前言
早就看到很多描述NIO相比传统IO性能上的各种优势,于是带着求证心里前来测试一番,场景如下:
- 写场景:将字符串内容
lu ben wei niu bi, stand up all! play game must be Laughing,play nm!作为一行内容,重复的写入到一个文件中大概十万行,最后比较两种IO模型下的耗时 - 读场景:将一个五十万行的文本(包含汉字)按行读取出来,统计两种IO模型下的耗时
写测试
传统IO都使用带缓存(buffer)的IO去操作,代码如下:
private static final String CONTENT = "lu ben wei niu bi, stand up all! play game must be Laughing,play nm!\r\n";
private final static int WRITE_COUNT = 100000;
private final static String FILE_PATH = "E:\\IOTest\\lbw.txt";
public static void testWrite_Buffer(String content) {
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
OutputStreamWriter writer = null;
BufferedWriter out = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(path);
writer = new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream, "GBK");
out = new BufferedWriter(writer);
for (int i = 0; i < WRITE_COUNT; i++) {
out.write(content);
}
System.err.println("buffer->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(out, writer, outputStream);
}
}
运行结果大致在57-60ms左右
然后是nio写操作:
private static final String CONTENT = "lu ben wei niu bi, stand up all! play game must be Laughing,play nm!\r\n";
private final static int WRITE_COUNT = 100000;
private final static String FILE_PATH = "E:\\IOTest\\lbw.txt";
public static void testNio_write(String content) {
FileChannel channel = null;
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(path);
channel = outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(content.getBytes().length * WRITE_COUNT);
for (int i = 0; i < WRITE_COUNT; i++) {
buffer.put(content.getBytes());
}
buffer.flip();
channel.write(buffer);
System.err.println("channel->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(channel, outputStream);
}
}
运行结果大致在45-49ms左右。。
最后用mmap(内存映射机制)测试:
private static final String CONTENT = "lu ben wei niu bi, stand up all! play game must be Laughing,play nm!\r\n";
private final static int WRITE_COUNT = 100000;
private final static String FILE_PATH = "E:\\IOTest\\lbw.txt";
public static void testRandomAccessFile_write(String content) {
FileChannel channel = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile(path, "rw");
channel = accessFile.getChannel();
long offset = 0;
MappedByteBuffer map;
byte[] bytes = content.getBytes();
map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, offset, bytes.length * WRITE_COUNT);
for (int i = 0; i < WRITE_COUNT; i++) {
map.put(bytes);
}
System.err.println("mmap->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(channel);
}
}
运行结果大致是15-19ms Oh!!!
mmap比传统io快了一倍多!NIO提升不明显,快了20%左右
完整代码:
package rpf.study.excel.nio;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.Closeable;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
import java.nio.charset.CoderResult;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
/**
* @program: java-excel
* @description:
* @author: ranpengfeng
* @create: 2019-11-15 11:21
*/
public class Test {
private static final String CONTENT = "lu ben wei niu bi, stand up all! play game must be Laughing,play nm!\r\n";
private final static int WRITE_COUNT = 100000;
/**
* 测试路径
*/
private final static String FILE_PATH = "E:\\IOTest\\lbw.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
executorService.submit(() -> {
//testNio_write(CONTENT);
});
executorService.submit(() -> {
//testWrite_Buffer(CONTENT);
});
executorService.submit(() -> {
testRandomAccessFile_write(CONTENT);
});
