测试集mAP计算
本篇博客的代码采用的是基于MobileNet网络的Yolov4模型修改的,对Yolov4感兴趣的同学可以看下面的这篇博客,写的很详细,而且b站上还有相关视频的讲解:
睿智的目标检测50——Tensorflow2 利用mobilenet系列(v1,v2,v3)搭建yolov4-lite目标检测平台.
将测试集数据转换成xml格式
生成txt文件
from yolo import YOLO
from PIL import Image
import os
yolo = YOLO()
path = 'D:/mobilenet-yolov4-lite-keras-main/test_img/'
res_path = 'D:/mobilenet-yolov4-lite-keras-main/test_res/'
count = 0
for img in sorted(os.listdir(path)):
count += 1
print('count--------------', count)
filename = os.path.join(path, img)
print('file_name----------', filename)
try:
image = Image.open(filename)
except:
print('Open Error! Try again!')
continue
else:
try:
r_image, box, class_sta, class_num = yolo.detect_image(image)
r_image.save(res_path + img)
print('box', box)
print('class_num', class_num)
print('class_sta', class_sta)
print('box-----------len', len(box))
with open('D:/mobilenet-yolov4-lite-keras-main/test_txt/' + img.split('.')[0] + '.txt', 'w') as file:
if len(class_sta) == 1:
for i in range(len(box)):
for index, value in enumerate(class_sta):
file.write(value + ' ')
file.write(str(box[i][0]) + ' ')
file.write(str(box[i][1]) + ' ')
file.write(str(box[i][2]) + ' ')
file.write(str(box[i][3]) + ' ' + '\n')
elif len(class_sta) > 1:
# file.write(img + ' ')
for i, value in enumerate(class_num):
file.write(value + ' ')
file.write(str(box[i][0]) + ' ')
file.write(str(box[i][1]) + ' ')
file.write(str(box[i][2]) + ' ')
file.write(str(box[i][3]) + ' ' + '\n')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
yolo.close_session()
效果图

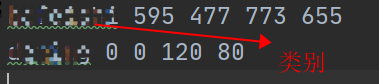
转换成xml文件
import os
import glob
from PIL import Image
# 图像存储位置
src_img_dir = "D:/mobilenet-yolov4-lite-keras-main/test_img" # 添加你的路径
# 图像的txt文件存放位置
src_txt_dir = "D:/mobilenet-yolov4-lite-keras-main/test_txt"
src_xml_dir = "D:/mobilenet-yolov4-lite-keras-main/test_res"
img_Lists = glob.glob(src_img_dir + '/*.jpg')
img_basenames = []
for item in img_Lists:
img_basenames.append(os.path.basename(item))
img_names = []
for item in img_basenames:
temp1, temp2 = os.path.splitext(item)
img_names.append(temp1)
for img in img_names:
im = Image.open((src_img_dir + '/' + img + '.jpg'))
width, height = im.size
# 打开txt文件
gt = open(src_txt_dir + '/' + img + '.txt').read().splitlines()
print(gt)
if gt:
# 将主干部分写入xml文件中
xml_file = open((src_xml_dir + '/' + img + '.xml'), 'w')
xml_file.write('<annotation>\n')
xml_file.write(' <folder>VOC2007</folder>\n')
xml_file.write(' <filename>' + str(img) + '.jpg' + '</filename>\n')
xml_file.write(' <size>\n')
xml_file.write(' <width>' + str(width) + '</width>\n')
xml_file.write(' <height>' + str(height) + '</height>\n')
xml_file.write(' <depth>3</depth>\n')
xml_file.write(' </size>\n')
# write the region of image on xml file
for img_each_label in gt:
spt = img_each_label.split(' ') # 这里如果txt里面是以逗号‘,’隔开的,那么就改为spt = img_each_label.split(',')。
xml_file.write(' <object>\n')
xml_file.write(' <name>' + str(spt[0]) + '</name>\n')
xml_file.write(' <pose>Unspecified</pose>\n')
xml_file.write(' <truncated>0</truncated>\n')
xml_file.write(' <difficult>0</difficult>\n')
xml_file.write(' <bndbox>\n')
xml_file.write(' <xmin>' + str(spt[1]) + '</xmin>\n')
xml_file.write(' <ymin>' + str(spt[2]) + '</ymin>\n')
xml_file.write(' <xmax>' + str(spt[3]) + '</xmax>\n')
xml_file.write(' <ymax>' + str(spt[4]) + '</ymax>\n')
xml_file.write(' </bndbox>\n')
xml_file.write(' </object>\n')
xml_file.write('</annotation>')
效果图

