECTION:
index = mNextSelectedPosition - mFirstPosition;
if (index >= 0 && index < childCount) {
newSel = getChildAt(index);
}
break;
case LAYOUT_FORCE_TOP:
case LAYOUT_FORCE_BOTTOM:
case LAYOUT_SPECIFIC:
case LAYOUT_SYNC:
break;
case LAYOUT_MOVE_SELECTION:
default:
// Remember the previously selected view
index = mSelectedPosition - mFirstPosition;
if (index >= 0 && index < childCount) {
oldSel = getChildAt(index);
}
// Remember the previous first child
oldFirst = getChildAt(0);
if (mNextSelectedPosition >= 0) {
delta = mNextSelectedPosition - mSelectedPosition;
}
// Caution: newSel might be null
newSel = getChildAt(index + delta);
}
boolean dataChanged = mDataChanged;
if (dataChanged) {
handleDataChanged();
}
// Handle the empty set by removing all views that are visible
// and calling it a day
if (mItemCount == 0) {
resetList();
invokeOnItemScrollListener();
return;
} else if (mItemCount != mAdapter.getCount()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The content of the adapter has changed but "
+ "ListView did not receive a notification. Make sure the content of "
+ "your adapter is not modified from a background thread, but only from "
+ "the UI thread. Make sure your adapter calls notifyDataSetChanged() "
+ "when its content changes. [in ListView(" + getId() + ", " + getClass()
+ ") with Adapter(" + mAdapter.getClass() + ")]");
}
setSelectedPositionInt(mNextSelectedPosition);
AccessibilityNodeInfo accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreNode = null;
View accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView = null;
int accessibilityFocusPosition = INVALID_POSITION;
// Remember which child, if any, had accessibility focus. This must
// occur before recycling any views, since that will clear
// accessibility focus.
final ViewRootImpl viewRootImpl = getViewRootImpl();
if (viewRootImpl != null) {
final View focusHost = viewRootImpl.getAccessibilityFocusedHost();
if (focusHost != null) {
final View focusChild = getAccessibilityFocusedChild(focusHost);
if (focusChild != null) {
if (!dataChanged || isDirectChildHeaderOrFooter(focusChild)
|| (focusChild.hasTransientState() && mAdapterHasStableIds)) {
// The views won't be changing, so try to maintain
// focus on the current host and virtual view.
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView = focusHost;
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreNode = viewRootImpl
.getAccessibilityFocusedVirtualView();
}
// If all else fails, maintain focus at the same
// position.
accessibilityFocusPosition = getPositionForView(focusChild);
}
}
}
View focusLayoutRestoreDirectChild = null;
View focusLayoutRestoreView = null;
// Take focus back to us temporarily to avoid the eventual call to
// clear focus when removing the focused child below from messing
// things up when ViewAncestor assigns focus back to someone else.
final View focusedChild = getFocusedChild();
if (focusedChild != null) {
// TODO: in some cases focusedChild.getParent() == null
// We can remember the focused view to restore after re-layout
// if the data hasn't changed, or if the focused position is a
// header or footer.
if (!dataChanged || isDirectChildHeaderOrFooter(focusedChild)
|| focusedChild.hasTransientState() || mAdapterHasStableIds) {
focusLayoutRestoreDirectChild = focusedChild;
// Remember the specific view that had focus.
focusLayoutRestoreView = findFocus();
if (focusLayoutRestoreView != null) {
// Tell it we are going to mess with it.
focusLayoutRestoreView.dispatchStartTemporaryDetach();
}
}
requestFocus();
}
// Pull all children into the RecycleBin.
