探讨批量更新数据三种写法的效率问题。
实现方式有三种,
1> 循环列表集合, 遍历更新,需要在db链接url后面带一个参数 &allowMultiQueries=true
2> 用mysql的case when 条件判断变相的进行批量更新(推荐使用)
3> 用ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE进行批量更新
<!-- 批量更新第一种方法,通过接收传进来的参数list进行循环着组装sql ;号分割 -->
<update id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List" >
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" open="" close="" separator=";">
update standard_relation
<set >
<if test="item.standardFromUuid != null" >
standard_from_uuid = #{item.standardFromUuid,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="item.standardToUuid != null" >
standard_to_uuid = #{item.standardToUuid,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="item.gmtModified != null" >
gmt_modified = #{item.gmtModified,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{item.id,jdbcType=BIGINT}
</foreach>
</update>
<!-- 批量更新第二种方法,通过 case when语句变相的进行批量更新 -->
prefix:在trim标签内sql语句加上前缀。
suffix:在trim标签内sql语句加上后缀。
prefixOverrides:指定去除多余的前缀内容
suffixOverrides:指定去除多余的后缀内容,如:suffixOverrides=",",去除trim标签内sql语句多余的后缀","。
<update id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List" >
update standard_relation
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<trim prefix="standard_from_uuid =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="i" index="index">
<if test="i.standardFromUuid!=null">
when id=#{i.id} then #{i.standardFromUuid}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
<trim prefix="standard_to_uuid =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="i" index="index">
<if test="i.standardToUuid!=null">
when id=#{i.id} then #{i.standardToUuid}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
<trim prefix="gmt_modified =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="i" index="index">
<if test="i.gmtModified!=null">
when id=#{i.id} then #{i.gmtModified}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
</trim>
where
<foreach collection="list" separator="or" item="i" index="index" >
id=#{i.id}
</foreach>
</update>
<!-- 批量更新第三种方法,用ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE -->
<insert id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List">
insert into standard_relation(id,relation_type, standard_from_uuid,
standard_to_uuid, relation_score, stat,
last_process_id, is_deleted, gmt_created,
gmt_modified,relation_desc)VALUES
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=",">
(#{item.id,jdbcType=BIGINT},#{item.relationType,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{item.standardFromUuid,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{item.standardToUuid,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{item.relationScore,jdbcType=DECIMAL}, #{item.stat,jdbcType=TINYINT},
#{item.lastProcessId,jdbcType=BIGINT}, #{item.isDeleted,jdbcType=TINYINT}, #{item.gmtCreated,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
#{item.gmtModified,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},#{item.relationDesc,jdbcType=VARCHAR})
</foreach>
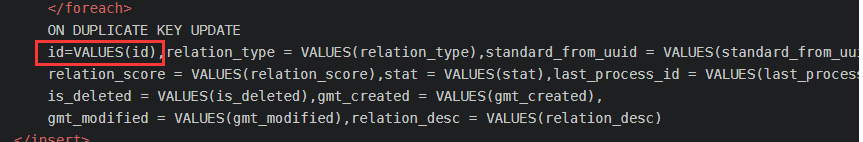
ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE
id=VALUES(id),relation_type = VALUES(relation_type),standard_from_uuid = VALUES(standard_from_uuid),standard_to_uuid = VALUES(standard_to_uuid),
relation_score = VALUES(relation_score),stat = VALUES(stat),last_process_id = VALUES(last_process_id),
is_deleted = VALUES(is_deleted),gmt_created = VALUES(gmt_created),
gmt_modified = VALUES(gmt_modified),relation_desc = VALUES(relation_desc)
</insert>方案二中的实际瓶装后的sql:
update standard_relation
set standard_from_uuid =case when id=#{i.id} then #{i.standardFromUuid}
when id=#{i.id} then #{i.standardFromUuid} end,
standard_to_uuid =case when id=#{i.id} then #{i.standardToUuid}
when id=#{i.id} then #{i.standardToUuid} end,
gmt_modified =case when id=#{i.id} then #{i.gmtModified}
when id=#{i.id} then #{i.gmtModified} end
where id=#{i.id} or id=#{i.id}
CASE WHEN的两种写法:
Type 1: CASE value WHEN [compare-value] THEN result [WHEN [compare-value] THEN result ...] [ELSE result] END
Type 2: CASE WHEN [condition] THEN result [WHEN [condition] THEN result ...] [ELSE result] END对应的Java代码:
@Override
public void updateStandardRelations() {
List<StandardRelation> list=standardRelationMapper.selectByStandardUuid("xiemingjieupdate");
for(StandardRelation tmp:list){
tmp.setStandardFromUuid(tmp.getStandardFromUuid()+"update");
tmp.setStandardToUuid(tmp.getStandardToUuid()+"update");
}
long begin=System.currentTimeMillis();
standardRelationManager.updateBatch(list);
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.print("当前的批量更新的方法用时"+(end-begin)+"ms");
}扩展: 多个条件批量更新 ( 注意: update的字段不要包含 条件字段 !!! , field2也需要set, 那么mysql回先执行setfield2字段,导致其他字段条件不匹配!!! )
<update id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List">
update demo_table
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
status=
<foreach collection="list" item="item" open="case " close=" end,">
when field2=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3} then #{item.status}
</foreach>
create_time =
<foreach collection="list" item="item" open="case " close=" end,">
when field2=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3} then
<choose>
<when test="item.createTime!=null">
#{item.createTime}
</when>
<otherwise>now()</otherwise>
</choose>
</foreach>
</trim>
WHERE
<foreach collection="list" item="item" open="( " separator=") or (" close=" )">
device_num=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3}
</foreach>
</update>对应的sql
update demo_table set
status = case when field2=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3} then #{item.status}
when field2=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3} then #{item.status} end,
create_time= case when field2=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3} then #{item.createTime}
when field2=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3} then #{item.createTime} end,
WHERE (device_num=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3})or (device_num=#{item.field2} and company_id=#{item.field3})效率比较:
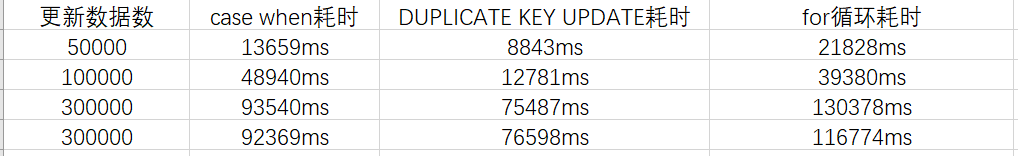
sql语句for循环效率其实相当高的,因为它仅仅有一个循环体,只不过最后update语句比较多,量大了就有可能造成sql阻塞。
case when虽然最后只会有一条更新语句,但是xml中的循环体有点多,每一个case when 都要循环一遍list集合,所以大批量拼sql的时候会比较慢,所以效率问题严重。使用的时候建议分批插入。
duplicate key update可以看出来是最快的,但是一般大公司都禁用,公司一般都禁止使用replace into和INSERT INTO … ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE,这种sql有可能会造成数据丢失和主从上表的自增id值不一致。而且用这个更新时,记得一定要加上id,而且values()括号里面放的是数据库字段,不是java对象的属性字段。
根据效率,安全方面综合考虑,选择适合的很重要。
参考原文:mybatis批量更新数据三种方法效率对比_oneStep->next=CloserNow-CSDN博客_mybatis 批量更新
延伸: 批量插入-- list分批后多线程插入
在第二版插入的时候,我使用了 values 批量插入代替逐行插入。每 30000 行拼接一个长 SQL、顺序插入。整个导入方法这块耗时最多,非常拉跨。后来我将每次拼接的行数减少到 10000、5000、3000、1000、500 发现执行最快的是 1000。结合网上一些对 innodb_buffer_pool_size 描述我猜是因为过长的 SQL 在写操作的时候由于超过内存阈值,发生了磁盘交换。限制了速度,另外测试服务器的数据库性能也不怎么样,过多的插入他也处理不过来。所以最终采用每次 1000 条插入。
每次 1000 条插入后,为了榨干数据库的 CPU,那么网络IO的等待时间就需要利用起来,这个需要多线程来解决,而最简单的多线程可以使用 并行流 来实现,接着我将代码用并行流来测试了一下:
10w行的 excel、42w 欠单、42w记录详情、2w记录、16 线程并行插入数据库、每次 1000 行。插入时间 72s,导入总时间 95 s。
**
* 功能:利用并行流快速插入数据
*
* @author Keats
* @date 2020/7/1 9:25
*/
public class InsertConsumer {
/**
* 每个长 SQL 插入的行数,可以根据数据库性能调整
*/
private final static int SIZE = 1000;
/**
* 如果需要调整并发数目,修改下面方法的第二个参数即可
*/
static {
System.setProperty("java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism", "4");
}
/**
* 插入方法
*
* @param list 插入数据集合
* @param consumer 消费型方法,直接使用 mapper::method 方法引用的方式
* @param <T> 插入的数据类型
*/
public static <T> void insertData(List<T> list, Consumer<List<T>> consumer) {
if (list == null || list.size() < 1) {
return;
}
List<List<T>> streamList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i += SIZE) {
int j = Math.min((i + SIZE), list.size());
List<T> subList = list.subList(i, j);
streamList.add(subList);
}
// 并行流使用的并发数是 CPU 核心数,不能局部更改。全局更改影响较大,斟酌
streamList.parallelStream().forEach(consumer);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Lists.newArrayList();
//并行插入
InsertConsumer.insertData(list, arrearageMapper::insertList);
}
}//两表关联更新
UPDATE video_audit_picture t1 JOIN video_audit t2
ON t1.video_id = t2.id
SET t1.video_code = t2.video_code;























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








