In this article, we show you how to integrate Maven3, Hibernate3.6 and Oracle11g together. In the end of this article, you will create a Java project with Maven, and insert a record into Oracle database via Hibernate framework.
Tools & technologies used in this article :
- Maven 3.0.3
- JDK 1.6.0_13
- Hibernate 3.6.3.final
- Oracle 11g
1. Table Creation
Oracle SQL script to create a “DBUSER” table in database.
CREATE TABLE DBUSER (
USER_ID NUMBER (5) NOT NULL,
USERNAME VARCHAR2 (20) NOT NULL,
CREATED_BY VARCHAR2 (20) NOT NULL,
CREATED_DATE DATE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ( USER_ID )
)2. Create Project with Maven
Use Maven to create a standard project structure.
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.mkyong -DartifactId=HibernateExample
-DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=false3. Maven to Eclipse IDE
Convert the generated Maven based project to Eclipse project, and import it into your Eclipse IDE.
mvn eclipse:eclipse4. Add Hibernate and Oracle Dependency
Update your pom.xml file, and add all related dependencies.
You need declared “JBoss repository” for the latest Hibernate jar and its dependency.
For Oracle JDBC driver, you need to install it into your local maven repository manually.
File : pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.mkyong.common</groupId>
<artifactId>HibernateExample</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<version>1.0</version>
<name>HibernateExample</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<!-- JBoss repository for Hibernate -->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>JBoss repository</id>
<url>http://repository.jboss.org/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.8.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- ORACLE JDBC driver, need install yourself -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javassist</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>3.12.1.GA</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>5. Hibernate Mapping file (hbm) + Model
Create a Hibernate XML mapping file and Model class for table “DBUSER“.
– Create following “DBUser.hbm.xml” file and put it under “src/main/resources/com/mkyong/user“.
Note
Create the folder if it does not exists.
File : DBUser.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.mkyong.user.DBUser" table="DBUSER">
<id name="userId" type="int">
<column name="USER_ID" precision="5" scale="0" />
<generator class="assigned" />
</id>
<property name="username" type="string">
<column name="USERNAME" length="20" not-null="true" />
</property>
<property name="createdBy" type="string">
<column name="CREATED_BY" length="20" not-null="true" />
</property>
<property name="createdDate" type="date">
<column name="CREATED_DATE" length="7" not-null="true" />
</property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>– Create a “DBUser.java” file and put it under “src/main/java/com/mkyong/user/”
File : DBUser.java
package com.mkyong.user;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Dbuser generated by hbm2java
*/
public class DBUser implements java.io.Serializable {
private int userId;
private String username;
private String createdBy;
private Date createdDate;
public DBUser() {
}
public DBUser(int userId, String username, String createdBy,
Date createdDate) {
this.userId = userId;
this.username = username;
this.createdBy = createdBy;
this.createdDate = createdDate;
}
public int getUserId() {
return this.userId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getCreatedBy() {
return this.createdBy;
}
public void setCreatedBy(String createdBy) {
this.createdBy = createdBy;
}
public Date getCreatedDate() {
return this.createdDate;
}
public void setCreatedDate(Date createdDate) {
this.createdDate = createdDate;
}
}6. Hibernate Configuration File
Create a Hibernate configuration file “hibernate.cfg.xml” and put it under the root of resources folder, “src/main/resources/hibernate.cfg.xml“, and fill in your Oracle database details. And map to above Hibernate mapping file – “DBUser.hbm.xml“.
File : hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:MKYONG</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">mkyong</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">password</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.default_schema">MKYONG</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="com/mkyong/user/DBUser.hbm.xml"></mapping>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>7. Hibernate Utility
Create a classic “HibernateUtil.java” class to take care of Hibernate session management. And put under “src/main/java/com/mkyong/util/HibernateUtil.java”
File : HibernateUtil.java
package com.mkyong.util;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory();
private static SessionFactory buildSessionFactory() {
try {
// Create the SessionFactory from hibernate.cfg.xml
return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// Make sure you log the exception, as it might be swallowed
System.err.println("Initial SessionFactory creation failed." + ex);
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
public static void shutdown() {
// Close caches and connection pools
getSessionFactory().close();
}
}8. Review Final Project Structure
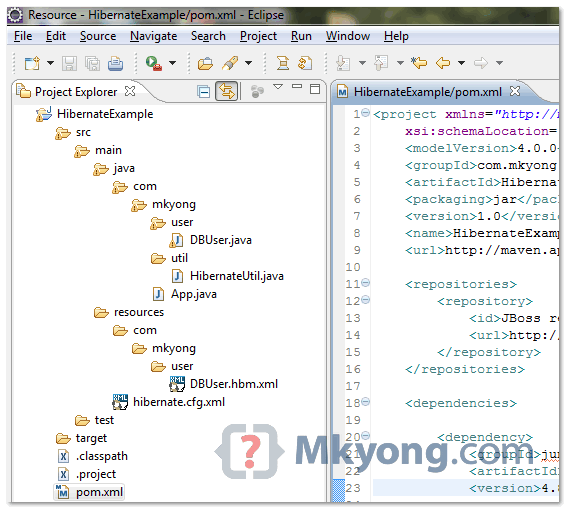
Review it, and your project structure should look like following :
9. Hibernate Coding
Update “App.java“, to code Hibernate to save a dummy user record into a table “DBUSER“.
File : App.java
package com.mkyong;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import com.mkyong.util.HibernateUtil;
import com.mkyong.user.DBUser;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Maven + Hibernate + Oracle");
Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
DBUser user = new DBUser();
user.setUserId(100);
user.setUsername("superman");
user.setCreatedBy("system");
user.setCreatedDate(new Date());
session.save(user);
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
}10. Run It
Run your “App.java“, and see the output in Eclipse console view :
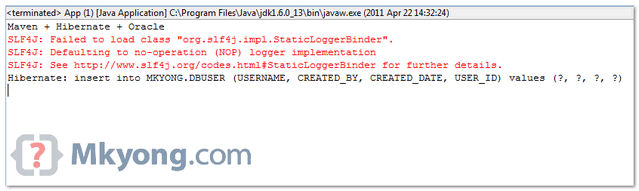
Done.






















 449
449











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








