一.线程的概念,什么是线程,线程和进程的区别
线程是可以理解成进程多条执行线索,有着自己独立的生命周期,进程就是应用程序执行的一个过程,进程中有多个线程 线程是程序执行的最小单位
二.实现线程的三种方式
Thread Runnable Callable
- Thread 继承Thread,会重写里边的run方法 代码如下
//线程的知识 写一个窗口售票的例子
public class Demo01 {
//通过Thread书写
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Ticket().start();
new Ticket().start();
new Ticket().start();
}
}
class Ticket extends Thread{
//定义票数
private static int ticket = 100;
public void run(){
while (true){
//如果要使用成员变量需要加静态static 这里要特别注意同时启动四个线程执行对象锁需要是唯一的
synchronized (Ticket.class){
if (ticket <= 0){
break;
}
System.out.println(getName()+"......开始售票"+ ticket-- + "售票数");
}
}
}
}2.实现Runnable接口 实现run方法 通过new Thread (Runnable实现类).start()调用线程
package com.allan.controller.thread;
/**
* 使用runable实现售票 需要注意的点是static this关键字的用法wait方法让线程等待
* notify 随机唤醒正在等待的线程notifyAll 唤醒正在等待的所有的线程
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试runnable线程
Tickets1 ticket = new Tickets1();
new Thread(ticket).start();
new Thread(ticket).start();
new Thread(ticket).start();
new Thread(ticket).start();
}
}
class Tickets1 implements Runnable{
/**
* 多次启动一个线程是非法的 需要注意下
*/
//1.给定票数
private int ticket = 100;
//给定条件
public void run() { //run 方法中的线程没发对外抛出异常
while (true){
synchronized(this){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (ticket <= 0){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"当前执行的线程出售的"+ticket-- +"票数");
}
}
}
}
3.第三种实现线程的方式 实现callable接口 这种方式有返回值
package com.allan.controller.thread.Thread2;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
/**
* 实现线程的第三种方式
* 实现Callable接口 有返回值
*
*/
public class CallableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试类
Callable01 callable01 = new Callable01();
FutureTask<Integer> integerFutureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(callable01);
new Thread(integerFutureTask,"有返回值的线程").start();
try {
System.out.println("返回值"+integerFutureTask.get());
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Callable01 implements Callable<Integer>{
int i = 1;
public Integer call() throws InterruptedException {
for (; i < 15; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"循环的变量"+i);
}
return i;
}
}三.线程的五中状态 如下图
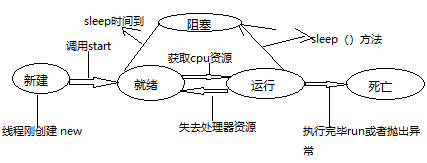
四.线程中常用的几个方法
notify随机唤醒等待的线程 notifyAll唤醒所有等待的线程 join等待线程死忘 yield对当前正在执行的线程失去资源
sleep wait 两个方法都是让线程等待 sleep方法有时间限制,wait没有时间限制,需要唤醒 sleep方法不释放锁,wait方法释放锁
五.线程之间怎么通信
多线程之间的通信就是共同执行一个资源,但是操作的动作不同 wait多用在多线程的同步和synchronized一起使用
notify wait一起使用,用来唤醒wait的线程,线程状态从阻塞变成运行
jdk1.5之后特性 ReentrantLock
class Printer3{
//定义标识符
private ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
private int flag = 1;
public void Printer01() throws InterruptedException{
Condition c1= reentrantLock.newCondition();
Condition c2= reentrantLock.newCondition();
synchronized (Printer.class) {
while (flag != 1) { //if语句在哪里等待就在那里起来
c1.await();// 让线程等待
}
System.out.print("你");
System.out.print("好");
System.out.print("\r\n");
flag = 2;
c2.signal();
}
}
}





















 41万+
41万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