Yolo主要逻辑代码
import colorsys
import copy
import os
from timeit import default_timer as timer
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.layers import Input
from keras.models import load_model
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
from nets.yolo4 import yolo_body, yolo_eval
from utils.utils import letterbox_image
# --------------------------------------------#
# 使用自己训练好的模型预测需要修改4个参数
# model_path、classes_path、
# backbone和alpha都需要修改!
# 如果出现shape不匹配,一定要注意
# 训练时的model_path和classes_path参数的修改
# --------------------------------------------#
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
"model_path": 'logs/mobilev3.h5',
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"classes_path": 'model_data/voc_classes.txt',
"backbone": 'mobilenetv3',
"alpha": 1,
"score": 0.5,
"iou": 0.2,
"max_boxes": 100,
# 显存比较小可以使用416x416
# 显存比较大可以使用608x608
"model_image_size": (416, 416),
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 该变量用于控制是否使用letterbox_image对输入图像进行不失真的resize,
# 在多次测试后,发现关闭letterbox_image直接resize的效果更好
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"letterbox_image": False,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化yolo
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得所有的分类
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def _get_class(self):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
with open(classes_path, encoding='utf-8') as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip().split(' ')[1] for c in class_names]
return class_names
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得所有的先验框
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def _get_anchors(self):
anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 载入模型
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 计算先验框的数量和种类的数量
# ---------------------------------------------------#
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 载入模型,如果原来的模型里已经包括了模型结构则直接载入。
# 否则先构建模型再载入
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
self.yolo_model = yolo_body(Input(shape=(None, None, 3)), num_anchors // 3, num_classes, self.backbone,
self.alpha)
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path)
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
num_anchors / len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# 画框设置不同的颜色
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
# 打乱颜色
np.random.seed(10101)
np.random.shuffle(self.colors)
np.random.seed(None)
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2,))
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在yolo_eval函数中,我们会对预测结果进行后处理
# 后处理的内容包括,解码、非极大抑制、门限筛选等
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
num_classes, self.input_image_shape, max_boxes=self.max_boxes,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou,
letterbox_image=self.letterbox_image)
return boxes, scores, classes
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image):
class_sta = {}
bbox = []
class_num = []
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
if self.letterbox_image:
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, (self.model_image_size[1], self.model_image_size[0]))
else:
boxed_image = image.convert('RGB')
boxed_image = boxed_image.resize((self.model_image_size[1], self.model_image_size[0]), Image.BICUBIC)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
image_data /= 255.
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0})
print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 设置字体
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/simhei.ttf',
size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = max((image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300, 1)
for i, c in list(enumerate(out_classes)):
predicted_class = self.class_names[int(c)]
if predicted_class in class_sta:
class_sta[predicted_class] += 1
else:
class_sta[predicted_class] = 1
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = top - 5
left = left - 5
bottom = bottom + 5
right = right + 5
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bbox.append([left, top, right, bottom])
# 画框框
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
label = label.encode('utf-8')
print(label, top, left, bottom, right)
class_num.append(predicted_class)
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle(
[left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
outline=self.colors[c])
draw.rectangle(
[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
fill=self.colors[c])
draw.text(text_origin, str(label, 'UTF-8'), fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
del draw
return image, bbox, class_sta, class_num
def close_session(self):
self.sess.close()
计算mAP
获得测试集预测位置和概率
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 获取测试集的detection-result和images-optional
# 具体视频教程可查看
# https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1zE411u7Vw
# ----------------------------------------------------#
import colorsys
import os
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
from keras.layers import Input
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
from nets.yolo4 import yolo_body, yolo_eval
from utils.utils import letterbox_image
from yolo import YOLO
'''
这里设置的门限值较低是因为计算map需要用到不同门限条件下的Recall和Precision值。
所以只有保留的框足够多,计算的map才会更精确,详情可以了解map的原理。
计算map时输出的Recall和Precision值指的是门限为0.5时的Recall和Precision值。
此处获得的./input/detection-results/里面的txt的框的数量会比直接predict多一些,这是因为这里的门限低,
目的是为了计算不同门限条件下的Recall和Precision值,从而实现map的计算。
这里的self.iou指的是非极大抑制所用到的iou,具体的可以了解非极大抑制的原理,
如果低分框与高分框的iou大于这里设定的self.iou,那么该低分框将会被剔除。
可能有些同学知道有0.5和0.5:0.95的mAP,这里的self.iou=0.5不代表mAP0.5。
如果想要设定mAP0.x,比如设定mAP0.75,可以去get_map.py设定MINOVERLAP。
'''
class mAP_YOLO(YOLO):
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得所有的分类
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
self.score = 0.01
self.iou = 0.5
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 计算先验框的数量和种类的数量
# ---------------------------------------------------#
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 载入模型,如果原来的模型里已经包括了模型结构则直接载入。
# 否则先构建模型再载入
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
self.yolo_model = yolo_body(Input(shape=(None, None, 3)), num_anchors // 3, num_classes, self.backbone,
self.alpha)
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path)
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
num_anchors / len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# 画框设置不同的颜色
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
# 打乱颜色
np.random.seed(10101)
np.random.shuffle(self.colors)
np.random.seed(None)
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2,))
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在yolo_eval函数中,我们会对预测结果进行后处理
# 后处理的内容包括,解码、非极大抑制、门限筛选等
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
num_classes, self.input_image_shape, max_boxes=self.max_boxes,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou,
letterbox_image=self.letterbox_image)
return boxes, scores, classes
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image_id, image):
f = open("./input/detection-results/" + image_id + ".txt", "w")
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
if self.letterbox_image:
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, (self.model_image_size[1], self.model_image_size[0]))
else:
boxed_image = image.convert('RGB')
boxed_image = boxed_image.resize((self.model_image_size[1], self.model_image_size[0]), Image.BICUBIC)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
image_data /= 255.
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0})
for i, c in enumerate(out_classes):
predicted_class = self.class_names[int(c)]
score = str(out_scores[i])
top, left, bottom, right = out_boxes[i]
f.write("%s %s %s %s %s %s\n" % (
predicted_class, score[:6], str(int(left)), str(int(top)), str(int(right)), str(int(bottom))))
f.close()
return
yolo = mAP_YOLO()
image_ids = open('VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt').read().strip().split()
if not os.path.exists("./input"):
os.makedirs("./input")
if not os.path.exists("./input/detection-results"):
os.makedirs("./input/detection-results")
if not os.path.exists("./input/images-optional"):
os.makedirs("./input/images-optional")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
#验证集
image_path = "./VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages/" + image_id + ".jpg"
#测试集
image_path = "./VOCdevkit/VOC2007/test_jpegimages/" + image_id + ".jpg"
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 开启后在之后计算mAP可以可视化
# image.save("./input/images-optional/"+image_id+".jpg")
yolo.detect_image(image_id, image)
print("Conversion completed!")
效果图

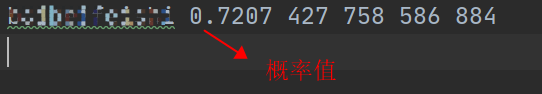
获得测试集真实位置
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 获取测试集的ground-truth
# 具体视频教程可查看
# https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1zE411u7Vw
# ----------------------------------------------------#
import sys
import os
import glob
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
'''
!!!!!!!!!!!!!注意事项!!!!!!!!!!!!!
