二、生产者/消费者模式实现
生产者/消费者模式是等待/唤醒机制的经典案例
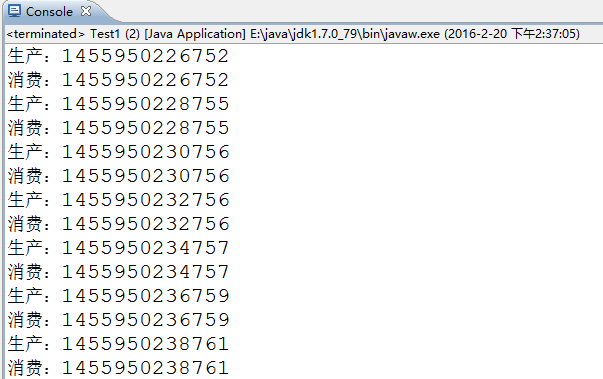
1、一生产与一消费:操作值
package org.jksoft.thread.product;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* 测试一:一生产者与一消费者
*
* @author mcl
*
* 2016-2-20-下午1:34:39
*/
public class Test1 {
// value为空字符串时:代表没有生产货品
private static String value = "";
class ThreadP extends Thread {
private Productor p;
public ThreadP(Productor p) {
this.p = p;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
p.run();
}
}
}
class ThreadS extends Thread {
private Spendor p;
public ThreadS(Spendor p) {
this.p = p;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
p.run();
}
}
}
// 生产者
class Productor {
private String lock;
public Productor(String lock) {
this.lock = lock;
}
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
if (!(value.equals(""))) {
lock.wait();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
value = System.currentTimeMillis() + "";
System.out.println("生产:" + value);
lock.notify();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 消费者
class Spendor extends Thread {
private String lock;
public Spendor(String lock) {
this.lock = lock;
}
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
if (value.equals("")) {
lock.wait();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("消费:" + value);
value = "";
lock.notify();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String lock = new String("");
Test1 t = new Test1();
Spendor s = t.new Spendor(lock);
Productor p = t.new Productor(lock);
t.new ThreadP(p).start();
t.new ThreadS(s).start();
}
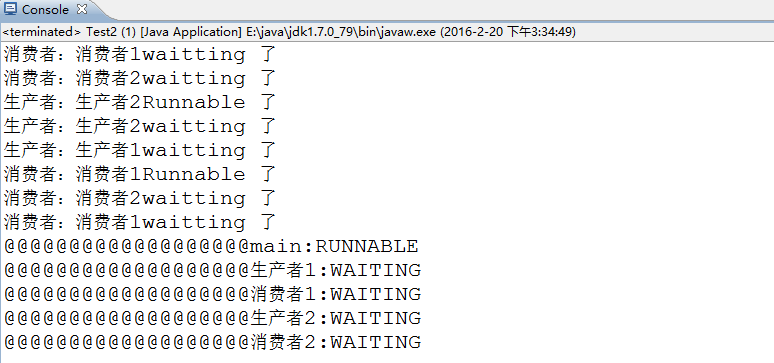
} 2 多生产与多消费:操作值-假死
代码清单:
package org.jksoft.thread.product;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* 测试二:多生产者与多消费者-会造成假死
*
* @author mcl
*
* 2016-2-20-下午1:34:39
*/
public class Test2 {
// value为空字符串时:代表没有生产货品
private static String value = "";
class ThreadP extends Thread {
private Productor p;
public ThreadP(Productor p) {
this.p = p;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
p.run();
}
}
}
class ThreadS extends Thread {
private Spendor p;
public ThreadS(Spendor p) {
this.p = p;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
p.run();
}
}
}
// 生产者
class Productor {
private String lock;
public Productor(String lock) {
this.lock = lock;
}
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
while (!(value.equals(""))) {
System.out.println("生产者:" +Thread.currentThread().getName()+"waitting 了");
lock.wait();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
value = System.currentTimeMillis() + "";
System.out.println("生产者:" +Thread.currentThread().getName()+"Runnable 了");
lock.notify();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 消费者
class Spendor extends Thread {
private String lock;
public Spendor(String lock) {
this.lock = lock;
}
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
while(value.equals("")) {
System.out.println("消费者:" +Thread.currentThread().getName()+"waitting 了");
lock.wait();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("消费者:" +Thread.currentThread().getName()+"Runnable 了");
value = "";
lock.notify();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
String lock = new String("");
Test2 t = new Test2();
Spendor s = t.new Spendor(lock);
Productor p = t.new Productor(lock);
ThreadP[] threadP = new ThreadP[2];
ThreadS[] threadS = new ThreadS[2];
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
threadP[i] = t.new ThreadP(p);
threadP[i].setName("生产者"+(i+1));
threadS[i] = t.new ThreadS(s);
threadS[i].setName("消费者"+(i+1));
threadP[i].start();
threadS[i].start();
}
Thread.sleep(10000);
Thread[] threads = new Thread[Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().activeCount()];
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().enumerate(threads);
for(int i=0;i<threads.length;i++){
System.out.println("@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@"+threads[i].getName()+":"+threads[i].getState());
}
}
}
结果分析:产生假死的原因在,notify唤醒的可能不是异类,也许是同类。这就导致了所有的线程都处于wait状态,造成一种线程假死的状态。
解决方案很简单,把唤醒的notify()方法,换成 notifyAll()就可以了。
小结:if与where的切换,,可以解决当wait的条件发生改变时,系统正常运行。
notify与noifyAll的切换,可以解决线程可能唤醒的是同类,而不是异类的情况所造成的线程假死。






















 168
168

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








