一.LruCache算法
LruCache算法就是Least Recently Used,也就是最近最少使用算法。
他的算法就是当缓存空间满了的时候,将最近最少使用的数据从缓存空间中删除以增加可用的缓存空间来缓存新内容。
这个算分的内部有一个缓存列表。每当一个缓存数据被访问的时候,这个数据就会被提到列表头部,每次都这样的话,列表的尾部数据就是最近最不常使用的了,当缓存空间不足时,就会删除列表尾部的缓存数据。
二.LruCache部分源码
Least Recently Used,最近最少使用
下面只是部分源码
package android.util;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* LruCache通过强引用来缓存一定数量的值.
* 每当一个值被访问的时候,这个值就会移动到缓存队列的头部.
* 如果插入数据时发现缓存不够了,就会将队列中访问次数最少的数据删掉.
* 可以设置缓存大小:设为4M
* <pre> {@code
* int cacheSize = 4 * 1024 * 1024; // 4MiB
* LruCache<String, Bitmap> bitmapCache = new LruCache<String, Bitmap>(cacheSize) {
* protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
* return value.getByteCount();
* }
* }}</pre>
*
*/
public class LruCache<K, V> {
/**
* 真正放置缓存内容的map。
*/
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
/** Size of this cache in units. Not necessarily the number of elements.
* 当前缓存已经使用用的大小,不一定是元素的个数。*/
private int size;
/** 内存的最大值 */
private int maxSize;
//各个方法被调用的次数
private int putCount;
private int createCount;
private int evictionCount;
private int hitCount;
private int missCount;
/**
* 构造方法,传入缓存的最大值maxSize。
*/
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
//初始化LinkedHashMap。
//第一个参数是初始容量
//第二个参数是填装因子,或叫加载因子
//第三个参数是排序模式,true表示在访问的时候进行排序,否则只在插入的时候才排序。
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
/**
* 重新设置最大缓存
*/
public void resize(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
synchronized (this) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
}
/**
* 通过key获取缓存的数据,如果通过这个方法得到的需要的元素,
* 那么这个元素会被放在缓存队列的头部,
* 可以理解成最近常用的元素,不会在缓存空间不够的时候自动清理掉
*/
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
//这里用同步代码块,
synchronized (this) {
//从LinkedHashMap中获取数据。
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
/**
* 如果通过key从缓存集合中获取不到缓存数据,就尝试使用creat(key)方法创造一个新数据。
* create(key)默认返回的也是null,需要的时候可以重写这个方法。
*/
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
//如果重写了create(key)方法,创建了新的数据,就讲新数据放入缓存中。
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
/**
* 往缓存中添加数据
*/
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
//safeSizeOf(key, value)。
// 这个方法返回的是1,也就是将缓存的个数加1.
// 当缓存的是图片的时候,这个size应该表示图片占用的内存的大小,
// 所以应该重写里面调用的sizeOf(key, value)方法
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
//将创建的新元素添加进缓存队列,并添加成功后返回这个元素
previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
//如果返回的是null,说明添加缓存失败,在已用缓存大小中减去这个元素的大小。
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
/**
* 修改缓存大小,使已用的缓存不大于设置的缓存最大值
*/
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) { //开启一个死循环
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//当已用的缓存小于最大缓存,完成任务,退出循环
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
//否则就在缓存队列中先找到最近最少使用的元素,调用LinkedHashMap的eldest()方法返回最不经常使用的方法。
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
//然后删掉这个元素,并减少已使用的缓存空间
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
/**
* 删除 很简单
*/
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
/**
* 这个方法在前面很多地方都会被调用,默认是空方法,有需要的时候自己实现
* evicted如果是true,则表示这个元素是因为空间不够而被自动清理了,
* 所以可以在这个地方对这个被清理的元素进行再次缓存
*/
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {}
/**
* 一个空方法,也是在需要的时候重写实现
*/
protected V create(K key) {
return null;
}
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = sizeOf(key, value);
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
}
return result;
}
/**
* 这个方法可以说是用来定义已用缓存的数量算法,默认是返回数量
*/
protected int sizeOf(K key, V value) {
return 1;
}
/**
* 清空所有缓存
*/
public final void evictAll() {
trimToSize(-1); // -1 will evict 0-sized elements
}
.......
