IO是什么?
IO指对数据的输入和输出,其Java类库采用装饰者模式实现,可按需封装对数据的操作
常用方法
| 方法 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| read() | 读取一个字节(Unicode码元),遇到结尾返回-1 |
| read(byte[]) | 读取特定容量字节到数组 |
| available() | 在非阻塞情况下获取字节数量,read之前调用可避免流阻塞 |
| skip(long) | 在输入流中跳过n个字节,返回实际跳过的字节数 |
| write(int) | 写出一个字节(Unicode码元) |
| write(byte[]) | 写出一个字节数组 |
| flush() | 刷新缓冲区 |
| close() | 关闭IO并刷新缓冲区 |
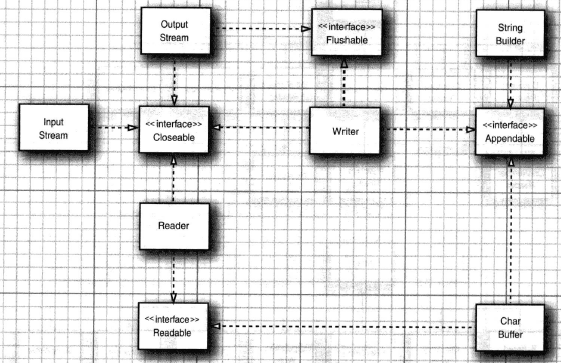
顶级接口
| 接口 | 子类 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| Closeable | InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer | 其close()用于关闭流及try-with-resource语句 |
| Flushable | OutputStream、Writer | 其flush()用于刷新缓冲区 |
| Readable | Reader | 其read(CharBuffer)实现顺序和随机读写 |
| Appenable | Writer | 其append()用于实现添加字符或字符串 |
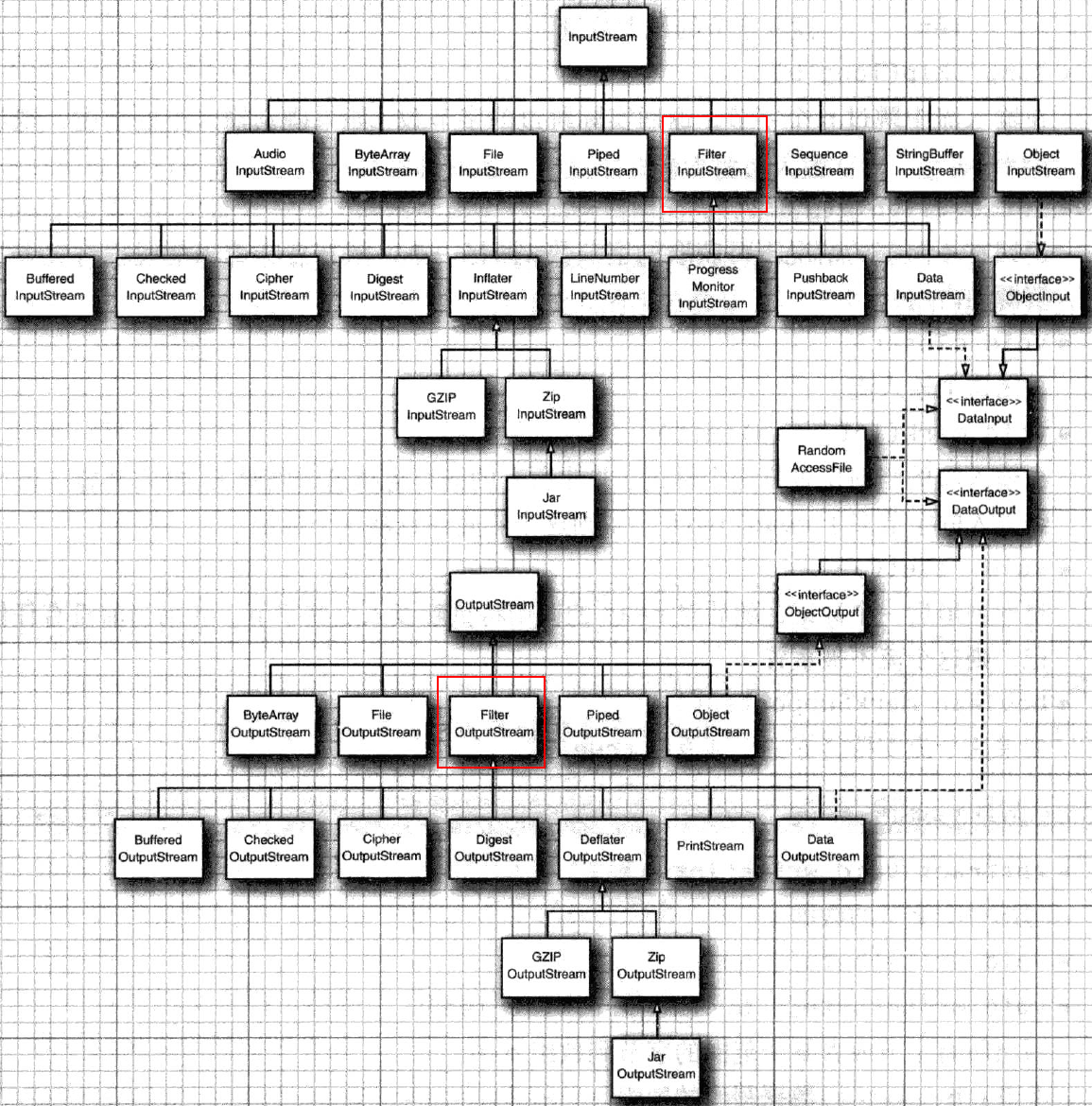
IO字节流家族
FilterInputStream及其子类用于装饰InputStream子类,输出同理
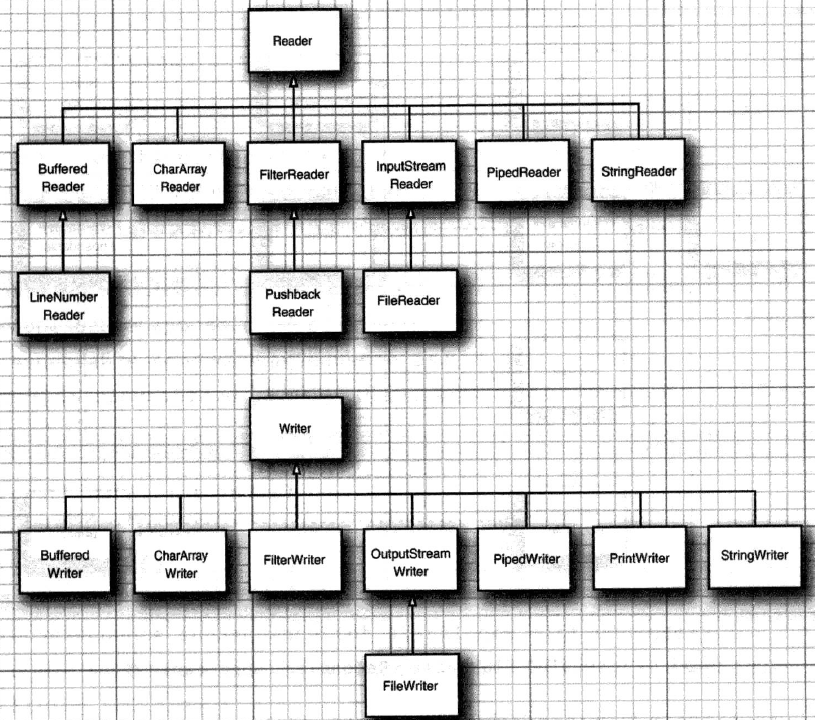
IO字符流家族
Reader及其子类将字节输入流转为Unicode码元输入流
Writer及其子类将Unicode码元输出流转为字节输出流
对字节的IO操作
对字节的IO操作由InputStream、OutputStream及它们的子类组成
写控制台——System.out
System.out是PrintStream(FilterOutputStream)类型,其输出位置为控制台
System.out.println(1);
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.println(1);
读控制台——Scanner和System.in
System.in是InputStream类型,其输入位置为控制台
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
if (scan.hasNext()) {
String str = scan.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
scan.close();
通过Scanner可以获得从控制台的输入,此外Scanner还可以读取文件
- nextLine 读取一行,以回车换行为结束标致
- next 读取一个单词,以空白符作为结束标志
- nextInt 读取一个整数
写文件——FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream用于写文件,其write()写入byte[],如下实现对特定文件写入字符串
private void write(File file, String msg) {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
fileOutputStream.write(msg.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
调用过程,如向文件data.txt写0123456
write(new File(getExternalFilesDir(DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS), "data.txt"),"0123456")
二进制写文件——DataOutputStream+FileOutputStream
writeInt将整数写为4字节的二进制值
public void write(File file, int msg) {
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null;
try {
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
dataOutputStream.writeInt(msg);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (dataOutputStream != null) {
try {
dataOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
