字符串是Python中最常用的数据类型之一,也是可迭代对象,无论是数据处理、Web开发还是自动化脚本,都离不开字符串操作。本文将详细介绍Python字符串的常见操作,包括函数原型说明和实际示例。
字符串基础
字符串创建
# 单引号
str1 = 'Hello World'
# 双引号
str2 = "Python Programming"
# 三引号(多行字符串)
str3 = '''这是一个
多行字符串'''
# 转义字符
str4 = "这是一个\"引号\"示例"
访问字符串元素
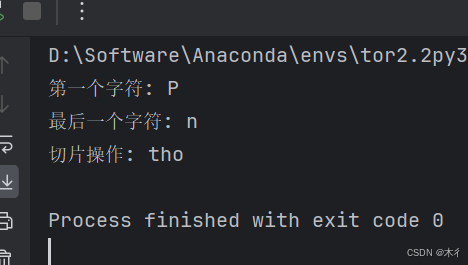
text = "Python"
print("第一个字符:", text[0]) # P
print("最后一个字符:", text[-1]) # n
print("切片操作:", text[2:5]) # tho
字符串查找操作
find() 和 rfind()
函数原型: str.find(sub[, start[, end]])
查找子字符串,返回第一次出现的索引,找不到返回-1
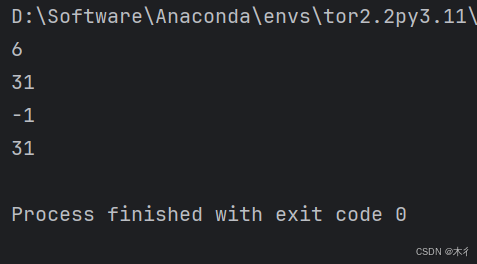
text = "hello world, welcome to python world"
# find() 从左向右查找
print(text.find("world")) # 6
print(text.find("world", 10)) # 31 (从索引10开始查找)
print(text.find("java")) # -1 (未找到)
# rfind() 从右向左查找
print(text.rfind("world")) # 31
输出:
index() 和 rindex()
函数原型: str.index(sub[, start[, end]])
与find()类似,查看子集字符是否在字符串中,若不在会抛出ValueError异常
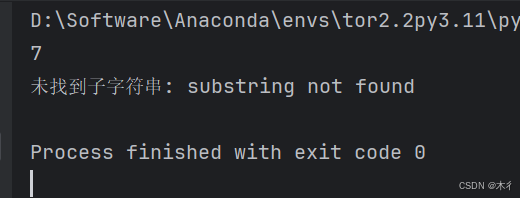
text = "python programming"
print(text.index("pro")) # 7
try:
print(text.index("java")) # ValueError
except ValueError as e:
print("未找到子字符串:", e)
count()
函数原型: str.count(sub[, start[, end]])
统计子字符串出现的次数
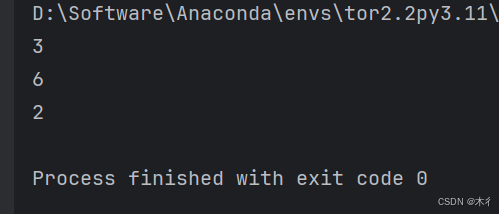
text = "apple banana apple cherry apple"
print(text.count("apple")) # 3
print(text.count("a")) # 6
print(text.count("apple", 10)) # 2 (从索引10开始统计)
字符串修改操作
replace()
函数原型: str.replace(old, new[, count])
替换字符串中的内容
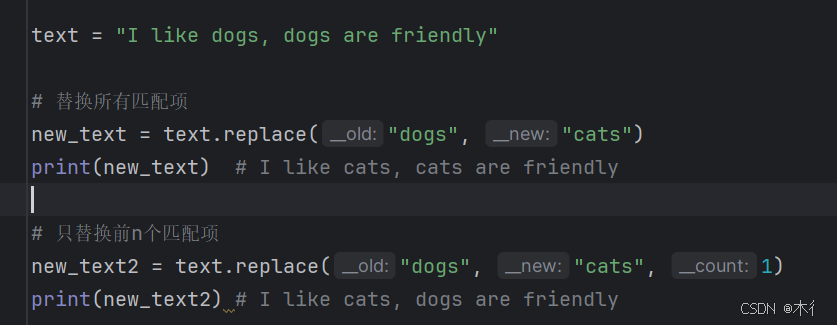
text = "I like dogs, dogs are friendly"
# 替换所有匹配项
new_text = text.replace("dogs", "cats")
print(new_text) # I like cats, cats are friendly
# 只替换前n个匹配项
new_text2 = text.replace("dogs", "cats", 1)
print(new_text2) # I like cats, dogs are friendly
pycharm中会提示函数参数

upper() 和 lower()
函数原型: str.upper() 和 str.lower()
转换大小写
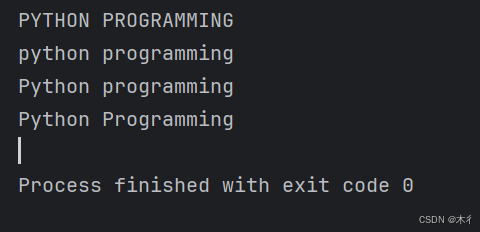
text = "Python Programming"
print(text.upper()) # PYTHON PROGRAMMING
print(text.lower()) # python programming
# 首字母大写
print(text.capitalize()) # Python programming
# 每个单词首字母大写
print(text.title()) # Python Programming
strip(), lstrip(), rstrip()
函数原型: str.strip([chars])
去除字符串两端的空白字符或指定字符
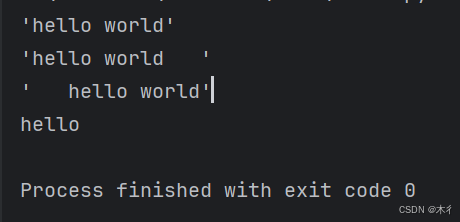
