1 概述
1.1 定义
Mapreduce 是一个分布式运算程序的编程框架,是用户开发“基于 hadoop 的数据分析应用”的核心框架。
Mapreduce 核心功能是将用户编写的业务逻辑代码和自带默认组件整合成一个完整的分布式运算程序,并发运行在一个 hadoop 集群上。
1.2 优缺点
1.2.1 优点
- MapReduce 易于编程。它简单的实现一些接口,就可以完成一个分布式程序,这个分布式程序可以分布到大量廉价的 PC 机器上运行。也就是说你写一个分布式程序,跟写一个简单的串行程序是一模一样的。就是因为这个特点使得 MapReduce 编程变得非常流行。
- 良好的扩展性。当你的计算资源不能得到满足的时候,你可以通过简单的增加机器来扩展它的计算能力。
- 高容错性。MapReduce 设计的初衷就是使程序能够部署在廉价的 PC 机器上,这就要求它具有很高的容错性。比如其中一台机器挂了,它可以把上面的计算任务转移到另外一个节点上运行,不至于这个任务运行失败,而且这个过程不需要人工参与,而完全是由Hadoop 内部完成的。
- 适合 PB 级以上海量数据的离线处理。这里加红字体离线处理,说明它适合离线处理而不适合在线处理。比如像毫秒级别的返回一个结果,MapReduce 很难做到。
1.2.2 缺点
MapReduce 不擅长做实时计算、流式计算、DAG(有向图)计算。
- 实时计算。MapReduce 无法像 Mysql 一样,在毫秒或者秒级内返回结果
- 流式计算。流式计算的输入数据是动态的,而 MapReduce 的输入数据集是静态的,不能动态变化。这是因为 MapReduce 自身的设计特点决定了数据源必须是静态的。
- DAG(有向图)计算。多个应用程序存在依赖关系,后一个应用程序的输入为前一个的输出。在这种情况下,MapReduce 并不是不能做,而是使用后,每个 MapReduce 作业的输出结果都会写入到磁盘,会造成大量的磁盘 IO,导致性能非常的低下。
1.3 核心思想
- 分布式的运算程序往往需要分成至少 2 个阶段。
- 第一个阶段的 maptask 并发实例,完全并行运行,互不相干。
- 第二个阶段的 reduce task 并发实例互不相干,但是他们的数据依赖于上一个阶段的所有maptask 并发实例的输出。
- MapReduce 编程模型只能包含一个 map 阶段和一个 reduce 阶段,如果用户的业务逻辑非常复杂,那就只能多个 mapreduce 程序,串行运行。
1.4 MapReduce 进程
一个完整的 mapreduce 程序在分布式运行时有三类实例进程:
- MrAppMaster:负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调。
- MapTask:负责 map 阶段的整个数据处理流程。
- ReduceTask:负责 reduce 阶段的整个数据处理流程
1.5 MapReduce 编程规范(八股文)
用户编写的程序分成三个部分:Mapper,Reducer,Driver(提交运行 mr 程序的客户端)
- Mapper 阶段
- 用户自定义的 Mapper 要继承自己的父类
- Mapper 的输入数据是 KV 对的形式(KV 的类型可自定义)
- Mapper 中的业务逻辑写在 map()方法中
- Mapper 的输出数据是 KV 对的形式(KV 的类型可自定义)
- map()方法(maptask 进程)对每一个<K,V>调用一次
代码示例:
/**
* @author huwenlong
* @date 2019/1/27 17:17
* 输入的key:行号
* 输入的value:一行内容
* 输出的key:单词
* 输出的value:单词个数
*/
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final Text text = new Text();
private final IntWritable intWritable = new IntWritable(1);
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 一行内容转换为字符串
String line = value.toString();
// 切割成单词
String[] words = line.split(" ");
// 循环写出到下一阶段
for(String word: words) {
text.set(word);
context.write(text, intWritable);
}
}
}
- Reducer 阶段
- 用户自定义的 Reducer 要继承自己的父类
- Reducer 的输入数据类型对应 Mapper 的输出数据类型,也是 KV
- Reducer 的业务逻辑写在 reduce()方法中
- Reducetask 进程对每一组相同 k 的<k,v>组调用一次 reduce()方法
代码示例
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author huwenlong
* @date 2019/1/27 18:09
*/
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private final Text text = new Text();
private final IntWritable intWritable = new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String word = key.toString();
Integer count = 0;
for (IntWritable value: values) {
count += value.get();
}
text.set(word);
intWritable.set(count);
context.write(text, intWritable);
}
}
- Driver 阶段
整个程序需要一个 Drvier 来进行提交,提交的是一个描述了各种必要信息的 job 对象
代码示例
/**
* @author jiguang.qi
* @date 2019/1/27 18:52
*/
public class WordCountDriver {
static {
try {
System.load("D:/java/hadoop-2.9.2/bin/hadoop.dll");
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError e) {
System.err.println("Native code library failed to load." + e);
System.exit(1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
// 1 获取配置信息
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// 开启 map 端输出压缩
configuration.setBoolean("mapreduce.map.output.compress", true);
// 设置 map 端输出压缩方式
configuration.setClass("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec", BZip2Codec.class, CompressionCodec.class);
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
// 2 设置 jar 加载路径
job.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class);
// 3 设置 map 和 Reduce 类
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
// 4 设置 map 输出
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 5 设置 Reduce 输出
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 如果不设置 InputFormat,它默认用的是 TextInputFormat.class
job.setInputFormatClass(CombineTextInputFormat.class);
CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 4194304);// 4m
CombineTextInputFormat.setMinInputSplitSize(job, 2097152);// 2m
// 设置 reduce 端输出压缩开启
FileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
// 设置压缩的方式
FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, BZip2Codec.class);
// FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class);
// FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, DefaultCodec.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, "D:\\file\\hadoop\\wordcount\\input");
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("D:\\file\\hadoop\\wordcount\\output"));
// 7 提交
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(result ? 0 : 1);
}
}
2 序列化
2.1 为什么要序列化?
一般来说,“活的”对象只生存在内存里,关机断电就没有了。而且“活的”对象只能由本地的进程使用,不能被发送到网络上的另外一台计算机。 然而序列化可以存储“活的”对象,可以将“活的”对象发送到远程计算机。
2.2 什么是序列化?
序列化就是把内存中的对象,转换成字节序列(或其他数据传输协议)以便于存储(持久化)和网络传输。
反序列化就是将收到字节序列(或其他数据传输协议)或者是硬盘的持久化数据,转换成内存中的对象
2.3 为什么不用 Java 的序列化?
Java 的序列化是一个重量级序列化框架(Serializable),一个对象被序列化后,会附带很多额外的信息(各种校验信息,header,继承体系等),不便于在网络中高效传输。所以,hadoop 自己开发了一套序列化机制(Writable),精简、高效。
2.4 为什么序列化对 Hadoop 很重要?
