一、概述
Java 8 是一个非常成功的版本,这个版本新增的Stream,配合同版本出现的Lambda ,给我们操作集合(Collection)提供了极大的便利。Stream流是JDK8新增的成员,允许以声明性方式处理数据集合,可以把Stream流看作是遍历数据集合的一个高级迭代器。Stream 是 Java8 中处理集合的关键抽象概念,它可以指定你希望对集合进行的操作,可以执行非常复杂的查找/筛选/过滤、排序、聚合和映射数据等操作。使用Stream API 对集合数据进行操作,就类似于使用 SQL 执行的数据库查询。也可以使用 Stream API 来并行执行操作。简而言之,Stream API 提供了一种高效且易于使用的处理数据的方式。
1、使用流的好处
代码以声明性方式书写,说明想要完成什么,而不是说明如何完成一个操作。
可以把几个基础操作连接起来,来表达复杂的数据处理的流水线,同时保持代码清晰可读。
2、流是什么?
从支持数据处理操作的源生成元素序列.数据源可以是集合,数组或IO资源。
从操作角度来看,流与集合是不同的. 流不存储数据值; 流的目的是处理数据,它是关于算法与计算的。
如果把集合作为流的数据源,创建流时不会导致数据流动; 如果流的终止操作需要值时,流会从集合中获取值; 流只使用一次。
流中心思想是延迟计算,流直到需要时才计算值。

Stream可以由数组或集合创建,对流的操作分为两种:
中间操作,每次返回一个新的流,可以有多个。
终端操作,每个流只能进行一次终端操作,终端操作结束后流无法再次使用。终端操作会产生一个新的集合或值。
特性:
不是数据结构,不会保存数据。
不会修改原来的数据源,它会将操作后的数据保存到另外一个对象中。(保留意见:毕竟peek方法可以修改流中元素)
惰性求值,流在中间处理过程中,只是对操作进行了记录,并不会立即执行,需要等到执行终止操作的时候才会进行实际的计算。
二、分类
| Stream操作分类 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 中间操作(Intermediate operations) | 无状态(Stateless) | unordered() filter() map() mapToInt() mapToLong() mapToDouble() flatMap() flatMapToInt() flatMapToLong() flatMapToDouble() peek() |
| 有状态(Stateful) | distinct() sorted() sorted() limit() skip() | |
| 结束操作(Terminal operations) | 非短路操作 | forEach() forEachOrdered() toArray() reduce() collect() max() min() count() |
| 短路操作(short-circuiting) | anyMatch() allMatch() noneMatch() findFirst() findAny() |
- 无状态:指元素的处理不受之前元素的影响;
- 有状态:指该操作只有拿到所有元素之后才能继续下去。
- 非短路操作:指必须处理所有元素才能得到最终结果;
- 短路操作:指遇到某些符合条件的元素就可以得到最终结果,如 A || B,只要A为true,则无需判断B的结果。
三、Stream的创建
Stream可以通过集合数组创建。
1、Collection.stream()
通过 java.util.Collection.stream() 方法用集合创建流
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
// 创建一个顺序流
Stream<String> stream = list.stream();
// 创建一个并行流
Stream<String> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();
12345
2、Arrays.stream(T[]array)
使用 java.util.Arrays.stream(T[]array)方法用数组创建流
int[] array={1,3,5,6,8};
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(array);
12
3、of()、iterate()、generate()
使用 Stream的静态方法:of()、iterate()、generate()
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.iterate(0, (x) -> x + 3).limit(4);
stream2.forEach(System.out::println);
Stream<Double> stream3 = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(3);
stream3.forEach(System.out::println);
1234567
输出结果:
0 3 6 9
0.6796156909271994
0.1914314208854283
0.8116932592396652
1234
stream和 parallelStream的简单区分:stream是顺序流,由主线程按顺序对流执行操作,而 parallelStream是并行流,内部以多线程并行执行的方式对流进行操作,但前提是流中的数据处理没有顺序要求。例如筛选集合中的奇数,两者的处理不同之处:
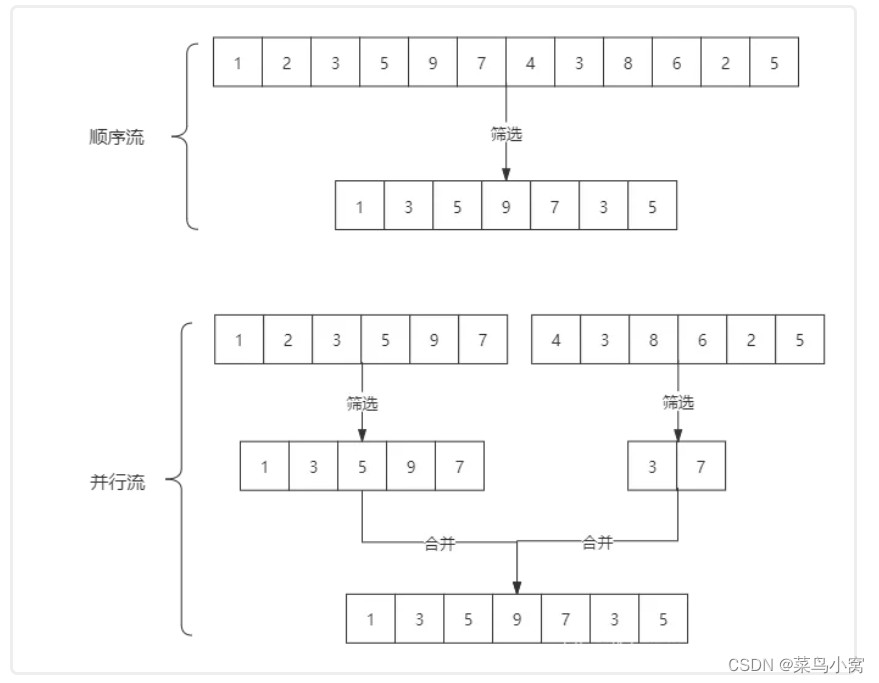
如果流中的数据量足够大,并行流可以加快处速度。
除了直接创建并行流,还可以通过 parallel()把顺序流转换成并行流:
Optional<Integer> findFirst = list.stream().parallel().filter(x->x>6).findFirst();
四、Stream API 简介
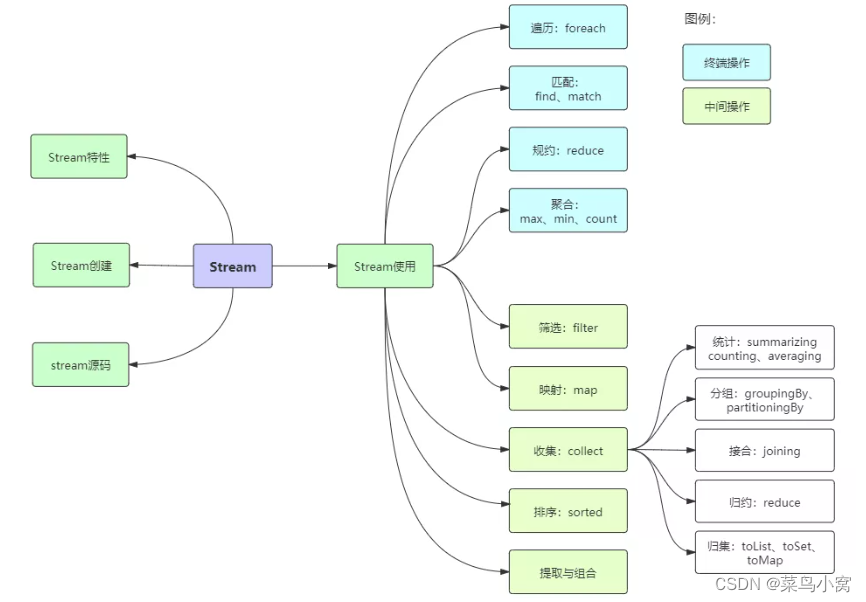
五、Stream API 案例
以下为案例的测试数据
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
public class PersonTest {
static List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<Person>();
private static void initPerson() {
/*personList.add(new Person("张三", 8, 3000));
personList.add(new Person("李四", 18, 5000));
personList.add(new Person("王五", 28, 7000));
personList.add(new Person("孙六", 38, 9000));*/
personList.add(new Person("张三", 25, 3000, "male", "上海"));
personList.add(new Person("李四", 27, 5000, "male", "上海"));