text = " hello world "
print(f"'{text.strip()}'") # 'hello world'
print(f"'{text.lstrip()}'") # 'hello world '
print(f"'{text.rstrip()}'") # ' hello world'
text2 = "***hello***"
print(text2.strip('*')) # hello
split() 和 join()
函数原型: str.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) 和 str.join(iterable)
# split() 分割字符串
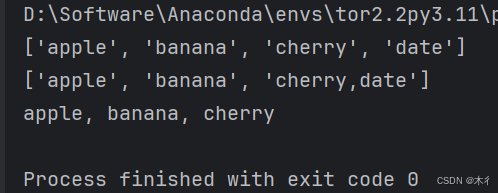
text = "apple,banana,cherry,date"
fruits = text.split(",")
print(fruits) # ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date']
# 限制分割次数
fruits2 = text.split(",", 2)
print(fruits2) # ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry,date']
# join() 连接字符串
fruits_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
result = ", ".join(fruits_list)
print(result) # apple, banana, cherry
其中,fruits2 = text.split(“,”, 2)是按照“,”分割两次,所以最后两个没有分隔开。
result = ", ".join(fruits_list)是拼接时,返回连接后的新字符串,“,”是连接符,可以设置成任意字符
字符串判断操作
startswith() 和 endswith()
函数原型: str.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]])
startswith()判断字符串的开始位置
endswith()判断字符串的结束位置
text = "hello_world.py"
print(text.startswith("hello")) # True
print(text.endswith(".py")) # True
print(text.startswith("world", 6)) # True (从索引6开始检查)
isalpha(), isdigit(), isalnum()
函数原型: str.isalpha() - 是否全是字母
str.isdigit() - 判断字符串是否只包含数字字符
str.isalnum() - 判断字符串是否只包含字母和数字字符
str.isspace() - 判断字符串是否只包含空白字符
str.istitle() - 判断字符串是否符合标题格式(每个单词首字母大写)
str.isupper() - 判断字符串中的所有字母字符是否都是大写
str.islower() -判断字符串中的所有字母字符是否都是小写
str.isdecimal() -判断是否为十进制数字
str.isnumeric() -判断是否为数字
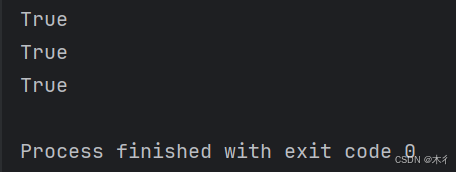
print("hello".isalpha()) # True
print("123".isdigit()) # True
print("hello123".isalnum()) # True
print("hello world".isalpha()) # False (包含空格)
print(" ".isspace()) # True
print("Hello".istitle()) # True
print("HELLO".isupper()) # True
print("123".isdecimal()) # True - 十进制数字
print("½".isdecimal()) # False - 分数不算十进制
print("½".isnumeric()) # True - 分数被认为是数字
print("一二三".isnumeric()) # True - 中文数字
in 和 not in 运算符
检查子字符串是否存在
text = "python programming"
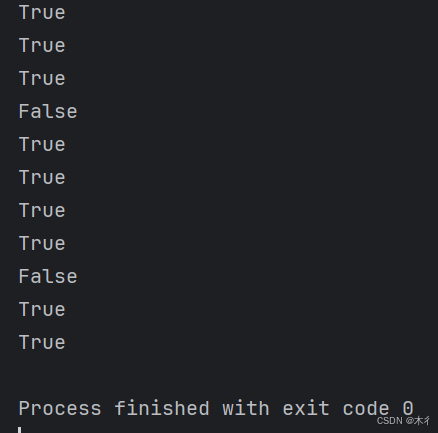