# 这一部分是当xml有无关的类的时候,下方有代码可以进行筛选!
'''
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得类
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def get_classes(classes_path):
'''loads the classes'''
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
image_ids = open('VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt').read().strip().split()
if not os.path.exists("./input"):
os.makedirs("./input")
if not os.path.exists("./input/ground-truth"):
os.makedirs("./input/ground-truth")
for image_id in image_ids:
with open("./input/ground-truth/" + image_id + ".txt", "w") as new_f:
# root = ET.parse("VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations/" + image_id + ".xml").getroot()
root = ET.parse("VOCdevkit/VOC2007/test_annotations/" + image_id + ".xml").getroot()
for obj in root.findall('object'):
difficult_flag = False
if obj.find('difficult') != None:
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
if int(difficult) == 1:
difficult_flag = True
obj_name = obj.find('name').text
'''
!!!!!!!!!!!!注意事项!!!!!!!!!!!!
# 这一部分是当xml有无关的类的时候,可以取消下面代码的注释
# 利用对应的classes.txt来进行筛选!!!!!!!!!!!!
'''
# classes_path = 'model_data/voc_classes.txt'
# class_names = get_classes(classes_path)
# if obj_name not in class_names:
# continue
bndbox = obj.find('bndbox')
left = bndbox.find('xmin').text
top = bndbox.find('ymin').text
right = bndbox.find('xmax').text
bottom = bndbox.find('ymax').text
if difficult_flag:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s difficult\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
else:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
print("Conversion completed!")
效果图
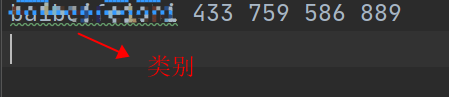
计算mAP主要代码
import glob
import json
import os
import shutil
import operator
import sys
import argparse
import math
import numpy as np
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 用于计算mAP
# 代码克隆自https://github.com/Cartucho/mAP
#----------------------------------------------------#
MINOVERLAP = 0.5 # default value (defined in the PASCAL VOC2012 challenge)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-na', '--no-animation', help="no animation is shown.", action="store_true")
parser.add_argument('-np', '--no-plot', help="no plot is shown.", action="store_true")
parser.add_argument('-q', '--quiet', help="minimalistic console output.", action="store_true")
# argparse receiving list of classes to be ignored
parser.add_argument('-i', '--ignore', nargs='+', type=str, help="ignore a list of classes.")
# argparse receiving list of classes with specific IoU (e.g., python main.py --set-class-iou person 0.7)
parser.add_argument('--set-class-iou', nargs='+', type=str, help="set IoU for a specific class.")
args = parser.parse_args()
'''
0,0 ------> x (width)
|
| (Left,Top)
| *_________
| | |
| |
y |_________|
(height) *
(Right,Bottom)
'''
# if there are no classes to ignore then replace None by empty list
if args.ignore is None:
args.ignore = []
specific_iou_flagged = False
if args.set_class_iou is not None:
specific_iou_flagged = True
# make sure that the cwd() is the location of the python script (so that every path makes sense)
os.chdir(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
GT_PATH = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'input', 'ground-truth')
DR_PATH = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'input', 'detection-results')
# if there are no images then no animation can be shown
IMG_PATH = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'input', 'images-optional')
if os.path.exists(IMG_PATH):
for dirpath, dirnames, files in os.walk(IMG_PATH):
if not files:
# no image files found
args.no_animation = True
else:
args.no_animation = True
# try to import OpenCV if the user didn't choose the option --no-animation
show_animation = False
if not args.no_animation:
try:
import cv2
show_animation = True
except ImportError:
print("\"opencv-python\" not found, please install to visualize the results.")
args.no_animation = True
# try to import Matplotlib if the user didn't choose the option --no-plot
draw_plot = False
if not args.no_plot:
try:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
draw_plot = True
except ImportError:
print("\"matplotlib\" not found, please install it to get the resulting plots.")
args.no_plot = True
def log_average_miss_rate(precision, fp_cumsum, num_images):
"""
log-average miss rate:
Calculated by averaging miss rates at 9 evenly spaced FPPI points
between 10e-2 and 10e0, in log-space.
output:
lamr | log-average miss rate
mr | miss rate
fppi | false positives per image
references:
[1] Dollar, Piotr, et al. "Pedestrian Detection: An Evaluation of the
State of the Art." Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE
Transactions on 34.4 (2012): 743 - 761.
"""
# if there were no detections of that class
if precision.size == 0:
lamr = 0
mr = 1
fppi = 0
return lamr, mr, fppi
fppi = fp_cumsum / float(num_images)
mr = (1 - precision)
fppi_tmp = np.insert(fppi, 0, -1.0)
mr_tmp = np.insert(mr, 0, 1.0)
# Use 9 evenly spaced reference points in log-space
ref = np.logspace(-2.0, 0.0, num = 9)
for i, ref_i in enumerate(ref):
# np.where() will always find at least 1 index, since min(ref) = 0.01 and min(fppi_tmp) = -1.0
j = np.where(fppi_tmp <= ref_i)[-1][-1]
ref[i] = mr_tmp[j]
# log(0) is undefined, so we use the np.maximum(1e-10, ref)
lamr = math.exp(np.mean(np.log(np.maximum(1e-10, ref))))
return lamr, mr, fppi
"""
throw error and exit
"""
def error(msg):
print(msg)
sys.exit(0)
"""
check if the number is a float between 0.0 and 1.0
"""
def is_float_between_0_and_1(value):
try:
val = float(value)
if val > 0.0 and val < 1.0:
return True
else:
return False
except ValueError:
return False
"""
Calculate the AP given the recall and precision array
1st) We compute a version of the measured precision/recall curve with
precision monotonically decreasing
2nd) We compute the AP as the area under this curve by numerical integration.
