In Spring, you can use ResourceBundleMessageSource to resolve text messages from properties file, base on the selected locales. See following example :
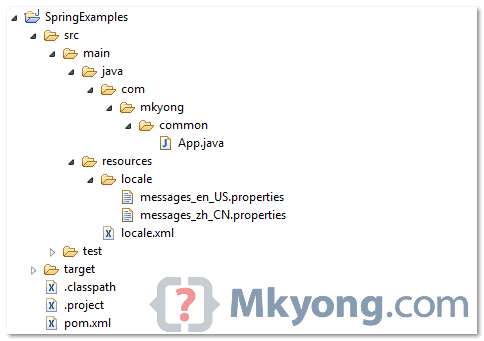
- Directory Structure
Review directory structure of this example.
2. Properties file
Create two properties files, one for English characters (messages_en_US.properties), other one for Chinese characters (messages_zh_CN.properties). Put it into the project class path (see figure above).
File : messages_en_US.properties
customer.name=Yong Mook Kim, age : {0}, URL : {1}File : messages_zh_CN.properties
customer.name=\ufeff\u6768\u6728\u91d1, age : {0}, URL : {1}The ‘\ufeff\u6768\u6728\u91d1‘ is Unicode characters in Chinese.
Note
To display the Chinese characters correctly, you have to use “native2ascii” tool to convert the Chinese characters into Unicode characters.
3. Bean configuration file
Include the properties file into the bean configuration file. Both “messages_en_US.properties” and “messages_zh_CN.properties” are consider one file in Spring, you just need to include the file name once, and Spring will find the correct locale automatically.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename">
<value>locale\customer\messages</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>P.S Assume both files are located at “
resources\locale\customer\” folder.
4. Run it
package com.mkyong.common;
import java.util.Locale;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("locale.xml");
String name = context.getMessage("customer.name",
new Object[] { 28,"http://www.mkyong.com" }, Locale.US);
System.out.println("Customer name (English) : " + name);
String namechinese = context.getMessage("customer.name",
new Object[] {28, "http://www.mkyong.com" },
Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE);
System.out.println("Customer name (Chinese) : " + namechinese);
}
}Output
Note
Make sure your Eclipse is able to display Chinese output.
Explanation
- In
context.getMessage(), the second argument is message parameters, you have to pass it as object array. You can just pass anullif no parameter values available.
context.getMessage("customer.name",null, Locale.US);- The
Locale.USwill retrieve the messages from ‘messages_en_US.properties‘, whileLocale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESEwill retrieve the messages from ‘messages_zh_CN.properties‘.























 386
386

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








