C++的STL
1. STL
1.1 STL诞生
① 长久以来,软件界一直希望建立一种可重复利用的东西。
② C++的面向对象和泛型编程思想,目的就是复用性的提升。
③ 大多数情况下,数据结构和算法都未能有一套标准,导致被迫从事大量重复工作。
④ 为了建立数据结构和算法的一套标准,诞生了STL。
1.2 STL基本概念
① STL(Standard Template Library,标准模板库)
② STL 从广义上分为:容器(container)、算法(algorithm)、迭代器(iterator)
③ 容器和算法之间通过迭代器进行无缝连接。
④ STL 几乎所有的代码都采用了模板类或者模板函数。
1.3 STL六大组件
① STL大体分为六大组件,分别是:容器、算法、迭代器、仿函数、适配器(配接器)、空间配准器。
- 容器:各种数据结构,如vector、list、deque、set、map等,用来存放数据。
- 算法:各种常用的算法,如sort、find、copy、for_each等。
- 迭代器:扮演了容器与算法之间的胶合剂。
- 仿函数:行为类似函数,可作为算法的某种策略。
- 适配器:一种用来修饰容器或者仿函数或迭代器接口的东西。
- 空间配置器:负责空间的配置与管理。
1.4 STL容器
① 容器:置物之所也。
② STL容器就是将运用最广泛的一些数据结构实现出来。
③ 常用的数据结构:数组、链表、树、栈、队列、集合、映射表 等。
④ 这些容器分为序列式容器和关联式容器两种:
- 序列式容器:强调值的排序,序列式容器中每个元素均有固定的位置(怎么往里放,位置就固定了)。
- 关联式容器:二叉树结构,各元素之间没有严格的物理上的顺序关系(不是怎么往里放就怎么排序,它会自动进行排序,然后固定位置)。
1.5 STL算法
① 算法:问题之解法
② 有限的步骤,解决逻辑或数学上的问题,这一门学科我们叫算法(Algorithms)
③ 算法分为:质变算法和非质变算法。
- 质变算法:是指运算过程中会更改区间内的元素内容,例如拷贝、替换、删除等等。
- 非质变算法:是指运算过程中不会更改区间内的元素,例如查找、计数、遍历、寻找极值等等。
1.6 STL迭代器
① 迭代器:容器和算法之间粘合剂。
② 提供一种方法,使之能够依序寻找某个容器所含的各个元素,而无需暴露容器的内部表示方式。
③ 每个容器都有自己专属的迭代器。
④ 迭代器使用非常类似于指针,可以先理解迭代器为指针。
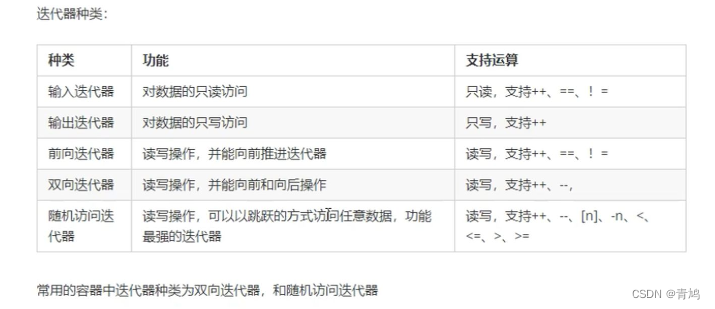
1.7 STLvector存放内置数据类型
① STL中最常用的容器为Vector,可以理解为数组。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector> //STL中每个容器要使用,都要包含对应的头文件
#include<algorithm> //这是标准算法的头文件
//vector容器存放内置数据类型
void myPrint(int val)
{
cout << val << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建一个vector容器,数组
vector<int> v; //容器中的数据类型为int
//向容器中插入数据
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
//通过迭代器访问容器中的数据
vector<int>::iterator itBegin = v.begin(); //起始迭代器itBegin 指向容器中第一个元素的位置
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = v.end(); // 结束迭代器itEnd 指向容器中最后一个元素的下一个位置
//第一种遍历方式
while (itBegin != itEnd)
{
cout << *itBegin << endl; //类似指针,解引用,取出值
itBegin++; //往后偏移
}
//第二种遍历方式
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
//第三种遍历方式,利用STL提供遍历算法
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint); //要用STL中的标准算法,就要提供标准算法的头文件
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10
- 20
- 30
- 40
- 10
- 20
- 30
- 40
- 10
- 20
- 30
- 40
- 请按任意键继续. . .
1.8 STL存放自定义数据类型
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector> //STL中每个容器要使用,都要包含对应的头文件
//vector容器中存放自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
vector<Person>v; //容器中放的是Person的数据类型
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
Person p5("eee", 50);
//向容器中添加数据
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
//遍历容器中的数据
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it).m_Age << endl; //<>是什么类型,*it就是什么类型
//第二种拿到属性的方法,由于已知it是个指针,所以也可以通过it->m_Name拿到属性
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
//存放自定义数据类型 指针
void test02()
{
vector<Person*>v;
Person p1("aaa", 10);
Person p2("bbb", 20);
Person p3("ccc", 30);
Person p4("ddd", 40);
Person p5("eee", 50);
//向容器中添加数据
v.push_back(&p1);
v.push_back(&p2);
v.push_back(&p3);
v.push_back(&p4);
v.push_back(&p5);
//遍历容器
for (vector<Person*>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << (*it)->m_Name << " 年龄:" << (*it)->m_Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 姓名:aaa 年龄:10
- 姓名:aaa 年龄:10
- 姓名:bbb 年龄:20
- 姓名:bbb 年龄:20
- 姓名:ccc 年龄:30
- 姓名:ccc 年龄:30
- 姓名:ddd 年龄:40
- 姓名:ddd 年龄:40
- 姓名:eee 年龄:50
- 姓名:eee 年龄:50
- 姓名:aaa 年龄:10
- 姓名:bbb 年龄:20
- 姓名:ccc 年龄:30
- 姓名:ddd 年龄:40
- 姓名:eee 年龄:50
- 请按任意键继续. . .
1.9 STL容器嵌套容器
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
//容器嵌套容器
void test01()
{
vector<vector<int>>v;
//创建小容器
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
vector<int>v3;
vector<int>v4;
//向4个小容器中添加数据
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 1);
v2.push_back(i + 2);
v3.push_back(i + 3);
v4.push_back(i + 4);
}
//将小容器插入到大容器中
v.push_back(v1);
v.push_back(v2);
v.push_back(v3);
v.push_back(v4);
//通过大容器,把所有数据遍历一遍
for (vector<vector<int>>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//(*it) 是一个容器 vector<int>
for (vector<int>::iterator vit = (*it).begin(); vit != (*it).end(); vit++)
{
cout << *vit << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 1 2 3 4
- 2 3 4 5
- 3 4 5 6
- 4 5 6 7
请按任意键继续. . .
