一、概述
- linux内核提供了一个经典通用的双向循环链表list的实现,任何模块都可以借助该接口实现自己的内部循环链表。因为是通用的,可以直接移植到用户态中使用。
- 下面介绍相关链表的插入、查询、修改和删除操作。想深入了解的话直接阅读内核list源代码,代码不是很多,只有list.h 和 types.h。内核源码可以直接下载也可以使用下文给出的链接。
二、API接口
内核定义了链表的结构体,任何链表的实现只要在相关结构体中包含下面这个结构体就可以使用。
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
2.1 初始化
- 两种方式初始化
//第一种初始化方式
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
LIST_HEAD(name) //name就是链表头的名字,该宏会自动定义一个名字为name 的 list_head 结构体。
//第二种初始化方式
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
//在某些情况下CPU对内存中变量读写并不是一次完成的,这可能会出现竞争(多线程)。
//而READ_ONCE和WRITE_ONCE实现对变量一次性读取和一次性写入。
WRITE_ONCE(list->next, list);
list->prev = list;
}
struct list_head head; //声明链表头
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&head); //链表头初始化
2.2 插入
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, new);
}
//头插法
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
//尾插法
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
- 头插法

- 尾插法

2.3 删除
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{
next->prev = prev;
WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, next);
}
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = NULL;
entry->prev = NULL;
}
2.4 遍历
//通过结构体变量内的成员找到该结构体变量的首地址
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
//获取链表的数据指针
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
//遍历链表
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
//遍历过程中如果对链表有删除操作需要使用这个接口
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \
pos = n, n = pos->next)
//遍历链表元素
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))
- list_entry 宏