// These views will be reused if possible
final int firstPosition = mFirstPosition;
final RecycleBin recycleBin = mRecycler;
// 关键一:
if (dataChanged) {
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
recycleBin.addScrapView(getChildAt(i), firstPosition+i);
}
} else {
recycleBin.fillActiveViews(childCount, firstPosition);
}
// Clear out old views
// 关键二:清空所有子 View,执行 detach 操作
detachAllViewsFromParent();
recycleBin.removeSkippedScrap();
switch (mLayoutMode) {
case LAYOUT_SET_SELECTION:
if (newSel != null) {
sel = fillFromSelection(newSel.getTop(), childrenTop, childrenBottom);
} else {
sel = fillFromMiddle(childrenTop, childrenBottom);
}
break;
case LAYOUT_SYNC:
sel = fillSpecific(mSyncPosition, mSpecificTop);
break;
case LAYOUT_FORCE_BOTTOM:
sel = fillUp(mItemCount - 1, childrenBottom);
adjustViewsUpOrDown();
break;
case LAYOUT_FORCE_TOP:
mFirstPosition = 0;
sel = fillFromTop(childrenTop);
adjustViewsUpOrDown();
break;
case LAYOUT_SPECIFIC:
final int selectedPosition = reconcileSelectedPosition();
sel = fillSpecific(selectedPosition, mSpecificTop);
/**
* When ListView is resized, FocusSelector requests an async selection for the
* previously focused item to make sure it is still visible. If the item is not
* selectable, it won't regain focus so instead we call FocusSelector
* to directly request focus on the view after it is visible.
*/
if (sel == null && mFocusSelector != null) {
final Runnable focusRunnable = mFocusSelector
.setupFocusIfValid(selectedPosition);
if (focusRunnable != null) {
post(focusRunnable);
}
}
break;
case LAYOUT_MOVE_SELECTION:
sel = moveSelection(oldSel, newSel, delta, childrenTop, childrenBottom);
break;
default:
// 关键三:
if (childCount == 0) {
if (!mStackFromBottom) {
final int position = lookForSelectablePosition(0, true);
setSelectedPositionInt(position);
sel = fillFromTop(childrenTop);
} else {
final int position = lookForSelectablePosition(mItemCount - 1, false);
setSelectedPositionInt(position);
sel = fillUp(mItemCount - 1, childrenBottom);
}
} else {
if (mSelectedPosition >= 0 && mSelectedPosition < mItemCount) {
sel = fillSpecific(mSelectedPosition,
oldSel == null ? childrenTop : oldSel.getTop());
} else if (mFirstPosition < mItemCount) {
sel = fillSpecific(mFirstPosition,
oldFirst == null ? childrenTop : oldFirst.getTop());
} else {
sel = fillSpecific(0, childrenTop);
}
}
break;
}
// Flush any cached views that did not get reused above
recycleBin.scrapActiveViews();
// remove any header/footer that has been temp detached and not re-attached
removeUnusedFixedViews(mHeaderViewInfos);
removeUnusedFixedViews(mFooterViewInfos);
if (sel != null) {
// The current selected item should get focus if items are
// focusable.
if (mItemsCanFocus && hasFocus() && !sel.hasFocus()) {
final boolean focusWasTaken = (sel == focusLayoutRestoreDirectChild &&
focusLayoutRestoreView != null &&
focusLayoutRestoreView.requestFocus()) || sel.requestFocus();
if (!focusWasTaken) {
// Selected item didn't take focus, but we still want to
// make sure something else outside of the selected view
// has focus.
final View focused = getFocusedChild();
if (focused != null) {
focused.clearFocus();
}
positionSelector(INVALID_POSITION, sel);
} else {
sel.setSelected(false);
mSelectorRect.setEmpty();
}
} else {
positionSelector(INVALID_POSITION, sel);
}
mSelectedTop = sel.getTop();
} else {
final boolean inTouchMode = mTouchMode == TOUCH_MODE_TAP
|| mTouchMode == TOUCH_MODE_DONE_WAITING;
if (inTouchMode) {
// If the user's finger is down, select the motion position.
final View child = getChildAt(mMotionPosition - mFirstPosition);
if (child != null) {
positionSelector(mMotionPosition, child);
}
} else if (mSelectorPosition != INVALID_POSITION) {
// If we had previously positioned the selector somewhere,
// put it back there. It might not match up with the data,
// but it's transitioning out so it's not a big deal.
final View child = getChildAt(mSelectorPosition - mFirstPosition);
if (child != null) {
positionSelector(mSelectorPosition, child);
}
} else {
// Otherwise, clear selection.
mSelectedTop = 0;
mSelectorRect.setEmpty();
}
// Even if there is not selected position, we may need to
// restore focus (i.e. something focusable in touch mode).