executorService.shutdown();
}
public static void testWrite_Buffer(String content) {
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
OutputStreamWriter writer = null;
BufferedWriter out = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(path);
writer = new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream, "GBK");
out = new BufferedWriter(writer);
for (int i = 0; i < WRITE_COUNT; i++) {
out.write(content);
}
System.err.println("buffer->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(out, writer, outputStream);
}
}
public static void testRandomAccessFile_write(String content) {
FileChannel channel = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile(path, "rw");
channel = accessFile.getChannel();
long offset = 0;
MappedByteBuffer map;
byte[] bytes = content.getBytes();
map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, offset, bytes.length * WRITE_COUNT);
for (int i = 0; i < WRITE_COUNT; i++) {
map.put(bytes);
}
System.err.println("mmap->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(channel);
}
}
public static void testNio_write(String content) {
FileChannel channel = null;
FileOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(path);
channel = outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(content.getBytes().length * WRITE_COUNT);
for (int i = 0; i < WRITE_COUNT; i++) {
buffer.put(content.getBytes());
}
buffer.flip();
channel.write(buffer);
System.err.println("channel->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(channel, outputStream);
}
}
/**
* 可变参数关闭closeable实现
*
* @param readers
*/
private static void close(Closeable... readers) {
try {
for (Closeable reader : readers) {
if (Objects.nonNull(reader)) {
reader.close();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.err.println("流关闭失败");
}
}
}
读取测试
读取还是和IOBuffer(BufferedReader)一行,一行一行读,最终统计总共耗时。BufferedReader有自己的解码器(字节码转字符),这里需要创建一个NIO的节码器,以及按行读取的function。
思路:首先是以换行符结尾(\r,\n)作为完整一行的标志。解析时,以8k大小作为一个解析块,因为考虑到文件大小,内存占用关系,以一个固定大小的ByteBuffer去循环的获取文件内容。由于无法每次都保证8K解析块的末尾刚好是某一行的结束位置,因此需要将上一次不完整行的内容保存到StringBuffer中。图形话来说就是:
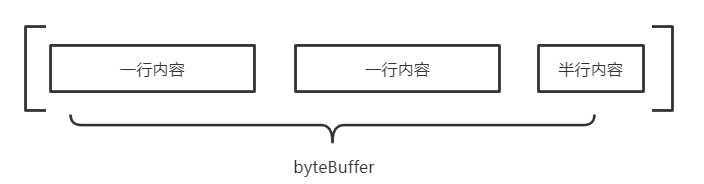
这个时候需要把byteBuffer中剩余的半行内容编码成字符串放到StringBuffer,再解析下一行时候,就在StringBuffer后面追加既是完整一行。
其次是汉字问题,由于一个汉字在gbk编码下占用两个字节,所以有可能出现ByteBuffer末尾包含一个汉字的其中一个字节,而下一次读取的时候ByteBuffer头部则是汉字的另一个字节,这样会导致两行内容编码失败,图形解释:

解决办法就是,在节码失败后,将失败的汉字编码放到leftBuffer中去暂存起来,下一次直接将两部分字节码连接在一起编码
首先是传统IO代码:
private final static String FILE_PATH = "E:\\IOTest\\sx.txt";
public static void testBuffer(BiConsumer<Integer, String> consumer) {
InputStreamReader reader = null;
BufferedReader in = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path), "GBK");
in = new BufferedReader(reader);
String line;
int lineCount = 0;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
lineCount++;
consumer.accept(lineCount, line);
}
System.out.println("buffer->lineCount: " + lineCount);
System.err.println("buffer->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(reader, in);
}
}
由于读相互不影响,因此可以一起运行。
NIO代码:
/**
*解码器配置
*/
private static Charset cs = Charset.forName("GBK");
private static CharsetDecoder charsetDecoder = cs.newDecoder();
/**
* 测试路径
*/
private final static String FILE_PATH = "E:\\IOTest\\sx.txt";
public static void testNio(BiConsumer<Integer, String> consumer) {
FileChannel channel = null;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path);
channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