- container_of 参考 http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-23069658-id-4745433.html
2.5 搬移
- Linux提供了将原本属于一个链表的节点移动到另一个链表的操作,并根据插入到新链表的位置分为两类
/**
* list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will precede our entry
*/
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add(list, head);
}
/**
* list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
*/
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del_entry(list);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
2.6 合并
static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev;
first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first;
last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
}
/**
* list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
}
/**
* list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
}
/**
* list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
/**
* list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* Each of the lists is a queue.
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
if (!list_empty(list)) {
__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
}
}
- 假设当前有两个链表,表头分别是list1和list2(都是struct list_head变量),当调用list_splice(&list1,&list2)时,只要list1非空,list1链表的内容将被挂接在list2链表上,位于list2和list2.next(原list2表的第一个节点)之间。新list2链表将以原list1表的第一个节点为首节点,而尾节点不变。如图(虚箭头为next指针):
图下 链表合并list_splice(&list1,&list2)
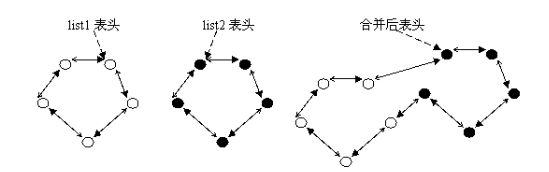
- 当list1被挂接到list2之后,作为原表头指针的list1的next、prev仍然指向原来的节点,为了避免引起混乱,Linux提供了一个list_splice_init()函数:该函数在将list合并到head链表的基础上,调用INIT_LIST_HEAD(list)将list设置为空链。
2.7 其他
//判断链表是否为空
/**
* list_empty - tests whether a list is empty
* @head: the list to test.
*/
/* if empty return 1,else 0 */
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
/** 判断该结点是否是最后一个结点
* list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head
* @list: the entry to test
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
const struct list_head *head)
{
return list->next == head;
}
/** 取该结点下一个结点
* list_first_entry - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
/** 取该结点上一个结点
* list_last_entry - get the last element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define list_last_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->prev, type, member)
//判断链表中是否只有一个节点
static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head)
{
return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}
//将链表进行翻转,也就是将head的next和head的本身做交换
static inline void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first;
if (!list_empty(head)) {
first = head->next;
list_move_tail(first, head);
}
}
//将老的节点old换成新的节点new
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}
- 其他参考 linux源码/include/linux/list.h
三、示例
/*
* Description : linux应用层编程之内核链表list的使用
* Date :20180610
* Author :mason
* Mail : mrsonko@126.com
*
*/
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "listdemo.h"
#define log(fmt, arg...) printf(""fmt,##arg)
//自定义消息结构体
struct msg {
int msgid;
char msginfo[50];
struct list_head list;
};
void main() {
int quit = 0;
int flag = 0;
int opt, key;
struct list_head msg_head, *pos, *n; //声明链表首部,注意这pos, n的定义,遍历链表会使用
struct msg msg1, msg2, *pmsg; //自定义的链表结点,结构体中嵌套list_head结构体
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&msg_head); //链表初始化
log("*********************\n\n"
"input options:\n"
"1: insert\n" //插入
"2: serach\n" //查询
"3: search all \n" //查询所有
"4: modify\n" //修改
"5: delete\n" //删除
"6: delete all\n" //删除全部
"0: quit\n"
"\n*********************\n");
while(!quit) {
log("\ninput options:");
scanf("%d", &opt);
switch(opt){
//插入链表,相同结点可重复插入,也可以在加入前比较判断防止插入重复
case 1:
pmsg = calloc(1, sizeof(struct msg));
if(!pmsg){
log("insert fail \n");
break;
}
log("input msgid : ");
scanf("%d", &pmsg->msgid);
log("input msg info:");
getchar();
gets(pmsg->msginfo);
log("[Your have input : msgid : %d, msginfo : %s ]\n", pmsg->msgid, pmsg->msginfo);
list_add_tail(&pmsg->list, &msg_head); //插入尾部,list_add()插入首部
break;
//查询
case 2:
flag = 0 ;
log("input msg id:");
scanf("%d", &key);
//遍历查询
list_for_each_entry(pmsg, &msg_head, list) {
if(pmsg->msgid == key){
log("[msgid: %d, msginfo: %s ]\n", key, pmsg->msginfo);
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if(!flag)
log("%d not found! \n", key);
break;
//查询所有
case 3:
log("\n***** msg start *****\n\n");
list_for_each_entry(pmsg, &msg_head, list){
log("[msgid: %d, msginfo: %s ]\n", key, pmsg->msginfo);
}
log("\n***** msg end *****\n");
break;
//修改结点
case 4:
flag = 0;
log("input msg id:");
scanf("%d", &key);
//修改
list_for_each_entry(pmsg, &msg_head, list) {
if(pmsg->msgid == key){
log("[msgid: %d, msginfo: %s ]\n", key, pmsg->msginfo);
log("input msg you want to set:");
memset(pmsg->msginfo, 0, sizeof(pmsg->msginfo));
getchar();
gets(pmsg->msginfo);
flag = 1;
}
}
if(!flag){
log("msgid : %d not fount !\n", key);
}
flag = 0;
break;
//删除结点
case 5:
flag = 0;
log("input msg id:");
scanf("%d", &key);
//遍历链表并且执行删除操作需要使用这个接口 _safe
list_for_each_safe(pos, n, &msg_head){
pmsg = list_entry(pos, struct msg, list);
if(pmsg->msgid == key){
log("[delete msg, msgid:%d, msginfo:%s]\n", pmsg->msgid, pmsg->msginfo);
list_del(pos);
free(pmsg);
flag = 1;
}
}
if(!flag)
log("msgid : %d not found!\n", key);
flag = 0;
break;
//删除所有
case 6:
list_for_each_safe(pos, n, &msg_head){
pmsg = list_entry(pos, struct msg, list);
log("[delete msg, msgid:%d, msginfo:%s]\n", pmsg->msgid, pmsg->msginfo);
list_del(pos);
free(pmsg);
}
break;
default:
//退出前释放资源
list_for_each_safe(pos, n, &msg_head){
pmsg = list_entry(pos, struct msg, list);
list_del(pos);
free(pmsg);
}
quit = 1;
break;
}
}
return ;
}
参考博客
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/kernel/l-chain/
https://blog.csdn.net/fuyuande/article/details/80646294
https://blog.csdn.net/YAOZHENGUO2006/article/details/7621551?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant_right.none-task-blog-OPENSEARCH-4.nonecase&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant_right.none-task-blog-OPENSEARCH-4.nonecase
























 270
270











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








