1. 官方链接
2. 题目:
给你单链表的头节点
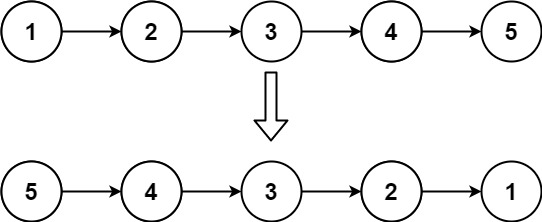
head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]示例 2:
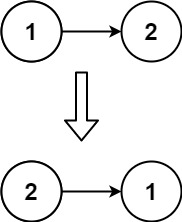
输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1]示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000]-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000进阶:链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
3. 方案
解决方式1:
迭代链表,每次new一个节点,并将老节点放入newNode 的next
我认为这种很容易理解,当然缺点就是每次new一个对象
package com.nami.algorithm.study.chain2;
/**
* 描述: 反转链表
* <p>
* 构造一个新链表,从旧链表依次拿到每个节点,创建新节点添加至新链表头部,完成后新链表即是倒序的
*
* @Author: lbc
* @Date: 2024-04-16 18:39
* @email: 594599620@qq.com
* @Description: keep coding
*/
public class ChainTest {
/**
* 每次新增一个node 将 next 指向上一个节点。
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverse(ListNode node) {
ListNode head = null;
ListNode cur = node;
while (cur != null) {
// new一个新节点,将老的放到新节点next
ListNode o1 = new ListNode(cur.value, head);
head = o1;
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5, null);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4, n5);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3, n4);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2, n3);
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1, n2);
ListNode reverse = reverse(n1);
while (reverse != null) {
System.out.println(reverse.value);
reverse = reverse.next;
}
}
static class ListNode {
protected int value;
protected ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value, ListNode next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
方法2:
使用自定义容器类,链表放入容器类。使用容器方法removeFirst, addFirst 将老链表数据转换新容器对象内
package com.nami.algorithm.study.chain3;
/**
* 描述:
* 单项链表反转
*
* @Author: lbc
* @Date: 2024-04-16 20:49
* @email: 594599620@qq.com
* @Description: keep coding
*/
public class ChainTest {
/**
* 构造一个新链表,从旧链表头部移除节点,添加到新链表头部,完成后新链表是倒序的,
* 使用两个自定义容器,容器内有移除与新增方法
*
* @param node
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverse(ListNode node) {
ChainList result = new ChainList(null);
ChainList list = new ChainList(node);
while (true) {
ListNode listNode = list.removeFirst();
if (listNode == null) {
break;
}
result.addFirst(listNode);
}
return result.head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5, null);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4, n5);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3, n4);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2, n3);
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1, n2);
ListNode node = reverse(n1);
while (node != null) {
System.out.println(node.value);
node = node.next;
}
}
/**
* 容器类
* 核心 removeFirst
* addFirst
*/
static class ChainList {
private ListNode head;
public ChainList(ListNode head) {
this.head = head;
}
public void addFirst(ListNode node) {
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
public ListNode removeFirst() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode first = head;
head = head.next;
return first;
}
}
static class ListNode {
protected int value;
protected ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value, ListNode next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
方法3:
头插法
package com.nami.algorithm.study.chain;
/**
* 描述: 反转链表
* 头插法
*
* @Author: lbc
* @Date: 2024-04-17 9:38
* @email: 594599620@qq.com
* @Description: keep coding
*/
public class ChainTest {
public static ListNode reverseNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
// 这样好理解 ==! 但是感觉跟方法一 差不多
ListNode node = new ListNode(cur.value, cur.next);
node.next = prev;
prev = node;
// 循环
cur = cur.next;
}
return prev;
}
public static ListNode reverseNode2(ListNode head) {
// 最终节点
ListNode prev = null;
// 当前节点
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
// 想想上面的reverseNode() 方法不难,主要是解决一个 ”引用问题“
// 相当于将cur = cur.next; 放在第一行。拿出next节点。防止cur.next 这个循环条件被污染
// 建议比较方法1 比较着看
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
// 循环
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5);
n1.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
n4.next = n5;
ListNode listNode = reverseNode2(n1);
while (listNode != null) {
System.out.println(listNode.value);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
static class ListNode {
protected int value;
protected ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public ListNode(int value, ListNode next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
方法4:
还是使用容器
采用栈,先进后出思路解决
package com.nami.algorithm.study.chain;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 描述: 反转链表
* 头插法
*
* @Author: lbc
* @Date: 2024-04-17 9:38
* @email: 594599620@qq.com
* @Description: keep coding
*/
public class ChainTest2 {
public static ListNode reverseNode(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.next;
}
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
ListNode newHead = stack.pop();
head = newHead;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
head.next = stack.pop();
head = head.next;
}
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5);
n1.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
n4.next = n5;
ListNode listNode = reverseNode(n1);
while (listNode != null) {
System.out.println(listNode.value);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
static class ListNode {
protected int value;
protected ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public ListNode(int value, ListNode next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
方法5:
递归方式
package com.nami.algorithm.study.chain;
/**
* 描述: 反转链表
* 头插法
*
* @Author: lbc
* @Date: 2024-04-17 9:38
* @email: 594599620@qq.com
* @Description: keep coding
*/
public class ChainTest3 {
/**
* 递归 注意层数问题,别 stackOverFlow 喽
* 堆栈溢出异常
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode last = reverseNode(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5);
n1.next = n2;
n2.next = n3;
n3.next = n4;
n4.next = n5;
ListNode listNode = reverseNode(n1);
while (listNode != null) {
System.out.println(listNode.value);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
}
static class ListNode {
protected int value;
protected ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public ListNode(int value, ListNode next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
最后:
如果觉得困难 建议debug, 跟下。 多看代码,多思考,相信很快就明白了






















 284
284











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