2. string容器
2.1 简介
① string是C++风格的字符串,而string本质上是一个类。
② string 和 char * 区别:
- char * 是一个指针
- string 是一个类,类内部封装了 char *,管理这个字符串是一个char型容器。
③ string特点:
- string类内部封装了很多成员方法。
- 例如,查找find,拷贝copy,删除delete,替换replace,插入insert。
- string管理char * 所分配的内存,不用担心复制越界和取值越界等,由类内部进行负责。
2.2 构造函数
① string构造函数原型:
- string(); // 创建一个空的字符串 例如:string str;
- string(const char * s); // 使用字符串s初始化
- string(const string & str); // 使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象
- string(int n,char c); //使用n个字符c初始化
② string的多种构造方式没有可比性,灵活使用即可。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string的构造函数
/*
1. string(); // 创建一个空的字符串 例如:string str;
2. string(const char* s); // 使用字符串s初始化
3. string(const string & str); // 使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象
4. string(int n, char c); //使用n个字符c初始化
*/
void test01()
{
string s1; //默认构造就是空字符串
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
const char* str = "hello world"; //使用字符串s初始化
string s2(str);
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
string s3(s2);
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
string s4(10, 'a');
cout << "s4 = " << s4 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- s1 =
- s2 = hello world
- s3 = hello world
- s4 = aaaaaaaaaa
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2.3 赋值操作
① 给string字符串进行赋值。
② 赋值的函数原型:
- string& operator=(const char* s); //char * 类型字符串赋值给当前的字符串
- string& operator=(const strinng &s); //把字符串s赋给当前的字符串
- string& operator=(char c); //字符赋值给当前的字符串
- string& assign(const char *s); //把字符串s赋给当前的字符串
- string& assign(const char *s,int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串
- string& assign(const string &s); //把字符串s赋给当前字符串
- string& assign(int n, char c); //用n个字符c赋给当前字符串
③ string的赋值方式很多,operator=这种方式是比较常用的。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string赋值操作
/*
1. string& operator=(const char* s); //char * 类型字符串赋值给当前的字符串
2. string& operator=(const string &s); //把字符串s赋给当前的字符串
3. string& operator=(char c); //字符赋值给当前的字符串
4. string& assign(const char *s); //把字符串s赋给当前的字符串
5. string& assign(const char *s,int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串
6. string& assign(const string &s); //把字符串s赋给当前字符串
7. string& assign(int n, char c); //用n个字符c赋给当前字符串
*/
void test01()
{
string str1;
str1 = "hello world"; //第一种等号方式
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2;
str2 = str1; //第二种等号方式
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
string str3;
str3 = 'a'; //第三种等号方式
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
string str4;
str4.assign("hello C++"); //第一种assign方式
cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
string str5;
str5.assign("hello C++",5); //第二种assign方式,取字符串"hello C++"中的前五个字符赋值给str5
cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;
string str6;
str6.assign(str5); //第三种assign方式
cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;
string str7;
str7.assign(10,'w'); //第四种assign方式
cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- str1 = hello world
- str2 = hello world
- str3 = a
- str4 = hello C++
- str5 = hello
- str6 = hello
- str7 = wwwwwwwwww
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2.4 字符串拼接
① 实现在字符串末尾拼接字符串。
② 函数原型:
- string& operator+=(const char* str); //重载+=操作符
- string& operator+=(const char c); //重载+=操作符
- string& operator+=(const string& str); //重载+=操作符
- string& append+=(const char* s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
- string& append+=(const char* s, int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
- string& append+=(const string &s); //同operator+=(const string& str)
- string& append+=(const char &s, int pos, int n); //字符串s从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string赋值操作
/*
1. string& operator+=(const char* str); //重载+=操作符
2. string& operator+=(const char c); //重载+=操作符
3. string& operator+=(const string& str); //重载+=操作符
4. string& append+=(const char* s); //把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
5. string& append+=(const char* s, int n); //把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
6. string& append+=(const string &s); //同operator+=(const string& str)
7. string& append+=(const char &s, int pos, int n); //字符串s从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
*/
void test01()
{
string str1 = "我"; //字符串初始化
str1 += "爱玩游戏";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
str1 += ':'; //追加一个字符
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str2 = " LOL DNF";
str1 += str2; //追加字符串
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str3 = "I";
str3.append(" love ");
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append("game abcde ",4); //只把字符串的前4个拼接过去
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append(str2);
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append(str2,0,4); //只截取到LoL,参数2表示从哪个位置开始截取,参数3表示截取字符个数
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- str1 = 我爱玩游戏
- str1 = 我爱玩游戏:
- str1 = 我爱玩游戏: LOL DNF
- str3 = I love
- str3 = I love game
- str3 = I love game LOL DNF
- str3 = I love game LOL DNF LOL
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2.5 字符串查找和替换
① 查找:查找指定字符串是否存在。
② 替换:在指定的位置替换字符串。
③ 函数原型:
//查找str第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
- int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const;
// 查找s第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
- int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const;
//从pos位置查找s的前n个字符第一次位置
- int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;
//查找字符c第一次出现位置
- int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const;
//查找str最后一次位置,从pos开始查找
- int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const;
//查找s最后一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
- int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const;
//从pos查找s的前n个字符最后一次位置
- int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;
//查找字符c最后一次出现位置
- int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const;
//替换从pos开始n个字符为字符串str
- string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str) const;
//替换从pos开始的n个字符为s
- string& replace(int pos, int n, const string* s) const;
④ find查找是从左往右,rfind从右往左。
⑤ find找到字符串后返回查找的第一个字符位置,找不到返回-1。
⑥ replace在替换时,要知道从哪个位置起,多少个字符,替换成什么样的字符串。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string查找和替换
/*
//查找str第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
1. int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const;
// 查找s第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
2. int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const;
//从pos位置查找s的前n个字符第一次位置
3. int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;
//查找字符c第一次出现位置
4. int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const;
//查找str最后一次位置,从pos开始查找
5. int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const;
//查找s最后一次出现位置,从pos开始查找
6. int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const;
//从pos查找s的前n个字符最后一次位置
7. int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;
//查找字符c最后一次出现位置
8. int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const;
//替换从pos开始n个字符为字符串str
9. string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str) const;
//替换从pos开始的n个字符为s
10. string& replace(int pos, int n, const string* s) const;
*/
//1、查找
void test01()
{
string str1 = "abcdefgde";
int pos = str1.find("de"); //从零开始索引,返回值为d出现的位置"3",若找不到子字符串,就返回-1
if (pos == -1)
{
cout << "未找到字符串 pos = " << pos << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到字符串 pos = " << pos << endl;
}
//rfind
pos = str1.rfind("de"); //rfind是从右往左查找,find是从左往右查找
cout << "pos=" << pos << endl;
}
void test02()
{
string str1 = "abcdefg";
str1.replace(1, 3, "1111"); // 从 "1" 号位置起,"1111"有四个字符,所以变为4个字符替换成 "1111",而不是出现3个字符替换成"111"
cout << "str1= " << str1 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 找到字符串 pos = 3
- pos=7
- str1= a1111efg
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2.6 字符串比较
① 功能描述:字符串之间比较。
② 比较方式:字符串比较是按字符的ASCII码进行对比。
- = = = 返回 0
- > > > 返回 1
- < < < 返回 -1
③ 函数原型:
- int compare(const string & s) const; //与字符串s比较
- int compare(const char * s) const; //与字符串s比较
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//字符串比较
//1、查找
void test01()
{
string str1 = "hello";
string str2 = "hello";
//compar常用于比较两个字符串相等或不相等,判断谁大谁小的意义并不是很大
if (str1.compare(str2) == 0)
{
cout << "str1 等于 str2" << endl;
}
else if (str1.compare(str2) > 0)
{
cout << "str1 大于 str2" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "str1 小于 str2" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- str1 等于 str2
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2.7 字符串存取
① string中单个字符存取方式有两种:
- char& operator[](int n); //通过[]方式取字符
- char& at(int n); //通过at方式取字符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string 字符存取
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
cout << "str= " << str << endl;
//1、通过[]访问单个字符
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl; //换行符
//2、通过at方式访问单个字符
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//修改单个字符
str[0] = 'x';
cout << "str= " << str << endl;
str.at(1) = 'x';
cout << "str= " << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- str= hello
- h e l l o
- h e l l o
- str= xello
- str= xxllo
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2.8 字符串插入和删除
① 功能描述:对string字符串进行插入和删除字符操作。
② 函数原型:
- string& insert(int pos, const char * s); // 插入字符串
- string& insert(int pos, const string& str); //插入字符串
- string& insert(int pos, int n, char c); //在指定位置插入n个字符c
- string& erase(int pos, int n = npos); //删除从Pos开始的n个字符
③ 插入和删除的起始下标都是从0开始。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//字符串 插入和删除
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
//插入
str.insert(1, "111");
//hello
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
//删除
str.erase(1, 3); //从第“1”个位置起,删3个
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- str = h111ello
- str = hello
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2.9 子串获取
① 功能描述:从字符串中获取想要的子串。
② 函数原型:
- string substr(int pos = 0, int n = npos) const; //返回由pos开始的n个字组成的字符串。
③ 灵活的运用求子串功能,可以在实际开发中获取有效的信息。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//string 求子串
void test01()
{
string str = "abcdef";
string subStr = str.substr(1, 3);
cout << "subStr = " << subStr << endl;
}
//实用操作
void test02()
{
string email = "zhangsan@sina.com";
//从邮件地址中 获取 用户名称
int pos = email.find("@");
cout << pos << endl;
string usrName = email.substr(0, pos);
cout << usrName << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- subStr = bcd
- 8
- zhangsan
- 请按任意键继续. . .
3.vector容器
3.1 简介
① vector数据结构和数组非常相似,也称为单端数组。
② vector与普通数组区别:不同之处在于数组是静态空间,而vector可以动态扩展。
③ 动态扩展并不是在原空间之后续接新空间,而是找更大的内存空间,然后将原数据拷贝新空间,释放原空间。
④ vector容器的迭代器是支持随机访问的迭代器。
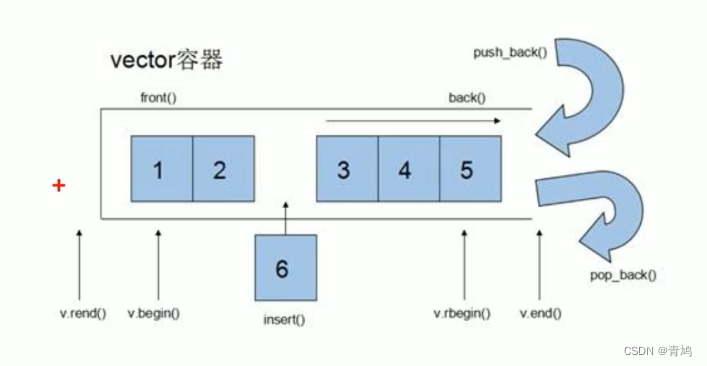
3.2 构造函数
① 功能描述:创建vector容器
② 函数原型:
- vector v;
- vector(v.begin(), v,end()); //将v[begin().end())区间(前闭后开)中的元素拷贝给本身。
- vector(n, elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身
- vector(const vector &vec); //拷贝构造函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
void printVector(vector<int>&v) //各种容器的接口,v1容器传进去,就打印v1容器
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end();it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//vector容器构造
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1; //默认构造 无参构造
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//通过区间方式进行构造
vector<int>v2(v1.begin(), v1.end()); //把v1.begin()-v1.end()区间内数给v2
printVector(v2);
//n个elem方式构造
vector<int>v3(10, 100); //这是10个100,不是100个10
printVector(v3);
//拷贝构造
vector<int>v4(v3);
printVector(v4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- 请按任意键继续. . .
