学习完了有关二叉树的搜索结构,今天我们来接触另外一种结构,叫做哈希表。
1.什么是哈希表
哈希表:是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。它的所保存的数据和位置会有一种关系,这种关系我们叫做哈希函数。
2.构建哈希表的方法
常用的构建哈希表的方法有5种。
这5种方法分别是:
构建哈希表的方法有:
1)直接定址法: 该方法是取关键字的某个线性函数值为哈希地址
2)除留余数法: 它是用数据元素关键字除以某个常数所得的余数作为哈希地址。
3)折叠法:将关键字分割成位数相同的几部分,最后一部分位数可以不同,然后取这几部分的叠加和(去除进位)作为散列地址。数位叠加可以有移位叠加和间界叠加两种方法。
4)随机数法::选择一随机函数,取关键字的随机值作为散列地址,通常用于关键字长度不同的场合。
5)*数学分析法:找出数字的规律,尽可能利用这些数据来构造冲突几率较低的散列地址。
一般常用的方法是直接定址法和数学分析法。下面我通过数学分析法来说明。
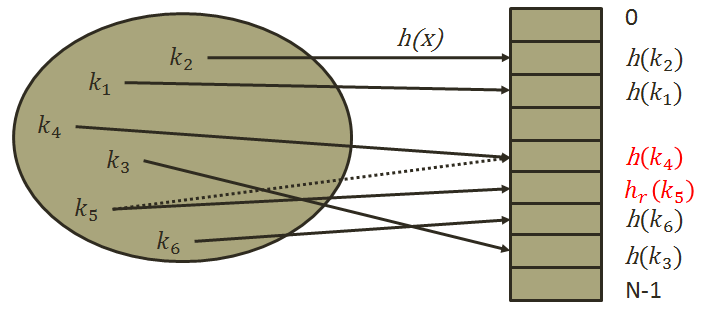
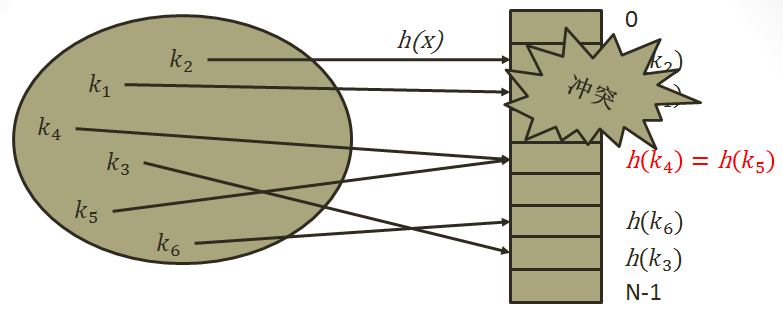
在这不得不说的是一个叫做哈希冲突的问题:因为你散列函数所计算的位置很可能有多个值,所以这多个值就会造成冲突,我们也就叫做哈希冲突,为了解决哈希冲突,研究了这几种方法。
3.开放定址法
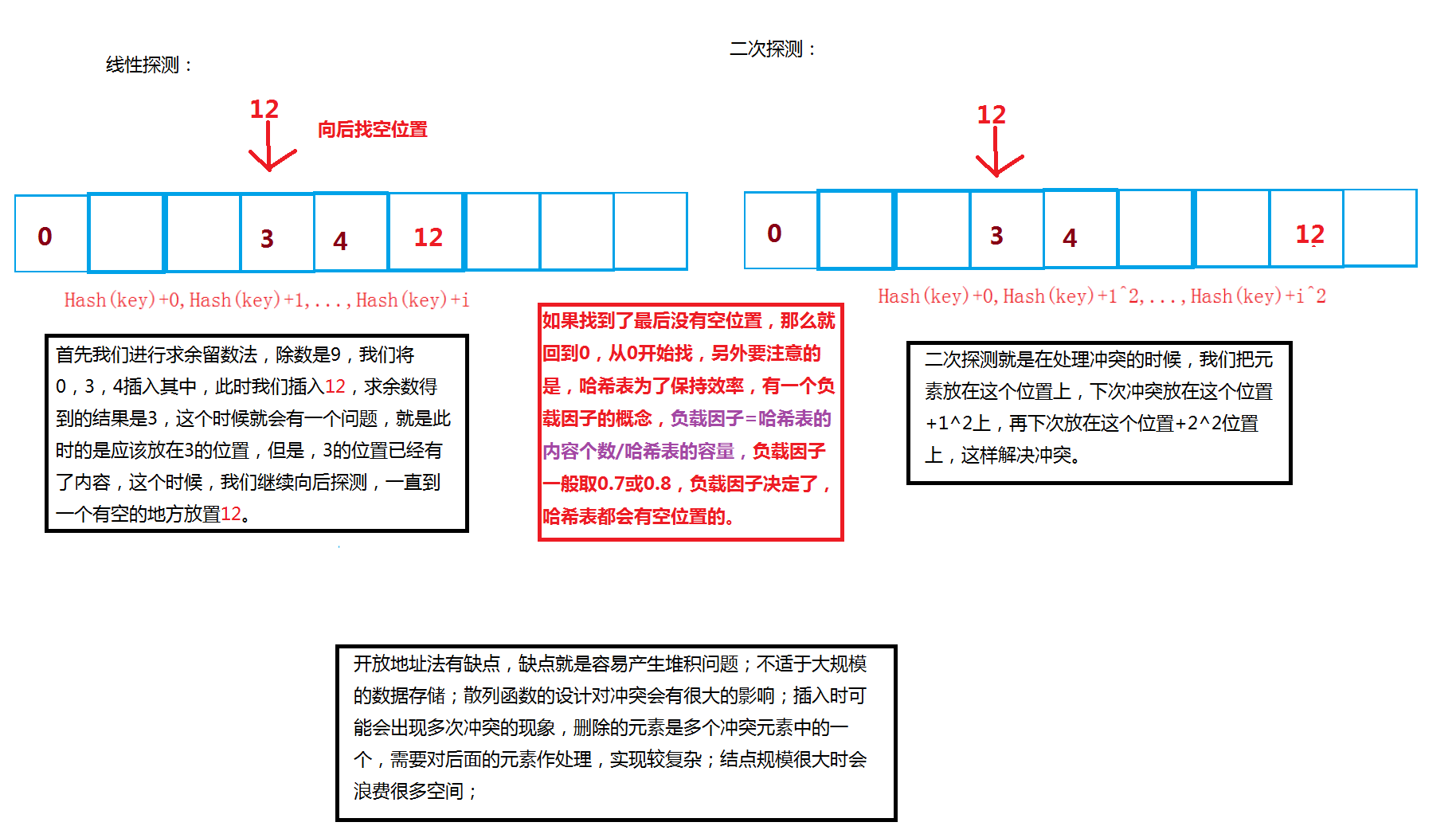
也叫做闭散列法,我们在这里提供两种思路,一种是线性探测,一种是二次探测。
线性探测:线性探测说的就是,当你插入的一个数和所在位置上的数冲突了,这个时候,你就向后找,找到为空的位置进行存放这个数。
正是因为开放地址法的缺点,所以我们在对哈希表进行删除的时候,所要采取的删除方式采用懒惰删除,就是对需要删除的元素,我们不直接删除,而是给它一个标记,表示它已经被删除,我们不对它访问就好了。
另外,哈希的容量根据研究如果采用素数来说,冲突概率更小,所以我们提供一个素数表来取容量。
代码实现:
namespace open
{
enum Status
{
EMPTY,
DELETE,
EXIST
};
template<typename K, typename V>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode(const K &key = K(), const V&value = V())//给出默认实参
: _key(key)
, _value(value)
, _status(EMPTY)
{
}
K _key;
V _value;
Status _status;
};
template<typename K>
struct _Hashfunc
{
size_t operator ()(const K &key)
{
return key;
}
};
template<>
struct _Hashfunc<string>
{
static size_t BKDRHash(const char*str)
{
unsigned int seed = 131;// 31 131 1313 13131 131313
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash*seed + (*str++);
}
return(hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
size_t operator ()(const string &key)
{
return BKDRHash(key.c_str());
}
};
template<typename K, typename V, typename HashFunc = _Hashfunc<K>>
class Hashtable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
typedef Hashtable<K, V, HashFunc> HashTable;
public:
Hashtable()
:_size(0)
{
_ht.resize(GetNewSize());
}
~Hashtable()
{
;
}
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
//进行是否增容的检查。
_CheckCapacity();