if (hasFocus() && focusLayoutRestoreView != null) {
focusLayoutRestoreView.requestFocus();
}
}
// Attempt to restore accessibility focus, if necessary.
if (viewRootImpl != null) {
final View newAccessibilityFocusedView = viewRootImpl.getAccessibilityFocusedHost();
if (newAccessibilityFocusedView == null) {
if (accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView != null
&& accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView.isAttachedToWindow()) {
final AccessibilityNodeProvider provider =
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView.getAccessibilityNodeProvider();
if (accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreNode != null && provider != null) {
final int virtualViewId = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getVirtualDescendantId(
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreNode.getSourceNodeId());
provider.performAction(virtualViewId,
AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS, null);
} else {
accessibilityFocusLayoutRestoreView.requestAccessibilityFocus();
}
} else if (accessibilityFocusPosition != INVALID_POSITION) {
// Bound the position within the visible children.
final int position = MathUtils.constrain(
accessibilityFocusPosition - mFirstPosition, 0,
getChildCount() - 1);
final View restoreView = getChildAt(position);
if (restoreView != null) {
restoreView.requestAccessibilityFocus();
}
}
}
}
// Tell focus view we are done mucking with it, if it is still in
// our view hierarchy.
if (focusLayoutRestoreView != null
&& focusLayoutRestoreView.getWindowToken() != null) {
focusLayoutRestoreView.dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach();
}
mLayoutMode = LAYOUT_NORMAL;
mDataChanged = false;
if (mPositionScrollAfterLayout != null) {
post(mPositionScrollAfterLayout);
mPositionScrollAfterLayout = null;
}
mNeedSync = false;
setNextSelectedPositionInt(mSelectedPosition);
updateScrollIndicators();
if (mItemCount > 0) {
checkSelectionChanged();
}
invokeOnItemScrollListener();
} finally {
if (mFocusSelector != null) {
mFocusSelector.onLayoutComplete();
}
if (!blockLayoutRequests) {
mBlockLayoutRequests = false;
}
}
}
ListView 会经历两次 Layout 过程:
第一次 Layout:
此时数据还都在 Adapter 中保存,还没有展示到 ListView 上,对应上面的 layoutChildren() 方法的关键一处的代码
关键一:
// dataChanged:当在数据发生变化时才为 true,其它情况下都为 false
if (dataChanged) {
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
recycleBin.addScrapView(getChildAt(i), firstPosition+i);
}
} else { // 此时代码进入 else 部分执行,但此时并没有数据需要填充
recycleBin.fillActiveViews(childCount, firstPosition);
}
接着执行上面的 layoutChildren() 方法的关键二处的代码:
// 清空所有子 View,执行 detach 操作
detachAllViewsFromParent();
继续执行上面的 layoutChildren() 方法的关键三处的代码:
// 因为此时 ListView 中没有数据,进入此 if 语句执行
if (childCount == 0) {
// 布局时默认是从上到下布局,mStackFromBottom 默认为 false,进入此 if 语句执行
if (!mStackFromBottom) {
final int position = lookForSelectablePosition(0, true);
setSelectedPositionInt(position);
sel = fillFromTop(childrenTop);
} else {
final int position = lookForSelectablePosition(mItemCount - 1, false);
setSelectedPositionInt(position);
sel = fillUp(mItemCount - 1, childrenBottom);
}
} else {
if (mSelectedPosition >= 0 && mSelectedPosition < mItemCount) {
sel = fillSpecific(mSelectedPosition,
oldSel == null ? childrenTop : oldSel.getTop());
} else if (mFirstPosition < mItemCount) {
sel = fillSpecific(mFirstPosition,
oldFirst == null ? childrenTop : oldFirst.getTop());
} else {
sel = fillSpecific(0, childrenTop);
}
}
ListView#fillFromTop() -> ListView#fillDown():
// 从 pos 位置到列表视图的结尾填充列表
private View fillDown(int pos, int nextTop) {
View selectedView = null;
int end = (mBottom - mTop);
if ((mGroupFlags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) {
end -= mListPadding.bottom;
}
// 当前布局的条目的 nextTop 的值(当前条目到顶部的距离,初始值为 0)小于列表的 end 值,且当前位置小于适配器中的项数,进行布局
// 每执行一次,nextTop 高度增加,同时 pos 加 1
// 当子元素超出屏幕(nextTop >= end),或循环之后的 pos >= 适配器中的项数,表示适配器中的所有项都遍历完成,此时跳出循环
// 即最多显示一屏的数据
while (nextTop < end && pos < mItemCount) {
// is this the selected item?