3.3 赋值操作
① 功能描述:给vector容器进行赋值。
② 函数原型:
- vector& operator=(const vector &vec); //重载等号操作符。
- assign(beg,end); //将[beg,end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
- assign(n,elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
③ vector赋值方式比较简单,使用operator=,或者assign都可以。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
//vector赋值
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << "";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//赋值 operator=
vector<int>v2;
v2 = v1;
printVector(v2);
//assign
vector<int>v3;
v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end()); //提供两个迭代器,两个迭代器区间中的元素都赋值给vector容器,区间为前闭后开
printVector(v3);
//n个elem方式赋值
vector<int>v4;
v4.assign(10, 100);
printVector(v4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 0123456789
- 0123456789
- 0123456789
- 100100100100100100100100100100
- 请按任意键继续. . .
3.4 容量和大小
① 功能描述:对vector容器的容量和大小操作。
② 函数原型:
//判断容器是否为空
- empy();
//容器的容量
- capacity();
//返回容器中元素的个数
- size();
//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。
//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- resize(int num);
//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变成,则以elem值填充新位置。
//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- resize(int num, elem);
③ vector 容器的容量(用 capacity 表示),指的是在不分配更多内存的情况下,容器可以保存的最多元素个数;而 vector 容器的大小(用 size 表示),指的是它实际所包含的元素个数。
④ vector 容器的大小不能超出它的容量,在大小等于容量的基础上,只要增加一个元素,就必须分配更多的内存。注意,这里的“更多”并不是 1 个。换句话说,当 vector 容器的大小和容量相等时,如果再向其添加(或者插入)一个元素,vector 往往会申请多个存储空间,而不仅仅只申请 1 个。
⑤ 一旦 vector 容器的内存被重新分配,则和 vector 容器中元素相关的所有引用、指针以及迭代器,都可能会失效,最稳妥的方法就是重新生成。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
//vector容器的容量和大小操作
void printVector(vector<int>&v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << "";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
if (v1.empty()) //为真 代表容器为空
{
cout << "v1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v1不为空:" << endl;
cout << "capacity容量:" << v1.capacity() <<endl;
cout << "v1的大小为:" << v1.size() << endl;
//重新指定大小
v1.resize(15); //如果重新指定的比原来长了,默认用0填充新的位置
printVector(v1);
v1.resize(20,100); //利用重载版本,参数2可以指定默认填充值
printVector(v1);
v1.resize(5); //如果重新指定的比原来短了,超出的部分会删除掉
printVector(v1);
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 0123456789
- v1不为空:
- capacity容量:13
- v1的大小为:10
- 012345678900000
- 012345678900000100100100100100
- 01234
- 请按任意键继续. . .
3.5 插入删除
① 功能描述:对vector容器进行插入、删除操作。
② 函数原型:
- push_back(ele); //尾部插入元素ele
- pop__back(); //删除最后一个元素
- insert(const_iterator pos, ele); //迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele
- insert(const_iterator pos, int count ele); //迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素
- erase(const_iterator pos); //删除迭代器指向的元素
- erase(cons_titerator start, const_iterator end); //删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素
- clear(); //删除容器中所有元素
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
void printVector(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
//尾插
v1.push_back(10);
v1.push_back(20);
v1.push_back(30);
v1.push_back(40);
v1.push_back(50);
//遍历
printVector(v1);
//尾删
v1.pop_back();
printVector(v1);
//插入 参数是迭代器
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 100);
printVector(v1);
//删除 参数也是迭代器
v1.insert(v1.begin(),2,999);
printVector(v1);
//删除
v1.erase(v1.begin());
printVector(v1);
//清空 方式一:
v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v1);
//清空 方式二:
v1.clear();
printVector(v1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40 50
- 10 20 30 40
- 100 10 20 30 40
- 999 999 100 10 20 30 40
- 999 100 10 20 30 40
-
-
- 请按任意键继续. . .
3.6 数据存取
① 功能描述:对vector中的数据存取操作。
② 函数原型:
- at(int idx); ///返回索引idx所指的数据。
- operator[]; //返回索引idx所指的数据。
- front(); //返回容器中第一个数据元素
- back(); //返回容器中最后一个数据元素
③ 除了用迭代器获取vector容器中元素,[]和at也可以。
④ front返回容器第一个元素。
⑤ back返回容器最后一个元素。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
void printVector(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
//利用[]方式访问数组中元素
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//利用at方式访问元素
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//获取第一个元素
cout << "第一个元素为:" << v1.front() << endl;
//获取最后一个元素
cout << "最后一个元素为:" << v1.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 第一个元素为:0
- 最后一个元素为:9
- 请按任意键继续. . .
3.7 互换容器
① 功能描述:实现两个容器内元素进行互换。
② 函数原型:swao(vec); //将vec与本身的元素互换
③ swap可以使两个容器互换,可以达到实用的收缩内存效果。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
//vector容器互换
void printVector(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//1、基本使用
void test01()
{
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--)
{
v2.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
v1.swap(v2);
printVector(v1);
printVector(v2);
}
//2、实际用途
//巧用swap可以收缩内存空间
void test02()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
v.resize(3); //重新指定大小
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl; //resize操作,容量并没有变,多余的容量浪费了
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
//巧用swap收缩内存
vector<int>(v).swap(v); //vector<int>(v)创建了一个为匿名对象,会按v的大小初始化这个匿名对象容器的大小
//.swap(v)会对匿名对象容器与原容器做一个交换,则原容器的指针指向匿名对象的容器,匿名对象的容器的指针改为指向原容器
// 系统运行完创建匿名函数这一句语句后对匿名对象的指针(即地址、内存)进行回收
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 交换前:
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 交换后:
- 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- v的容量为:138255
- v的大小为:100000
- v的容量为:138255
- v的大小为:3
- v的容量为:3
- v的大小为:3
- 请按任意键继续. . .
3.8 预留空间
① 功能描述:减少vector在动态扩展容量时的扩展次数。
② 函数原型:
- reserve(int len); //容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
//vector容器 预留空间
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
int num = 0; //统计开辟次数
int* p = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
if (p != &v[0]) //一开始指针不指向容量首地址,所以让指针指向容量首地址,开辟内存次数加1
{
p = &v[0];
num++; //由于容量不够,会再次开辟一段容量更大的内存空间,原小容量的内存空间被释放
}
}
cout << "num:" << num << endl;
}
void test02()
{
vector<int>v;
//预留空间
v.reserve(100000);
int num = 0; //统计开辟次数
int* p = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
if (p != &v[0])
{
p = &v[0];
num++;
}
}
cout << "num:" << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- num:30
- num:1
- 请按任意键继续. . .
4. deque容器
4.1 简介
① 功能:双端数组,可以对头端进行插入删除操作,也可以对尾端进行插入和删除操作。
② deque与vector区别:
- vector对于头部的插入效率低,数据量越大,效率越低,例如头部后有十万个数据,则往头部插入一个数据时,十万个数据都需要往后挪一挪才能在头部插入数据。
- deque相对而言,对头部的插入删除速度会比vector快
- vector访问元素时的速度会比deque快,这和两者内部实现有关。
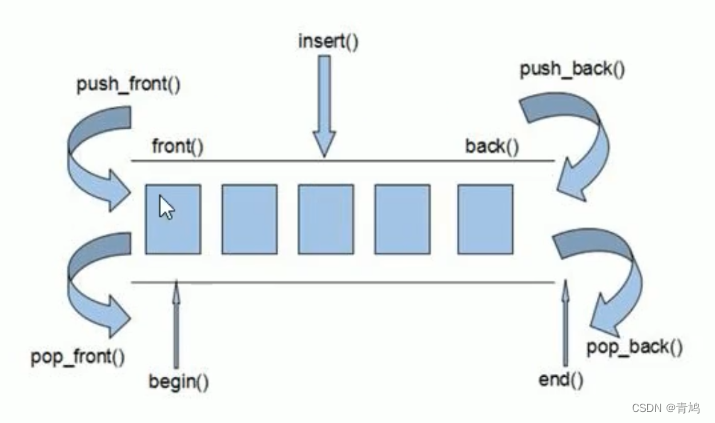
③ deque内部工作原理:
- deque内部有个中控器,维护每段缓冲区中的内容,缓冲区中存放真实数据。
- 中控器维护的是每个缓冲区的地址,使得使用deque时像一片连续的内存空间。
④ deque容器的迭代器也是支持随机访问的。
4.2 构造函数
① 功能描述:deque容器构造。
② 函数原型:
- dequedeqT; //默认构造形式
- 构造函数将[beg,end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
- deque(n,elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身
- deque(const deque &deq); //拷贝构造函数
③ deque荣哪个器和vector容器的构造方式几乎一致,灵活使用即可。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<deque>
//deque容器 构造函数
void printDeuque(const deque<int>& d) //const 防止进行写操作,只能进行读
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) //表示只读迭代器
{
//*it = 100; const使得当进行写操作时,会报错,会提示,避免了进行修改操作
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1; //无参构造函数
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeuque(d1);
//区间的方式构造
deque<int>d2(d1.begin(),d1.end());
printDeuque(d2);
//n个值的方式构造
deque<int>d3(10,100);
printDeuque(d3);
//拷贝构造
deque<int>d4(d3);
printDeuque(d4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- 请按任意键继续. . .