print("python" in text) # True
print("java" in text) # False
print("python" not in text) # False
字符串格式化
传统格式化 (%)
#%s 字符串, %d 整数, %f 浮点数
name = "Alice"
age = 25
score = 95.5
# %s 字符串, %d 整数, %f 浮点数
text = "姓名: %s, 年龄: %d, 分数: %.2f" % (name, age, score)
print(text) # 姓名: Alice, 年龄: 25, 分数: 95.50
输出:
姓名: Alice, 年龄: 25, 分数: 95.50
%.2f表示保留两位小数
format() 方法
name = "Bob"
age = 30
# 位置参数
text1 = "姓名: {}, 年龄: {}".format(name, age)
print(text1) # 姓名: Bob, 年龄: 30
# 关键字参数
text2 = "姓名: {name}, 年龄: {age}".format(name=name, age=age)
print(text2) # 姓名: Bob, 年龄: 30
# 格式化数字
pi = 3.1415926
print("PI的值: {:.2f}".format(pi)) # PI的值: 3.14
姓名: Bob, 年龄: 30
姓名: Bob, 年龄: 30
PI的值: 3.14
字符串编码解码
encode() 和 decode()
text = "你好,世界"
# 编码为字节
encoded = text.encode('utf-8')
print(encoded) # b'\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd\xef\xbc\x8c\xe4\xb8\x96\xe7\x95\x8c'
# 解码回字符串
decoded = encoded.decode('utf-8')
print(decoded) # 你好,世界
b'\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd\xef\xbc\x8c\xe4\xb8\x96\xe7\x95\x8c'
你好,世界
实战示例
示例1:用户输入验证
def validate_username(username):
"""
验证用户名格式
要求:3-20个字符,只能包含字母、数字和下划线
"""
if 3 <= len(username) <= 20:
if username.isalnum() or '_' in username:
return True
return False
# 测试
usernames = ["user123", "abc", "user_name", "user@name", "a"]
for user in usernames:
print(f"{user}: {validate_username(user)}")
输出:
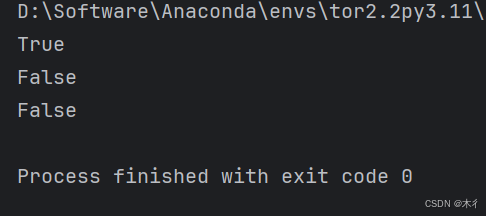
user123: True
abc: True
user_name: True
user@name: False
a: False
示例2 文本处理工具
def text_analyzer(text):
"""
分析文本统计信息
"""
# 移除标点符号
import string
clean_text = text.translate(str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation))
words = clean_text.split()
analysis = {
'字符数': len(text),
'单词数': len(words),
'句子数': text.count('.') + text.count('!') + text.count('?'),
'平均单词长度': sum(len(word) for word in words) / len(words) if words else 0,
'大写字母数': sum(1 for char in text if char.isupper()),
'小写字母数': sum(1 for char in text if char.islower())
}
return analysis
# 测试
sample_text = "Hello World! This is a sample text. It contains multiple sentences."