boolean selected = pos == mSelectedPosition;
View child = makeAndAddView(pos, nextTop, true, mListPadding.left, selected);
// 更新 nextTop 的值,nextTop 高度增加,每次增加一个条目的高度和一个分割线的高度
nextTop = child.getBottom() + mDividerHeight;
if (selected) {
selectedView = child;
}
// pos 加 1
pos++;
}
setVisibleRangeHint(mFirstPosition, mFirstPosition + getChildCount() - 1);
return selectedView;
}
ListView#makeAndAddView():
// 获取视图添加到列表中作为子项
private View makeAndAddView(int position, int y, boolean flow, int childrenLeft, boolean selected) {
// 此时 mDataChanged 为 false,代码进入此 if 语句执行
if (!mDataChanged) {
// 此时 ListView 中没有数据,获取的 activeView 为空,代码跳过当前 if 语句往下执行
final View activeView = mRecycler.getActiveView(position);
if (activeView != null) {
setupChild(activeView, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, true);
return activeView;
}
}
// 代码从这里开始执行
// 先从废弃视图数组中获取视图,作为参数传递给 getView() 方法的第二个参数
final View child = obtainView(position, mIsScrap);
// 再把获取的视图 child 添加到父布局上,执行 attach 操作
// 最后一个参数意思是当前视图之前是否有过 attach 操作(添加到 Window),这里肯定为 false
setupChild(child, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, mIsScrap[0]);
return child;
}
ListView#obtainView():
View obtainView(int position, boolean[] outMetadata) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "obtainView");
outMetadata[0] = false;
...
// 从废弃视图缓存数组 mScrapViews 中获取对应位置 position 的视图
final View scrapView = mRecycler.getScrapView(position);
// 调用 ListView 的 Adapter#getView() 方法,将上面获取的视图作为方法的第二个参数,这也是平时我们所说的 convertView 缓存的来源
// 第二个参数为空,就通过 Inflater#inflate() 方法解析布局文件生成视图
// 第二个参数不为空,就直接使用缓存即可,不用再次解析布局文件
final View child = mAdapter.getView(position, scrapView, this);
if (scrapView != null) {
if (child != scrapView) {
// Failed to re-bind the data, return scrap to the heap.
mRecycler.addScrapView(scrapView, position);
} else if (child.isTemporarilyDetached()) {
outMetadata[0] = true;
// Finish the temporary detach started in addScrapView().
child.dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach();
}
}
if (mCacheColorHint != 0) {
child.setDrawingCacheBackgroundColor(mCacheColorHint);
}
if (child.getImportantForAccessibility() == IMPORTANT_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY_AUTO) {
child.setImportantForAccessibility(IMPORTANT_FOR_ACCESSIBILITY_YES);
}
setItemViewLayoutParams(child, position);
...
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
return child;
}
ListView#setupChild():
// 传入的最后一个参数为 false
private void setupChild(View child, int position, int y, boolean flowDown, int childrenLeft, boolean selected, boolean isAttachedToWindow) {
...
// 当前 isAttachedToWindow 为 false,代码跳过当前 if 语句往下执行
// 但在 ListView 第二次 Layout 过程或滑动时,那时 isAttachedToWindow 为 true,代码执行下面的 if 语句
// 调用 attachViewToParent() 方法去添加当前视图 child 到 ListView
if ((isAttachedToWindow && !p.forceAdd) || (p.recycledHeaderFooter
&& p.viewType == AdapterView.ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER)) {
attachViewToParent(child, flowDown ? -1 : 0, p);
if (isAttachedToWindow
&& (((AbsListView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).scrappedFromPosition)
!= position) {
child.jumpDrawablesToCurrentState();
}
} else { // 当前传入的 isAttachedToWindow 为 false,代码进入 else 语句执行
...
// 添加当前视图 child 到 ListView
addViewInLayout(child, flowDown ? -1 : 0, p, true);
...
}
...