4.3 赋值操作
① 功能描述:给deque容器进行赋值。
② 函数原型:
- deque& operator=(const deque &deq); //重载等号操作符
- assign(beg, end); //将[beg,end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
- assign(n,elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
③ deque赋值操作与vector相同。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<deque>
//deque容器 赋值操作
void printDeuque(const deque<int>&d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) //表示只读迭代器
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeuque(d1);
//operator= 赋值
deque<int>d2;
d2 = d1;
printDeuque(d2);
//assign 赋值
deque<int>d3;
d3.assign(d1.begin(), d1.end());
printDeuque(d3);
deque<int>d4(10,100);
printDeuque(d4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- 请按任意键继续. . .
4.4 大小操作
① 功能描述:对deque容器的大小进行操作。
② 函数原型:
//判断容器是否为空
deque.empty();
//返回容器中的元素的个数
deque.size();
//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。
//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
deque.resize(num);
//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。
//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
deque.resize(num,elem);
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<deque>
//deque容器 大小操作
void printDeuque(const deque<int>&d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) //表示只读迭代器
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeuque(d1);
if (d1.empty())
{
cout << "d1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "d1不为空" << endl;
cout << "d1的大小为:" << d1.size() << endl;
//deque容器没有容量概念
}
//重新指定大小
d1.resize(15, 1); //这里指定填充值为1,如果没有第二个参数,默认的填充值为0
printDeuque(d1);
d1.resize(5);
printDeuque(d1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- d1不为空
- d1的大小为:10
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 1 1 1 1
- 0 1 2 3 4
- 请按任意键继续. . .
4.5 插入和删除
① 功能描述:向deque容器中插入和删除数据。
② 函数原型:
两端插入操作:
- push_back(elem); //在容器尾部添加一个数据
- push_front(elem); //在容器头部插入一个数据
- pop_back(); //删除容器最后一个数据
- pop_front(); //删除容器第一个数据
指定位置操作:
- insert(pos,elem); //在pos位置插入一个elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。
- insert(pos,n,elem); //在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值
- insert(pos,beg,end); //在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值
- clear(); //清空容器的所有数据
- erase(beg,end); //删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
- erase(pos); //删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<deque>
//deque容器 插入和删除
void printDeuque(const deque<int>&d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) //表示只读迭代器
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
//尾插
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
//头插
d1.push_front(100);
d1.push_front(200);
printDeuque(d1);
//尾删
d1.pop_back();
printDeuque(d1);
//头删
d1.pop_front();
printDeuque(d1);
}
void test02()
{
deque<int>d2;
d2.push_back(10);
d2.push_back(20);
d2.push_front(100);
d2.push_front(200);
printDeuque(d2);
d2.insert(d2.begin(), 1000);
printDeuque(d2);
d2.insert(d2.begin(), 2, 9999);
printDeuque(d2);
deque<int>d3;
d3.push_back(1);
d3.push_back(2);
d3.push_front(3);
d3.insert(d3.begin(), d2.begin(), d2.end()); //在d3.begin()的位置,插入区间d2.begin()-d2.end()之间的数
printDeuque(d3);
}
void test03()
{
deque<int>d1;
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_front(100);
d1.push_front(200);
//删除
deque<int>::iterator it = d1.begin();
it++;
d1.erase(it); //d1.erase()为删除所有;d1.clear()也为清空容器所有数据
printDeuque(d1);
//按区间方式删除
d1.erase(d1.begin(), d1.end());
printDeuque(d1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
test03();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 200 100 10 20
- 200 100 10
- 100 10
- 200 100 10 20
- 1000 200 100 10 20
- 9999 9999 1000 200 100 10 20
- 9999 9999 1000 200 100 10 20 3 1 2
- 200 10 20
- 空
- 请按任意键继续. . .
4.6 数据存取
① 功能描述:对deque中的数据的存取操作。
② 函数原型:
- at(int idx); //返回索引idx所指的数据
- operator[]; //返回索引idx所指的数据
- front(); //返回容器中第一个数据元素
- back(); //返回容器中最后一个数据元素
③ 除了用迭代器获取deque容器中元素,[]和at也可以。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<deque>
//deque容器 数据存取
void printDeuque(const deque<int>&d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) //表示只读迭代器
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
//尾插
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(30);
//头插
d1.push_front(100);
d1.push_front(200);
d1.push_front(300);
//通过[]方式访问元素
//
for (int i = 0; i < d1.size(); i++)
{
cout << d1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//通过at方式访问元素
for (int i = 0; i < d1.size(); i++)
{
cout << d1.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "第一个元素为:" << d1.front() << endl;
cout << "最后一个元素为:" << d1.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 300 200 100 10 20 30
- 300 200 100 10 20 30
- 第一个元素为:300
- 最后一个元素为:30
- 请按任意键继续. . .
4.7 排序
① 利用算法实现对deque容器进行排序。
② 算法:
- sort(iterator beg, iterator end) //对beg和end区间内元素进行排序
③ sort算法非常实用,使用时包含头文件algorithm即可。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<deque>
#include<algorithm> //标准算法头文件
//deque容器 排序操作
void printDeuque(const deque<int>&d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) //表示只读迭代器
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int>d1;
//尾插
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_back(30);
//头插
d1.push_front(100);
d1.push_front(200);
d1.push_front(300);
printDeuque(d1);
//排序 默认排序规则 从小到大 升序
//对于支持随机访问的迭代器的容器,都可以利用sort算法直接对其进行排序
//vector容器也可以利用sort进行排序
sort(d1.begin(), d1.end());
cout << "排序后:" << endl;
printDeuque(d1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 300 200 100 10 20 30
- 排序后:
- 10 20 30 100 200 300
- 请按任意键继续. . .
5. stack容器
5.1 简介
① stack是一种先进后出的容器,它只有一个出口。
② 栈中只有顶端的元素才可以被外界使用,因此栈不允许有遍历行为。
③ 栈中进入数据称为:入栈 push
④ 栈中弹出数据称为:出栈 pop
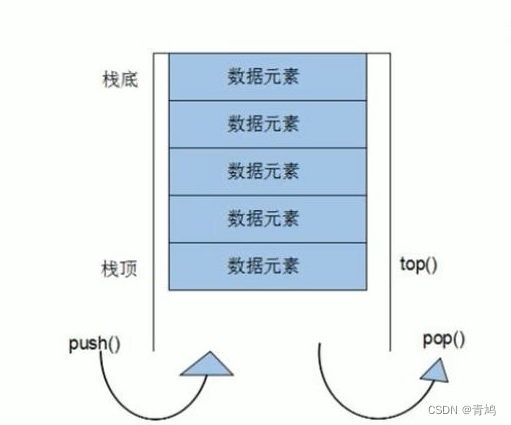
5.2 常用接口
① 功能描述:栈容器常用的对外接口。
② 构造函数:
- stack stk; //stack采用模板类实现,stack对象的默认构造形式
- stack(const stack &stk); //拷贝构造函数
③ 赋值操作:
- stack& operator=(const stack &stk); //重载等号操作符
④ 数据存取:
- push(elem); //向栈顶添加元素
- pop(); //从栈顶移除第一个元素
- top(); //返回栈顶元素
⑤ 大小操作:
- empty(); //判断堆栈是否为空
- size(); //返回栈的大小
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <stack>
//栈stack容器
void test01()
{
//特点:符合先进后出数据结构
stack<int>s;
//入栈
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
s.push(30);
s.push(40);
//只要栈不为空,查看栈顶,并且执行出栈操作
while (!s.empty())
{
//查看栈顶元素
cout << "栈顶元素为:" << s.size() << endl;
//出栈
s.pop();
}
cout << "栈的大小:" << s.size() << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 栈顶元素为:4
- 栈顶元素为:3
- 栈顶元素为:2
- 栈顶元素为:1
- 栈的大小:0
- 请按任意键继续. . .