因为 Hadoop 在集群之间进行通讯或者 RPC 调用的时候,需要序列化,而且要求序列化要快,且体积要小,占用带宽要小。所以必须理解 Hadoop 的序列化机制。
序列化和反序列化在分布式数据处理领域经常出现:进程通信和永久存储。然而 Hadoop中各个节点的通信是通过远程调用(RPC)实现的,那么 RPC 序列化要求具有以下特点:
- 紧凑:紧凑的格式能让我们充分利用网络带宽,而带宽是数据中心最稀缺的资
- 快速:进程通信形成了分布式系统的骨架,所以需要尽量减少序列化和反序列化的性能开销,这是基本的;
- 可扩展:协议为了满足新的需求变化,所以控制客户端和服务器过程中,需要直接引进相应的协议,这些是新协议,原序列化方式能支持新的协议报文;
- 互操作:能支持不同语言写的客户端和服务端进行交互;
2.5 常用数据序列化类型
常用的数据类型对应的 hadoop 数据序列化类型
| Java 类型 | Hadoop Writable 类型 |
|---|---|
| boolean | BooleanWritable |
| byte | ByteWritable |
| int | IntWritable |
| float | FloatWritable |
| long | LongWritable |
| double | DoubleWritable |
| string | Text |
| map | MapWritable |
| array | ArrayWritable |
2.6 自定义 bean 对象实现序列化接口(Writable)
自定义 bean 对象要想序列化传输,必须实现序列化接口,需要注意以下 7 项。
- 必须实现 Writable 接口
- 反序列化时,需要反射调用空参构造函数,所以必须有空参构造
- 重写序列化方法
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(upFlow);
out.writeLong(downFlow);
out.writeLong(sumFlow);
}
- 重写反序列化方法
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
upFlow = in.readLong();
downFlow = in.readLong();
sumFlow = in.readLong();
}
- 注意反序列化的顺序和序列化的顺序完全一致
- 要想把结果显示在文件中,需要重写 toString(),属性之间用”\t”分开,方便后续用。
- 如果需要将自定义的 bean 放在 key 中传输,则还需要实现 comparable 接口,因为mapreduce 框中的 shuffle 过程一定会对 key 进行排序。
@Override
public int compareTo(FlowBean o) {
// 倒序排列,从大到小
return this.sumFlow > o.getSumFlow() ? -1 : 1;
}
3 核心框架原理
3.1 工作流程
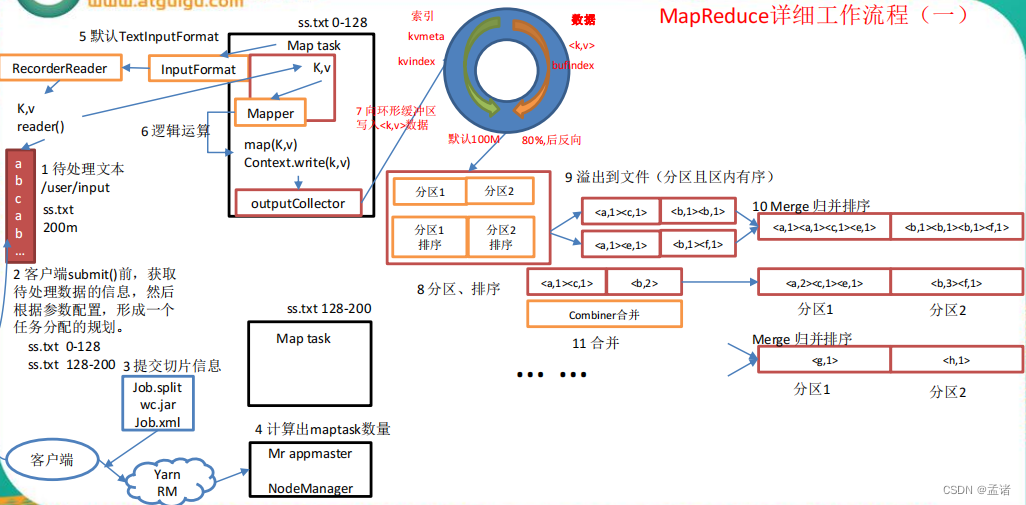
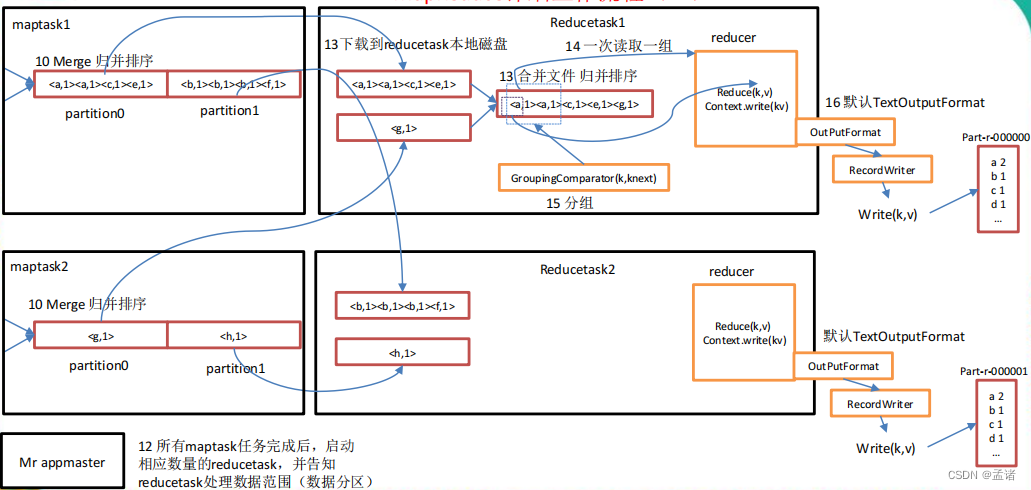
上面的流程是整个 mapreduce 最全工作流程,但是 shuffle 过程只是从第 7 步开始到第16 步结束,具体 shuffle 过程详解,如下:
- maptask 收集我们的 map()方法输出的 kv 对,放到内存缓冲区中
- 从内存缓冲区不断溢出本地磁盘文件,可能会溢出多个文件
- 多个溢出文件会被合并成大的溢出文件
- 在溢出过程中,及合并的过程中,都要调用 partitioner 进行分区和针对 key 进行排序
- reducetask 根据自己的分区号,去各个 maptask 机器上取相应的结果分区数据
- reducetask 会取到同一个分区的来自不同 maptask 的结果文件,reducetask 会将这些文件再进行合并(归并排序)
- 合并成大文件后,shuffle 的过程也就结束了,后面进入 reducetask 的逻辑运算过程(从文件中取出一个一个的键值对 group,调用用户自定义的 reduce()方法)
注意:Shuffle 中的缓冲区大小会影响到 mapreduce 程序的执行效率,原则上说,缓冲区越大,磁盘 io 的次数越少,执行速度就越快。缓冲区的大小可以通过参数调整,参数:io.sort.mb 默认 100M。
3.2 InputFormat 数据输入
- 找到你数据存储的目录。
- 开始遍历处理(规划切片)目录下的每一个文件
- 遍历第一个文件 ss.txt
- 获取文件大小 fs.sizeOf(ss.txt);
- 计算切片大小
computeSliteSize(Math.max(minSize,Math.min(maxSize,blocksize)))=blocksize=128M默认情况下,切片大小=blocksize- 开始切,形成第 1 个切片:ss.txt—0:128M 第 2 个切片 ss.txt—128:256M 第 3个切片 ss.txt—256M:300M(每次切片时,都要判断切完剩下的部分是否大于块的 1.1 倍,不大于 1.1 倍就划分一块切片)
- 将切片信息写到一个切片规划文件中
- 整个切片的核心过程在 getSplit()方法中完成。
- 数据切片只是在逻辑上对输入数据进行分片,并不会再磁盘上将其切分成分片进行存储。InputSplit 只记录了分片的元数据信息,比如起始位置、长度以及所在的节点列表等。
- 注意:block 是 HDFS 物理上存储的数据,切片是对数据逻辑上的划分。
- 提交切片规划文件到 yarn 上,yarn 上的 MrAppMaster 就可以根据切片规划文件计算开启 maptask 个数。
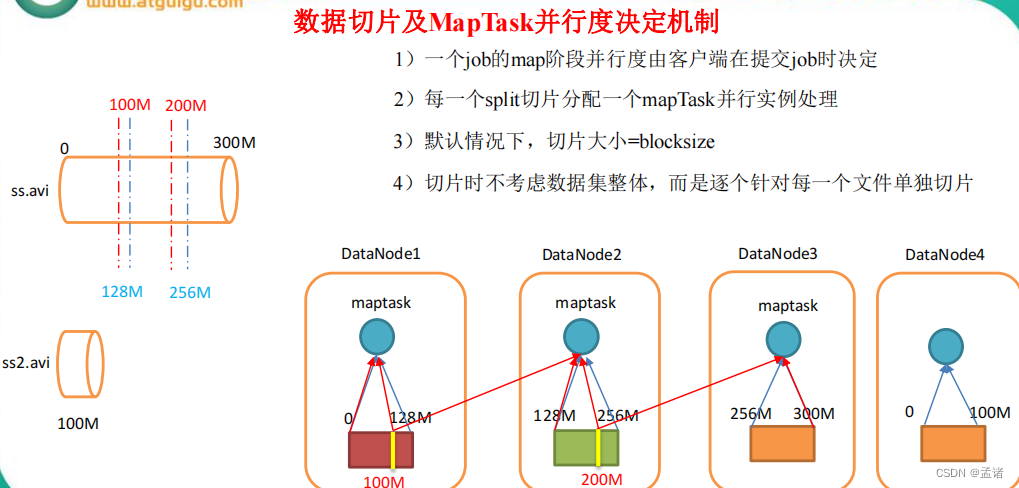
3.2.1 FileInputFormat 切片机制
- 简单地按照文件的内容长度进行切片
- 切片大小,默认等于 block 大小
- 切片时不考虑数据集整体,而是逐个针对每一个文件单独切片
比如待处理数据有两个文件:
file1.txt 320M
file2.txt 10M
经过 FileInputFormat 的切片机制运算后,形成的切片信息如下:
file1.txt.split1-- 0~128
file1.txt.split2-- 128~256
file1.txt.split3-- 256~320
file2.txt.split1-- 0~10M
FileInputFormat 切片大小的参数配置:
通过分析源码,在 FileInputFormat 中,计算切片大小的逻辑:
Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
切片主要由这几个值来运算决定
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize=1 默认值为 1
