最近正在看android官方文档,看到Displaying Bitmaps Efficiently部分,正好看到LruCache,所以便想了解LruCache的源码。
正文
先从LruCache类的成员变量
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
/** Size of this cache in units. Not necessarily the number of elements. */
private int size;//已经存储的大小
private int maxSize;//规定的最大存储空间
private int putCount;//put的次数
private int createCount;//create的次数
private int evictionCount;//回收的次数
private int hitCount;//命中的次数
private int missCount;//丢失的次数LruCache成员变量不多,其中最重要的是size,maxSize和map这三个成员变量,前两个用于缓存大小的管理,后一个则用于存放缓存的内容。LruCache保存一个LinkedHashMap(双链表),每当value被访问的时候,此value就会移动到队列的头部,当cache已满的时候加入新的value时,在队列尾巴的value会被回收。
LruCache的构造函数
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}传入maxSize即是我们限定的缓存大小,在构造函数中对map进行了初始化,传入的三个参数中最重要的是第三个参数,将accessOrder设置为true。即访问顺序(从近期访问最少到近期访问最多的顺序来保存元素)符合Lru算法。
如果不是很清楚访问顺序和插入顺序,可以看下
http://www.cnblogs.com/yejg1212/archive/2013/04/01/2992921.html
接下来看LruCache的put方法
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
//新加进来的value将会被放置在链表的尾部,put方法会返回key对应的原value,若没有则返回null
previous = map.put(key, value);
//如果key对应的value被替换,删除原有value的内存大小
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}上述代码中,可以发现LruCache的put方法主要是调用了HashMap的put方法
@Override public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return putValueForNullKey(value);
}
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
preModify(e);
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// No entry for (non-null) key is present; create one
modCount++;
if (size++ > threshold) {
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
addNewEntry(key, value, hash, index);
return null;
}addNewEntry以上的代码主要是判断传进来的key是否已经存在,如果存在则更换对应的value并返回上一个value,如果key不存在,则执行addNewEntry方法。
LinkedHashMap继承自HashMap,LinkedHashMap本身并没有重写put方法,而是通过重写addNewEntry方法实现value的添加。
@Override void addNewEntry(K key, V value, int hash, int index) {
LinkedEntry<K, V> header = this.header;
// Remove eldest entry if instructed to do so.
LinkedEntry<K, V> eldest = header.nxt;
if (eldest != header && removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
remove(eldest.key);
}
// Create new entry, link it on to list, and put it into table
LinkedEntry<K, V> oldTail = header.prv;
LinkedEntry<K, V> newTail = new LinkedEntry<K,V>(
key, value, hash, table[index], header, oldTail);
table[index] = oldTail.nxt = header.prv = newTail;
}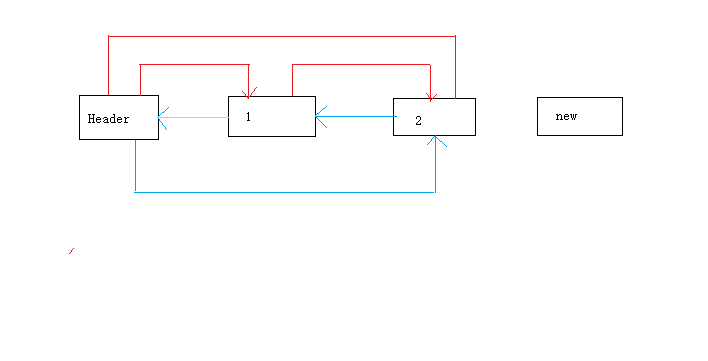
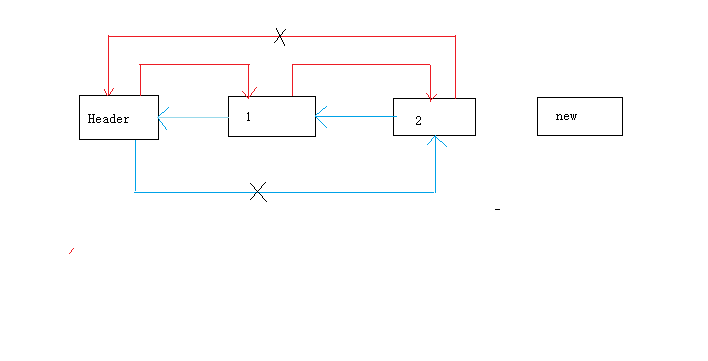
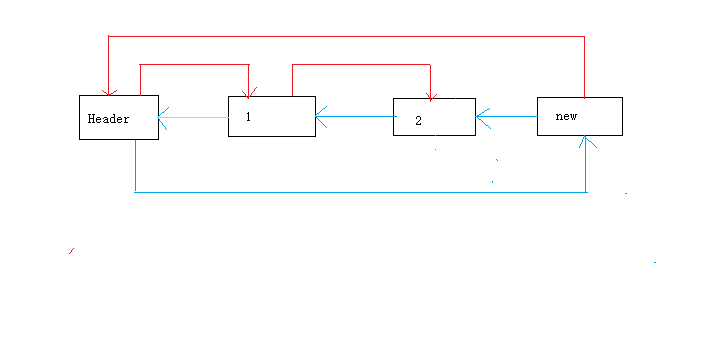