}
通过这个源码,可以发现,LruCache的算法实现主要是依靠LinkedHashMap来实现的。
三.为什么用LinkedHashMap
为什么要用LinkedHashMap来存缓存呢,这个跟算法有关,LinkedHashMap刚好能提供LRUCache需要的算法。
这个集合内部本来就有个排序功能,当第三个参数是true的时候,数据在被访问的时候就会排序,这个排序的结果就是把最近访问的数据放到集合的最后面。
到时候删除的时候就从前面开始删除。
1.构造方法
LinkedHashMap有个构造方法是这样的:
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}2.Entity的定义
LinkedHashMap内部是使用双向循环链表来存储数据的。也就是每一个元素都持有他上一个元素的地址和下一个元素的地址,看Entity的定义:
/**
* LinkedHashMap entry.
*/
private static class LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> extends HashMapEntry<K,V> {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> before, after;
LinkedHashMapEntry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMapEntry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
/**
* 从链表中删除这个元素
*/
private void remove() {
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
}
/**
* Inserts this entry before the specified existing entry in the list.
*/
private void addBefore(LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
/**
* 当集合的get方法被调用时,会调用这个方法。
* 如果accessOrder为true,就把这个元素放在集合的最末端。
*/
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
remove();
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
remove();
}
}3.get方法的排序过程
看LinkedHashMap的get方法:
public V get(Object key) {
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> e = (LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V>)getEntry(key);
if (e == null)
return null;
e.recordAccess(this);
return e.value;
}具体是怎么进行排序的,画个图看看:
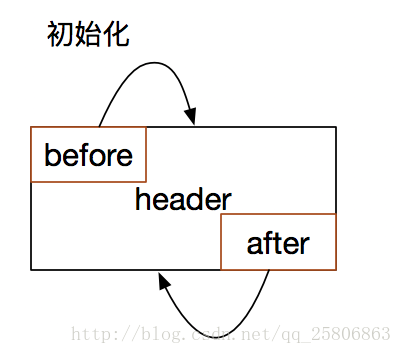
- 当LinkedHashMap初始化的时候,会有一个头节点header。
void init() {
header = new LinkedHashMapEntry<>(-1, null, null, null);
header.before = header.after = header;
}可以看到这个头节点的前节点和后节点都指向自己。
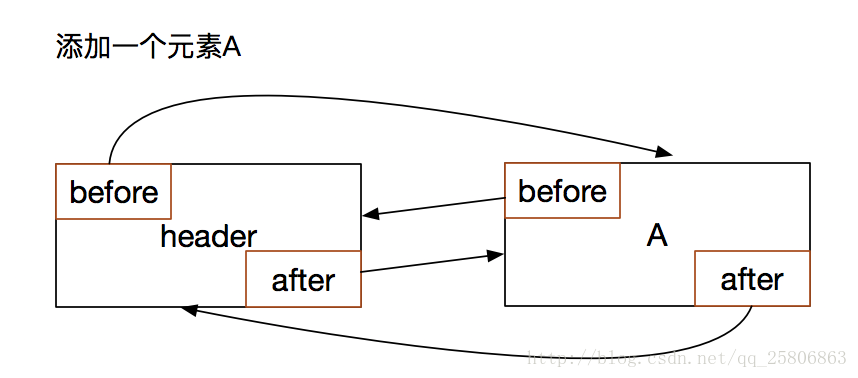
添加一个数据A
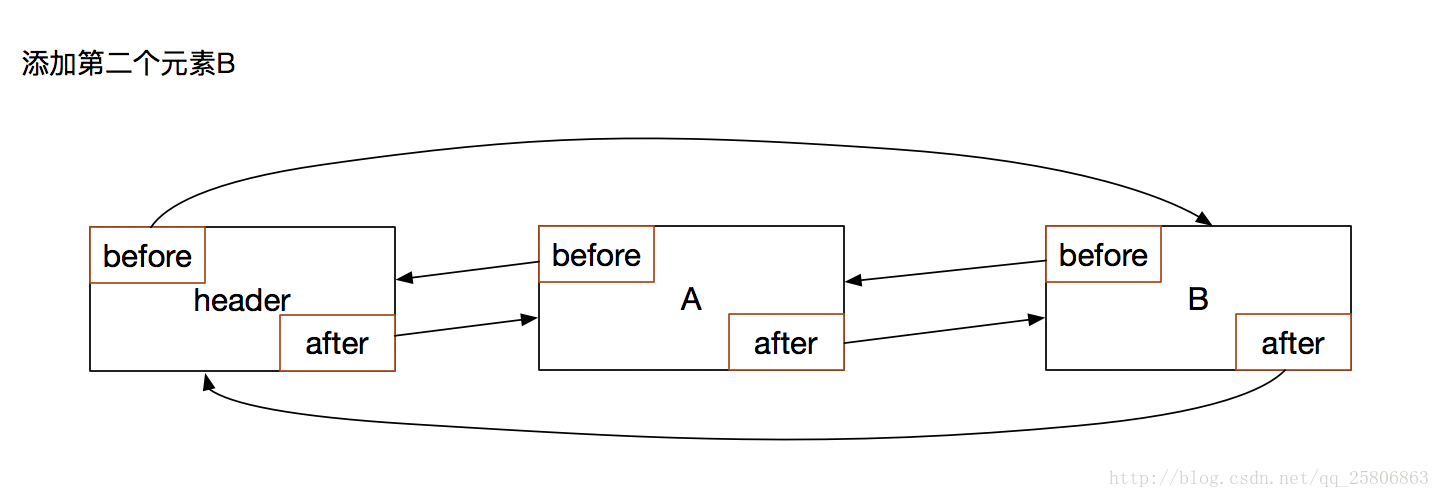
添加一个数据B
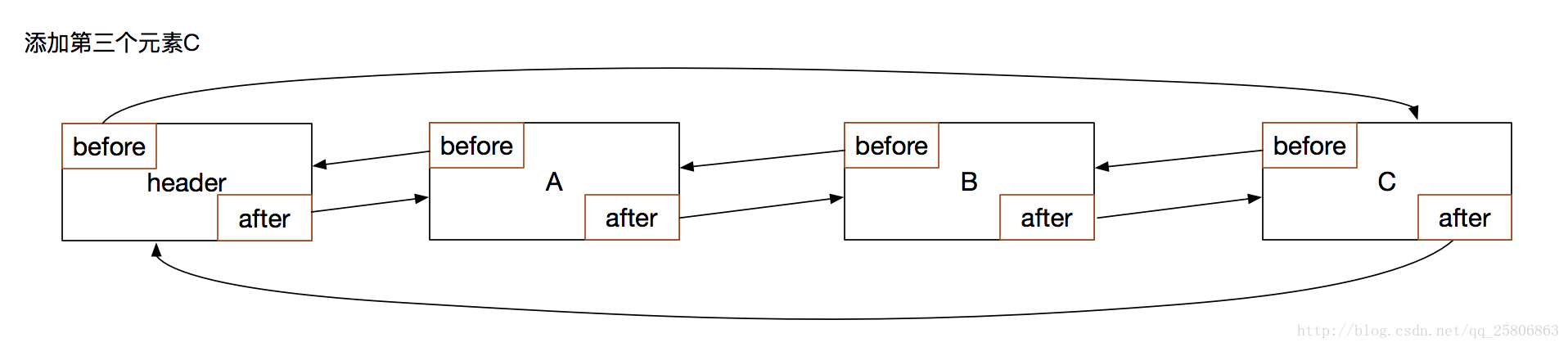
再添加一个数据C
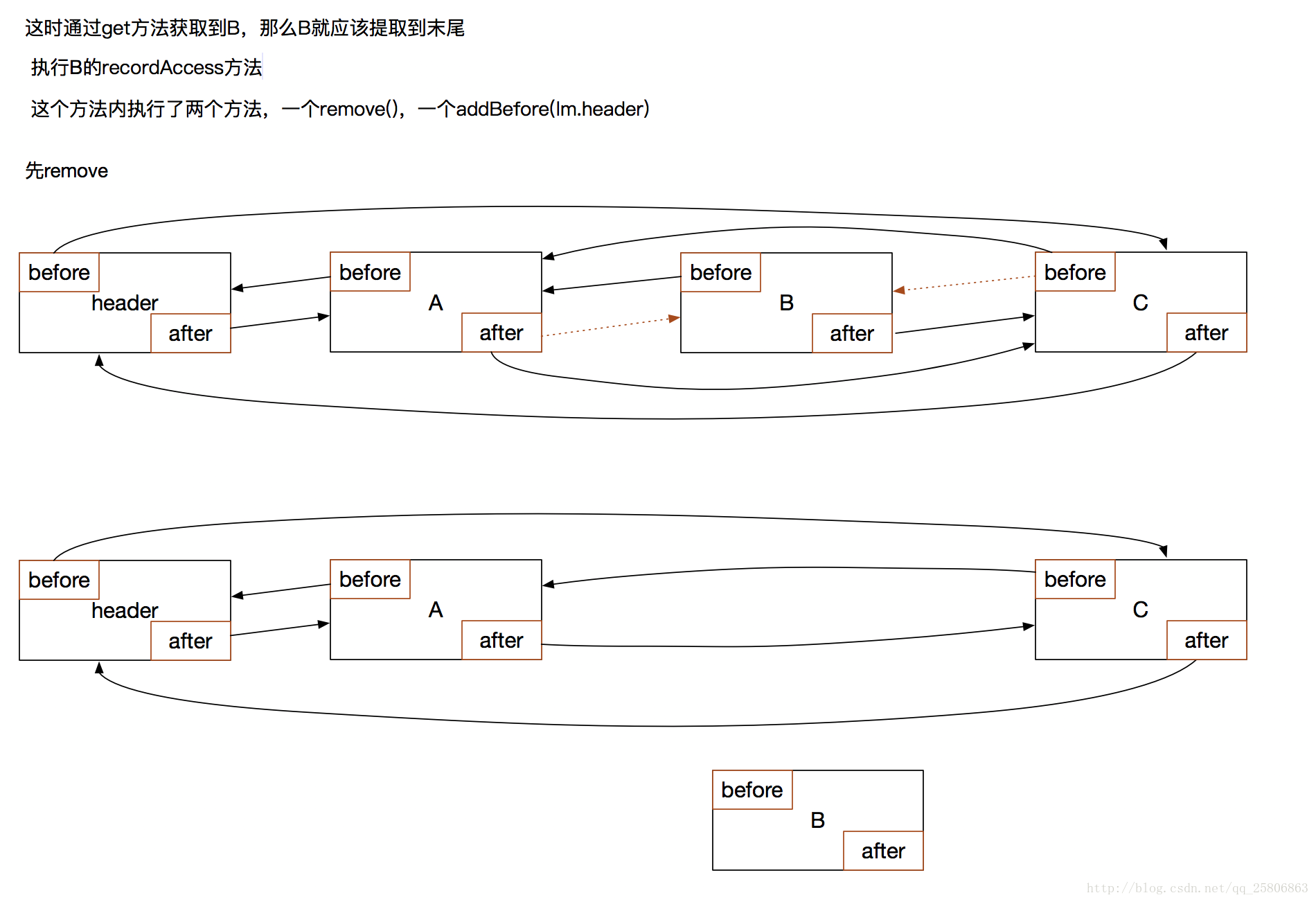
这是通过get访问数据B
看上面的get方法就知道,他会调用B的recordAccess(this)方法,这个this就是这个LinkedHashMap。
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