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize= Long.MAXValue 默认值 Long.MAXValue
因此,默认情况下,切片大小=blocksize。
- maxsize(切片最大值):参数如果调得比 blocksize 小,则会让切片变小,而且就等于配置的这个参数的值。
- minsize(切片最小值):参数调的比 blockSize 大,则可以让切片变得比 blocksize 还大。 3)获取切片信息 API
// 根据文件类型获取切片信息
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
// 获取切片的文件名称
String name = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
3.2.2 CombineTextInputFormat 切片机制
默认情况下 TextInputformat 对任务的切片机制是按文件规划切片,不管文件多小,都会是一个单独的切片,都会交给一个 maptask,这样如果有大量小文件,就会产生大量的maptask,处理效率极其低下。
优化策略:
- 最好的办法,在数据处理系统的最前端(预处理/采集),将小文件先合并成大文件,再上传到 HDFS 做后续分析。
- 补救措施:如果已经是大量小文件在 HDFS 中了,可以使用另一种 InputFormat来做切片(CombineTextInputFormat),它的切片逻辑跟 TextFileInputFormat 不同:它可以将多个小文件从逻辑上规划到一个切片中,这样,多个小文件就可以交给一个 maptask。
- 优先满足最小切片大小,不超过最大切片大小
CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 4194304);// 4m
CombineTextInputFormat.setMinInputSplitSize(job, 2097152);// 2m
举例:0.5m+1m+0.3m+5m=2m + 4.8m=2m + 4m + 0.8m
具体实现步骤:
// 如果不设置 InputFormat,它默认用的是 TextInputFormat.class
job.setInputFormatClass(CombineTextInputFormat.class)
CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 4194304);// 4m
CombineTextInputFormat.setMinInputSplitSize(job, 2097152);// 2m
3.2.3 InputFormat 接口实现类
- TextInputFormat
TextInputFormat 是默认的 InputFormat。每条记录是一行输入。键是 LongWritable 类型,存储该行在整个文件中的字节偏移量。值是这行的内容,不包括任何行终止符(换行符和回车符)。以下是一个示例,比如,一个分片包含了如下 4 条文本记录。
Rich learning form
Intelligent learning engine
Learning more convenient
From the real demand for more close to the enterprise
每条记录表示为以下键/值对:
(0,Rich learning form)
(19,Intelligent learning engine)
(47,Learning more convenient)
(72,From the real demand for more close to the enterprise)
很明显,键并不是行号。一般情况下,很难取得行号,因为文件按字节而不是按行切分为分片。
- KeyValueTextInputFormat
每一行均为一条记录,被分隔符分割为 key,value。可以通过在驱动类中设置conf.set(KeyValueLineRecordReader.KEY_VALUE_SEPERATOR, " ");
来设定分隔符。默认分隔符是 tab(\t)。
以下是一个示例,输入是一个包含 4 条记录的分片。其中——>表示一个(水平方向的)制表符。
line1 ——>Rich learning form
line2 ——>Intelligent learning engine
line3 ——>Learning more convenient
line4 ——>From the real demand for more close to the enterprise
每条记录表示为以下键/值对:
(line1,Rich learning form)
(line2,Intelligent learning engine)
(line3,Learning more convenient)
(line4,From the real demand for more close to the enterprise)
此时的键是每行排在制表符之前的 Text 序列。
- NLineInputFormat
如果使用 NlineInputFormat,代表每个 map 进程处理的 InputSplit 不再按 block 块去划分,而是按 NlineInputFormat 指定的行数 N 来划分。即输入文件的总行数/N=切片数,如果不整除,切片数=商+1。
以下是一个示例,仍然以上面的 4 行输入为例。
Rich learning form
Intelligent learning engine
Learning more convenient
From the real demand for more close to the enterprise
例如,如果 N 是 2,则每个输入分片包含两行。开启 2 个 maptask。
(0,Rich learning form)
(19,Intelligent learning engine)
另一个 mapper 则收到后两行:
(47,Learning more convenient)
(72,From the real demand for more close to the enterprise)
这里的键和值与 TextInputFormat 生成的一样。
- 自定义 InputFormat
(1)自定义一个类继承 FileInputFormat。
(2)改写 RecordReader,实现一次读取一个完整文件封装为 KV。
(3)在输出时使用 SequenceFileOutPutFormat 输出合并文件。
3.3 MapTask 工作机制
3.3.1 并行度决定机制
1)问题引出
maptask 的并行度决定 map 阶段的任务处理并发度,进而影响到整个 job 的处理速度。那么,mapTask 并行任务是否越多越好呢?