result = text_analyzer(sample_text)
for key, value in result.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")
输出:
字符数: 67
单词数: 11
句子数: 3
平均单词长度: 4.909090909090909
大写字母数: 4
小写字母数: 50
其中,clean_text = text.translate(str.maketrans(’ ', ’ ', string.punctuation))是删除文本中所有的标点符号。
示例3:密码强度检查器
def check_password_strength(password):
"""
检查密码强度
"""
strength = 0
feedback = []
# 长度检查
if len(password) >= 8:
strength += 1
else:
feedback.append("密码长度至少8个字符")
# 包含大写字母
if any(char.isupper() for char in password):
strength += 1
else:
feedback.append("至少包含一个大写字母")
# 包含小写字母
if any(char.islower() for char in password):
strength += 1
else:
feedback.append("至少包含一个小写字母")
# 包含数字
if any(char.isdigit() for char in password):
strength += 1
else:
feedback.append("至少包含一个数字")
# 包含特殊字符
special_chars = "!@#$%^&*()_+-=[]{}|;:,.<>?"
if any(char in special_chars for char in password):
strength += 1
else:
feedback.append("至少包含一个特殊字符")
# 评估强度
if strength == 5:
level = "非常强"
elif strength == 4:
level = "强"
elif strength == 3:
level = "中等"
else:
level = "弱"
return {
'strength_level': level,
'score': strength,
'feedback': feedback
}
# 测试密码
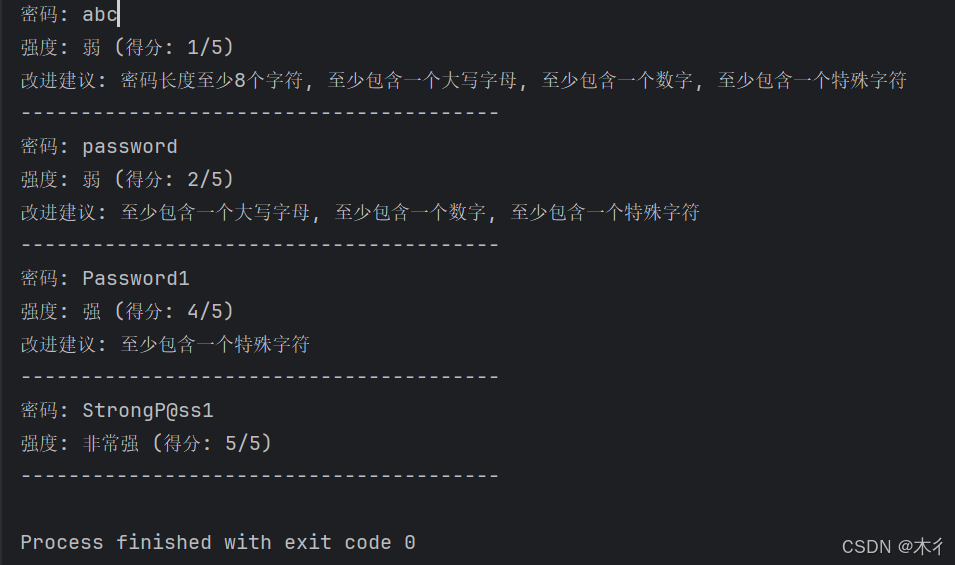
passwords = ["abc", "password", "Password1", "StrongP@ss1"]
for pwd in passwords:
result = check_password_strength(pwd)
print(f"密码: {pwd}")
print(f"强度: {result['strength_level']} (得分: {result['score']}/5)")
if result['feedback']:
print("改进建议:", ", ".join(result['feedback']))
print("-" * 40)
输出:
总结
Python提供了丰富而强大的字符串操作功能,包括:
查找操作: find(), index(), count() 等
修改操作: replace(), upper(), split(), join() 等
判断操作: startswith(), isalpha(), in 运算符等
格式化: % 操作符, format(), f-string
编码解码: encode(), decode()
掌握这些字符串操作技巧对于Python编程至关重要,它们能帮助我们高效地处理文本数据,完成各种复杂的字符串处理任务。在实际开发中,根据具体需求选择合适的字符串方法,可以大大提高代码的效率和可读性。






















 430
430

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