对象写文件——ObjectOutputStream+FileOutputStream
要写入的对象需实现Serializable接口
public void write(File file, Person person) {
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null;
try {
objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(person);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (objectOutputStream != null) {
objectOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
读文件——FileInputStream
FileInputStream用于读文件,其read()方法默认读取第一个字节,返回其int类型的ASCII码
public int read(File file) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
int result = -1;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
result = fileInputStream.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileInputStream != null) {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return result;
}
调用过程,如从data.txt(0123456)读第一个字节的ASSIC码(0→48),并将其转为String
byte[] read = read(new File(getExternalFilesDir(DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS), "data.txt"));
String s = new String(read);
System.out.println(s);
利用其重载方法read(byte[] byte)可实现读取特定字节到byte数组
public byte[] read(File file) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
byte[] result = new byte[10];
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
fileInputStream.read(result);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileInputStream != null) {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
return result;
}
调用过程,如从data.txt(123456)读10个字节的ASSIC码,最终为[49,50,51,52,53,54,0,0](00为\r\n)并去掉多余字符
byte[] temp = read(new File(getExternalFilesDir(DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS), "data.txt"));
int reallyLength = 0;
while (reallyLength < temp.length) {
if (temp[reallyLength] == 0) {
break;
}
reallyLength++;
}
byte[] read = Arrays.copyOf(temp, reallyLength);
String s = new String(read);
System.out.println(s);
通常我们不知道文件具体的字节数,可能导致对byte[]设置过小无法读取全部数据,那如何判断文件的末尾并读取全部数据呢
二进制读文件——DataInputStream+FileInputStream
readInt将4字节的二进制值读取为整型
private int read(File file) {
DataInputStream dataInputStream = null;
int result = -1;
try {
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
result = dataInputStream.readInt();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (dataInputStream != null) {
try {
dataInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return result;
}
对象读文件——ObjectInputStream+FileInputStream