size_t index = _HashFunc(key);
while (_ht[index]._status == EXIST)
{
if (_ht[index]._key == key)
return false;
++index;
if (index == _size)
index = 0;
}
_size++;
_ht[index]._status = EXIST;
_ht[index]._key = key;
_ht[index]._value = value;
return true;
}
bool Delete(const K& key)
{
size_t index = _HashFunc(key);
size_t pos = index;
while (_ht[index]._status != EMPTY)
{
if (_ht[index]._key == key)
{
_ht[index]._status = DELETE;
_size--;
return true;
}
++index;
if (pos == index)
{
break;
}
}
return false;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t index = _HashFunc(key);
size_t pos = index;
while (_ht[index]._status != EMPTY)
{
if (_ht[index]._key == key&&_ht[index]._status == EXIST)
{
return &_ht[index];
}
index++;
if (pos == index)
{
break;
}
}
return NULL;
}
protected:
void _CheckCapacity()
{
//判断负载因子是否小于0.8
if (_ht.size() == 0 || _size * 10 / _ht.size() >= 8)
{
size_t newindex = 0;
size_t newsize = GetNewSize();
HashTable tmp;
tmp._ht.resize(newsize);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_ht[i]._status == EXIST)
{
tmp.Insert(_ht[i]._key, _ht[i]._value);
}
}
this->Swap(tmp);
}
else
return;
}
void Swap(Hashtable & t)
{
_ht.swap(t._ht);
swap(_size, t._size);
}
size_t _HashFunc(const K& key)
{
//利用仿函数进行处理其他像string和结构体带来的问题。
HashFunc hf;
return hf(key) % _ht.size();
}
size_t GetNewSize()
{
const int _PrimeSize = 28;
//采用素数表
static const unsigned long _PrimeList[_PrimeSize] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul,
786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul,
25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul,
805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
for (size_t i = 0; i < _PrimeSize; ++i)
{
if (_ht.size() < _PrimeList[i])
{
return _PrimeList[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
protected:
std::vector<Node> _ht;
size_t _size;
};
}4.拉链法
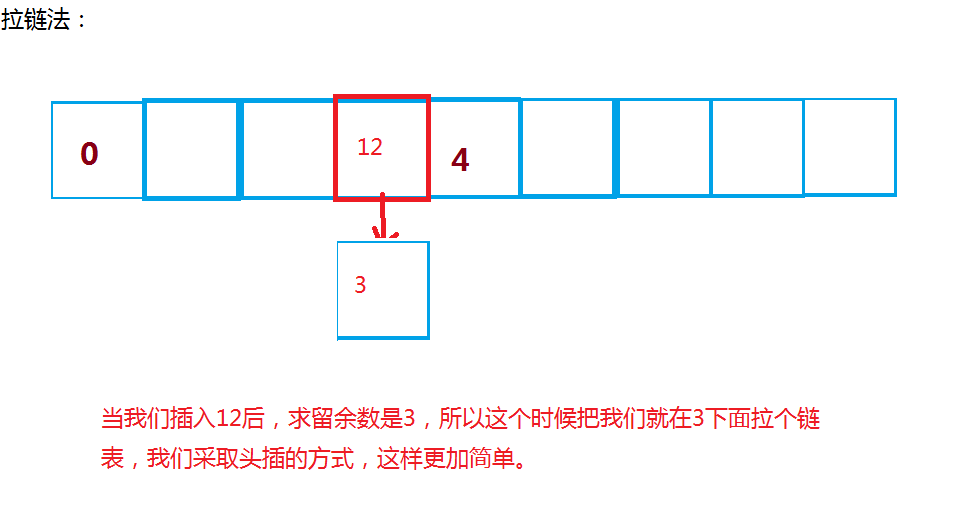
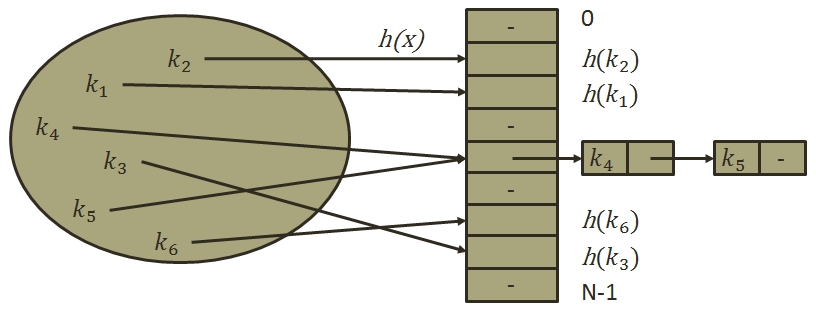
为了让哈希表更加高效,人们又想出了拉链法。也叫做哈希桶。