2)MapTask 并行度决定机制
一个 job 的 map 阶段 MapTask 并行度(个数),由客户端提交 job 时的切片个数决定。
3.3.2 MapTask 工作机制
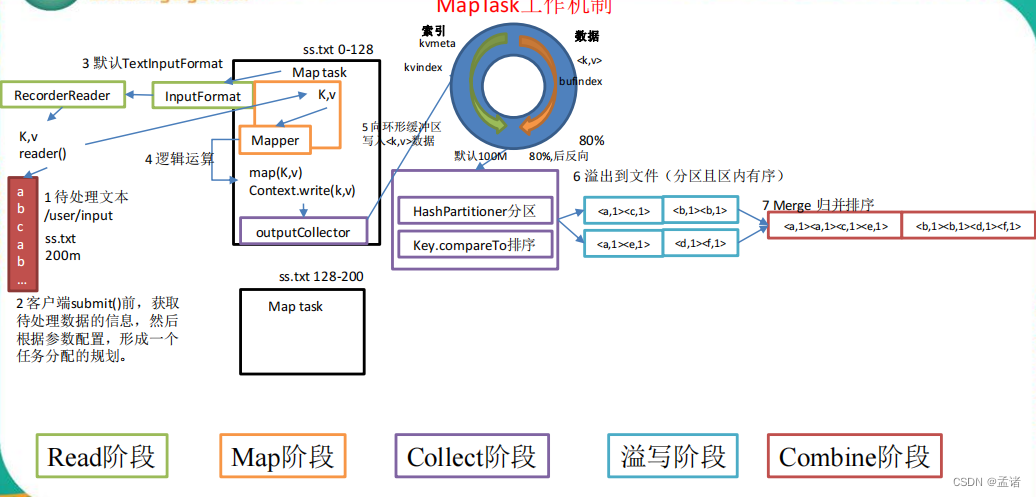
- Read 阶段:Map Task 通过用户编写的 RecordReader,从输入 InputSplit 中解析出一个个 key/value。
- Map 阶段:该节点主要是将解析出的 key/value 交给用户编写 map()函数处理,并产生一系列新的 key/value。
- Collect 收集阶段:在用户编写 map()函数中,当数据处理完成后,一般会调用 OutputCollector.collect()输出结果。在该函数内部,它会将生成的 key/value 分区(调用 Partitioner)并写入一个环形内存缓冲区中。
- Spill 阶段:即“溢写”,当环形缓冲区满后,MapReduce 会将数据写到本地磁盘上,生成一个临时文件。需要注意的是,将数据写入本地磁盘之前,先要对数据进行一次本地排序,并在必要时对数据进行合并、压缩等操作。 溢写阶段详情:
- 步骤 1:利用快速排序算法对缓存区内的数据进行排序,排序方式是,先按照分区编号 partition 进行排序,然后按照 key 进行排序。这样,经过排序后,数据以分区为单位聚集在一起,且同一分区内所有数据按照 key 有序。
- 步骤 2:按照分区编号由小到大依次将每个分区中的数据写入任务工作目录下的临时文件 output/spillN.out(N 表示当前溢写次数)中。如果用户设置了 Combiner,则写入文件之前,对每个分区中的数据进行一次聚集操作。
- 步骤 3:将分区数据的元信息写到内存索引数据结构 SpillRecord 中,其中每个分区的元信息包括在临时文件中的偏移量、压缩前数据大小和压缩后数据大小。如果当前内存索引大小超过 1MB,则将内存索引写到文件 output/spillN.out.index 中。
- Combine 阶段:当所有数据处理完成后,MapTask 对所有临时文件进行一次合并,以确保最终只会生成一个数据文件。
当所有数据处理完后,MapTask 会将所有临时文件合并成一个大文件,并保存到文件 output/file.out 中,同时生成相应的索引文件 output/file.out.index。 在进行文件合并过程中,MapTask 以分区为单位进行合并。对于某个分区,它将采用多轮递归合并的方式。每轮合并 io.sort.factor(默认 100)个文件,并将产生的文件重新加入待合并列表中,对文件排序后,重复以上过程,直到最终得到一个大文件。让每个 MapTask 最终只生成一个数据文件,可避免同时打开大量文件和同时读取大量小文件产生的随机读取带来的开销
3.4 Shuffle 机制
3.4.1 Shuffle 机制
Mapreduce 确保每个 reducer 的输入都是按键排序的。系统执行排序的过程(即将 map输出作为输入传给 reducer)称为 shuffle。
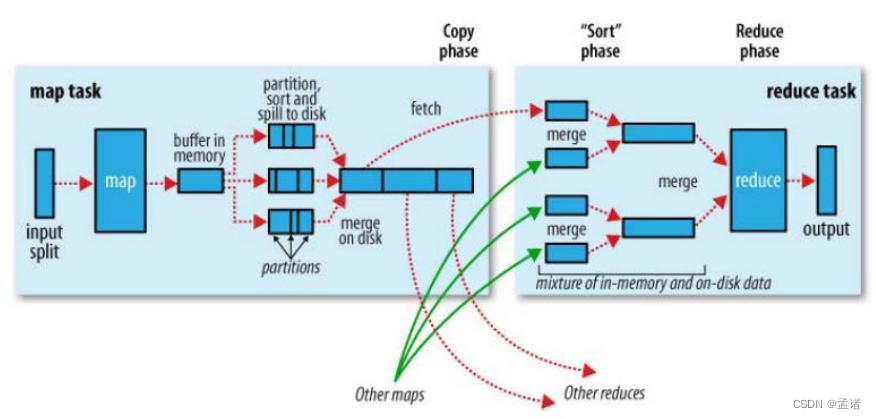
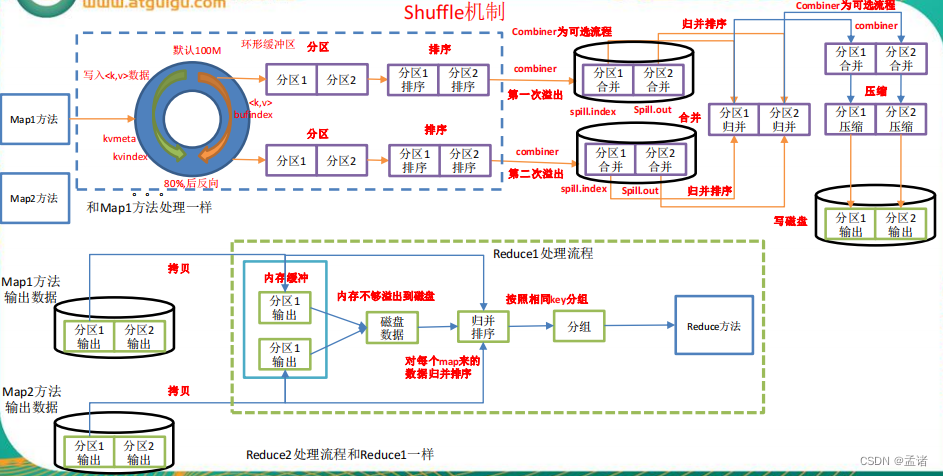
3.4.2 Partition 分区
问题引出:要求将统计结果按照条件输出到不同文件中(分区)。比如:将统计结果按照手机归属地不同省份输出到不同文件中(分区)
- 默认 partition 分区
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
- 自定义 partition 分区
public class PhoneDataPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, PhoneData> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, PhoneData value, int numReduceTask) {
// 和 reduceTask 个数保持一致
return (int) (Long.parseLong(key.toString()) % 5);
}
}
// 自定义分区
job.setPartitionerClass(PhoneDataPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(5);
注意:
- 如果 reduceTask 的数量> getPartition 的结果数,则会多产生几个空的输出文件
- 如果 1<reduceTask 的数量<getPartition 的结果数,则有一部分分区数据无处安放,会Exception;
- 如果 reduceTask 的数量=1,则不管 mapTask 端输出多少个分区文件,最终结果都交给这一个 reduceTask,最终也就只会产生一个结果文件 part-r-00000;
例如:假设自定义分区数为 5,则
(1)job.setNumReduceTasks(1);会正常运行,只不过会产生一个输出文件
(2)job.setNumReduceTasks(2);会报错
(3)job.setNumReduceTasks(6);大于 5,程序会正常运行,会产生空文件
3.4.3 WritableComparable 排序
排序是 MapReduce 框架中最重要的操作之一。Map Task 和 Reduce Task 均会对数据(按 照 key)进行排序。该操作属于 Hadoop 的默认行为。任何应用程序中的数据均会被排序,而不管逻辑上是否需要。默认排序是按照字典顺序排序,且实现该排序的方法是快速排序。
对于 Map Task,它会将处理的结果暂时放到一个缓冲区中,当缓冲区使用率达到一定阈值后,再对缓冲区中的数据进行一次排序,并将这些有序数据写到磁盘上,而当数据处理完毕后,它会对磁盘上所有文件进行一次合并,以将这些文件合并成一个大的有序文件。
对于 Reduce Task,它从每个 Map Task 上远程拷贝相应的数据文件,如果文件大小超过一定阈值,则放到磁盘上,否则放到内存中。如果磁盘上文件数目达到一定阈值,则进行一次合并以生成一个更大文件;如果内存中文件大小或者数目超过一定阈值,则进行一次合并后将数据写到磁盘上。当所有数据拷贝完毕后,Reduce Task 统一对内存和磁盘上的所有数据进行一次合并。
每个阶段的默认排序
1)排序的分类:
(1)部分排序:
MapReduce 根据输入记录的键对数据集排序。保证输出的每个文件内部排序。
(2)全排序:
如何用 Hadoop 产生一个全局排序的文件?最简单的方法是使用一个分区。但该方法在处理大型文件时效率极低,因为一台机器必须处理所有输出文件,从而完全丧失了 MapReduce 所提供的并行架构。
替代方案:首先创建一系列排好序的文件;其次,串联这些文件;最后,生成一个全局排序的文件。主要思路是使用一个分区来描述输出的全局排序。例如:可以为上述文件创建3 个分区,在第一分区中,记录的单词首字母 a-g,第二分区记录单词首字母 h-n, 第三分区记录单词首字母 o-z。
(3)辅助排序:(GroupingComparator 分组)
Mapreduce 框架在记录到达 reducer 之前按键对记录排序,但键所对应的值并没有被排序。甚至在不同的执行轮次中,这些值的排序也不固定,因为它们来自不同的 map 任务且这些 map 任务在不同轮次中完成时间各不相同。一般来说,大多数 MapReduce 程序会避免让 reduce 函数依赖于值的排序。但是,有时也需要通过特定的方法对键进行排序和分组等以实现对值的排序。
(4)二次排序:
在自定义排序过程中,如果 compareTo 中的判断条件为两个即为二次排序。
2)自定义排序 WritableComparable
bean 对象实现 WritableComparable 接口重写 compareTo 方法,就可以实现排序
@Override
