LruCache源码的理解
使用场景
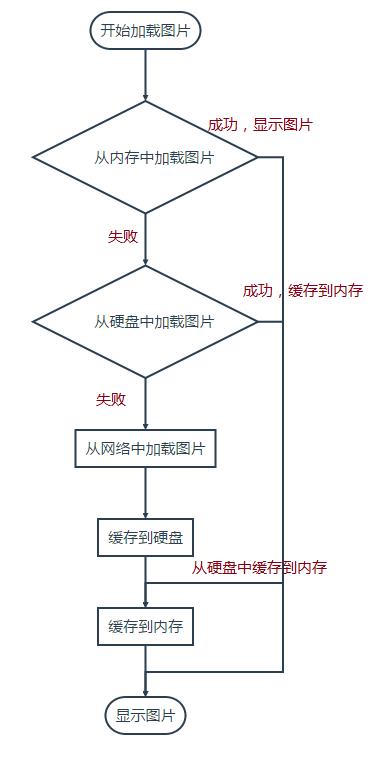
在Android手机上加载图片,一般会用到三级缓存策略
内存的缓存策略,一般会用到LruCache来解决
内存用于缓存遇到的问题
1. 手机给每个应用分配的内存空间是有限的,如果内存中数据量过大,会造成OOM,所以,我们需要适当的清理内存
2. 在清理内存的时候,我们希望最老的部分最先被清除,从而让出空间来
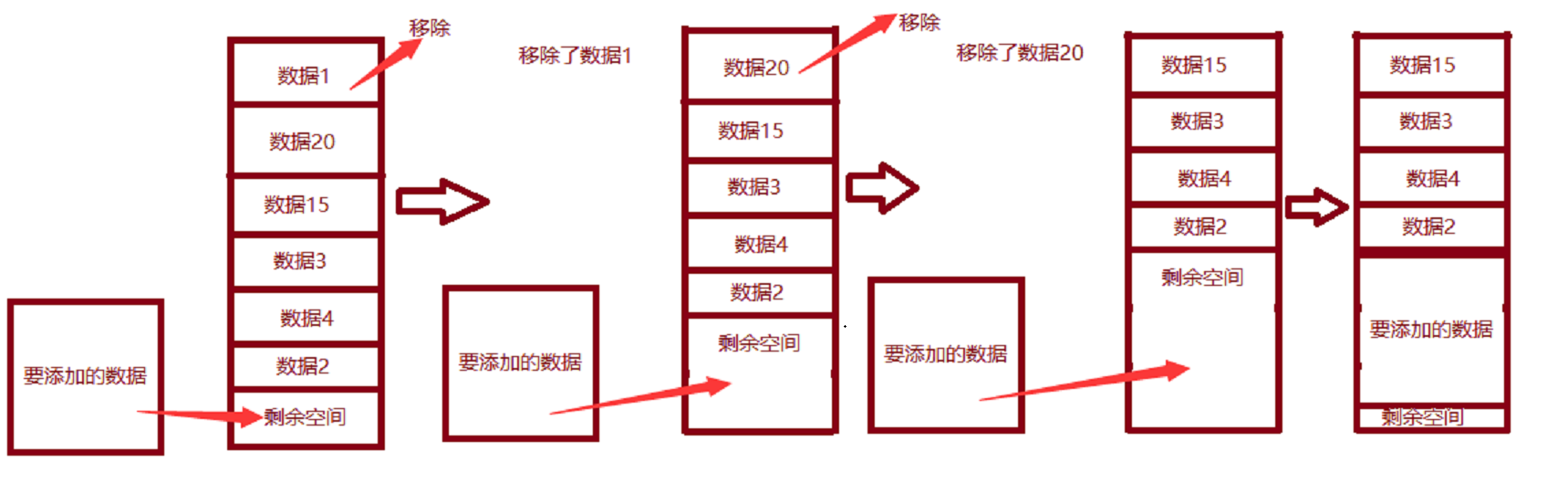
LruCache中使用LinkedHashMap可以解决的问题
1. LinkedHashMap可以当做一个容器来使用
2. LinkedHashMap是一个Map,可以用key来给数据做标记
3. LinkedHashMap支持访问顺序,每次get()或者add()一个数据,都会把相应的数据放到链表的尾部,这样,链表头部的数据就是没怎么用过的数据,也就是最老的数据
图形解释
RTFRS解释
public class LruCache<K, V> {
//正真用于缓存的容器
//支持访问顺序呢:指在迭代遍历列表中的元素时最近访问的元素会排在LinkedHashMap的尾部
//清除操作是从头部开始清除的,可以实现“最近最少使用”的需求
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
//当前换粗的大小
private int size;
//最大容量
private int maxSize;
//put进来的数量
private int putCount;
//create出来的数量
private int createCount;
//清除的数量
private int evictionCount;
//get到值的数量
private int hitCount;
//没有get到值得数量
private int missCount;
//构造方法
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
//异常的处理
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
//设置最大容量
this.maxSize = maxSize;
//初始化容器
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
//重新设置最大容量
public void resize(int maxSize) {
//异常处理
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
//更新最大容量
synchronized (this) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
//size的值可能变小,尝试清除部分缓存
trimToSize(maxSize);
}
//通过key来获取相应的值
public final V get(K key) {
//异常处理
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
//获取到相应的对象
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
//当容器中储存了相应的值,且不为空,那么:更新hitCount的数据
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
//当容器中没有储存相应的值,那么:更新missCount的数据
missCount++;
}
//create一个值,默认为null
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
//重写create()方法后执行下面的代码
synchronized (this) {
//create出了一个值,那么:更新createCount的数据
createCount++;
//放入容器,map.put()的返回值:
//1.null,新添加的数据
//2.不为null,表示链表中存在相应的value,put()表示更新数据,将旧的数据返回
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
//对mapValue的判断表示put()的操作是更新还是添加
if (mapValue != null) {
//更新操作,那么create出来的值不能覆盖以前的值
//将旧的值重新放回到容器中
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
//添加进来新的值,那么容器的大小会发生变化,更新size的值
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
//默认什么都没有做
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
//size变大,尝试清除部分缓存
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
//添加到缓存中
public final V put(K key, V value) {
//异常的处理
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
//有新的对象添加到缓存中:那么,更新putCount的数据
putCount++;
//size变化,更新size的值
