最大流问题比较好理解,就是给出一个图,每条边有限制的最大容量,要求从起始节点输出到结束节点,所有中间节点的输入与输出相等,求一条能带来最大流量的路径。
这里,我们直接讲解比较成熟的Ford-Fulkerson算法,在求增广路径时,我们采用的是广度优先搜索。效率可达O(VE^2)。
算法步骤:
1.输入数据,作为图G的边及边的容量;
2.跟据图G,通过广度优先搜索,选出一条从起始节点到结束节点的路径path,并记录路径中的流大小(即流量最小的段的流量);
3.根据图G与path构造图Gf:Gf每条边有容量和当前流量两个数据,容量即为图G的容量,流量即为路径path的流量;
4.根据图Gf构造新的图G:对于Gf中的边(u,v),流量/容量 为 m/n,则在Gf中构造两条边,分别为边(u,v),容量 = n - m ; 边(v,u),容量 = m;
5.同第2步;
6.根据得到的path,更新图Gf;
7.重复4,5,6步,直到不再有新的增广路径path产生;
8.输出结果。
具体代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Founder
* 输入方式:采用矩阵输入法,第一行输入节点个数,第二行输入源节点与终节点编号,后面的行输入矩阵
*
*/
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
G g = initialize();
Gf gf = new Gf(g);
while(!gf.isEnd()){
g = new G(gf);
gf.setFlowByPath(g.getPath());
}
print(gf);
}
private static G initialize(){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt();
G g = new G(n,input.nextInt(),input.nextInt());
int[][] matrix = g.getMatrix();
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
matrix[i][j] = input.nextInt();
return g;
}
private static void print(Gf gf){
System.out.println("最大流为:" + gf.getFlowAmount());
int[][] flow = gf.getFlow();
int[][] capacity = gf.getCapacity();
for(int m = 0; m < flow.length; ++m){
for(int n = 0; n < flow.length; ++n)
System.out.print(flow[m][n] + "/" + capacity[m][n] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class G{
public final static int WHITE = 0;
public final static int GRAY = 1;
public final static int BLACK = 2;
private int[] color;
private int[] parent;
private int[][] matrix;
private int size;
private int source;
private int terminal;
public int[] getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setNodeColor(int position,int color) {
this.color[position] = color;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public int[][] getMatrix() {
return matrix;
}
public void setMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
this.matrix = matrix;
}
/**
*
* @return path的最后一个数字为path的流量大小
*/
public ArrayList<Integer> getPath(){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(source);
int current = source;
while(!queue.isEmpty() && current != terminal){
current = queue.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
if(matrix[current][i] != 0 && color[i] == WHITE){
queue.offer(i);
color[i] = GRAY;
parent[i] = current;
if( i == terminal){
current = terminal;
break;
}
}
}
color[current] = BLACK;
}
if(current != terminal)
return null;
else{
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
int amount = 2000000000;
while(current != source){
path.add(current);
current = parent[current];
int tempAmount = matrix[current][path.get(path.size() - 1)];
amount = amount > tempAmount?tempAmount:amount;
}
path.add(source);
path.add(amount);
return path;
}
}
public int getSource() {
return source;
}
public void setSource(int source) {
this.source = source;
}
public int getTerminal() {
return terminal;
}
public void setTerminal(int terminal) {
this.terminal = terminal;
}
public G(int n,int source,int terminal) {
size = n;
this.source = source;
this.terminal = terminal;
color = new int[n];
parent = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
color[i] = WHITE;
parent[i] = -1;
}
matrix = new int[n][n];
}
public G(Gf gf){
size = gf.getSize();
this.source = gf.getSource();
this.terminal = gf.getTerminal();
color = new int[size];
parent = new int[size];
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
color[i] = WHITE;
parent[i] = -1;
}
matrix = new int[size][size];
int[][] capacity = gf.getCapacity();
int[][] flow = gf.getFlow();
for(int m = 0; m < size; ++m)
for(int n = 0; n < size; ++n){
if(capacity[m][n] != 0){
matrix[m][n] = capacity[m][n] - flow[m][n];
matrix[n][m] = flow[m][n];
}
}
}
}
class Gf{
private int[][] flow;
private int[][] capacity;
private int size;
private int source;
private int terminal;
private int flowAmount = 0;
private boolean isEnd = false;
public int[][] getFlow() {
return flow;
}
public void setFlow(int[][] flow) {
this.flow = flow;
}
public int[][] getCapacity() {
return capacity;
}
public void setCapacity(int[][] capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public int getSource() {
return source;
}
public void setSource(int source) {
this.source = source;
}
public int getTerminal() {
return terminal;
}
public void setTerminal(int terminal) {
this.terminal = terminal;
}
public int getFlowAmount() {
return flowAmount;
}
public void setFlowAmount(int flowAmount) {
this.flowAmount = flowAmount;
}
public boolean isEnd() {
return isEnd;
}
public void setEnd(boolean isEnd) {
this.isEnd = isEnd;
}
public Gf(int n) {
size = n;
flow = new int[size][size];
capacity = new int[size][size];
}
public Gf(G g) {
size = g.getSize();
this.source = g.getSource();
this.terminal = g.getTerminal();
capacity = g.getMatrix();
flow = new int[size][size];
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < size; ++j)
flow[i][j] = 0;
setFlowByPath(g.getPath());
}
public void setFlowByPath(ArrayList<Integer> path){
if(path != null){
int amount = path.get(path.size() - 1);
flowAmount += amount;
for(int i = path.size() - 2; i > 0; --i){
int u = path.get(i);
int v = path.get(i - 1);
if(capacity[u][v] == 0)
flow[v][u] -= amount;
else
flow[u][v] += amount;
}
}else
setEnd(true);
}
}测试用例:
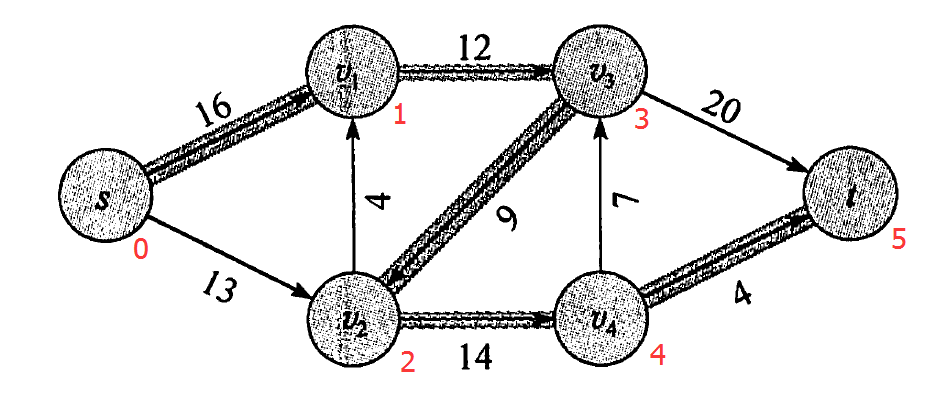
输入:
6
0 5
0 16 13 0 0 0
0 0 0 12 0 0
0 4 0 0 14 0
0 0 9 0 0 20
0 0 0 7 0 4
0 0 0 0 0 0输出:
最大流为:23
0/0 12/16 11/13 0/0 0/0 0/0
0/0 0/0 0/0 12/12 0/0 0/0
0/0 0/4 0/0 0/0 11/14 0/0
0/0 0/0 0/9 0/0 0/0 19/20
0/0 0/0 0/0 7/7 0/0 4/4
0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 0/0 





















 1069
1069

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