int capacity = 1024 * 8;
//直接获取通道中的字节
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(capacity);
//暂存节码出现问题的字节,通常由于汉字的2字节存在不同的批次的buffer中引起
ByteBuffer leftBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(capacity * 2);
int lineCount = 0;
CharBuffer cb = CharBuffer.allocate(buffer.capacity());
//连接buffer中末尾不足一行的内容,缓存于此
StringBuffer attach = new StringBuffer();
while (channel.read(buffer) != -1) {
buffer.flip();
//解码字节
decodeBytes(buffer, leftBuffer, cb);
char[] chars = cb.array();
int pChar = 0;
String line;
int min = Math.min(cb.position(), chars.length);
for (int i = 0; i < min; i++) {
char c = chars[i];
if (c == '\n' || c == '\r') {
if (pChar < i || attach.length() > 0) {
if (attach.length() == 0) {
line = new String(chars, pChar, i - pChar);
} else {
attach.append(chars, pChar, i - pChar);
line = attach.toString();
attach.delete(0, attach.length());
}
lineCount++;
consumer.accept(lineCount, line);
pChar = i + 1;
continue;
}
if (c == '\r') {
lineCount++;
consumer.accept(lineCount, "");
pChar = i + 1;
}
}
}
//将不是完整一行数据的内容放入attach
if (pChar < min) {
attach.append(chars, pChar, min - pChar);
}
buffer.clear();
}
System.out.println("channel->lineCount:" + lineCount);
System.err.println("channel->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(channel, fileInputStream);
}
}
/**
* 解码字节->字符
* @param buffer
* @param leftBuffer
* @param cb
*/
private static void decodeBytes(ByteBuffer buffer, ByteBuffer leftBuffer, CharBuffer cb) {
int capacity = buffer.capacity();
cb.clear();
//假定刚好不存在汉字字节被断开的问题,则直接解析,大多数情况
CoderResult decode = charsetDecoder.decode(buffer, cb, true);
//处理遇到汉字字节被断开的解析格式问题
while (decode.isMalformed()) {
//查询leftBuffer是否有上次未处理的字节码
if (leftBuffer.position() == 0) {
int position = buffer.position();
//将本次出现解码错误位置的字节放到leftBuffer中
for (; position < capacity; position++) {
leftBuffer.put(buffer.get(position));
}
//将limit移动到解码出错的位置
buffer.limit(buffer.position());
//重新解码
decode = charsetDecoder.decode(buffer, cb, true);
} else {
//将解码错误的字节append到leftBuffer的后面,构造成完整的汉字解码
buffer.position(0);
cb.position(0);
leftBuffer.put(buffer);
//写模式切换读模式
leftBuffer.flip();
decode = charsetDecoder.decode(leftBuffer, cb, true);
int position = leftBuffer.position();
int limit = leftBuffer.limit();
leftBuffer.clear();
//如果末尾再次遇到汉字解码问题,则将出现问题的字节同理移动到leftBuffer开头位置,并结束循环,下次read(buffer)的时候再处理
if (decode.isMalformed()) {
for (; position < limit; position++) {
leftBuffer.put(leftBuffer.get(position));
}
break;
}
}
}
}
最后是mmap的代码:
/**
*解码器配置
*/
private static Charset cs = Charset.forName("GBK");
private static CharsetDecoder charsetDecoder = cs.newDecoder();
/**
* 测试路径
*/
private final static String FILE_PATH = "E:\\IOTest\\sx.txt";
public static void testRandomAccessFile(BiConsumer<Integer, String> consumer) {
FileChannel channel = null;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String path = FILE_PATH;
RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile(path, "r");
channel = accessFile.getChannel();
//偏移位置
long offset = 0;
//映射mmap容量
int max = 1024 * 1000;
//总字节大小
long len = channel.size();
int lineCount = 0;
MappedByteBuffer map;
CharBuffer cb;
ByteBuffer leftBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(max * 2);
//连接buffer中末尾不足一行的内容,缓存于此
StringBuffer attach = new StringBuffer();
while (offset <= len) {
if (offset + max > len) {
map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, offset, len - offset);