"""
def voc_ap(rec, prec):
"""
--- Official matlab code VOC2012---
mrec=[0 ; rec ; 1];
mpre=[0 ; prec ; 0];
for i=numel(mpre)-1:-1:1
mpre(i)=max(mpre(i),mpre(i+1));
end
i=find(mrec(2:end)~=mrec(1:end-1))+1;
ap=sum((mrec(i)-mrec(i-1)).*mpre(i));
"""
rec.insert(0, 0.0) # insert 0.0 at begining of list
rec.append(1.0) # insert 1.0 at end of list
mrec = rec[:]
prec.insert(0, 0.0) # insert 0.0 at begining of list
prec.append(0.0) # insert 0.0 at end of list
mpre = prec[:]
"""
This part makes the precision monotonically decreasing
(goes from the end to the beginning)
matlab: for i=numel(mpre)-1:-1:1
mpre(i)=max(mpre(i),mpre(i+1));
"""
# matlab indexes start in 1 but python in 0, so I have to do:
# range(start=(len(mpre) - 2), end=0, step=-1)
# also the python function range excludes the end, resulting in:
# range(start=(len(mpre) - 2), end=-1, step=-1)
for i in range(len(mpre)-2, -1, -1):
mpre[i] = max(mpre[i], mpre[i+1])
"""
This part creates a list of indexes where the recall changes
matlab: i=find(mrec(2:end)~=mrec(1:end-1))+1;
"""
i_list = []
for i in range(1, len(mrec)):
if mrec[i] != mrec[i-1]:
i_list.append(i) # if it was matlab would be i + 1
"""
The Average Precision (AP) is the area under the curve
(numerical integration)
matlab: ap=sum((mrec(i)-mrec(i-1)).*mpre(i));
"""
ap = 0.0
for i in i_list:
ap += ((mrec[i]-mrec[i-1])*mpre[i])
return ap, mrec, mpre
"""
Convert the lines of a file to a list
"""
def file_lines_to_list(path):
# open txt file lines to a list
with open(path) as f:
content = f.readlines()
# remove whitespace characters like `\n` at the end of each line
content = [x.strip() for x in content]
return content
"""
Draws text in image
"""
def draw_text_in_image(img, text, pos, color, line_width):
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN
fontScale = 1
lineType = 1
bottomLeftCornerOfText = pos
cv2.putText(img, text,
bottomLeftCornerOfText,
font,
fontScale,
color,
lineType)
text_width, _ = cv2.getTextSize(text, font, fontScale, lineType)[0]
return img, (line_width + text_width)
"""
Plot - adjust axes
"""
def adjust_axes(r, t, fig, axes):
# get text width for re-scaling
bb = t.get_window_extent(renderer=r)
text_width_inches = bb.width / fig.dpi
# get axis width in inches
current_fig_width = fig.get_figwidth()
new_fig_width = current_fig_width + text_width_inches
propotion = new_fig_width / current_fig_width
# get axis limit
x_lim = axes.get_xlim()
axes.set_xlim([x_lim[0], x_lim[1]*propotion])
"""
Draw plot using Matplotlib
"""
def draw_plot_func(dictionary, n_classes, window_title, plot_title, x_label, output_path, to_show, plot_color, true_p_bar):
# sort the dictionary by decreasing value, into a list of tuples
sorted_dic_by_value = sorted(dictionary.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1))
# unpacking the list of tuples into two lists
sorted_keys, sorted_values = zip(*sorted_dic_by_value)
#
if true_p_bar != "":
"""
Special case to draw in:
- green -> TP: True Positives (object detected and matches ground-truth)
- red -> FP: False Positives (object detected but does not match ground-truth)
- orange -> FN: False Negatives (object not detected but present in the ground-truth)
"""
fp_sorted = []
tp_sorted = []
for key in sorted_keys:
fp_sorted.append(dictionary[key] - true_p_bar[key])
tp_sorted.append(true_p_bar[key])
plt.barh(range(n_classes), fp_sorted, align='center', color='crimson', label='False Positive')
plt.barh(range(n_classes), tp_sorted, align='center', color='forestgreen', label='True Positive', left=fp_sorted)
# add legend
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
"""
Write number on side of bar
"""
fig = plt.gcf() # gcf - get current figure
axes = plt.gca()
r = fig.canvas.get_renderer()
for i, val in enumerate(sorted_values):
fp_val = fp_sorted[i]
tp_val = tp_sorted[i]
fp_str_val = " " + str(fp_val)
tp_str_val = fp_str_val + " " + str(tp_val)
# trick to paint multicolor with offset:
# first paint everything and then repaint the first number
t = plt.text(val, i, tp_str_val, color='forestgreen', va='center', fontweight='bold')
plt.text(val, i, fp_str_val, color='crimson', va='center', fontweight='bold')
if i == (len(sorted_values)-1): # largest bar
adjust_axes(r, t, fig, axes)
else:
plt.barh(range(n_classes), sorted_values, color=plot_color)
"""
Write number on side of bar
"""
fig = plt.gcf() # gcf - get current figure
axes = plt.gca()
r = fig.canvas.get_renderer()
for i, val in enumerate(sorted_values):
str_val = " " + str(val) # add a space before
if val < 1.0:
str_val = " {0:.2f}".format(val)
t = plt.text(val, i, str_val, color=plot_color, va='center', fontweight='bold')
# re-set axes to show number inside the figure
if i == (len(sorted_values)-1): # largest bar
adjust_axes(r, t, fig, axes)
# set window title
fig.canvas.set_window_title(window_title)
# write classes in y axis
tick_font_size = 12
plt.yticks(range(n_classes), sorted_keys, fontsize=tick_font_size)
"""
Re-scale height accordingly
"""
init_height = fig.get_figheight()
# comput the matrix height in points and inches
dpi = fig.dpi
height_pt = n_classes * (tick_font_size * 1.4) # 1.4 (some spacing)
height_in = height_pt / dpi
# compute the required figure height
top_margin = 0.15 # in percentage of the figure height
bottom_margin = 0.05 # in percentage of the figure height
figure_height = height_in / (1 - top_margin - bottom_margin)
# set new height
if figure_height > init_height:
fig.set_figheight(figure_height)
# set plot title
plt.title(plot_title, fontsize=14)
# set axis titles
# plt.xlabel('classes')
plt.xlabel(x_label, fontsize='large')
# adjust size of window
fig.tight_layout()
# save the plot
fig.savefig(output_path)
# show image
if to_show:
plt.show()
# close the plot
plt.close()
"""
Create a ".temp_files/" and "results/" directory
"""
TEMP_FILES_PATH = ".temp_files"
if not os.path.exists(TEMP_FILES_PATH): # if it doesn't exist already
os.makedirs(TEMP_FILES_PATH)
results_files_path = "results"
if os.path.exists(results_files_path): # if it exist already
# reset the results directory
shutil.rmtree(results_files_path)
os.makedirs(results_files_path)
if draw_plot:
os.makedirs(os.path.join(results_files_path, "AP"))
os.makedirs(os.path.join(results_files_path, "F1"))
os.makedirs(os.path.join(results_files_path, "Recall"))
os.makedirs(os.path.join(results_files_path, "Precision"))
if show_animation:
os.makedirs(os.path.join(results_files_path, "images", "detections_one_by_one"))
"""
ground-truth
Load each of the ground-truth files into a temporary ".json" file.