6. queue容器
6.1 简介
① queue是一种先进先出的数据结构,它有两个出口。
② 队列容器允许一段新增元素,从另一端移除元素。
③ 队列中只有对头和队尾才可以被外界使用,因此队列不运行有遍历行为。
④ 队列中进数据称为入队。
⑤ 队列中出数据称为出队。
6.2 常用接口
① 功能描述:栈容器常用的对外接口。
② 构造函数:
- queue que; //queue采用模板类实现,queue对象的默认构造形式
- queue(const queue &que); //拷贝构造函数
③ 赋值操作:
- queue& operator=(const queue &que); //重载等号操作符
④ 数据存储:
- push(elem); //往队尾添加元素
- pop(); //从对头移除第一个元素
- back(); //返回最后一个元素
- front(); //返回第一个元素
⑤ 大小操作:
- empty(); //判断堆栈是否为空
- size(); //返回栈的大小
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <queue>
#include<string>
//队列 Queue
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
//创建队列
queue<Person>q;
//准备数据
Person p1("唐僧", 30);
Person p2("孙悟空", 1000);
Person p3("猪八戒", 900);
Person p4("沙僧", 800);
//入队
q.push(p1);
q.push(p2);
q.push(p3);
q.push(p4);
cout << "队列大小为:" << q.size() << endl;
//判断只要队列不为空,查看对头,查看队尾,出对
while (!q.empty())
{
//查看对头
cout << "对头元素 -- 姓名:" << q.front().m_Name << " 年龄:" << q.front().m_Age << endl;
//查看队尾
cout << "队尾元素 -- 姓名:" << q.back().m_Name << " 年龄:" << q.back().m_Age << endl;
//出对
q.pop(); //出队是出对头元素
}
cout << "队列大小为:" << q.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 队列大小为:4
- 对头元素 -- 姓名:唐僧 年龄:30
- 队尾元素 -- 姓名:沙僧 年龄:800
- 对头元素 -- 姓名:孙悟空 年龄:1000
- 队尾元素 -- 姓名:沙僧 年龄:800
- 对头元素 -- 姓名:猪八戒 年龄:900
- 队尾元素 -- 姓名:沙僧 年龄:800
- 对头元素 -- 姓名:沙僧 年龄:800
- 队尾元素 -- 姓名:沙僧 年龄:800
- 队列大小为:0
- 请按任意键继续. . .
7. list容器
7.1 简介
① 功能:将数据进行链式存储。
② 链表(list)是一种物理存储单元上非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接实现的。
③ 链表的组成:链表由一系列结点组成。
④ 结点的组成:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
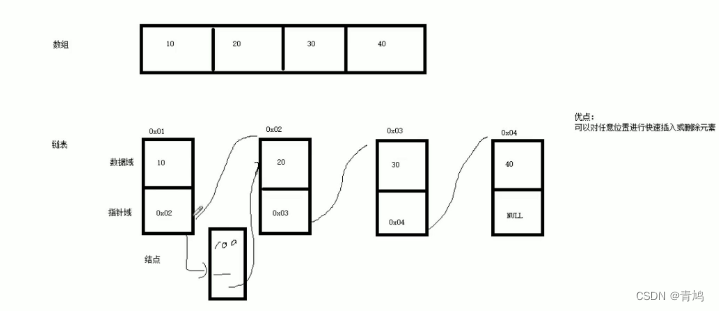
⑤ 添加元素,将原指向下一个元素的指针指向新元素即可,新元素指向下一个元素
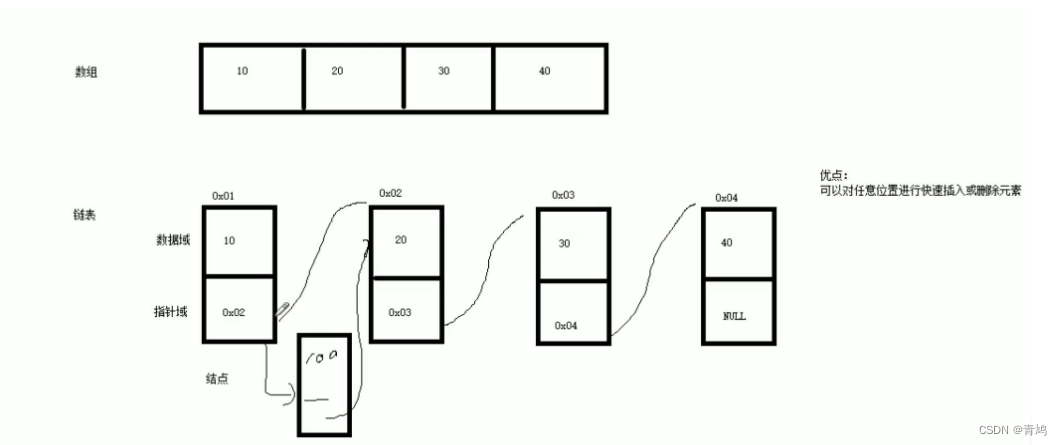
⑥ STL中的链表是一个双向循环链表。
- 双向:每一个指针既指向下一个结点的元素,也指向上一个结点的元素。
- 循环:最后一个结点的指针会指向第一个结点的元素,第一个结点的指针会指向最后一个结点的元素。
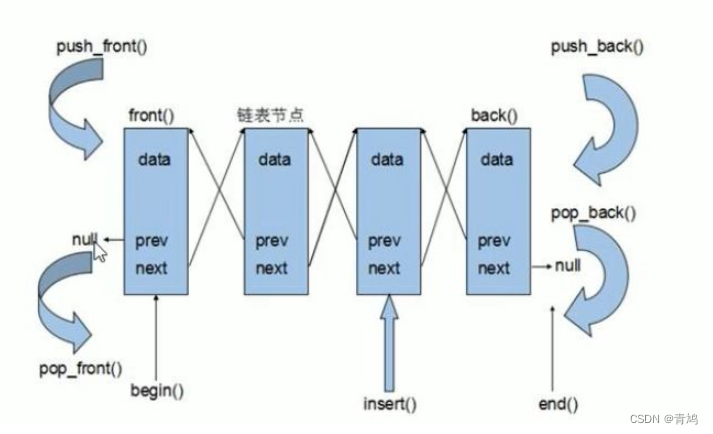
⑦ 由于链表的存储方式并不是连续的内存空间,因此链表list中的迭代器只支持前移和后移,属于双向迭代器。
- 它只能通过指针域一个一个前移/后移去找,而不能连续的内存空间,指针加一个数字,就可以找到数据。
⑧ list的优点:
- 采用动态存储分配,不会造成内存浪费和溢出。
- 链表执行插入和删除操作十分方便,修改指针即可,不需要移动大量数据。
⑨ list的缺点:
- 链表灵活,但是空间(指针域)和时间(遍历)额外耗费较大。
10.list有一个重要的性质,插入操作和删除操作都不会造成原有list迭代器的失效,这在vector中是不成立的,vector当插入操作会创建一个更大的数据内容,而vector容器的迭代器却指向原有内存,所以原有的vector容器失效了。
11.STL中list和vector是两个最长被用的容器,各有优缺点。
7.2 构造函数
① 功能描述:创建list容器。
② 函数原型:
- list lst; //list采用模板类实现对象的默认构造形式
- list(beg,end); //构造函数将[beg,end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
- list(n,elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
- list(const list &lst); //拷贝构造函数。
③ list构造方式同其他几个STL容器一样。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建list容器
list<int>L1; //默认构造
//添加数据
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
//遍历容器
printList(L1);
//区间方式构造
list<int>L2(L1.begin(), L1.end());
printList(L2);
//拷贝构造
list<int>L3(L2);
printList(L3);
//n个elem
list<int>L4(10, 1000);
printList(L4);
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40
- 10 20 30 40
- 10 20 30 40
- 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000
- 请按任意键继续. . .
7.3 赋值和交换
① 功能描述:给list容器进行赋值,以及交换list容器。
② 函数原型:
- assign(beg,end); //将[beg,end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
- assign(n,elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
- list& operator=(const list &list); //重载等号操作符。
- swap(list); //将lst与本身的元素互换。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
//list容器赋值和交换
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建list容器
list<int>L1; //默认构造
//添加数据
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
//遍历容器
printList(L1);
list<int>L2;
L2 = L1; //operator= 赋值
printList(L2);
list<int>L3;
L3.assign(L2.begin(), L2.end());
printList(L3);
list<int>L4;
L4.assign(10, 100);
printList(L4);
}
//交换
void test02()
{
//创建list容器
list<int>L1; //默认构造
//添加数据
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
list<int>L2;
L2.assign(10, 100);
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
printList(L1);
printList(L2);
L1.swap(L2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
printList(L1);
printList(L2);
}
int main() {
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40
- 10 20 30 40
- 10 20 30 40
- 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- 交换前:
- 10 20 30 40
- 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- 交换后:
- 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- 10 20 30 40
- 请按任意键继续. . .
