本篇文章采用的是单机模式,具体可以参考官网redisson介绍。
Redisson源码分析
Redisson实现了Lock接口,对比Lock而言,是可重入锁,功能强大,源码复杂。
加锁
用代码举例子
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
RedissonClient client = Redisson.create(config);
RLock lock = client.getLock("lock1");
try {
// 加锁
lock.lock();
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}RLock lock = client.getLock("lock1");这句代码就是为了获取锁的实例。
查看 lock.lock(); 的源码
@Override
public void lock() {
try {
lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}查看 lockInterruptibly 方法
@Override
public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// 获取当前线程的id
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// 尝试获取锁
Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired ,ttl为空,说明成功获取锁,返回
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
// 如果获取锁失败,则订阅到对应这个锁的channel
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
try {
//
while (true) {
// 再次尝试获取锁
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired , ttl为空,说明成功获取锁,返回
if (ttl == null) {
break;
}
// waiting for message , ttl大于0 则等待ttl时间后继续尝试获取
if (ttl >= 0) {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
}
}
} finally {
// 取消对channel的订阅
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
// get(lockAsync(leaseTime, unit));
}流程图:

查看 tryAcquireAsync 方法
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {
// 如果存在过期时间,按照正常费那事获取锁
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
// 读取配置的默认加锁时间30秒执行获取锁的 private long lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000;
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
// 如果一直持有这个锁,开启监听通过定时任务不断刷新锁的过期时间
ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
return;
}
Long ttlRemaining = future.getNow();
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}继续看 tryLockInnerAsync 方法,采用LUA脚本代码加锁。
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
// 设置过期时间
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
// 如果锁不存在,则通过hset设置它的值,并设置过期时间
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// 如果锁已存在,并且锁的是当前线程,则通过hincrby给数值递增1
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// //如果锁已存在,但并非本线程,则返回过期时间ttl
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
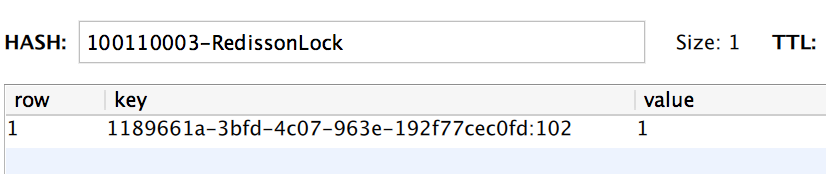
}加锁成功后,redis会存在加锁的hash结构数据,key为随机字符串+线程ID;value值为1。如果同一线程多次调用lock方法,值递增1。
解锁
@Override
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(final long threadId) {
final RPromise<Void> result = new RedissonPromise<Void>();
// 解锁方法
RFuture<Boolean> future = unlockInnerAsync(threadId);
future.addListener(new FutureListener<Boolean>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Boolean> future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
result.tryFailure(future.cause());
return;
}
Boolean opStatus = future.getNow();
// 如果返回值为空,说明解锁个当前加锁不是一个线程,抛出异常
if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: "
+ id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
result.tryFailure(cause);
return;
}
// 解说成功,取消刷新过期时间的定时任务
if (opStatus) {
cancelExpirationRenewal(null);
}
result.trySuccess(null);
}
});
return result;
}核心解锁代码
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
// 如果锁已经不存在, 发布锁释放的消息
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end;" +
// 如果释放锁的线程和已存在锁的线程不是同一个线程,返回null
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
// 通过hincrby递减1的方式,释放一次锁
// 若剩余次数大于0 ,则刷新过期时间
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
// 否则证明锁已经释放,删除key并发布锁释放的消息
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.unlockMessage, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}代码部分
pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.10.1</version>
</dependency>其他的辅助util依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.58</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.8</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>application.properties
redis.config.host=redis://localhost:6379Redisson配置类
package com.wjx.config;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* Created by dingguo on 2020/5/15 下午3:47
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${redis.config.host}")
private String address;
@Bean
public RedissonClient getRedissonClient() {
// 创建 Config
Config config = new Config();
// 设置为单节点redis
config.useSingleServer().setAddress(this.address);
// 通过Redisson创建client实例
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
Service秒杀处理类
package com.wjx.service;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.MapUtils;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* Created by dingguo on 2020/5/15 下午3:53
* 使用 Redission 分布式锁,实现秒杀商品功能
*/
@Service
public class KillItmsService {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
/**
* 模拟多线程每次请求的用户id
*/
private static List<Integer> userIds;
/**
* 初始秒杀商品的库存,实际情况可能存在redis
*/
private static ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, AtomicInteger> killQuantityMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 记录秒杀成功的用户,实际情况可能存在redis
*/
private static ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Integer> killUserIdMaps = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static {
userIds = Lists.newArrayList(10001, 10002, 10003, 10004, 10005, 10006, 10007, 10008, 10009, 10010);
killQuantityMap.put(1001, new AtomicInteger(6));
}
/**
* 秒杀抢商品
*/
public Boolean killItem(Integer killId) {
// 随机获取访问的用户,模拟不同用户请求
int index = new Random().nextInt(9);
Integer userId = userIds.get(index);
boolean result = false;
final String lockKey = String.valueOf(killId) + userId + "-RedissonLock";
// 加锁
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
try {
// TODO: 2020/5/15 第一个参数为 30, 尝试获取锁的的最大等待时间为30s
// TODO: 2020/5/15 第二个参数为 60, 上锁成功后60s后锁自动失效
// 尝试获取锁(可重入锁,不会造成死锁)
boolean lockFlag = lock.tryLock(30, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (lockFlag) {
// 做幂等性处理
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(killUserIdMaps) && killUserIdMaps.get(userId) != null) {
System.err.println("用户:" + userId + "---已抢到商品:" + killId + ",不可以重新领取");
return false;
}
/*
* ***************************************************************
* 处理核心内容
* ***************************************************************
*/
AtomicInteger quantity = killQuantityMap.get(killId);
if (quantity.get() > 0) {
quantity.decrementAndGet();
// TODO: 2020/5/15 killUserIdMaps 实际业务场景,秒杀抢到商品的用户可以存入redis缓存
killUserIdMaps.put(userId, killId);
// TODO: 2020/5/15 killQuantityMap 实际业务场景,读取数据库或者缓存的商品库存,判断是否被抢完了
killQuantityMap.put(killId, quantity);
System.out.println("用户:" + userId + "---抢到商品:" + killId);
} else {
System.err.println("用户:" + userId + "---未抢到商品:" + killId);
}
result = true;
} else {
System.out.println("当前锁资源被占用<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<未获取到锁");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>.出现了错误");
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
return result;
}
public void init() {
killQuantityMap.put(1001, new AtomicInteger(6));
killUserIdMaps.clear();
}
}
参考文章:






















 3001
3001











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