Create a list of all the class names present in the ground-truth (gt_classes).
"""
# get a list with the ground-truth files
ground_truth_files_list = glob.glob(GT_PATH + '/*.txt')
if len(ground_truth_files_list) == 0:
error("Error: No ground-truth files found!")
ground_truth_files_list.sort()
# dictionary with counter per class
gt_counter_per_class = {}
counter_images_per_class = {}
for txt_file in ground_truth_files_list:
#print(txt_file)
file_id = txt_file.split(".txt", 1)[0]
file_id = os.path.basename(os.path.normpath(file_id))
# check if there is a correspondent detection-results file
temp_path = os.path.join(DR_PATH, (file_id + ".txt"))
if not os.path.exists(temp_path):
error_msg = "Error. File not found: {}\n".format(temp_path)
error_msg += "(You can avoid this error message by running extra/intersect-gt-and-dr.py)"
error(error_msg)
lines_list = file_lines_to_list(txt_file)
# create ground-truth dictionary
bounding_boxes = []
is_difficult = False
already_seen_classes = []
for line in lines_list:
try:
if "difficult" in line:
class_name, left, top, right, bottom, _difficult = line.split()
is_difficult = True
else:
class_name, left, top, right, bottom = line.split()
except:
if "difficult" in line:
line_split = line.split()
_difficult = line_split[-1]
bottom = line_split[-2]
right = line_split[-3]
top = line_split[-4]
left = line_split[-5]
class_name = ""
for name in line_split[:-5]:
class_name += name
is_difficult = True
else:
line_split = line.split()
bottom = line_split[-1]
right = line_split[-2]
top = line_split[-3]
left = line_split[-4]
class_name = ""
for name in line_split[:-4]:
class_name += name
# check if class is in the ignore list, if yes skip
if class_name in args.ignore:
continue
bbox = left + " " + top + " " + right + " " +bottom
if is_difficult:
bounding_boxes.append({"class_name":class_name, "bbox":bbox, "used":False, "difficult":True})
is_difficult = False
else:
bounding_boxes.append({"class_name":class_name, "bbox":bbox, "used":False})
# count that object
if class_name in gt_counter_per_class:
gt_counter_per_class[class_name] += 1
else:
# if class didn't exist yet
gt_counter_per_class[class_name] = 1
if class_name not in already_seen_classes:
if class_name in counter_images_per_class:
counter_images_per_class[class_name] += 1
else:
# if class didn't exist yet
counter_images_per_class[class_name] = 1
already_seen_classes.append(class_name)
# dump bounding_boxes into a ".json" file
with open(TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + file_id + "_ground_truth.json", 'w') as outfile:
json.dump(bounding_boxes, outfile)
gt_classes = list(gt_counter_per_class.keys())
# let's sort the classes alphabetically
gt_classes = sorted(gt_classes)
n_classes = len(gt_classes)
#print(gt_classes)
#print(gt_counter_per_class)
"""
Check format of the flag --set-class-iou (if used)
e.g. check if class exists
"""
if specific_iou_flagged:
n_args = len(args.set_class_iou)
error_msg = \
'\n --set-class-iou [class_1] [IoU_1] [class_2] [IoU_2] [...]'
if n_args % 2 != 0:
error('Error, missing arguments. Flag usage:' + error_msg)
# [class_1] [IoU_1] [class_2] [IoU_2]
# specific_iou_classes = ['class_1', 'class_2']
specific_iou_classes = args.set_class_iou[::2] # even
# iou_list = ['IoU_1', 'IoU_2']
iou_list = args.set_class_iou[1::2] # odd
if len(specific_iou_classes) != len(iou_list):
error('Error, missing arguments. Flag usage:' + error_msg)
for tmp_class in specific_iou_classes:
if tmp_class not in gt_classes:
error('Error, unknown class \"' + tmp_class + '\". Flag usage:' + error_msg)
for num in iou_list:
if not is_float_between_0_and_1(num):
error('Error, IoU must be between 0.0 and 1.0. Flag usage:' + error_msg)
"""
detection-results
Load each of the detection-results files into a temporary ".json" file.