7.4 大小操作
① 功能描述:对list容器的大小进行操作。
② 函数原型:
//返回容器中元素的个数。
- size();
//判断容器是否为空。
- empty();
//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。
//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- resize(num);
//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变成,则以elem值填充新位置。
//如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- resize(num,elem);
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
//list容器赋值和交换
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建list容器
list<int>L1; //默认构造
//添加数据
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
//遍历容器
printList(L1);
//判断容器是否为空
if(L1.empty())
{
cout << "L1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "L1不为空:" << endl;
cout << "L1的元素个数为:" << L1.size() << endl;
}
//重新指定大小
L1.resize(10,10000);
printList(L1);
L1.resize(2);
printList(L1);
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40
- L1不为空:
- L1的元素个数为:4
- 10 20 30 40 10000 10000 10000 10000 10000 10000
- 10 20
- 请按任意键继续. . .
7.5 插入和删除
① 功能描述:对list容器进行数据的插入和删除。
② 函数原型:
- push_back(elem); //在容器尾部加入一个元素。
- pop_back(); //删除容器中最后一个元素。
- push_front(elem); //在容器开头插入一个元素。
- pop_front(); //从哪个容器开头移除第一个元素
- insert(pos,elem); //在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。
- insert(pos,n,elem); //在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。
- insert(pos,beg,end); //在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。
- clear(); //移除容器的所有数据。
- erase(beg,end); //删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
- erase(pos); //删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
- remove(elem); //删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
//list容器赋值和交换
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建list容器
list<int>L1; //默认构造
//添加数据
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_front(100);
L1.push_front(200);
L1.push_front(300);
//遍历容器
printList(L1);
//尾删
L1.pop_back();
printList(L1);
//头删
L1.pop_front();
printList(L1);
//insert插入
list<int>::iterator it = L1.begin();
L1.insert(++it, 1000);
printList(L1);
//删除
it = L1.begin();
L1.erase(it);
printList(L1);
//移除
L1.push_back(10000);
L1.push_back(10000);
L1.push_back(10000);
L1.push_back(10000);
printList(L1);
L1.remove(10000);
printList(L1);
//清空
L1.clear();
printList(L1);
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 300 200 100 10 20 30
- 300 200 100 10 20
- 200 100 10 20
- 200 1000 100 10 20
- 1000 100 10 20
- 1000 100 10 20 10000 10000 10000 10000
- 1000 100 10 20
-
- 请按任意键继续. . .
7.6 数据存取
① 功能描述:对list容器中数据进行存取。
② 函数原型:
- front(); //返回第一个元素。
- back(); //返回最后一个元素。
③ list容器不是连续的内存空间,所以不能通过[]、at等方式随机访问。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
//list容器 数据存取
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建list容器
list<int>L1; //默认构造
//添加数据
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
//L1[0] 不可以用[]访问list容器中的元素
//L1.at(0) 不可以用at方式访问list容器中的元素
//原因是list本质链表,不是用连续线性空间存储数据,迭代器也是不支持随机访问的。
cout << "第一个元素为:" << L1.front() << endl;
cout << "第一个元素为:" << L1.back() << endl;
//验证迭代器是不支持随机访问的
list<int>::iterator it = L1.begin();
it++; //因为list是双向的,所以支持递增、递减++、--的操作,但是不支持it = it+1;it = it+2;....,即不支持这样的随机访问
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 第一个元素为:10
- 第一个元素为:40
- 请按任意键继续. . .
7.7 反转和排序
① 功能描述:将容器中的元素反转,以及将容器中的数据进行排序。
② 函数原型:
- reverse(); //反转链表
- sort(); //链表排序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
#include<algorithm>
//list容器 反转和排序
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool myCopare(int v1, int v2)
{
//降序 就让第一个数 大于第二个数为真
return v1 > v2;
}
void test01()
{
//反转
list<int>L1;
//添加数据
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(50);
L1.push_back(40);
L1.push_back(30);
cout << "反转前:" << endl;
printList(L1);
//反转
L1.reverse();
cout << "反转后:" << endl;
printList(L1);
//排序
cout << "排序前:" << endl;
printList(L1);
//所有不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,不可以用标准算法
//不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,内部会提供对应的一些算法
//sort(L1.begin(),L1.end()); //报错,这是标准算法,全局函数的sort()
L1.sort(); //默认排序规则 从小到大 升序
cout << "排序后:" << endl;
printList(L1);
L1.sort(myCopare); //降序排列 这是成员函数的sort()
cout << "重载排序算法,降序排序后:" << endl;
printList(L1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 反转前:
- 20 10 50 40 30
- 反转后:
- 30 40 50 10 20
- 排序前:
- 30 40 50 10 20
- 排序后:
- 10 20 30 40 50
- 重载排序算法,降序排序后:
- 50 40 30 20 10
- 请按任意键继续. . .
8. set容器
8.1 简介
① set容器中所有元素在插入时自动被排序。
② set容器和multiset容器属于关联式容器,底层结构用二叉树实现。
③ set容器与multiset容器区别:
- set容器不允许容器中有重复的元素。
- multiset容器允许容器中有重复的元素。
8.2 构造和赋值
① 功能描述:创建set容器以及赋值。
② 构造函数:
- set st; //默认构造函数
- set(const set &st); //拷贝构造函数
③ 赋值函数:
- set& operator=(const set &st); //重载等号操作符
④ set容器插入数据时用insert。
⑤ set容器插入的数据会自动排序。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
//set容器 构造和赋值
void printset(const set<int>&L)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool myCopare(int v1, int v2)
{
//降序 就让第一个数 大于第二个数为真
return v1 > v2;
}
void test01()
{
set<int>s1;
//插入数据 只有insert方式
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(30);
//遍历容器
//set容器特点:所有元素插入时候自动被排序
//set容器不允许插入重复值
printset(s1);
//拷贝构造
set<int>s2(s1);
printset(s2);
//赋值
set<int>s3;
s3 = s2;
printset(s3);
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40
- 10 20 30 40
- 10 20 30 40
- 请按任意键继续. . .
8.3 大小和交换
① 功能描述:统计set容器大小以及交换set容器。
② 函数原型:
- size(); //返回容器中元素的数目。
- empty(); //判断容器是否为空。
- swap(st); //交换两个集合容器
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
//set容器 大小和交换
void printset(const set<int>&L)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//大小
void test01()
{
set<int>s1;
//插入数据 只有insert方式
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(30);
printset(s1);
//判断是否为空
if (s1.empty())
{
cout << "s1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "s1不为空" << endl;
cout << "s1的大小为:" << s1.size() << endl;
}
}
//交换
void test02()
{
set<int>s1;
//插入数据 只有insert方式
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(30);
set<int>s2;
//插入数据 只有insert方式
s2.insert(100);
s2.insert(400);
s2.insert(300);
s2.insert(200);
s2.insert(300);
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
printset(s1);
printset(s2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
s1.swap(s2);
printset(s1);
printset(s2);
}
int main() {
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40
- s1不为空
- s1的大小为:4
- 交换前:
- 10 20 30 40
- 100 200 300 400
- 交换后:
- 100 200 300 400
- 10 20 30 40
- 请按任意键继续. . .
8.4 插入和删除
① 功能描述:set容器进行插入数据和删除数据。
② 函数原型:
- insert(elem); //在容器中插入元素。
- clear(); //清除所有元素。
- erase(pos); //删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
- erase(beg,end); //删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
- erase(elem); //删除容器中值为elem的元素。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
//set容器 插入和删除
void printset(const set<int>&L)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
set<int>s1;
//插入数据 只有insert方式
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(30);
printset(s1);
//删除
s1.erase(s1.begin()); //删掉的是排序后的第一个元素10
printset(s1);
//删除函数的重载版本
s1.erase(30); //删除30这个元素
printset(s1);
//清空方式一:
s1.erase(s1.begin(), s1.end());
printset(s1);
//清空方式二:
s1.clear();
printset(s1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40
- 20 30 40
- 20 40
-
-
- 请按任意键继续. . .
8.5 查找和统计
① 功能描述:对set容器进行查找书籍以及统计数据。
② 函数原型:
- find(key); //查找key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器,若不存在,返回set.end();
- cout(key); //统计key的元素个数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
//set容器 查找和统计
void printset(const set<int>&L)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
set<int>s1;
//插入数据 只有insert方式
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(30);
printset(s1);
//查找返回的是一个迭代器
set<int>::iterator pos = s1.find(30);
if (pos != s1.end())
{
cout << "找到元素:" << *pos << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到元素" << endl;
}
}
//统计
void test02()
{
set<int>s1;
//插入数据 只有insert方式
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(30);
int num = s1.count(30);
//对于set而言 统计结果要么是0 要么是1
cout << "num = " << num << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40
- 找到元素:30
- num = 1
- 请按任意键继续. . .