remove();
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}- recordAccess(this)方法
会先调用remove方法,把自己从链表中移除:
private void remove() {
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
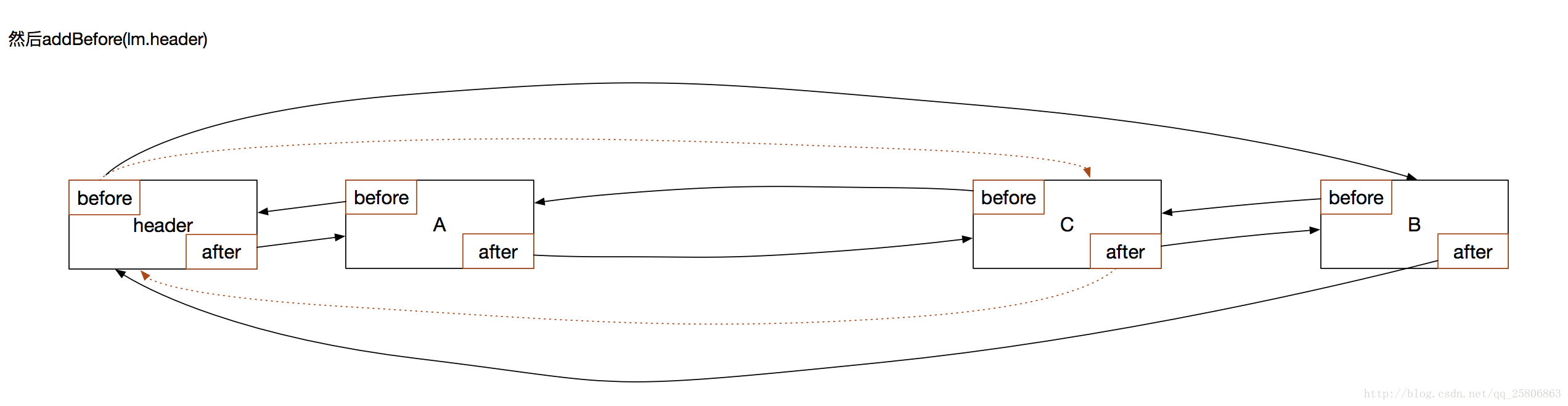
}在调用addBefore(lm.header)方法,把自己添加到链表的结尾:
private void addBefore(LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}大功告成。这样就完成了一次Lru排序。将最近访问的数据放在了链表的结尾,链表越靠前的越不常用,缓存空间不够就优先清楚前面的。
4.获取一个最该清除的不常用的元素
LinkedHashMap还有一个方法eldest(),提供的就是最近最少使用的元素:
public Map.Entry<K, V> eldest() {
Entry<K, V> eldest = header.after;
return eldest != header ? eldest : null;
}结合流程图片可以看到,header.after就是A,也就是符合要求的需要清除的数据。
四.回到LruCache类
在LruCache中是怎么结合LinkedHashMap实现这个缓存的呢?
前面的方法就很明显了。
- 首先在初始化LinkedHashMap的时候,是这样的:
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);第三个参数为true,因此每次访问LinkedHashMap的数据,LinkedHashMap都回去进行排序,将最近访问的放在链表末尾。
- LruCache的put方法调用了LinkedHashMap的put来存储数据,自己进行了对缓存空间的计算。LinkedHashMap的put方法也会进行排序。
- LruCache的get方法调用了LinkedHashMap的get来获取数据,由于上面的第三个参数是true,因此get也会触发LinkedHashMap的排序