personList.add(new Person("王五", 29, 7000, "female", "上海"));
personList.add(new Person("孙六", 26, 3000, "female", "北京"));
personList.add(new Person("王伟", 27, 5000, "male", "北京"));
personList.add(new Person("张丽", 21, 7000, "female", "北京"));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
initPerson();
}
}
class Person {
String name;
int age;
int salary;
String sex;
String area;
public Person(String name, int age, int salary) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Person(String name, int age, int salary, String sex, String area) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
this.sex = sex;
this.area = area;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getArea() {
return area;
}
public void setArea(String area) {
this.area = area;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", salary=" + salary +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", area='" + area + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
1、遍历、匹配
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
// 匹配第一个值
Integer first = list1.stream().findFirst().get();
// 匹配任意一个值(适用于并行流)
Integer any = list1.parallelStream().findAny().get();
// 是否包含符合特定条件的元素
boolean b = list1.stream().anyMatch(i -> i > 3);
2、过滤
List<Integer> newList = list1.stream().filter(i -> i > 3).collect(Collectors.toList());
3、聚合(最大、最小、计数)
(1)最大值 max
// 数字集合
List<Integer> numList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
Integer max = numList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingInt(i -> i)).get();
// 使用 IntStream
int max = personList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getSalary).max().getAsInt();
// 对象集合
Person maxPerson = personList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingInt(Person::getSalary)).get();
(2)最小值 min
// 自定义比较器
Person minPerson = personList.stream().min((v1, v2) -> v1.getSalary() - v2.getSalary()).get();
(3)计数 count
// 统计集合中元素的个数
long count = numList.stream().count();
4、peek、map、flatMap
peek:是个中间操作,它提供了一种对流中所有元素操作的方法。生成一个包含原Stream的所有元素的新Stream,同时会提供一个消费函数(Consumer实例),新Stream每个元素被消费的时候都会执行给定的消费函数;但一般不推荐使用,文档提示:该方法主要用于调试,做一些消耗这个对象但不修改它的东西(发送通知,打印模型等)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "tom");
map.put("2", "jerry");
// 将map中的value转大写
map = map.entrySet()//获取集合
.stream()//获取流
.peek(obj -> obj.setValue(obj.getValue().toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT)))//peek支持在每个元素上执行一个操作并且返回新的stream
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue));//collect方法用来将流转到集合对象
//遍历输出
map.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + ":" + value));
}
map:接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。
这个方法有三个对于原始类型的变种方法,分别 是:mapToInt,mapToLong和mapToDouble。这三个方法也比较好理解,比如mapToInt就是把原始Stream转换成一个新 的Stream,这个新生成的Stream中的元素都是int类型。之所以会有这样三个变种方法,可以免除自动装箱/拆箱的额外消耗;
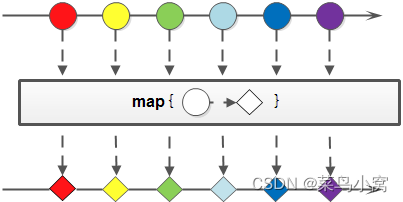
flatMap:接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。
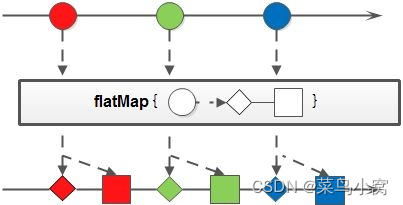
// 对集合中每个数字加3
List<Integer> newList = numList.stream().map(i -> i + 3).collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> nameList = Arrays.asList("张三", "李四");
// 取出流中的姓名,将姓取出转换为流返回,最后将返回流合并为一个