}
到这里,第一次 Layout 过程已经完成,fillDown() 方法使得 ListView 中有了最多一屏的数据
第二次 Layout:
代码流程和第一次类似,不是走的 if 就是走的 else,这里简单描述一下
layoutChildren():
1. fillActiveViews() // 此时 ListView 有最多一屏的数据,这里通过 fillActiveViews() 方法填充 mActiveViews 数组
2. detachAllViewsFromParent() // 清空所有的子视图,执行 detach 操作
3. 根据布局模式 LayoutMode 进行布局,默认情况下布局模式为 LAYOUT_NORMAL
会调用到 fillSpecific()
ListView#fillSpecific():
private View fillSpecific(int position, int top) {
boolean tempIsSelected = position == mSelectedPosition;
// makeAndAddView() 方法在第一次 Layout 过程时已经分析过,方法不长,放到下面再看看
View temp = makeAndAddView(position, top, true, mListPadding.left, tempIsSelected);
// Possibly changed again in fillUp if we add rows above this one.
mFirstPosition = position;
View above;
View below;
final int dividerHeight = mDividerHeight;
if (!mStackFromBottom) {
above = fillUp(position - 1, temp.getTop() - dividerHeight);
// This will correct for the top of the first view not touching the top of the list
adjustViewsUpOrDown();
below = fillDown(position + 1, temp.getBottom() + dividerHeight);
int childCount = getChildCount();
if (childCount > 0) {
correctTooHigh(childCount);
}
} else {
below = fillDown(position + 1, temp.getBottom() + dividerHeight);
// This will correct for the bottom of the last view not touching the bottom of the list
adjustViewsUpOrDown();
above = fillUp(position - 1, temp.getTop() - dividerHeight);
int childCount = getChildCount();
if (childCount > 0) {
correctTooLow(childCount);
}
}
if (tempIsSelected) {
return temp;
} else if (above != null) {
return above;
} else {
return below;
}
}
ListView#makeAndAddView():
private View makeAndAddView(int position, int y, boolean flow, int childrenLeft, boolean selected) {
if (!mDataChanged) {
// 此时 ListView 有最多一屏的数据,这里直接获取 mSctiveViews 数组中的视图并返回
final View activeView = mRecycler.getActiveView(position);
if (activeView != null) {
// 第四个参数为 true,会调用 attachViewToParent() 方法,将获取的 View 添加到 ListView 中,执行 attach 操作
setupChild(activeView, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, true);
// 返回上面获取的视图
return activeView;
}
}
final View child = obtainView(position, mIsScrap);
setupChild(child, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, mIsScrap[0]);
return child;
}
经过两次 Layout 过程,至此 ListView 显示了最多一屏的数据
三、ListView 滑动
只有在滑动时,有列表项滑出屏幕才会产生废弃数据,则对应 onTouchEvent() 方法的 onMove() 情况,onTouchEvent() 在 ListView 的父类 AbsListView 中
AbsListView#onTouchEvent():
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
onTouchMove(ev, vtev);
break;
}
...
}
AbsListView#onTouchMove():
private void onTouchMove(MotionEvent ev, MotionEvent vtev) {
...
// 当手指在屏幕上滑动时,TouchMode 等于 TOUCH_MODE_SCROLL
case TOUCH_MODE_SCROLL:
case TOUCH_MODE_OVERSCROLL:
scrollIfNeeded((int) ev.getX(pointerIndex), y, vtev);
break;
...
}
AbsListView#scrollIfNeeded():
private void scrollIfNeeded(int x, int y, MotionEvent vtev) {
...
if (mTouchMode == TOUCH_MODE_SCROLL) {
...
if (y != mLastY) {
...
// No need to do all this work if we're not going to move anyway
boolean atEdge = false;
if (incrementalDeltaY != 0) {
atEdge = trackMotionScroll(deltaY, incrementalDeltaY);
}
...