"""
# get a list with the detection-results files
dr_files_list = glob.glob(DR_PATH + '/*.txt')
dr_files_list.sort()
for class_index, class_name in enumerate(gt_classes):
bounding_boxes = []
for txt_file in dr_files_list:
#print(txt_file)
# the first time it checks if all the corresponding ground-truth files exist
file_id = txt_file.split(".txt",1)[0]
file_id = os.path.basename(os.path.normpath(file_id))
temp_path = os.path.join(GT_PATH, (file_id + ".txt"))
if class_index == 0:
if not os.path.exists(temp_path):
error_msg = "Error. File not found: {}\n".format(temp_path)
error_msg += "(You can avoid this error message by running extra/intersect-gt-and-dr.py)"
error(error_msg)
lines = file_lines_to_list(txt_file)
for line in lines:
try:
tmp_class_name, confidence, left, top, right, bottom = line.split()
except:
line_split = line.split()
bottom = line_split[-1]
right = line_split[-2]
top = line_split[-3]
left = line_split[-4]
confidence = line_split[-5]
tmp_class_name = ""
for name in line_split[:-5]:
tmp_class_name += name
if tmp_class_name == class_name:
#print("match")
bbox = left + " " + top + " " + right + " " +bottom
bounding_boxes.append({"confidence":confidence, "file_id":file_id, "bbox":bbox})
#print(bounding_boxes)
# sort detection-results by decreasing confidence
bounding_boxes.sort(key=lambda x:float(x['confidence']), reverse=True)
with open(TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + class_name + "_dr.json", 'w') as outfile:
json.dump(bounding_boxes, outfile)
"""
Calculate the AP for each class
"""
sum_AP = 0.0
ap_dictionary = {}
lamr_dictionary = {}
# open file to store the results
with open(results_files_path + "/results.txt", 'w') as results_file:
results_file.write("# AP and precision/recall per class\n")
count_true_positives = {}
for class_index, class_name in enumerate(gt_classes):
count_true_positives[class_name] = 0
"""
Load detection-results of that class
"""
dr_file = TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + class_name + "_dr.json"
dr_data = json.load(open(dr_file))
"""
Assign detection-results to ground-truth objects
"""
nd = len(dr_data)
tp = [0] * nd # creates an array of zeros of size nd
fp = [0] * nd
score = [0] * nd
score05_idx = 0
for idx, detection in enumerate(dr_data):
file_id = detection["file_id"]
score[idx] = float(detection["confidence"])
if score[idx] > 0.5:
score05_idx = idx
if show_animation:
# find ground truth image
ground_truth_img = glob.glob1(IMG_PATH, file_id + ".*")
#tifCounter = len(glob.glob1(myPath,"*.tif"))
if len(ground_truth_img) == 0:
error("Error. Image not found with id: " + file_id)
elif len(ground_truth_img) > 1:
error("Error. Multiple image with id: " + file_id)
else: # found image
#print(IMG_PATH + "/" + ground_truth_img[0])
# Load image
img = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH + "/" + ground_truth_img[0])
# load image with draws of multiple detections
img_cumulative_path = results_files_path + "/images/" + ground_truth_img[0]
if os.path.isfile(img_cumulative_path):
img_cumulative = cv2.imread(img_cumulative_path)
else:
img_cumulative = img.copy()
# Add bottom border to image
bottom_border = 60
BLACK = [0, 0, 0]
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, 0, bottom_border, 0, 0, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=BLACK)
# assign detection-results to ground truth object if any
# open ground-truth with that file_id
gt_file = TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + file_id + "_ground_truth.json"
ground_truth_data = json.load(open(gt_file))
ovmax = -1
gt_match = -1
# load detected object bounding-box
bb = [ float(x) for x in detection["bbox"].split() ]
for obj in ground_truth_data:
# look for a class_name match
if obj["class_name"] == class_name:
bbgt = [ float(x) for x in obj["bbox"].split() ]
bi = [max(bb[0],bbgt[0]), max(bb[1],bbgt[1]), min(bb[2],bbgt[2]), min(bb[3],bbgt[3])]
iw = bi[2] - bi[0] + 1
ih = bi[3] - bi[1] + 1
if iw > 0 and ih > 0:
# compute overlap (IoU) = area of intersection / area of union
ua = (bb[2] - bb[0] + 1) * (bb[3] - bb[1] + 1) + (bbgt[2] - bbgt[0]
+ 1) * (bbgt[3] - bbgt[1] + 1) - iw * ih
ov = iw * ih / ua
if ov > ovmax:
ovmax = ov
gt_match = obj
# assign detection as true positive/don't care/false positive
if show_animation:
status = "NO MATCH FOUND!" # status is only used in the animation
# set minimum overlap
min_overlap = MINOVERLAP
if specific_iou_flagged:
if class_name in specific_iou_classes:
index = specific_iou_classes.index(class_name)
min_overlap = float(iou_list[index])
if ovmax >= min_overlap:
if "difficult" not in gt_match:
if not bool(gt_match["used"]):
# true positive
tp[idx] = 1
gt_match["used"] = True
count_true_positives[class_name] += 1
# update the ".json" file
with open(gt_file, 'w') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(ground_truth_data))
if show_animation:
status = "MATCH!"
else:
# false positive (multiple detection)
fp[idx] = 1
if show_animation:
status = "REPEATED MATCH!"