List<Character> surNameList = nameList.stream().flatMap(s -> Stream.of(s.charAt(0))).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(surNameList);
5、规约 reduce
归约,也称缩减,顾名思义,是把一个流缩减成一个值,能实现对集合求和、求乘积和求最值操作。
// 求和案例
list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> {
System.out.println("x=" + x + ",y=" + y);
return x + y;
});
x=1,y=2
x=3,y=3
x=6,y=4
// 求积
Integer product = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x * y).get();
// 求最大值
Integer max = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x > y ? x : y).get();
// 求最大值
Integer max = list.stream().reduce(Integer::max).get();
求所有员工的工资之和和最高工资
Integer sum = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum).get();
Integer max = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::max).get();
6、收集(toList、toSet、toMap)
(1)toMap
// 将list转为map
Map<String, Person> personMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, p -> p));
System.out.println(personMap);
(2)toCollection
使用toCollection可以自定义转换后的集合对象。
// 将list转换set
Set personSet = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
// 将set转换list
LinkedList list = personSet.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));
(3)数据去重案例
// 根据区域进行去重
ArrayList<Person> list = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toCollection(() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(Person::getArea))), ArrayList::new));
// 去重结果
[Person{name='张三', age=25, salary=3000, sex='male', area='上海'}, Person{name='孙六', age=26, salary=3000, sex='female', area='北京'}]
7、collect
(1)统计
Collectors提供了一系列用于数据统计的静态方法:
计数: count
平均值: averagingInt、 averagingLong、 averagingDouble
最值: maxBy、 minBy
求和: summingInt、 summingLong、 summingDouble
统计以上所有: summarizingInt、 summarizingLong、 summarizingDouble
// 平均
Double avg = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Person::getSalary));
// 最大
Integer max = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compare)).get();
// 求和
Long sum = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingLong(Person::getSalary));
// 一次统计所有信息(DoubleSummaryStatistics{count=4, sum=24000.000000, min=3000.000000, average=6000.000000, max=9000.000000})
DoubleSummaryStatistics statistics = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Person::getSalary));
System.out.println(statistics);
(2)map转list
map.entrySet().stream().map(e -> new Person(e.getKey(),e.getValue())).collect(Collectors.toList());
map.keySet().stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
map.values().stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
(3)list转map
// list转换成map,并指定key重复时的覆盖规则,否则重复key会报错。
Map<String, Person> personMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, Function.identity(), (key1, key2) -> key2));
// list转换成map,指定具体的实现map
Map<String, Person> personMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, Function.identity(), (key1, key2) -> key2, LinkedHashMap::new));
(4)两个list转map
可变汇聚对应的只有一个方法:collect,正如其名字显示的,它可以把Stream中的要有元素收集到一个结果容器中(比如Collection)。先看一下最通用的collect方法的定义(还有其他override方法):
<R> R collect(Supplier<R> supplier,
ObjIntConsumer<R> accumulator,
BiConsumer<R, R> combiner);
先来看看这三个参数的含义:Supplier supplier是一个工厂函数,用来生成一个新的容器;BiConsumer accumulator也是一个函数,用来把Stream中的元素添加到结果容器中;BiConsumer combiner还是一个函数,用来把中间状态的多个结果容器合并成为一个(并发的时候会用到)。看晕了?来段代码!