trimToSize(int maxSize)
这是LruCache的核心方法了,get和put都可能会执行这个方法。
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}这个方法会检查已用的缓存大小和设置的最大缓存大小。
当发现需要进行删除数据来腾出缓存空间的时候,会调用LinkedHashMap的eldest()方法来获取最应该删除的那个数据,然后删除。
这样就完成了他的算法。
五.用LruCache来缓存Bitmap的初始化
LruCache<String, Bitmap> mLruCache;
//获取手机最大内存 单位 kb
int maxMemory = (int) (Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() / 1024);
//一般都将1/8设为LruCache的最大缓存
int cacheSize = maxMemory / 8;
mLruCache = new LruCache<String, Bitmap>(maxMemory / 8) {
/**
* 这个方法从源码中看出来是设置已用缓存的计算方式的。
* 默认返回的值是1,也就是没缓存一张图片就将已用缓存大小加1.
* 缓存图片看的是占用的内存的大小,每张图片的占用内存也是不一样的,一次不能这样算。
* 因此要重写这个方法,手动将这里改为本次缓存的图片的大小。
*/
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
return value.getByteCount() / 1024;
}
};使用:
//加入缓存
mLruCache.put("key", BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher));
//从缓存中读取
Bitmap bitmap = mLruCache.get("key");
























 1702
1702

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