8.6 set和multiset区别
① set和multiset区别:
- set不可以插入重复数据,而multiset可以。
- set插入数据的同时会返回插入结果,表示插入是否成功。
- mutiset不会检测数据,因此可以插入重复数据。
② 如果不允许插入重复数据可以利用set
③ 如果需要插入重复数据利用mutiset
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
//set容器 和 mutiset容器 的区别
void printset(const set<int>&L)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
set<int>s1;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret = s1.insert(10); //s.insert(数)返回的是pair类型,第一个数为迭代器,第二个数为布尔类型
if (ret.second)
{
cout << "第一次插入成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "第一次插入失败" << endl;
}
ret = s1.insert(10); //set不允许插入重复的值,当插入重复的值,返回的第二个参数为False,然后不会插入进去
if (ret.second)
{
cout << "第二次插入成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "第二次插入失败" << endl;
}
multiset<int>ms;
//运行插入重复值
ms.insert(10);
ms.insert(10);
ms.insert(10);
for (multiset<int>::const_iterator it = ms.begin(); it != ms.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 第一次插入成功
- 第二次插入失败
- 10 10 10
- 请按任意键继续. . .
8.7 内置类型指定排序规则
① set容器默认排序规则从小到大,利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
//set容器排序
class MyCompare
{
public:
bool operator()(int v1, int v2)const //第一个()表示重载符号,第二个()为参数列表
{
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void test01()
{
set<int>s1; //set容器默认从小到大排序
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(50);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(30);
for (set<int>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//指定排序规则为从大到小
set<int, MyCompare>s2; //此时指定set容器的排序规则为MyCompare,MyCompare()
s2.insert(10);
s2.insert(40);
s2.insert(50);
s2.insert(20);
s2.insert(30);
for (set<int, MyCompare>::iterator it = s2.begin(); it != s2.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 10 20 30 40 50
- 50 40 30 20 10
- 请按任意键继续. . .
8.8 自定义数据类型指定排序规则
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
//set容器排序
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class comparePerson //仿函数本质是一个类
{
public:
bool operator()(const Person& p1, const Person& p2)const
{
//安装年龄 降序
return p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age;
}
};
void test01()
{
//自定义数据类型 都会指定排序规则
set<Person, comparePerson>s1;
//创建Person对象
Person p1("刘备", 24);
Person p2("关羽", 28);
Person p3("张飞", 25);
Person p4("赵云", 21);
s1.insert(p1);
s1.insert(p2);
s1.insert(p3);
s1.insert(p4);
for (set<Person, comparePerson>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << "年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 姓名:关羽年龄:28
- 姓名:张飞年龄:25
- 姓名:刘备年龄:24
- 姓名:赵云年龄:21
- 请按任意键继续. . .
9. map容器
9.1 简介
① map容器中的所有元素都是pair。
② pair中第一个元素为key(键值),起到索引作用,第二个元素为value(实值)。
③ 所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动排序。
④ map容器和multimap容器属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现。
⑤ map容器可以根据key值快速找到value值。
⑥ map和multimap区别:
- map不允许容器中有重复key值元素。
- mutimap运行容器中有重复的key值元素。
9.2 pair对组的创建
① 功能描述:成对出现的数据,利用对组可以返回两个数据。
② 两种创建方式:
- pair<type,type> p (value1, value2);
- pair<type,type> p = make_pair(value1,value2);
② 两种方式都可以创建对组,记住一种即可。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
//pair对组的创建
void test01()
{
//第一种方式
pair<string, int>p("Tom", 20);
cout << "姓名:" << p.first << "年龄:" << p.second << endl;
//第二种方式
pair<string, int>p2 = make_pair("Jerry", 30);
cout << "姓名:" << p2.first << "年龄:" << p2.second << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 姓名:Tom年龄:20
- 姓名:Jerry年龄:30
- 请按任意键继续. . .
9.3 map容器构造和赋值
① 功能描述:对map容器进行构造和赋值操作。
② 构造函数:
- map<T1,T2> mp; //map默认构造函数
- map(const map &mp); //拷贝构造函数
③ 赋值操作:
- map& operator=(const map &mp); //重载等号操作符
④ map容器中所有元素都是成对出现,插入元素时候需要使用对组。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
//map容器 构造和赋值
void printMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int,int>::iterator it = m.begin();it!=m.end();it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建map容器
map<int, int>m;
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); //1为key;10为value
m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 40));
printMap(m);
//拷贝构造
map<int, int>m2(m);
printMap(m);
//赋值
map<int, int>m3;
m3 = m2;
printMap(m3);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- key = 1 value = 10
- key = 2 value = 20
- key = 3 value = 30
- key = 4 value = 40
-
- key = 1 value = 10
- key = 2 value = 20
- key = 3 value = 30
- key = 4 value = 40
-
- key = 1 value = 10
- key = 2 value = 20
- key = 3 value = 30
- key = 4 value = 40
-
- 请按任意键继续. . .
9.4 map容器大小和交换
① 功能描述:统计map容器大小以及交换map容器。
② 函数原型:
- size(); //返回容器中元素的数目。
- empty(); //判断容器是否为空。
- swap(st); //交换两个集合容器。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
void printMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int,int>::iterator it = m.begin();it!=m.end();it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
//大小
void test01()
{
//创建map容器
map<int, int>m;
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); //1为key;10为value
m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));
printMap(m);
if (m.empty())
{
cout << "m为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "m不为空" << endl;
cout << "m的大小" << m.size() << endl;
}
}
//交换
void test02()
{
map<int, int>m1;
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); //1为key;10为value
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));
map<int, int>m2;
m2.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 100));
m2.insert(pair<int, int>(5, 300));
m2.insert(pair<int, int>(6, 200));
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
printMap(m1);
printMap(m2);
m1.swap(m2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
printMap(m1);
printMap(m2);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- key = 1 value = 10
- key = 2 value = 20
- key = 3 value = 30
-
- m不为空
- m的大小3
- 交换前:
- key = 1 value = 10
- key = 2 value = 20
- key = 3 value = 30
-
- key = 4 value = 100
- key = 5 value = 300
- key = 6 value = 200
-
- 交换后:
- key = 4 value = 100
- key = 5 value = 300
- key = 6 value = 200
-
- key = 1 value = 10
- key = 2 value = 20
- key = 3 value = 30
-
- 请按任意键继续. . .
9.5 map容器插入和删除
① 功能描述:map容器进行插入数据和删除数据。
② 函数原型:
- insert(elem); //在容器中插入元素。
- clear(); //清除所有元素。
- erase(pos); //删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
- erase(beg,end); //删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。
- erase(key); //删除容器中值为key的元素。
③ map插入方式很多,记住其一即可。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
void printMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int,int>::iterator it = m.begin();it!=m.end();it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建map容器
map<int, int>m;
//第一种:
m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
//第二种:
m.insert(make_pair(2, 10));
//第三种:
m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30)); //map容器下为"值"为(3,30)
//第四种:
m[4] = 40;
cout << m[5] << endl; //由于没有m[5]没有数,它会自动创建出一个value为0的数
cout << m[4] << endl; //不建议用[]插入,但是可以利用key访问到value。
printMap(m);
//删除
m.erase(m.begin());
printMap(m);
m.erase(3); //安装key删除
printMap(m);
//清空方式一
m.erase(m.begin(),m.end());
//清空方式二
m.clear();
printMap(m);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 0
- 40
- key = 1 value = 10
- key = 2 value = 10
- key = 3 value = 30
- key = 4 value = 40
- key = 5 value = 0
-
- key = 2 value = 10
- key = 3 value = 30
- key = 4 value = 40
- key = 5 value = 0
-
- key = 2 value = 10
- key = 4 value = 40
- key = 5 value = 0
-
-
- 请按任意键继续. . .
9.6 map容器查找和统计
① 对map容器进行查找数据以及统计数据。
② 函数原型:
- find(key); //查找key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end();
- cout(key); //统计key的元素个数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
void test01()
{
//创建map容器
map<int, int>m;
m.insert(pair<int,int>(1, 10));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
m.insert(pair<int,int>(2, 20));
m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
map<int,int>::iterator pos = m.find(3);
if (pos != m.end())
{
cout << "查到了元素 key = " << (*pos).first << " value = " << pos->second << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到元素" << endl;
}
//统计
//map不允许插入重复key元素,count统计而言 结果要么是0 要么是1
//mutimap 的count统计可以大于1
int num = m.count(3);
cout << "num = " << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 查到了元素 key = 3 value = 30
- num = 1
- 请按任意键继续. . .