public int compareTo(FlowBean o) {
// 倒序排列,从大到小
return this.sumFlow > o.getSumFlow() ? -1 : 1;
}
3.4.4 GroupingComparator 分组
对 reduce 阶段的数据根据某一个或几个字段进行分组。
public class StudentComparator extends WritableComparator {
protected StudentComparator() {
super(Student.class, true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
Student student1 = (Student) a;
Student student2 = (Student) b;
return student1.getClassId().compareTo(student2.getClassId());
}
}
// 设置reduce端分组
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(StudentComparator.class);
3.4.5 Combiner 合并
combiner 是 MR 程序中 Mapper 和 Reducer 之外的一种组件,组件的父类就是 Reducer。combiner 和 reducer 的区别在于运行的位置:
- Combiner 是在每一个 maptask 所在的节点运行;
- Reducer 是接收全局所有 Mapper 的输出结果;
combiner 的意义就是对每一个 maptask 的输出进行局部汇总,以减小网络传输量。 combiner 能够应用的前提是不能影响最终的业务逻辑,而且,combiner 的输出 kv 应该跟 reducer 的输入 kv 类型要对应起来。
job.setCombinerClass(WordcountCombiner.class);
3.5 ReduceTask 工作机制
reducetask 的并行度同样影响整个 job 的执行并发度和执行效率,但与 maptask 的并发数由切片数决定不同,Reducetask 数量的决定是可以直接手动设置:
//默认值是 1,手动设置为 4
job.setNumReduceTasks(4);
注意
- reducetask=0 ,表示没有 reduce 阶段,输出文件个数和 map 个数一致。
- reducetask 默认值就是 1,所以输出文件个数为一个。
- 如果数据分布不均匀,就有可能在 reduce 阶段产生数据倾斜
- reducetask 数量并不是任意设置,还要考虑业务逻辑需求,有些情况下,需要计算全局汇总结果,就只能有 1 个 reducetask。
- 具体多少个 reducetask,需要根据集群性能而定。
- 如果分区数不是 1,但是 reducetask 为 1,是否执行分区过程。答案是:不执行分区过程。因为在 maptask 的源码中,执行分区的前提是先判断 reduceNum 个数是否大于1,不大于 1 肯定不执行。
3.6 OutputFormat 数据输出
3.6.1 OutputFormat 接口实现类
OutputFormat 是 MapReduce 输出的基类,所有实现 MapReduce 输出都实现了 OutputFormat 接口。下面我们介绍几种常见的 OutputFormat 实现类。
- TextOutputFormat
默认的输出格式是 TextOutputFormat,它把每条记录写为文本行。它的键和值可以是任意类型,因为 TextOutputFormat 调用 toString()方法把它们转换为字符串。 - SequenceFileOutputFormat
SequenceFileOutputFormat 将它的输出写为一个顺序文件。如果输出需要作为后续MapReduce 任务的输入,这便是一种好的输出格式,因为它的格式紧凑,很容易被压缩。
3.6.2 自定义 OutputFormat
为了实现控制最终文件的输出路径,可以自定义 OutputFormat。要在一个 mapreduce 程序中根据数据的不同输出两类结果到不同目录,这类灵活的输出需求可以通过自定义 outputformat 来实现。
- 自定义一个类继承 FileOutputFormat,改写 recordwriter,具体改写输出数据的方法 write()。
public class SelfOutputRecordWriter extends RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> {
private TaskAttemptContext context;
private Configuration configuration;
private FSDataOutputStream infoOutput;
private FSDataOutputStream errorOutput;
public SelfOutputRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext context) {
this.context = context;
this.configuration = context.getConfiguration();
try {
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(configuration);
infoOutput = fileSystem.create(new Path("D:\\file\\hadoop\\selfoutput\\output\\info.txt"));
errorOutput = fileSystem.create(new Path("D:\\file\\hadoop\\selfoutput\\output\\error.txt"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void write(Text text, NullWritable nullWritable) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String str = text.toString() + "\r\n";
if (str.contains("error")) {
// 计数器的应用
context.getCounter("log", "error").increment(1);
errorOutput.write(str.getBytes());
}else {
context.getCounter("log", "other").increment(1);
infoOutput.write(str.getBytes());
}
}
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext taskAttemptContext) {
IOUtils.closeStream(infoOutput);
IOUtils.closeStream(errorOutput);
}
}
public class SelfFileOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat<Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
public RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> getRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext taskAttemptContext) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return new SelfOutputRecordWriter(taskAttemptContext);