要读入的对象需实现Serializable接口
private Person read(File file) {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null;
Person person = null;
try {
objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
person = (Person) objectInputStream.readObject();
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (objectInputStream != null) {
try {
objectInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return person;
}
对字符的IO操作
一个字符可能由多个字节组成,故对字符的IO操作由Reader、Writer及它们的子类组成
写文件——OutputStreamWriter+FileOutputStream
public void write(File file, String msg) {
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = null;
try {
outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file));
outputStreamWriter.write(msg);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (outputStreamWriter != null) {
try {
outputStreamWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
缓冲写文件——BufferedWriter+OutputStreamWriter+FileOutputStream(常用)
public void write(File file, String msg) {
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;
try {
bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file)));
bufferedWriter.write(msg);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (bufferedWriter != null) {
bufferedWriter.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
打印写文件——PrintWriter+OutputStreamWriter+FileOutputStream
PrintWriter有print、print和printf用于打印各种类型的数据,其自带缓冲区,可通过构造函数设置自动缓冲模式
public void write(File file, String msg) {
PrintWriter printWriter = null;
try {
printWriter = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file)));
printWriter.print(msg);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (printWriter != null) {
printWriter.close();
}
}
}
print()不抛异常,可通过checkError查看是否出现异常
读文件——InputStreamReader+FileInputStream
缓冲读文件——BufferedReader+InputStreamReader+FileInputStream(常用)
private String read(File file) {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
try {
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)));
String line = "";
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
stringBuilder.append(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (bufferedReader != null) {
try {
bufferedReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}





















 211
211











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