9.7 map容器排序
① map容器默认排序规则为按照key值进行从小到大排序,利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则。
② 利用仿函数可以指定map容器的排序规则。
③ 对于自定义数据类型,map必须要指定排序规则,同set容器。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
class MyCompare
{
public:
bool operator()(int v1, int v2)const
{
//降序
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void printMap(map<int, int, MyCompare>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建map容器
//不是插了之后再排序,而是在创建的时候就排序
map<int, int, MyCompare>m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 10));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 30));
m.insert(make_pair(4, 40));
m.insert(make_pair(5, 50));
printMap(m);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- key = 5 value = 50
- key = 4 value = 40
- key = 3 value = 30
- key = 2 value = 20
- key = 1 value = 10
-
- 请按任意键继续. . .
10. 评委打分
① 案例描述:选手ABCDE,10个评委分别对每一名选手打分,去除最高分,去除评委中最低分,取平均分。
② 实现步骤:
- 创建五名选手,放到vector容器中。
- 遍历vector容器,取出来每一个选手,执行for循环,可以把10个评委打分存到deque容器中。
- sort算法对deque容器中分数进行排序,去除最高分和最低分。
- deque容器遍历一遍,累加总分。
- 获取平均分。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm> //标准算法头文件
#include<ctime>
//选手类
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int score)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Score = score;
}
string m_Name; //姓名
int m_Score; //平均分
};
void createPerson(vector<Person>& v)
{
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
string name = "选手";
name += nameSeed[i];
int score = 0;
Person p(name, score);
//将创建的person对象,放入到容器中
v.push_back(p);
}
}
//2、给5名选手打分
void setScore(vector<Person>& v)
{
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//将评委的分数 放入到deque容器中
deque<int>d;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
int score = rand() % 41 + 60; // 60~100
d.push_back(score);
}
cout << "选手:" << it->m_Name << "打分:" << endl;
for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++)
{
cout << *dit << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//排序
sort(d.begin(), d.end());
//去除最高分和最低分
d.pop_back();
d.pop_front();
//取平均分
int sum = 0;
for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++)
{
sum += *dit; //累加每个评委的分数
}
int avg = sum / d.size();
//将平均分 赋值给选手身上
it->m_Score = avg;
}
}
void showScore(vector<Person>&v)
{
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << "平均分" << it->m_Score << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//1、创建5名选手
vector<Person>v; //存放选手容器
createPerson(v);
//测试
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << "分数:" << (*it).m_Score << endl;
}
//2、给5名选手打分
setScore(v);
//3、显示最后得分
showScore(v);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 姓名:选手A分数:0
- 姓名:选手B分数:0
- 姓名:选手C分数:0
- 姓名:选手D分数:0
- 姓名:选手E分数:0
- 选手:选手A打分:
- 87 90 93 71 96 67 60 83 64 73
- 选手:选手B打分:
- 88 72 66 97 62 90 93 95 100 63
- 选手:选手C打分:
- 63 85 71 63 92 64 89 90 89 98
- 选手:选手D打分:
- 98 61 62 76 62 74 90 65 85 68
- 选手:选手E打分:
- 87 67 96 60 75 63 92 76 98 75
- 姓名:选手A平均分78
- 姓名:选手B平均分83
- 姓名:选手C平均分80
- 姓名:选手D平均分72
- 姓名:选手E平均分78
- 请按任意键继续. . .
11. 年龄排序
① 案例描述:将Person自定义数据类型进行排序,Person中属性有姓名、年龄、身高。
② 排序规则:按照年龄进行升序,如果年龄相同按照身高进行降序。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
//list容器 排序案例 对于自定义数据类型 做排序
//按照年龄进行升序 如果年龄相同 按照身高进行降序
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age, int height)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
this->m_Height = height;
}
string m_Name; //姓名
int m_Age; //年龄
int m_Height; //身高
};
//指定排序规则
bool comparePerson(Person &p1, Person &p2)
{
//按照年龄 升序
if (p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age)
{
//年龄相同 按照身高排序
return p1.m_Height > p2.m_Height;
}
return p1.m_Age < p2.m_Age;
}
void test01()
{
list<Person>L; //创建容器
//准备数据
Person p1("刘备", 35, 175);
Person p2("刘备", 45, 180);
Person p3("刘备", 50, 170);
Person p4("刘备", 25, 190);
Person p5("刘备", 35, 160);
Person p6("刘备", 35, 200);
//插入数据
L.push_back(p1);
L.push_back(p2);
L.push_back(p3);
L.push_back(p4);
L.push_back(p5);
L.push_back(p6);
for (list<Person>::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << " 身高:" << it->m_Height << endl;
}
//排序
cout << "---------------" << endl;
cout << "排序后:" << endl;
//L.sort(); 报错,自定义数据类型编译器不知道怎么排序
L.sort(comparePerson);
for (list<Person>::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << " 身高:" << it->m_Height << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:35 身高:175
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:45 身高:180
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:50 身高:170
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:25 身高:190
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:35 身高:160
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:35 身高:200
- $ --------------- $
- 排序后:
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:25 身高:190
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:35 身高:200
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:35 身高:175
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:35 身高:160
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:45 身高:180
- 姓名:刘备 年龄:50 身高:170
- 请按任意键继续. . .
12. 员工分组
案例描述:
- 公司今天招募了10个员工(ABCDEFGHIJ),10名员工进入公司之后,需要指派员工在那个部门工作。
- 员工信息由:姓名 工资。部门为:策划、美术、研发。
- 随机给10名员工分配部门和工资。
- 通过multimap进行信息的插入。key(部门编号)value(员工)
- 分部门显示员工信息。
实现步骤:
- 创建10名员工,放到vector中
- 遍历vector容器,取出每个员工,进行随机分组。
- 分组后,将员工部门编号为key,具体员工作为value,放入到multimao容器中。
- 分部门显示员工信息。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include<string>
#include<ctime>
/*
实现步骤:
1. 创建10名员工,放到vector中
2. 遍历vector容器,取出每个员工,进行随机分组。
3. 分组后,将员工部门编号为key,具体员工作为value,放入到multimao容器中。
4. 分部门显示员工信息。
*/
#define CEHUA 0
#define MEISHU 1
#define YANFA 2
class Worker
{
public:
string m_Name;
int m_Salary;
};
void createWorker(vector<Worker>&v)
{
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJ";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Worker worker;
worker.m_Name = "员工";
worker.m_Name += nameSeed[i];
worker.m_Salary = rand() % 10000 + 10000; //10000~19999
//将员工放入到容器中
v.push_back(worker);
}
}
void setGroup(vector<Worker>&v,multimap<int,Worker>&m)
{
for (vector<Worker>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
//产生随机部门编号
int depeId = rand() % 3;//0 1 2
//将员工插入到分组中
//key代表部门编号,value代表具体员工
m.insert(make_pair(depeId, *it));
}
}
void showWorkerByGourp(multimap<int,Worker>&m)
{
//0 A B C 1 D E 2 F G
cout << "策划部门:" << endl;
multimap<int, Worker>::iterator pos = m.find(CEHUA);
int count = m.count(CEHUA); //统计具体人数
int index = 0;
for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++,index++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << "工资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;
}
cout << "--------" << endl;
cout << "美术部门:" << endl;
pos = m.find(MEISHU);
count = m.count(MEISHU); //统计具体人数
index = 0;
for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++, index++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << "工资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;
}
cout << "--------" << endl;
cout << "研发部门:" << endl;
pos = m.find(YANFA);
count = m.count(YANFA); //统计具体人数
index = 0;
for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++, index++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << "工资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//1、创建员工
vector<Worker>vWorker;
createWorker(vWorker);
//2、员工分组
//0号、1号、2号代表不同部门
multimap<int, Worker>mWorker;
setGroup(vWorker, mWorker);
//3、分组显示员工
showWorkerByGourp(mWorker);
//测试
cout << "--------" << endl;
cout << "测试:" << endl;
for (vector<Worker>::iterator it = vWorker.begin(); it != vWorker.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 工资:" << it->m_Salary << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 策划部门:
- 姓名:员工B工资:11578
- - 姓名:员工D工资:11655
- 姓名:员工G工资:16818
- 姓名:员工J工资:12160
- $--------$
- 美术部门:
- 姓名:员工F工资:12782
- 姓名:员工H工资:15815
- $--------$
- 研发部门:
- 姓名:员工A工资:16686
- 姓名:员工C工资:10638
- 姓名:员工E工资:11730
- 姓名:员工I工资:17047
- $--------$
- 测试:
- 姓名:员工A 工资:16686
- 姓名:员工B 工资:11578
- 姓名:员工C 工资:10638
- 姓名:员工D 工资:11655
- 姓名:员工E 工资:11730
- 姓名:员工F 工资:12782
- 姓名:员工G 工资:16818
- 姓名:员工H 工资:15815
- 姓名:员工I 工资:17047
- 姓名:员工J 工资:12160
- 请按任意键继续. . .






















 254
254











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