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
//添加到容器中
previous = map.put(key, value);
//跟get()中的原理一样,这里判断是更新还是添加
if (previous != null) {
//更新操作,那么size多记录一份旧的value的大小,减去相应的值
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
//默认什么都没有做
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
//size可能变大,尝试清除部分缓存
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
//尝试清除部分缓存
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
//无限循环,与if (size <= maxSize)配合:可以将缓存清空到maxSize以下
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
//异常处理
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//当前size没有达到maxSize,结束循环
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
//获取链表的第一个条目
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
//没有缓存下数据,结束循环
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
//移除第一个条目
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
//更新size的数据
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
//这里执行了一次清除,那么,更新evictionCount的值
evictionCount++;
}
//默认什么都没有做
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
//移除相应的缓存
public final V remove(K key) {
//异常处理
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
//移除
previous = map.remove(key);
//判断是否真的从缓存中移除了
if (previous != null) {
//从缓存中移除了,更新size的数据
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
//默认什么都没有做
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
//默认什么都没有做;如果有相应的需求,可以重写该方法
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {}
//create出null;如果有相应的需求,可以重写该方法
protected V create(K key) {
return null;
}
//判断大小
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = sizeOf(key, value);
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
}
return result;
}
//开放人员需要重写的方法,用来标记每个item对应的大小
protected int sizeOf(K key, V value) {
return 1;
}
//获取各种成员变量的方法
//...
//这里获取的是一个map的副本
public synchronized final Map<K, V> snapshot() {
return new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(map);
}
//不解释
@Override public synchronized final String toString() {
int accesses = hitCount + missCount;
int hitPercent = accesses != 0 ? (100 * hitCount / accesses) : 0;
return String.format("LruCache[maxSize=%d,hits=%d,misses=%d,hitRate=%d%%]",
maxSize, hitCount, missCount, hitPercent);
}
}结语
通过对LruCache的理解,实际上,我们是更加了解了冷门的LinkedHashMap的一些功能:可以记录访问顺序。
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_26411333/article/details/51523790
























 247
247

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