}
}
}
AbsListView#trackMotionScroll():
boolean trackMotionScroll(int deltaY, int incrementalDeltaY) {
...
int start = 0;
intcount = 0;
// 手指往下滑
if (down) {
int top = -incrementalDeltaY;
if ((mGroupFlags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) {
top += listPadding.top;
}
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getBottom() >= top) {
break;
} else {
count++;
int position = firstPosition + i;
if (position >= headerViewsCount && position < footerViewsStart) {
// The view will be rebound to new data, clear any
// system-managed transient state.
child.clearAccessibilityFocus();
// 往下滑出屏幕,添加到废弃视图缓存数组 mScrapViews 中
mRecycler.addScrapView(child, position);
}
}
}
} else { // 手指往上滑
int bottom = getHeight() - incrementalDeltaY;
if ((mGroupFlags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) {
bottom -= listPadding.bottom;
}
for (int i = childCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getTop() <= bottom) {
break;
} else {
start = i;
count++;
int position = firstPosition + i;
if (position >= headerViewsCount && position < footerViewsStart) {
// The view will be rebound to new data, clear any
// system-managed transient state.
child.clearAccessibilityFocus();
// 往上滑出屏幕,添加到废弃视图缓存数组 mScrapViews 中
mRecycler.addScrapView(child, position);
}
}
}
}
...
if (count > 0) {
detachViewsFromParent(start, count);
mRecycler.removeSkippedScrap();
}
...
// 让 ListView 中所有的子 View 都按照传入的参数值进行相应的偏移
// 实现随着手指的拖动,ListView 的内容也随着滚动的效果
offsetChildrenTopAndBottom(incrementalDeltaY);
...
final int absIncrementalDeltaY = Math.abs(incrementalDeltaY);
// 加载屏幕外数据
// 在触摸屏滚动的过程中,留在屏幕上的孩子会被移动,而其他孩子则被丢弃
// incrementalDeltaY 小于 0,说明是向下滑动,否则就是向上滑动
if (spaceAbove < absIncrementalDeltaY || spaceBelow < absIncrementalDeltaY) {
fillGap(down);
}
...
}
ListView#fillGap(down):
@Override
void fillGap(boolean down) {
final int count = getChildCount();
// 手指往下滑
if (down) {
int paddingTop = 0;
if ((mGroupFlags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) {
paddingTop = getListPaddingTop();
}
final int startOffset = count > 0 ? getChildAt(count - 1).getBottom() + mDividerHeight :
paddingTop;
// 手指下滑,调用 fillDown() 方法
fillDown(mFirstPosition + count, startOffset);
correctTooHigh(getChildCount());
} else { //手指往上滑
int paddingBottom = 0;
if ((mGroupFlags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) {
paddingBottom = getListPaddingBottom();
}
final int startOffset = count > 0 ? getChildAt(0).getTop() - mDividerHeight :
getHeight() - paddingBottom;
// 手指上滑,调用 fillUp() 方法
fillUp(mFirstPosition - 1, startOffset);
correctTooLow(getChildCount());
}
}
上滑对应的 fillUp() 和下滑对应的 fillDown() 共同的逻辑如下:
① 将滑出屏幕的视图回收,添加到废弃视图缓存数组 mScrapViews 中
mRecycler.addScrapView(child, position);
② 最终都会调用 makeAndAddView() 方法
ListView#makeAndAddView():
private View makeAndAddView(int position, int y, boolean flow, int childrenLeft, boolean selected) {
if (!mDataChanged) {
final View activeView = mRecycler.getActiveView(position);
if (activeView != null) {
setupChild(activeView, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, true);
return activeView;
}
}
// 从废弃视图数组中获取视图,作为参数传递给 getView() 方法的第二个参数
// ListView 跟着手指上下滑动,就会有视图滑出屏幕变成废弃视图(会被废弃视图缓存数组 mScrapViews 中),之后 ListView 显示新视图都是从废弃视图缓存数组中获取视图缓存,所以即使 ListView 有大量需要显示的列表数据,也不会导致 OOM,所需的内存基本就对应屏幕可见的那些视图项所占用的内存
final View child = obtainView(position, mIsScrap);
// This needs to be positioned and measured.
