A. Codehorses T-shirts
Codehorses has just hosted the second Codehorses Cup. This year, the same as the previous one, organizers are giving T-shirts for the winners.
The valid sizes of T-shirts are either "M" or from 00 to 33 "X" followed by "S" or "L". For example, sizes "M", "XXS", "L", "XXXL"are valid and "XM", "Z", "XXXXL" are not.
There are nn winners to the cup for both the previous year and the current year. Ksenia has a list with the T-shirt sizes printed for the last year cup and is yet to send the new list to the printing office.
Organizers want to distribute the prizes as soon as possible, so now Ksenia is required not to write the whole list from the scratch but just make some changes to the list of the previous year. In one second she can choose arbitrary position in any word and replace its character with some uppercase Latin letter. Ksenia can't remove or add letters in any of the words.
What is the minimal number of seconds Ksenia is required to spend to change the last year list to the current one?
The lists are unordered. That means, two lists are considered equal if and only if the number of occurrences of any string is the same in both lists.
The first line contains one integer nn (1≤n≤1001≤n≤100) — the number of T-shirts.
The ii-th of the next nn lines contains aiai — the size of the ii-th T-shirt of the list for the previous year.
The ii-th of the next nn lines contains bibi — the size of the ii-th T-shirt of the list for the current year.
It is guaranteed that all the sizes in the input are valid. It is also guaranteed that Ksenia can produce list bb from the list aa.
Print the minimal number of seconds Ksenia is required to spend to change the last year list to the current one. If the lists are already equal, print 0.
3 XS XS M XL S XS
2
2 XXXL XXL XXL XXXS
1
2 M XS XS M
0
In the first example Ksenia can replace "M" with "S" and "S" in one of the occurrences of "XS" with "L".
In the second example Ksenia should replace "L" in "XXXL" with "S".
In the third example lists are equal.
题目分析:
第一眼看到多字符串,就想到字典树,故而套入字典树模版.
考虑数据量小故而改原本的标志末端的bool型end为int型num,表示当前剩余经过此结点的字符串数目
故而添加字符串时对经过的每个结点num++,
查询时就是返回目标串在字典树中的最大匹配长度,关键在于边查询边将经过的点num--,因此判断空时以为空或者num==0做判断.字符串需要change的字符个数就是字符串长度减去最大匹配长度.
这么做的优点在于利用字典树的同前缀特性利用贪心思想的同时不用去考虑该修改具体的前n个字符串中的哪个字符串.缺点是字典树26个分叉有点浪费.
ac代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
const int maxn=26; //这里假设字符串中只出现26个小写字母
const int maxm=100000;
struct treenode{
int num;
treenode* next[maxn];
}head;
treenode memory[maxm];
int mallocp=0;
void init(){
head.num=1;
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++) head.next[i]=NULL;
}
treenode* createnew(){
treenode* newnode;
newnode=&memory[mallocp++];
newnode->num=0;
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++) newnode->next[i]=NULL;
return newnode;
}
void update(char* s){
int k=0,temp;
treenode* t=&head;
while(s[k]){
temp=s[k]-'A';
if(!t->next[temp]) t->next[temp]=createnew();
t=t->next[temp];
t->num++;
k++;
}
}
int search(char* s){
int k=0;
treenode* t=&head;
while(s[k]){
int temp=s[k]-'A';
if(NULL==t->next[temp]||0==t->next[temp]->num) return k;
t=t->next[temp];
t->num--;
k++;
}
return k;
}
int main(){
init();
char x[1000];
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%s",&x);
update(x);
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%s",&x);
ans+=strlen(x);
ans-=search(x);
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
B. Light It Up
Recently, you bought a brand new smart lamp with programming features. At first, you set up a schedule to the lamp. Every day it will turn power on at moment 00 and turn power off at moment MM. Moreover, the lamp allows you to set a program of switching its state (states are "lights on" and "lights off"). Unfortunately, some program is already installed into the lamp.
The lamp allows only good programs. Good program can be represented as a non-empty array aa, where 0<a1<a2<⋯<a|a|<M0<a1<a2<⋯<a|a|<M. All aiai must be integers. Of course, preinstalled program is a good program.
The lamp follows program aa in next manner: at moment 00 turns power and light on. Then at moment aiai the lamp flips its state to opposite (if it was lit, it turns off, and vice versa). The state of the lamp flips instantly: for example, if you turn the light off at moment 11 and then do nothing, the total time when the lamp is lit will be 11. Finally, at moment MM the lamp is turning its power off regardless of its state.
Since you are not among those people who read instructions, and you don't understand the language it's written in, you realize (after some testing) the only possible way to alter the preinstalled program. You can insert at most one element into the program aa, so it still should be a good program after alteration. Insertion can be done between any pair of consecutive elements of aa, or even at the begining or at the end of aa.
Find such a way to alter the program that the total time when the lamp is lit is maximum possible. Maybe you should leave program untouched. If the lamp is lit from xx till moment yy, then its lit for y−xy−x units of time. Segments of time when the lamp is lit are summed up.
First line contains two space separated integers nn and MM (1≤n≤1051≤n≤105, 2≤M≤1092≤M≤109) — the length of program aa and the moment when power turns off.
Second line contains nn space separated integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (0<a1<a2<⋯<an<M0<a1<a2<⋯<an<M) — initially installed program aa.