String[] names = {"张三", "李四"};
int[] scores = {80, 90};
// 单线程
HashMap<Object, Object> map = IntStream.range(0, names.length).collect(HashMap::new, (m, i) -> m.put(names[i], scores[i]), null);
System.out.println(map);
// 多线程
HashMap<Object, Object> map2 = IntStream.range(0, names.length).parallel().collect(HashMap::new, (m, i) -> m.put(names[i], scores[i]), (m1, m2)->m1.putAll(m2));
System.out.println(map2);
8、分组
// 根据布尔值分组
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> booleanMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(p -> p.getSalary() > 5000));
// 根据性别分组
Map<String, List<Person>> sexMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(p -> p.getSex()));
// 先根据性别分组,再根据地区分组
Map<String, Map<String, List<Person>>> sexAreaMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(p -> p.getSex(), Collectors.groupingBy(p -> p.getArea())));
// 分组计数(键为元素,值为元素出现的次数)
Map<String, Long> sexCountMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(p -> p.getSex(), Collectors.counting()));
// 分组求和
Map<String, Integer> sumMap = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex, Collectors.summingInt(Person::getSalary)));
9、连接 joining
// joining可以将stream中的元素用特定的连接符(没有的话,则直接连接)连接成一个字符串。
String names = personList.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
// 张三,李四,王五,孙六,王伟,张丽
System.out.println(names);
10、排序 sorted
// 按工资排序(升序)
List<Person> sorted = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary)).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 按工资排序(降序)
personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 先按工资,再按年龄排序
List<Person> personList = PersonTest.personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).thenComparing(Person::getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 工资降序,年龄升序
List<Person> personList = PersonTest.personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).reversed().thenComparing(Person::getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 工资升序,年龄降序
List<Person> personList = PersonTest.personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).thenComparing((x, y) -> y.getAge() - x.getAge())).collect(Collectors.toList());
11、提取、组合
流也可以进行合并、去重、限制、跳过等操作。
String[] arr1 = {"a", "b", "c", "d"};
String[] arr2 = {"d", "e", "f", "g"};
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of(arr1);
Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of(arr2);
// concat:合并两个流 distinct:去重
List<String> concatList = Stream.concat(stream1, stream2).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// limit:限制从流中获得前n个数据
List<Integer> limitList = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).limit(10).collect(Collectors.toList());
// skip:跳过前n个数据
List<Integer> skipList = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).skip(1).limit(5).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("流合并:" + concatList);
System.out.println("limit:" + limitList);
System.out.println("skip:" + skipList);
12、读取文件流
File file = new File("F:\\filetest.txt");
// 代码放入try()中可以自动关闭流
try (Stream<String> stream = Files.lines(file.toPath(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) {
stream.onClose(() -> System.out.println("done!")).forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
13、计算差集
List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "d");
List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("d", "e", "f", "g");
List<String> list = list1.stream().filter(s -> !list2.contains(s)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
六、参考
Java8中Stream详细用法大全
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45228323/article/details/121328790深入理解Java Stream流水线
https://www.cnblogs.com/CarpenterLee/p/6637118.html深入理解 Java 8 Lambda(类库篇 - Streams API,Collectors 和并行)
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903458131148813























 447
447











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