简单的说拉链法就是,当出现冲突的时候,我们在这个冲突的位置下面挂一个链表,这样,就可以轻松加愉快的解决冲突问题。
拉链法就可以很好的解决了开放地址法出现的一些问题。
当然,为了提高哈希表的效率,在拉链法中我们依然要考虑负载因子,这样我们就能更加高效的查找,这里的负载因子,最好是每一个哈希下只有一个节点。
当哈希表拉链法中拉链的节点增多的时候,这个时候查找的效率就很低,为了解决效率问题,这个时候我们可以提供一种思路,把链表改成一棵红黑树就好了,就从本来的O(N)到了O(logN)。这样就更加高效了。
代码实现:
namespace link
{
template<typename K,typename V>
struct KVNode
{
KVNode(const K& key=K(),const V& value=V())
: _key(key)
, _value(value)
, _next(NULL)
{}
K _key;
V _value;
KVNode<K, V> *_next;
};
template<typename K>
struct __Hashfunc
{
size_t operator() (const K &key)
{
return key;
}
};
template<>
struct __Hashfunc<string>
{
static size_t BKDRHash(const char*str)
{
unsigned int seed = 131;// 31 131 1313 13131 131313
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash*seed + (*str++);
}
return(hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
size_t operator ()(const string &key)
{
return BKDRHash(key.c_str());
}
};
template<typename K,typename V,typename HashFunc=__Hashfunc<K> >
class HashTable
{
typedef KVNode<K, V> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, V, HashFunc> Hashtable;
public:
HashTable()
:_size(0)
{
_ht.resize(GetNewSize());
}
~HashTable()
{
Node* cur = NULL;
Node* del = NULL;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _ht.size(); i++)
{
cur = _ht[i];
if (_ht[i] == NULL)
continue;
while (cur)
{
del = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
delete del;
del = NULL;
}
}
}
HashTable(const HashTable& ht)
{
_Copy();
}
bool Insert(const K& key,const V& value)
{
CheckCapacity();
size_t index = Funcpos(key,_ht.size());
Node* newnode = new Node(key,value);
if (_ht[index])
{
Node* cur = _ht[index];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key == key)
return false;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
_size++;
newnode->_next = _ht[index];
_ht[index] = newnode;
return true;
}
bool Delete(const K& key)
{
size_t index = Funcpos(key,_ht.size());
Node* cur = _ht[index];
Node* prev = NULL;