setupChild(child, position, y, flow, childrenLeft, selected, mIsScrap[0]);
return child;
}
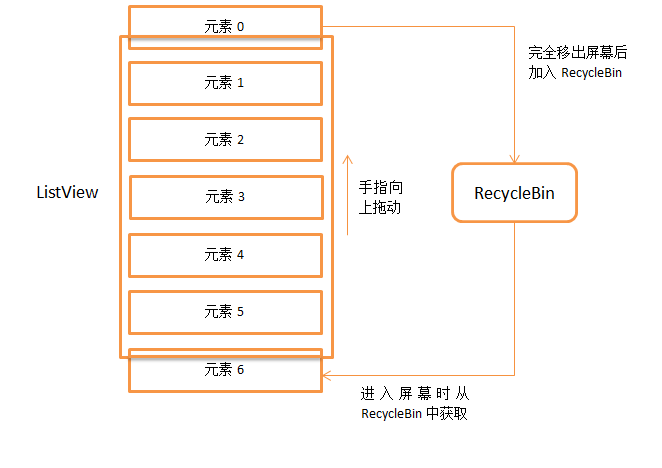
执行流程总结:
1.执行两次 Layout 过程
1.1 第一次 Layout 过程:
// 开始之前,ListView 中没有数据,数据在 Adapter 中
// 调用 fillDown() 方法,ListView 中有了最多一屏的数据
ListView#fillDown()
1.2 第二次 Layout 过程:
layoutChildren():
1. fillActiveViews() // 因为此时 ListView 有了最多一屏的数据,这里通过 fillActiveViews() 方法填充 mActiveViews 数组
2. detachAllViewsFromParent() // 清空所有的子视图,执行 detach 操作
3. 根据布局模式 LayoutMode 进行布局,默认情况下布局模式为 LAYOUT_NORMAL
会调用到 fillSpecific()
2.滑动过程
2.1 回收滑出屏幕的视图
// ListView 向上或向下滑动,把滑出屏幕的视图添加到废弃视图缓存数组 mScrapViews 中
mRecycler.addScrapView(child, position);
2.2 再次调用 makeAndAddView() 方法,之后滑入屏幕的视图就使用的是从废弃视图缓存数组 mScrapViews 中获取视图,这里就是不管 ListView 有多少的子项需要加载,都不会发生 OOM 的原因,所需的内存基本就对应屏幕可见的那些视图项所占用的内存
四、RecycleBin 相关
RecycleBin 有助于跨布局重用视图,包含两个级别的存储:ActiveView 和 ScrapView
ActiveView:是版面开始时屏幕上的视图。通过构造,它们显示当前信息(布局结束时,ActiveView 中的所有视图都将降级为 ScrapView)
ScrapView:是旧视图,适配器可能会使用它来避免不必要地分配视图
RecycleBin#fillActiveViews():
注:mActiveViews 是数组类型,用来装 ListView 在屏幕上那些可见的列表对应的 View,又因为此时传入的第一个参数 childCount 为 0
RecycleBin#fillActiveViews():
// 填充 mActiveViews 数组,但是因为此时 ListView 没有数据,方法此时不起作用
// childCount:ListView 中要存储的 View 的数量
// firstActivePosition:ListView 中第一个可见元素对应的 position
void fillActiveViews(int childCount, int firstActivePosition) {
// mActiveViews 数组长度小于 ListView 中存储的 View 的数量
if (mActiveViews.length < childCount) {
mActiveViews = new View[childCount];
}
mFirstActivePosition = firstActivePosition;
//noinspection MismatchedReadAndWriteOfArray
final View[] activeViews = mActiveViews;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
AbsListView.LayoutParams lp = (AbsListView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// Don't put header or footer views into the scrap heap
if (lp != null && lp.viewType != ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_HEADER_OR_FOOTER) {
// Note: We do place AdapterView.ITEM_VIEW_TYPE_IGNORE in active views.
// However, we will NOT place them into scrap views.
activeViews[i] = child;
// Remember the position so that setupChild() doesn't reset state.
lp.scrappedFromPosition = firstActivePosition + i;
}
}
}
RecycleBin#fillActiveViews():
// 获取 mActiveViews 指定位置对应的视图
View getActiveView(int position) {
int index = position - mFirstActivePosition;
final View[] activeViews = mActiveViews;
if (index >=0 && index < activeViews.length) {
final View match = activeViews[index];
// 从 mActiveViews 中删除
activeViews[index] = null;
return match;
}
return null;
}
// …
























 1737
1737











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