offset = len + 1;
} else {
map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, offset, max);
offset += max;
}
cb = CharBuffer.allocate(map.capacity());
String line;
decodeBytes(map,leftBuffer,cb);
char[] chars = cb.array();
int pChar = 0;
int min = Math.min(cb.position(), chars.length);
for (int i = 0; i < min; i++) {
char c = chars[i];
if (c == '\n' || c == '\r') {
if (pChar < i || attach.length() > 0) {
if (attach.length() == 0) {
line = new String(chars, pChar, i - pChar);
} else {
attach.append(chars, pChar, i - pChar);
line = attach.toString();
attach.delete(0, attach.length());
}
lineCount++;
consumer.accept(lineCount, line);
pChar = i + 1;
continue;
}
if (c == '\r') {
lineCount++;
consumer.accept(lineCount, "");
pChar = i + 1;
}
}
}
//将不是完整一行数据的内容放入attach
if (pChar < min) {
attach.append(chars, pChar, min - pChar);
}
}
System.out.println("mmap->lineCount:" + lineCount);
System.err.println("mmap->time:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(channel);
}
}
/**
* 解码字节->字符
* @param buffer
* @param leftBuffer
* @param cb
*/
private static void decodeBytes(ByteBuffer buffer, ByteBuffer leftBuffer, CharBuffer cb) {
int capacity = buffer.capacity();
cb.clear();
//假定刚好不存在汉字字节被断开的问题,则直接解析,大多数情况
CoderResult decode = charsetDecoder.decode(buffer, cb, true);
//处理遇到汉字字节被断开的解析格式问题
while (decode.isMalformed()) {
//查询leftBuffer是否有上次未处理的字节码
if (leftBuffer.position() == 0) {
int position = buffer.position();
//将本次出现解码错误位置的字节放到leftBuffer中
for (; position < capacity; position++) {
leftBuffer.put(buffer.get(position));
}
//将limit移动到解码出错的位置
buffer.limit(buffer.position());
//重新解码
decode = charsetDecoder.decode(buffer, cb, true);
} else {
//将解码错误的字节append到leftBuffer的后面,构造成完整的汉字解码
buffer.position(0);
cb.position(0);
leftBuffer.put(buffer);
//写模式切换读模式
leftBuffer.flip();
decode = charsetDecoder.decode(leftBuffer, cb, true);
int position = leftBuffer.position();
int limit = leftBuffer.limit();
leftBuffer.clear();
//如果末尾再次遇到汉字解码问题,则将出现问题的字节同理移动到leftBuffer开头位置,并结束循环,下次read(buffer)的时候再处理
if (decode.isMalformed()) {
for (; position < limit; position++) {
leftBuffer.put(leftBuffer.get(position));
}
break;
}
}
}
最后测试入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
BiConsumer<Integer, String> consumer = (i, line) -> {
if (i >= 1000 && i <= 2000) {
System.out.println("[" + i + "]:" + line);
}
};
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
executorService.submit(() -> {
testNio(consumer);
});
executorService.submit(() -> {
testBuffer(consumer);
});
executorService.submit(() -> {
testRandomAccessFile(consumer);
});
executorService.shutdown();
}
结果相当的意外:
第一次:
buffer->lineCount: 572585
buffer->time:513
channel->lineCount:572585
channel->time:902
mmap->time:1069
mmap->lineCount:572585
第二次:
buffer->lineCount: 572585
buffer->time:589
mmap->lineCount:572585
mmap->time:926
channel->lineCount:572585
channel->time:1025
第三次:
buffer->lineCount: 572585
buffer->time:505
mmap->lineCount:572585
channel->lineCount:572585
mmap->time:773
channel->time:776
第四次:
buffer->lineCount: 572585
buffer->time:651
channel->time:1073
channel->lineCount:572585
mmap->lineCount:572585
mmap->time:1177
结果:完败!读测试的代码我修改了很多次,最终还是没办法优化的和传统IO相当,BufferReader牛逼!
BufferReader获取字节数组的方法还是一个native的原生方法,并没有看到有什么独特的优化的地方。。
























 1927
1927











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