Print the only integer — maximum possible total time when the lamp is lit.
3 10 4 6 7
8
2 12 1 10
9
2 7 3 4
6
In the first example, one of possible optimal solutions is to insert value x=3x=3 before a1a1, so program will be [3,4,6,7][3,4,6,7] and time of lamp being lit equals (3−0)+(6−4)+(10−7)=8(3−0)+(6−4)+(10−7)=8. Other possible solution is to insert x=5x=5 in appropriate place.
In the second example, there is only one optimal solution: to insert x=2x=2 between a1a1 and a2a2. Program will become [1,2,10][1,2,10], and answer will be (1−0)+(10−2)=9(1−0)+(10−2)=9.
In the third example, optimal answer is to leave program untouched, so answer will be (3−0)+(7−4)=6(3−0)+(7−4)=6.
题目分析:
我们需要先将输入的n个数据转化为
a1-0,a2-a1,a3-a2,a4-a3...... m-an 这么n+1个数
然后我们要做的其实就是将这n+1个数其中某个大于1的数分解为两个大于等于1的数,或者选择不分解
而具体分解哪个要看哪种分解最终灯亮的时间最长,而灯亮时间其实就是下标为偶数的数的和,然而某个数分解为两个数会导致这个数后面部分原来是偶数的变成奇数,故而答案会截然不同,我们要克服的就是这个问题.
我选择的是先转化好n+1个数存进a数组,建立all数组,b数组,然后叠加法求出第i个下标位置时a0到ai的总和,以及i位置和它之前的灯亮时间总和
为了考虑到不做变化的情况,maxans初值为n+1个数的灯亮时间总和,然后就开始线性递推,寻找最大的答案
maxans=std::max(maxans,b[i]-1+all[n]-all[i]-b[n]+b[i]);
我解释一下这个公式,其实被分解的数无论是下标是奇数还是偶数,奇数分解为1,x-1,偶数分解为x-1,1就好了,故而前i个数包括第i个本身的灯亮时间为b[i]-1,而all[n]-all[i]-b[n]+b[i]实际为all[n]-all[i]-(b[n]-b[i]),其实就是求出了后半段中原来下标为奇数的和,现在前面因为分解多了一个数,故而他们下标都加1,成为了被点亮的偶数下标,
ac代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=100005;
ll a[maxn],b[maxn],all[maxn];
void solve(){
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
ll t1=0,t2;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%lld",&t2);
a[i]=t2-t1;
t1=t2;
}
a[n]=m-t2;
ll sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
if(i%2==0) sum+=a[i];
all[i]=all[i-1]+a[i];
b[i]=sum;
}
ll maxans=sum;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
maxans=std::max(maxans,b[i]-1+all[n]-all[i]-b[n]+b[i]);
}
printf("%lld",maxans);
}
int main(){
solve();
return 0;
}题目分析:
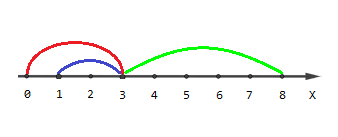
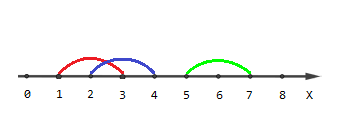
这道题就是给我们n条数轴上的线段让我们回答只被1条线覆盖的端点有多少,被2条线覆盖的端点有多少...只被n条线覆盖的有多少.
我们发现实际上我们不用逐个点去判断,所有的点被这n条线段的2*n个端点切割成了许多段,而每一段内的经过的线的条数在这个小段内是相同的,故而我们可以将所有线段的端点排序,排序后相邻两端点之间的一段线段a上面的所有点被覆盖的线段条数当然就是相同的了,然后将这线段a上点的数目加到对应的答案里.
核心思维就是上面这样子,排序用sort复杂度n*logn,求答案复杂度只为n,完全可以接受.
最关键的难点其实在于每个端点的处理,因为多线段端点可能重复,而线段又是闭区间,故而经过某端点的线段条数只有等到新端点开始计算时再计算老端点是最稳妥的,因为此时重复点都已经处理了.
ac代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,int> pali;
const int maxn=100005;
pali a[4*maxn];
ll num[4*maxn];
void solve(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
ll t1,t2;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%lld%lld",&t1,&t2);
a[2*i]=make_pair(t1,0); //second为0表示为线段起点,1表示终点
a[2*i+1]=make_pair(t2,1);
}
sort(a,a+2*n);
ll now=0,lastpos=-1,temp=0;
//now表示当前经过此端点的线段条数
//lastpos表示上一个端点的位置
//temp表示上一个端点上被删除的线段终点数目
//可以看出,我们把端点与线段中央是分开算的
for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++) num[i]=0;
for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++){
if(a[i].first>lastpos){ //以新点的接入做触发,将之前的答案统计一下
num[now+temp]++,temp=0; //前一个端点
num[now]+=a[i].first-lastpos-1; //此端点到前一个端点间线段上的点
lastpos=a[i].first;
}
if(a[i].second){
temp++;
now--;
}
else now++;
}
num[now+temp]++; //最后一个端点的收尾
printf("%lld",num[1]);
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) printf(" %lld",num[i]);
}
int main(){
solve();
return 0;
}























 1200
1200











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