}
}
// 设置 OutputFormat
job.setOutputFormatClass(SelfFileOutputFormat.class);
3.7 Join 多种应用
3.7.1 Reduce join
Map 端的主要工作:为来自不同表(文件)的 key/value 对打标签以区别不同来源的记录。然后用连接字段作为 key,其余部分和新加的标志作为 value,最后进行输出。
Reduce 端的主要工作:在 reduce 端以连接字段作为 key 的分组已经完成,我们只需要在每一个分组当中将那些来源于不同文件的记录(在 map 阶段已经打标志)分开,最后进行合并就 ok 了。
这种方式的缺点很明显就是会造成 map 和 reduce 端也就是 shuffle 阶段出现大量的数据
案例:订单、产品两个文件,把订单文件中的 pid 转换为 pName
mapper:
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
FileSplit fileSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
String fileName = fileSplit.getPath().getName();
String[] strs = value.toString().split("\\s+");
OrderProduct orderProduct = new OrderProduct();
if (Objects.equals(fileName, "order.txt")) {
orderProduct.setOrderId(strs[0]);
orderProduct.setProductId(strs[1]);
orderProduct.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(strs[2]));
// 订单文件标识为0
orderProduct.setFlag(0);
}else {
orderProduct.setProductId(strs[0]);
orderProduct.setProductName(strs[1]);
// 产品文件标识为1
orderProduct.setFlag(1);
}
this.key.set(orderProduct.getProductId());
context.write(this.key, orderProduct);
}
reducer:
public class TableJoinReducer extends Reducer<Text, OrderProduct, OrderProduct, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<OrderProduct> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
List<OrderProduct> list = new ArrayList<>();
OrderProduct product = new OrderProduct();
for (OrderProduct value : values) {
if (value.getFlag() == 0) {
OrderProduct order = new OrderProduct();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(value, order);
list.add(order);
}else {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(value, product);
}
}
for (OrderProduct orderProduct: list) {
orderProduct.setProductName(product.getProductName());
context.write(orderProduct, NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
3.7.2 Map join(Distributedcache 分布式缓存)
使用场景:一张表十分小、一张表很大。
解决方案:在 map 端缓存多张表,提前处理业务逻辑,这样增加 map 端业务,减少 reduce 端数据的压力,尽可能的减少数据倾斜。
public class DistributeCacheMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderProduct, NullWritable> {
private Map<String, String> productMap = new HashMap<>();
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException {
// 读取缓存文件
URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles();
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(context.getConfiguration());
FSDataInputStream fsDataInputStream = fileSystem.open(new Path(cacheFiles[0]));
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fsDataInputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String line;
while (StringUtils.notEmpty(line = bufferedReader.readLine())) {
String[] strs = line.split("\t+");
productMap.put(strs[0], strs[1]);
}
bufferedReader.close();
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] strs = value.toString().split("\\s+");
OrderProduct orderProduct = new OrderProduct();
orderProduct.setOrderId(strs[0]);
orderProduct.setProductName(productMap.get(strs[1]));
orderProduct.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(strs[2]));
context.write(orderProduct, NullWritable.get());
}
}
// 3 设置 map 类
job.setMapperClass(DistributeCacheMapper.class);
// 5 没有reduce阶段直接设置最终输出
job.setOutputKeyClass(OrderProduct.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
// 设置缓存文件
job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:///D:/file/hadoop/table_join/input/product.txt"));
4 压缩
4.1 概述
