JavaScript 有三种声明函数的方法
//function 命令
function print(s) {
console.log(s);
}
//函数表达式
var print = function(s) {
console.log(s);
};
var print = function x(){
console.log(typeof x);
};
//这个x只在函数体内部可用,指代函数表达式本身,其他地方都不可用。
这种写法的用处有两个,
一是可以在函数体内部调用自身,
二是方便除错(除错工具显示函数调用栈时,将显示函数名,而不再显示这里是一个匿名函数)。
因此,下面的形式声明函数也非常常见。
//Function 构造函数
var add = new Function(
'x',
'y',
'return x + y'
);
// 等同于
function add(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
//函数名后面紧跟一对圆括号,就会调用这个函数
function add(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
add(1, 1) // 2
//同时采用function命令和赋值语句声明同一个函数,最后总是采用赋值语句的定义。
var f = function () {
console.log('1');
}
function f() {
console.log('2');
}
f() // 1
函数的优先权是最高的,它永远被提升至作用域最顶部,然后才是函数表达式和变量按顺序执行
变量提升
js在预编译过程中,首先将变量声明及函数声明提升至当前作用域的顶端,然后进行接下来的处理。
function hoistVariable() {
if (!foo) {
var foo = 5;
}
console.log(foo); // 5
}
hoistVariable();
//变量提升
function hoistVariable() {
var foo; //变量声明提升到了函数顶部,初始值为undefined
if (!foo) {
foo = 5;
}
console.log(foo); // 5
}
hoistVariable();
//、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
var foo = 3;
function hoistVariable() {
var foo = foo || 5;
console.log(foo); // 5
}
hoistVariable();
//
//变量提升
var foo = 3;
function hoistVariable() {
var foo;
foo = foo || 5; //foo || 5这个表达式的结果是5而不是3,虽然外层作用域有个foo变量,但函数内是不会去引用的
console.log(foo); // 5
}
hoistVariable();
//
function foo(x) {
if (x > 100) {
var tmp = x - 100;
}
}
// 等同于
function foo(x) {
var tmp;
if (x > 100) {
tmp = x - 100;
};
}函数提升
function hoistFunction() {
foo(); // output: I am hoisted
function foo() {
console.log('I am hoisted');
}
}
hoistFunction();
//提升后
function hoistFunction() {
function foo() { //引擎是把函数声明整个地提升到了当前作用域的顶部
console.log('I am hoisted');
}
foo(); // output: I am hoisted
}
hoistFunction();
//、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
function hoistFunction() {
function foo() {
console.log(1);
}
foo(); // output: 2
function foo() {
console.log(2);
}
}
hoistFunction();
//提升后
function hoistFunction() {
function foo() {
console.log(1);
}
function foo() { //覆盖上一个foo
console.log(2);
}
foo(); // output: 2
}
hoistFunction();
//----------------------------------------
//所以第一次调用时实际执行了下面定义的函数声明,然后第二次调用时,由于前面的函数表达式与之前的函数声明同名,故将其覆盖,以后的调用也将会打印同样的结果
function hoistFunction() {
foo(); // 2
//匿名函数表达式
var foo = function() {
console.log(1);
};
foo(); // 1
//函数声明 优先级最高,会被提升至当前作用域最顶端
function foo() {
console.log(2);
}
//具名函数表达式
var foo = function bar() {
console.log('ff');
};
foo(); // 1
}
hoistFunction();
//提升后
function hoistFunction() {
var foo;
foo = function foo() {
console.log(2);
}
foo(); // 2
foo = function() {
console.log(1);
};
foo(); // 1
foo(); // 1
}
hoistFunction();
//函数和变量重名
var foo = 3;
function hoistFunction() {
console.log(foo); // function foo() {}
foo = 5;
console.log(foo); // 5
function foo() {}
}
hoistFunction();
console.log(foo); // 3
//提升后
var foo = 3;
function hoistFunction() {
var foo;
foo = function foo() {};
console.log(foo); // function foo() {}
foo = 5;
console.log(foo); // 5
}
hoistFunction();
console.log(foo); // 3
上面代码中,在函数f内部,参数对象obj被整个替换成另一个值。这时不会影响到原始值。这是因为,形式参数(o)的值实际是参数obj的地址,重新对o赋值导致o指向另一个地址,保存在原地址上的值当然不受影响。
arguments 对象
arguments对象包含了函数运行时的所有参数
如果要让arguments对象使用数组方法,真正的解决方法是将arguments转为真正的数组
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
// 或者
var args = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
args.push(arguments[i]);
}
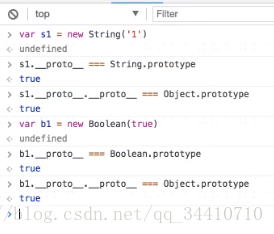
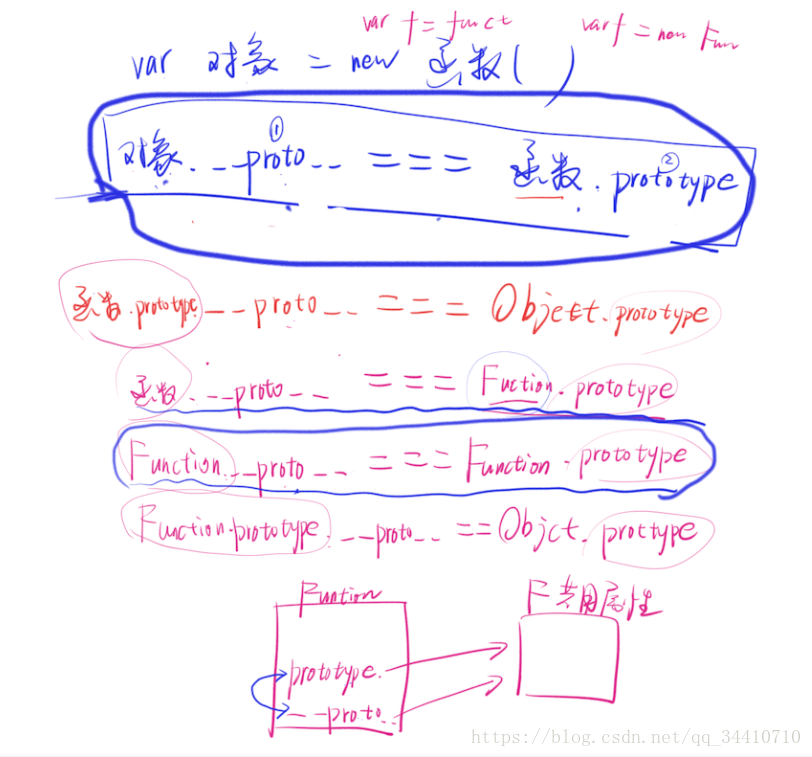
所有对象.__proto__.__proto__ === object.prototype
对象属性 函数属性
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/38429541
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/38425438























 291
291











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