else:
# false positive
fp[idx] = 1
if ovmax > 0:
status = "INSUFFICIENT OVERLAP"
"""
Draw image to show animation
"""
if show_animation:
height, widht = img.shape[:2]
# colors (OpenCV works with BGR)
white = (255,255,255)
light_blue = (255,200,100)
green = (0,255,0)
light_red = (30,30,255)
# 1st line
margin = 10
v_pos = int(height - margin - (bottom_border / 2.0))
text = "Image: " + ground_truth_img[0] + " "
img, line_width = draw_text_in_image(img, text, (margin, v_pos), white, 0)
text = "Class [" + str(class_index) + "/" + str(n_classes) + "]: " + class_name + " "
img, line_width = draw_text_in_image(img, text, (margin + line_width, v_pos), light_blue, line_width)
if ovmax != -1:
color = light_red
if status == "INSUFFICIENT OVERLAP":
text = "IoU: {0:.2f}% ".format(ovmax*100) + "< {0:.2f}% ".format(min_overlap*100)
else:
text = "IoU: {0:.2f}% ".format(ovmax*100) + ">= {0:.2f}% ".format(min_overlap*100)
color = green
img, _ = draw_text_in_image(img, text, (margin + line_width, v_pos), color, line_width)
# 2nd line
v_pos += int(bottom_border / 2.0)
rank_pos = str(idx+1) # rank position (idx starts at 0)
text = "Detection #rank: " + rank_pos + " confidence: {0:.2f}% ".format(float(detection["confidence"])*100)
img, line_width = draw_text_in_image(img, text, (margin, v_pos), white, 0)
color = light_red
if status == "MATCH!":
color = green
text = "Result: " + status + " "
img, line_width = draw_text_in_image(img, text, (margin + line_width, v_pos), color, line_width)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
if ovmax > 0: # if there is intersections between the bounding-boxes
bbgt = [ int(round(float(x))) for x in gt_match["bbox"].split() ]
cv2.rectangle(img,(bbgt[0],bbgt[1]),(bbgt[2],bbgt[3]),light_blue,2)
cv2.rectangle(img_cumulative,(bbgt[0],bbgt[1]),(bbgt[2],bbgt[3]),light_blue,2)
cv2.putText(img_cumulative, class_name, (bbgt[0],bbgt[1] - 5), font, 0.6, light_blue, 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
bb = [int(i) for i in bb]
cv2.rectangle(img,(bb[0],bb[1]),(bb[2],bb[3]),color,2)
cv2.rectangle(img_cumulative,(bb[0],bb[1]),(bb[2],bb[3]),color,2)
cv2.putText(img_cumulative, class_name, (bb[0],bb[1] - 5), font, 0.6, color, 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
# show image
cv2.imshow("Animation", img)
cv2.waitKey(20) # show for 20 ms
# save image to results
output_img_path = results_files_path + "/images/detections_one_by_one/" + class_name + "_detection" + str(idx) + ".jpg"
cv2.imwrite(output_img_path, img)
# save the image with all the objects drawn to it
cv2.imwrite(img_cumulative_path, img_cumulative)
# compute precision/recall
cumsum = 0
for idx, val in enumerate(fp):
fp[idx] += cumsum
cumsum += val
cumsum = 0
for idx, val in enumerate(tp):
tp[idx] += cumsum
cumsum += val
#print(tp)
rec = tp[:]
for idx, val in enumerate(tp):
rec[idx] = float(tp[idx]) / gt_counter_per_class[class_name]
#print(rec)
prec = tp[:]
for idx, val in enumerate(tp):
prec[idx] = float(tp[idx]) / (fp[idx] + tp[idx])
#print(prec)
ap, mrec, mprec = voc_ap(rec[:], prec[:])
F1 = np.array(rec)*np.array(prec)/(np.array(prec)+np.array(rec))*2
sum_AP += ap
text = "{0:.2f}%".format(ap*100) + " = " + class_name + " AP " #class_name + " AP = {0:.2f}%".format(ap*100)
if len(prec)>0:
F1_text = "{0:.2f}".format(F1[score05_idx]) + " = " + class_name + " F1 "
Recall_text = "{0:.2f}%".format(rec[score05_idx]*100) + " = " + class_name + " Recall "
Precision_text = "{0:.2f}%".format(prec[score05_idx]*100) + " = " + class_name + " Precision "
else:
F1_text = "0.00" + " = " + class_name + " F1 "
Recall_text = "0.00%" + " = " + class_name + " Recall "
Precision_text = "0.00%" + " = " + class_name + " Precision "
"""
Write to results.txt
"""
rounded_prec = [ '%.2f' % elem for elem in prec ]
rounded_rec = [ '%.2f' % elem for elem in rec ]
results_file.write(text + "\n Precision: " + str(rounded_prec) + "\n Recall :" + str(rounded_rec) + "\n\n")
if not args.quiet:
if(len(rec)!=0):
print(text + "\t||\tscore_threhold=0.5 : " + "F1=" + "{0:.2f}".format(F1[score05_idx])\
+ " ; Recall=" + "{0:.2f}%".format(rec[score05_idx]*100) + " ; Precision=" + "{0:.2f}%".format(prec[score05_idx]*100))
ap_dictionary[class_name] = ap
n_images = counter_images_per_class[class_name]
lamr, mr, fppi = log_average_miss_rate(np.array(rec), np.array(fp), n_images)
lamr_dictionary[class_name] = lamr
"""
Draw plot
"""
if draw_plot:
plt.plot(rec, prec, '-o')
# add a new penultimate point to the list (mrec[-2], 0.0)
# since the last line segment (and respective area) do not affect the AP value
area_under_curve_x = mrec[:-1] + [mrec[-2]] + [mrec[-1]]
area_under_curve_y = mprec[:-1] + [0.0] + [mprec[-1]]
plt.fill_between(area_under_curve_x, 0, area_under_curve_y, alpha=0.2, edgecolor='r')
# set window title
fig = plt.gcf() # gcf - get current figure
fig.canvas.set_window_title('AP ' + class_name)
# set plot title
plt.title('class: ' + text)
#plt.suptitle('This is a somewhat long figure title', fontsize=16)
# set axis titles
plt.xlabel('Recall')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
# optional - set axes
axes = plt.gca() # gca - get current axes
axes.set_xlim([0.0,1.0])
axes.set_ylim([0.0,1.05]) # .05 to give some extra space
# Alternative option -> wait for button to be pressed
# while not plt.waitforbuttonpress(): pass # wait for key display
# Alternative option -> normal display
# plt.show()
# save the plot
fig.savefig(results_files_path + "/AP/" + class_name + ".png")
plt.cla() # clear axes for next plot
