1、不要编写返回引用可变对象的访问器方法,请看下面Employee类;
public class Employee {
private String name;
private double salary;
private Date birthday;
public Employee(String n,double s,int year, int month,int day){
name = n;
salary = s;
GregorianCalendar calendar = new GregorianCalendar(year, month-1, day);
birthday = calendar.getTime();
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public double getSalary(){
return salary;
}
public Date getBirthday(){
return birthday;
}``
返回Date类型的对象,这样会破环封装性,例如:
public static void main(String[] args){
Employee emp= new Employee("chenjk", 7000, 1993, 9, 14);
Date d = emp.getBirthday();
Date now = new Date();
d.setTime(now.getTime() - d.getTime());
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
System.out.println(sdf.format(d));
System.out.println(sdf.format(emp.birthday));
}
执行结果
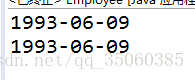
这是因为 d 对象和 emp.birthday引用的是同一个对象,对d调用更改器方法会改变对象emp的私有状态;如果需要返回一个可变对象的引用,需要对它进行克隆;
改写birthday属性的访问器方法
public Date getBirthday(){
return (Date)birthday.clone();
}
执行结果:
1993-06-09
1993-09-14
2、静态
静态域:每个类只有一个这样的域,而每个对象对于所有的实例域都有自己的一份拷贝;静态域属于类,而不属于对象;
静态方法:静态方法是一种不能向对象实施操作的方法。静态方法为类的方法,类被记载就已经执行;静态方法中不能访问实例域
常见用途:
Factory方法:
NumberFormat currencyFormatter = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
NumberFormat percentFormatter = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();
double x=0.2;
System.out.println(currencyFormatter.format(x));
System.out.println(percentFormatter.format(x));
输出:¥0.2,20%
使用 getCurrencyInstance 来获取货币数值格式。使用 getPercentInstance 来获取显示百分比的格式。
使用构造器和使用工厂方法的区别:使用构造器创建对象无法改变构造对象类型,但是用工厂方法可以返回例如上例中的DecimalFormat类对象;
3、方法参数
• 一个方法不能修改一个基本数据类型的参数(即数值型和布尔型) 。
• 一个方法可以改变一个对象参数的状态。
• 一个方法不能实现让对象参数引用一个新的对象。
例如:public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("1", "a");
map.put("2", "b");
getMap(map);
System.out.println(map);
}
public static void getMap(HashMap map){
HashMap<String, String> mapTest = new HashMap<String, String>();
mapTest.put("1", "c");
mapTest.put("2", "d");
mapTest.put("3", "a");
mapTest.put("4", "b");
map = mapTest;
}
“`
输出结果还是 {1=a, 2=b}






















 375
375











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








