转载轻注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_24692041/article/details/65435025
本文是在兰亭风雨的博文基础上加上了源代码,更利于理解,在这儿先感谢兰亭风雨的分享!当然网友想要更好的了解这个部分的东西,最好自己去IDE中看看源码。
Java集合工具包位于Java.util包下,包含了很多常用的数据结构,如数组、链表、栈、队列、集合、哈希表等。学习Java集合框架下大致可以分为如下五个部分:List列表、Set集合、Map映射、迭代器(Iterator、Enumeration)、工具类(Arrays、Collections)。
Java集合类的整体框架如下:
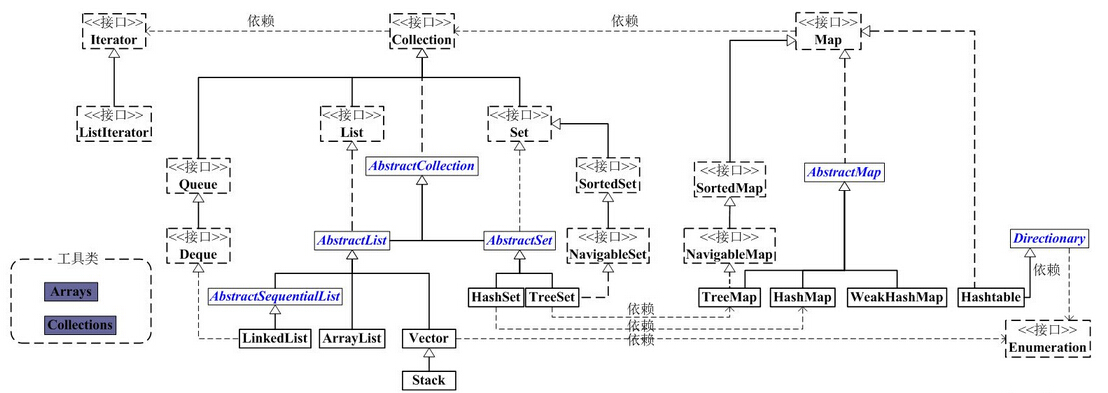
从上图中可以看出,集合类主要分为两大类:Collection和Map。
Collection是List、Set等集合高度抽象出来的接口,它包含了这些集合的基本操作,它主要又分为两大部分:List和Set。
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> { // Query Operations /** * Returns the number of elements in this list. If this list contains * more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns * <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>. * * @return the number of elements in this list */ int size(); /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements. * * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements */ boolean isEmpty();......}
public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> { // Query Operations /** * Returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality). If this * set contains more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns * <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>. * * @return the number of elements in this set (its cardinality) */ int size(); /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains no elements. * * @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains no elements */ boolean isEmpty(); .....}
List接口通常表示一个列表(数组、队列、链表、栈等),其中的元素可以重复,常用实现类为ArrayList和LinkedList,另外还有不常用的Vector。另外,LinkedList还是实现了Queue接口,因此也可以作为队列使用。
Set接口通常表示一个集合,其中的元素不允许重复(通过hashcode和equals函数保证),常用实现类有HashSet和TreeSet,HashSet是通过Map中的HashMap实现的,而TreeSet是通过Map中的TreeMap实现的。另外,TreeSet还实现了SortedSet接口,因此是有序的集合(集合中的元素要实现Comparable接口,并覆写Compartor函数才行)。
源码中可以看到HashSet其实是在构造方法中new了一个map,所有的操作都是对这个map的操作。而TreeSet则是创建了一个TreeMap,一直都是在操作这个map。
public class HashSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { static final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L; private transient HashMap<E,Object> map; // Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); /** * Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has * default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). */ public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); } /** * Constructs a new set containing the elements in the specified * collection. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with default load factor * (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to contain the elements in * the specified collection. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this set * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) { map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16)); addAll(c); } ......../** * Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. * More formally, adds the specified element <tt>e</tt> to this set if * this set contains no element <tt>e2</tt> such that * <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>. * If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set * unchanged and returns <tt>false</tt>. * * @param e element to be added to this set * @return <tt>true</tt> if this set did not already contain the specified * element */ public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; } .....}
public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { /** * The backing map. */ private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m; // Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); /** * Constructs a set backed by the specified navigable map. */ TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) { this.m = m; } /** * Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the * natural ordering of its elements. All elements inserted into * the set must implement the {@link Comparable} interface. * Furthermore, all such elements must be <i>mutually * comparable</i>: {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a * {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and * {@code e2} in the set. If the user attempts to add an element * to the set that violates this constraint (for example, the user * attempts to add a string element to a set whose elements are * integers), the {@code add} call will throw a * {@code ClassCastException}. */ public TreeSet() { this(new TreeMap<E,Object>()); } ....../** * Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. * More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if * the set contains no element {@code e2} such that * <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>. * If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set * unchanged and returns {@code false}. * * @param e element to be added to this set * @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified * element * @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared * with the elements currently in this set * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null * and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator * does not permit null elements */ public boolean add(E e) { return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null; } .......}
我们看到,抽象类AbstractCollection、AbstractList和AbstractSet分别实现了Collection、List和Set接口,这就是在Java集合框架中用的很多的适配器设计模式,用这些抽象类去实现接口,在抽象类中实现接口中的若干或全部方法,这样下面的一些类只需直接继承该抽象类,并实现自己需要的方法即可,而不用实现接口中的全部抽象方法。
Map是一个映射接口,其中的每个元素都是一个key-value键值对,同样抽象类AbstractMap通过适配器模式实现了Map接口中的大部分函数,TreeMap、HashMap、WeakHashMap等实现类都通过继承AbstractMap来实现,另外,不常用的HashTable直接实现了Map接口,它和Vector都是JDK1.0就引入的集合类。
Iterator是遍历集合的迭代器(不能遍历Map,只用来遍历Collection),Collection的实现类都实现了iterator()函数,它返回一个Iterator对象,用来遍历集合,ListIterator则专门用来遍历List。而Enumeration则是JDK1.0时引入的,作用与Iterator相同,但它的功能比Iterator要少,它只能再Hashtable、Vector和Stack中使用。
Arrays和Collections是用来操作数组、集合的两个工具类,例如在ArrayList和Vector中大量调用了Arrays.Copyof()方法,而Collections中有很多静态方法可以返回各集合类的synchronized版本,即线程安全的版本,当然了,如果要用线程安全的结合类,首选Concurrent并发包下的对应的集合类。






















 4702
4702

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