其中红色线段代表nxt,蓝色代表pre(画的丑,不要见怪)
回到LruCache中的put方法,在其中还有一个重要的方法trimToSize(int maxSize)其作用的是移除一直没被调用的项,直到剩余项的数小于请求的大小,如果maxSize传入-1,则清空缓存中的所有对象。
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//如果有剩余空间,就不用移除
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
//离header最近的,即上图中的1
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);//移除
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);//删除其占有的内存
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}将上述的进行总结:往cache中添加value时,会将加入的value添加到双链表的尾部,同时判断当前缓冲的大小是否已经超过了限定的大小,删除最“老”的。
接下来LruCache的get方法:
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
/*
* Attempt to create a value. This may take a long time, and the map
* may be different when create() returns. If a conflicting value was
* added to the map while create() was working, we leave that value in
* the map and release the created value.
*/
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
//如果mapValue不为空,则撤销上一步的put操作。
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
//每次新加入对象都需要调用trimToSize方法看是否需要回收
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
上面代码中出现的create方法需要我们去重写,但基本上不会去重写该方法,因为如果value丢失我们都会重新去获取。
相同的上述代码中最重要的是map.get(),查看LinkedHashMap的get方法。
@Override public V get(Object key) {
/*
* This method is overridden to eliminate the need for a polymorphic
* invocation in superclass at the expense of code duplication.
*/
if (key == null) {
HashMapEntry<K, V> e = entryForNullKey;
if (e == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
makeTail((LinkedEntry<K, V>) e);
return e.value;
}
//查询链表中是否已具有该key对应的value,如果有再判读accessOrder是否为true
int hash = Collections.secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[hash & (tab.length - 1)];
e != null; e = e.next) {
K eKey = e.key;
if (eKey == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(eKey))) {
if (accessOrder)
makeTail((LinkedEntry<K, V>) e);
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}put方法的功能就是从链表中获取key对应的value(因为不是解析LinkedHashMap所以不具体说明),这里需要关注的是makeTail方法
private void makeTail(LinkedEntry<K, V> e) {
// Unlink e
e.prv.nxt = e.nxt;
e.nxt.prv = e.prv;
// Relink e as tail
LinkedEntry<K, V> header = this.header;
LinkedEntry<K, V> oldTail = header.prv;
e.nxt = header;
e.prv = oldTail;
oldTail.nxt = header.prv = e;
modCount++;
}该方法将访问的key的项放到链表的尾部。
总结
可以发现Lru算法的实现是通过LinkedHashMap来实现的,通过将新添加的和最近访问的项放到链表的尾部,当缓存大于限制时,移除头部的项来实现近期最少使用算法。






















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