压缩技术能够有效减少底层存储系统(HDFS)读写字节数。压缩提高了网络带宽和磁 盘空间的效率。在 Hadoop 下,尤其是数据规模很大和工作负载密集的情况下,使用数据压缩显得非常重要。在这种情况下,I/O 操作和网络数据传输要花大量的时间。还有,Shuffle 与 Merge 过程同样也面临着巨大的 I/O 压力。
鉴于磁盘 I/O 和网络带宽是 Hadoop 的宝贵资源,数据压缩对于节省资源、最小化磁盘 I/O 和网络传输非常有帮助。不过,尽管压缩与解压操作的 CPU 开销不高,其性能的提升和资源的节省并非没有代价。
如果磁盘 I/O 和网络带宽影响了 MapReduce 作业性能,在任意 MapReduce 阶段启用压缩都可以改善端到端处理时间并减少 I/O 和网络流量。压缩 Mapreduce 的一种优化策略:通过压缩编码对 Mapper 或者 Reducer 的输出进行压缩,以减少磁盘 IO,提高 MR 程序运行速度(但相应增加了 cpu 运算负担)。
注意:压缩特性运用得当能提高性能,但运用不当也可能降低性能。
基本原则:
(1)运算密集型的 job,少用压缩
(2)IO 密集型的 job,多用压缩
4.2 MR 支持的压缩编码
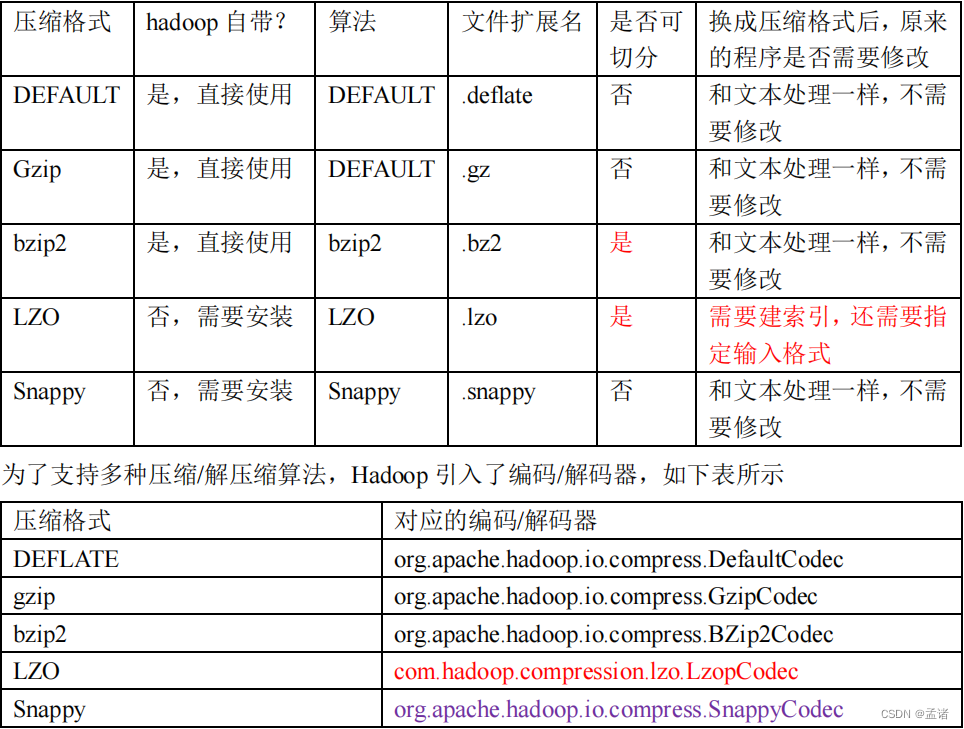
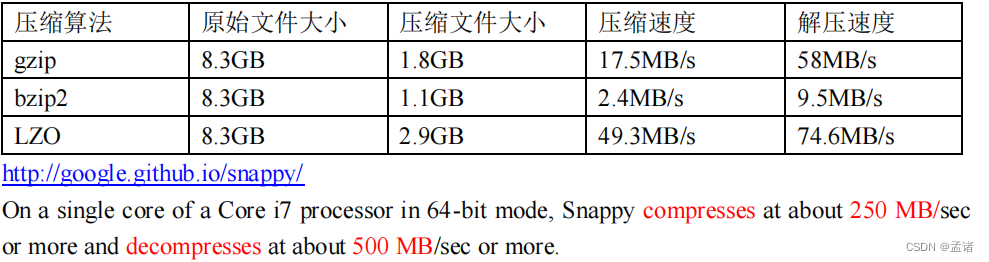
压缩性能比较:
4.3 压缩位置选择

4.4 压缩配置参数
// 开启 map 端输出压缩
configuration.setBoolean("mapreduce.map.output.compress", true);
// 设置 map 端输出压缩方式
configuration.setClass("mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec", BZip2Codec.class, CompressionCodec.class);
// 设置 reduce 端输出压缩开启
FileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true);
// 设置压缩的方式
FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, BZip2Codec.class);
// FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, GzipCodec.class);
// FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, DefaultCodec.class);
5 Yarn 资源调度器
Yarn 是一个资源调度平台,负责为运算程序提供服务器运算资源,相当于一个分布式的操作系统平台,而MapReduce 等运算程序则相当于运行于操作系统之上的应用程序。
5.1 Yarn 基础架构
YARN 主要由 ResourceManager、NodeManager、ApplicationMaster 和 Container 等组件构成
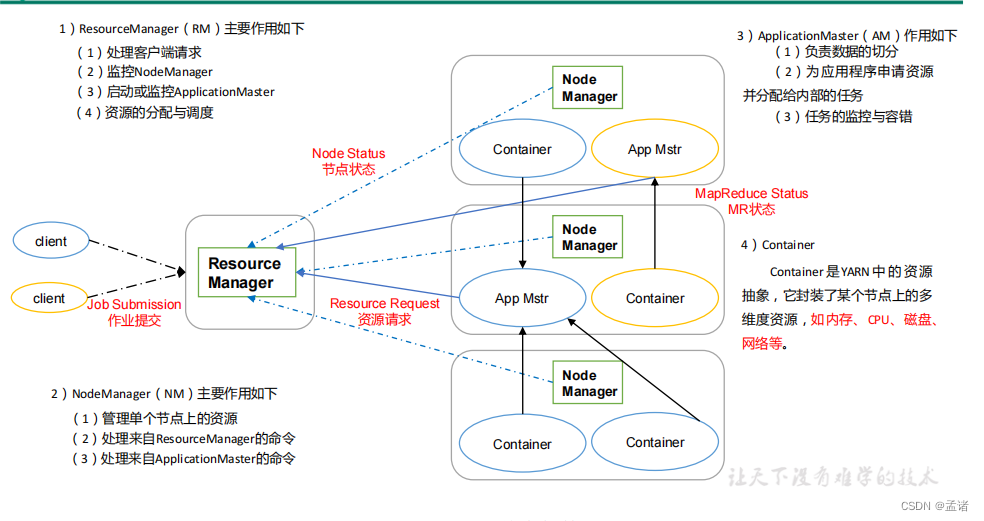
5.2 Yarn工作机制
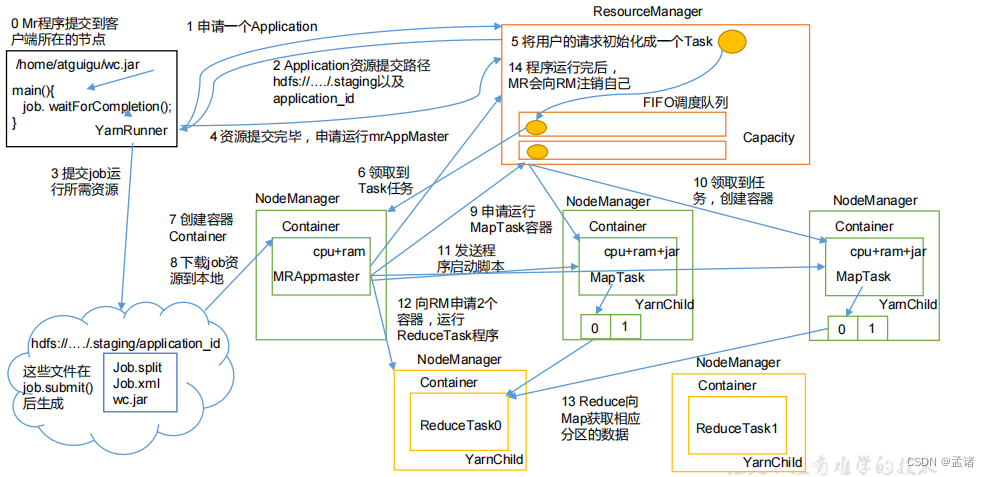
工作机制详解:
(1)MR 程序提交到客户端所在的节点。
(2)YarnRunner 向ResourceManager 申请一个 Application。
(3)RM 将该应用程序的资源路径返回给 YarnRunner。
(4)该程序将运行所需资源提交到 HDFS 上。
(5)程序资源提交完毕后,申请运行 MRAppMaster。
(6)RM将用户的请求初始化成一个 Task。
(7)其中一个 NodeManager 领取到Task任务。
(8)该 NodeManager 创建容器 Container,并产生 MRAppmaster。
(9)Container 从 HDFS 上拷贝资源到本地。
(10)MRAppmaster 向 RM 申请运行MapTask资源。
(11)RM将运行 MapTask 任务分配给另外两个 NodeManager,另两个 NodeManager 分别领取任务并创建容器。
(12)MR向两个接收到任务的 NodeManager 发送程序启动脚本,这两个 NodeManager 分别启动MapTask,MapTask 对数据分区排序。
(13)MrAppMaster 等待所有 MapTask 运行完毕后,向 RM 申请容器,运行 ReduceTask。
(14)ReduceTask 向 MapTask 获取相应分区的数据。
(15)程序运行完毕后,MR 会向 RM 申请注销自己。
5.3 作业提交全过程
5.3.1 作业提交过程之 YARN
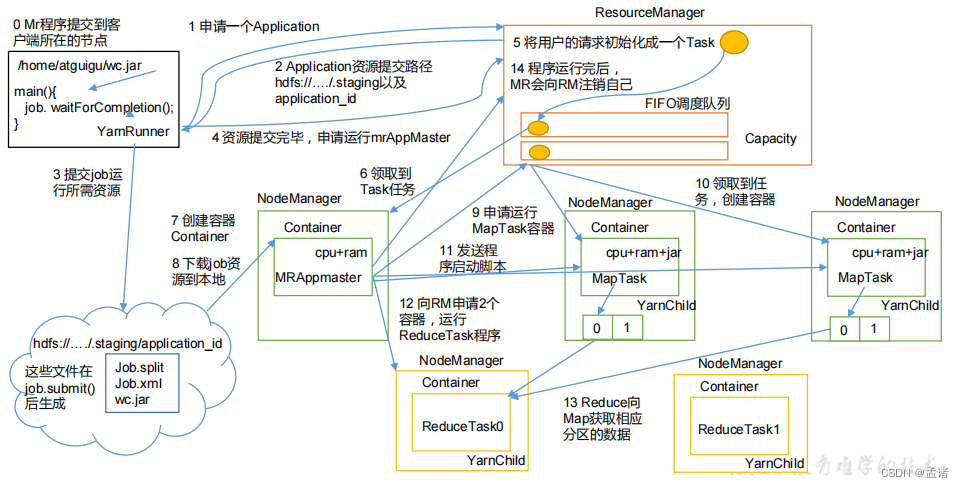
作业提交全过程详解
(1)作业提交
- 第 1 步:Client 调用 job.waitForCompletion 方法,向整个集群提交 MapReduce 作业。
- 第 2 步:Client 向 RM 申请一个作业 id。
- 第 3 步:RM 给 Client 返回该 job 资源的提交路径和作业 id。
- 第 4 步:Client 提交 jar 包、切片信息和配置文件到指定的资源提交路径。
- 第 5 步:Client 提交完资源后,向 RM 申请运行 MrAppMaster。
(2)作业初始化
- 第 6 步:当 RM 收到 Client 的请求后,将该 job 添加到容量调度器中。
- 第 7 步:某一个空闲的 NM 领取到该 Job。
- 第 8 步:该 NM 创建 Container,并产生 MRAppmaster。
- 第 9 步:下载 Client 提交的资源到本地。
(3)任务分配
- 第 10 步:MrAppMaster 向 RM 申请运行多个 MapTask 任务资源。
- 第 11 步:RM 将运行 MapTask 任务分配给另外两个 NodeManager,另两个 NodeManager 分别领取任务并创建容器。
(4)任务运行
- 第 12 步:MR 向两个接收到任务的 NodeManager 发送程序启动脚本,这两个 NodeManager 分别启动 MapTask,MapTask 对数据分区排序。
- 第13步:MrAppMaster等待所有MapTask运行完毕后,向RM申请容器,运行ReduceTask。
- 第 14 步:ReduceTask 向 MapTask 获取相应分区的数据。
- 第 15 步:程序运行完毕后,MR 会向 RM 申请注销自己。
(5)进度和状态更新
YARN 中的任务将其进度和状态(包括 counter)返回给应用管理器, 客户端每秒(通过
mapreduce.client.progressmonitor.pollinterval 设置)向应用管理器请求进度更新, 展示给用户。
(6)作业完成
除了向应用管理器请求作业进度外, 客户端每 5 秒都会通过调用 waitForCompletion()来检查作业是否完成。时间间隔可以通过 mapreduce.client.completion.pollinterval 来设置。作业完成之后, 应用管理器和 Container 会清理工作状态。作业的信息会被作业历史服务器存储以备之后用户核查。
5.3.2 作业提交过程之 MapReduce
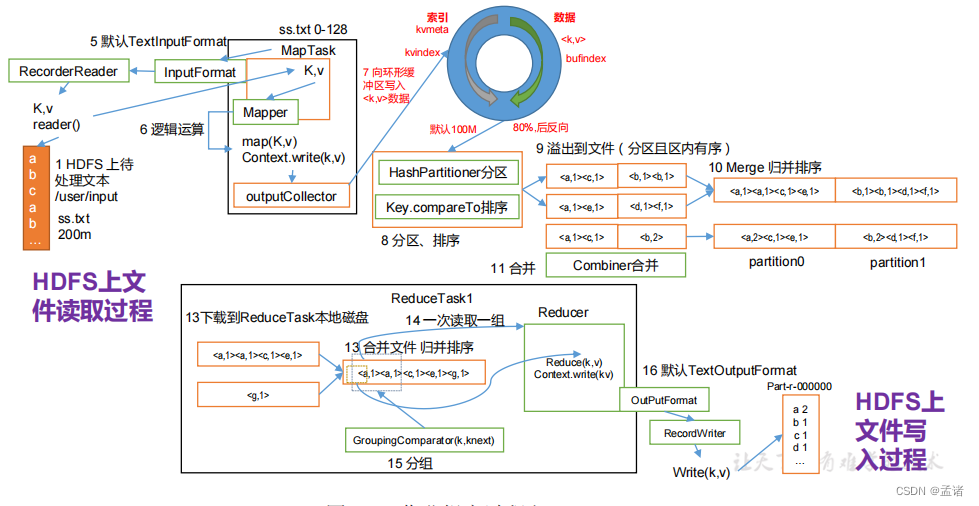
5.4 资源调度器
目前,Hadoop 作业调度器主要有三种:FIFO、Capacity Scheduler 和 Fair Scheduler。Hadoop2.7.2 默认的资源调度器是 Capacity Scheduler。
具体设置详见:yarn-default.xml 文件
<property>