plt.plot(score, F1, "-", color='orangered')
plt.title('class: ' + F1_text + "\nscore_threhold=0.5")
plt.xlabel('Score_Threhold')
plt.ylabel('F1')
axes = plt.gca() # gca - get current axes
axes.set_xlim([0.0,1.0])
axes.set_ylim([0.0,1.05]) # .05 to give some extra space
fig.savefig(results_files_path + "/F1/" + class_name + ".png")
plt.cla() # clear axes for next plot
plt.plot(score, rec, "-H", color='gold')
plt.title('class: ' + Recall_text + "\nscore_threhold=0.5")
plt.xlabel('Score_Threhold')
plt.ylabel('Recall')
axes = plt.gca() # gca - get current axes
axes.set_xlim([0.0,1.0])
axes.set_ylim([0.0,1.05]) # .05 to give some extra space
fig.savefig(results_files_path + "/Recall/" + class_name + ".png")
plt.cla() # clear axes for next plot
plt.plot(score, prec, "-s", color='palevioletred')
plt.title('class: ' + Precision_text + "\nscore_threhold=0.5")
plt.xlabel('Score_Threhold')
plt.ylabel('Precision')
axes = plt.gca() # gca - get current axes
axes.set_xlim([0.0,1.0])
axes.set_ylim([0.0,1.05]) # .05 to give some extra space
fig.savefig(results_files_path + "/Precision/" + class_name + ".png")
plt.cla() # clear axes for next plot
if show_animation:
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
results_file.write("\n# mAP of all classes\n")
mAP = sum_AP / n_classes
text = "mAP = {0:.2f}%".format(mAP*100)
results_file.write(text + "\n")
print(text)
# remove the temp_files directory
shutil.rmtree(TEMP_FILES_PATH)
"""
Count total of detection-results
"""
# iterate through all the files
det_counter_per_class = {}
for txt_file in dr_files_list:
# get lines to list
lines_list = file_lines_to_list(txt_file)
for line in lines_list:
class_name = line.split()[0]
# check if class is in the ignore list, if yes skip
if class_name in args.ignore:
continue
# count that object
if class_name in det_counter_per_class:
det_counter_per_class[class_name] += 1
else:
# if class didn't exist yet
det_counter_per_class[class_name] = 1
#print(det_counter_per_class)
dr_classes = list(det_counter_per_class.keys())
"""
Plot the total number of occurences of each class in the ground-truth
"""
if draw_plot:
window_title = "ground-truth-info"
plot_title = "ground-truth\n"
plot_title += "(" + str(len(ground_truth_files_list)) + " files and " + str(n_classes) + " classes)"
x_label = "Number of objects per class"
output_path = results_files_path + "/ground-truth-info.png"
to_show = False
plot_color = 'forestgreen'
draw_plot_func(
gt_counter_per_class,
n_classes,
window_title,
plot_title,
x_label,
output_path,
to_show,
plot_color,
'',
)
"""
Write number of ground-truth objects per class to results.txt
"""
with open(results_files_path + "/results.txt", 'a') as results_file:
results_file.write("\n# Number of ground-truth objects per class\n")
for class_name in sorted(gt_counter_per_class):
results_file.write(class_name + ": " + str(gt_counter_per_class[class_name]) + "\n")
"""
Finish counting true positives
"""
for class_name in dr_classes:
# if class exists in detection-result but not in ground-truth then there are no true positives in that class
if class_name not in gt_classes:
count_true_positives[class_name] = 0
#print(count_true_positives)
"""
Plot the total number of occurences of each class in the "detection-results" folder
"""
if draw_plot:
window_title = "detection-results-info"
# Plot title
plot_title = "detection-results\n"
plot_title += "(" + str(len(dr_files_list)) + " files and "
count_non_zero_values_in_dictionary = sum(int(x) > 0 for x in list(det_counter_per_class.values()))
plot_title += str(count_non_zero_values_in_dictionary) + " detected classes)"
# end Plot title
x_label = "Number of objects per class"
output_path = results_files_path + "/detection-results-info.png"
to_show = False
plot_color = 'forestgreen'
true_p_bar = count_true_positives
draw_plot_func(
det_counter_per_class,
len(det_counter_per_class),
window_title,
plot_title,
x_label,
output_path,
to_show,
plot_color,
true_p_bar
)
"""
Write number of detected objects per class to results.txt
"""
with open(results_files_path + "/results.txt", 'a') as results_file:
results_file.write("\n# Number of detected objects per class\n")
for class_name in sorted(dr_classes):
n_det = det_counter_per_class[class_name]
text = class_name + ": " + str(n_det)
text += " (tp:" + str(count_true_positives[class_name]) + ""
text += ", fp:" + str(n_det - count_true_positives[class_name]) + ")\n"
results_file.write(text)
"""
Draw log-average miss rate plot (Show lamr of all classes in decreasing order)
"""
if draw_plot:
window_title = "lamr"
plot_title = "log-average miss rate"
x_label = "log-average miss rate"
output_path = results_files_path + "/lamr.png"
to_show = False
plot_color = 'royalblue'
draw_plot_func(
lamr_dictionary,
n_classes,
window_title,
plot_title,
x_label,
output_path,
to_show,
plot_color,
""
)
"""
Draw mAP plot (Show AP's of all classes in decreasing order)
"""
if draw_plot:
window_title = "mAP"
plot_title = "mAP = {0:.2f}%".format(mAP*100)
x_label = "Average Precision"
output_path = results_files_path + "/mAP.png"
to_show = True
plot_color = 'royalblue'
draw_plot_func(
ap_dictionary,
n_classes,
window_title,
plot_title,
x_label,
output_path,
to_show,
plot_color,
""
)
写完博客发现,这个方法有一个问题,我生成的xml文件其实是我当前的权重预测生成的,并不能代表真实的泛化情况,主要是记录一下mAP的计算过程,标注推荐百度的easydl平台。
Yolov4完整代码
完整代码实现可以参考这个博主的实现
bubbliiiing/mobilenet-yolov4-lite-keras.




















 1426
1426











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