Node* del = NULL;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key == key)
{
if (prev == NULL)
{
del = cur;
delete cur;
_ht[index] = NULL;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
}
_size--;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t index = Funcpos(key,_ht.size());
Node *cur = _ht[index];
if (_ht.empty())
{
return NULL;
}
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return NULL;
}
protected:
void CheckCapacity()
{
if (_ht.size() == 0 || _size == _ht.size())
{
size_t newsize = GetNewSize();
Hashtable tmp;
tmp._ht.resize(newsize);
Node* cur = NULL;
Node* NewInsert = NULL;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _ht.size(); i++)
{
//采用移动法进行交换
//就是把原来的vector上面的节点进行移动到新的vector上面。
cur = _ht[i];
if (cur == NULL)
continue;
while (cur)
{
size_t newpos = Funcpos(cur->_key, tmp._ht.size());
NewInsert = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
NewInsert->_next = tmp._ht[newpos];
tmp._ht[newpos] = NewInsert;
}
_ht[i] = NULL;
}
NewSwap(tmp);
}
}
void Getnew()
{
Hash
}
void NewSwap( Hashtable &h)
{
_ht.swap(h._ht);
//std::swap(_size, h._size);
}
size_t GetNewSize()
{
const int _PrimeSize = 28;
static const unsigned long _PrimeList[_PrimeSize] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul,
786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul,
25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul,
805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
for (size_t i = 0; i < _PrimeSize; ++i)
{
if (_ht.size() < _PrimeList[i])
{
return _PrimeList[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
size_t Funcpos(const K& key,const size_t &size)
{
HashFunc h;
return h(key) % size;
}
protected:
std::vector<Node*> _ht;
size_t _size;
};
}5.哈希表的总结
对于哈希表,查找起来是相当方便,大致的效率为O(1),但是哈希表最大的问题就是太浪费空间。因为负载因子的原因,部分空间都是不用的,所以哈希也就是一种牺牲空间来提高时间的方式。另外哈希表不能够进行排序,作为一个使用key来决定储存位置的,它的key是关键,key当然不能重复。
代码已上传github:https://github.com/wsy081414
























 2671
2671

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