<description>The class to use as the resource scheduler.</description>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.class</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.capacity.CapacityScheduler</value>
</property>
5.4.1 先进先出调度器(FIFO)
FIFO调度器(First In First Out):单队列,根据提交作业的先后顺序,先来先服务。
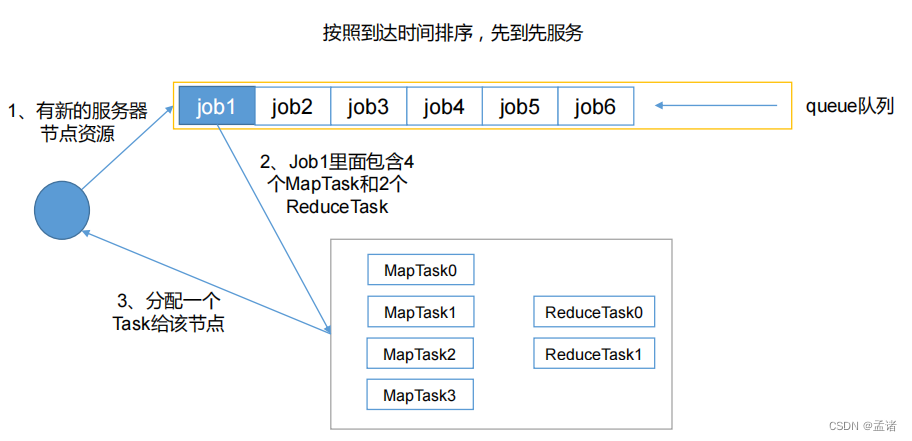
- 优点:简单易懂;
- 缺点:不支持多队列,生产环境很少使用;
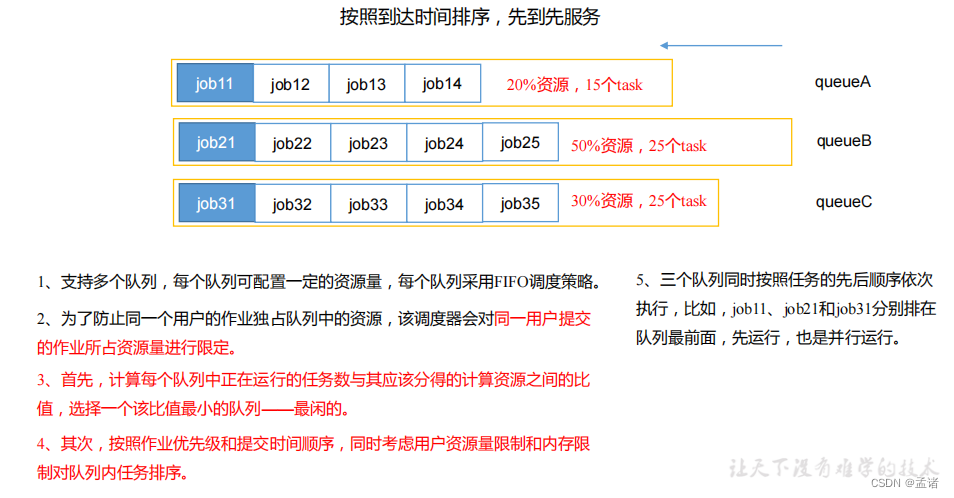
5.4.2 容量调度器(Capacity Scheduler)
Capacity Scheduler 是Yahoo开发的多用户调度器。
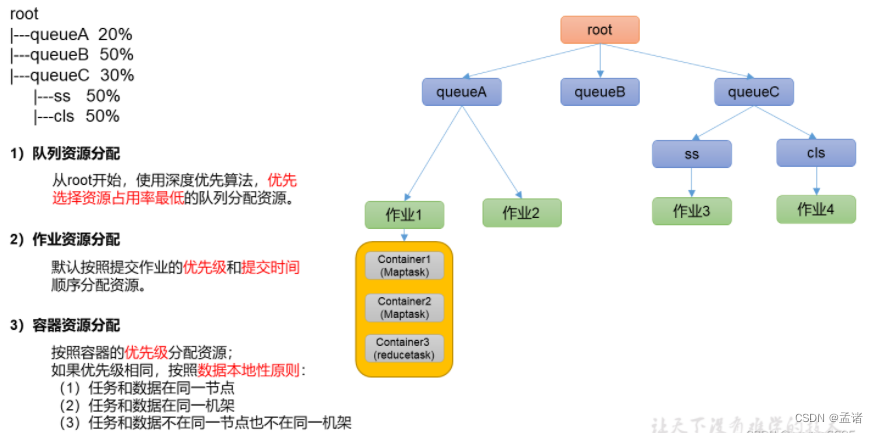
资源分配算法
5.4.3 公平调度器(Fair Scheduler)

5.5 Yarn常用命令
Yarn 状态的查询,除了可以在hadoop103:8088页面查看外,还可以通过命令操作。常见的命令操作如下所示:
需求:执行WordCount案例,并用Yarn命令查看任务运行情况。
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ myhadoop.sh start
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar wordcount /input /output
5.5.1 yarn application查看任务
(1)列出所有Application:
yarn application -list
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn application -list
2021-02-06 10:21:19,238 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Total number of applications (application-types: [], states: [SUBMITTED, ACCEPTED, RUNNING] and tags: []):0
Application-Id Application-Name Application-Type User Queue State Final-State Progress Tracking-URL
(2)根据Application状态过滤:
yarn application -list -appStates (所有状态:ALL、NEW、NEW_SAVING、SUBMITTED、ACCEPTED、RUNNING、FINISHED、FAILED、KILLED)
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn application -list -appStates FINISHED
2021-02-06 10:22:20,029 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Total number of applications (application-types: [], states: [FINISHED] and tags: []):1
Application-Id Application-Name Application-Type User Queue State Final-State Progress Tracking-URL
application_1612577921195_0001 word count MAPREDUCE atguigu default FINISHED SUCCEEDED 100% http://hadoop102:19888/jobhistory/job/job_1612577921195_0001
(3)Kill掉Application:
$ yarn application -kill application_1612577921195_0001
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn application -kill application_1612577921195_0001
2021-02-06 10:23:48,530 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Application application_1612577921195_0001 has already finished
5.5.2 yarn logs查看日志
(1)查询Application日志:
yarn logs -applicationId
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn logs -applicationId application_1612577921195_0001
(2)查询Container日志:
yarn logs -applicationId -containerId
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn logs -applicationId application_1612577921195_0001 -containerId container_1612577921195_0001_01_000001
5.5.3 yarn applicationattempt查看尝试运行的任务
(1)列出所有Application尝试的列表
yarn applicationattempt -list
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn applicationattempt -list application_1612577921195_0001
2021-02-06 10:26:54,195 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Total number of application attempts :1
ApplicationAttempt-Id State AM-Container-Id Tracking-URL
appattempt_1612577921195_0001_000001 FINISHED container_1612577921195_0001_01_000001 http://hadoop103:8088/proxy/application_1612577921195_0001/
(2)打印ApplicationAttemp状态
yarn applicationattempt -status
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn applicationattempt -status appattempt_1612577921195_0001_000001
2021-02-06 10:27:55,896 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Application Attempt Report :
ApplicationAttempt-Id : appattempt_1612577921195_0001_000001
State : FINISHED
AMContainer : container_1612577921195_0001_01_000001
Tracking-URL : http://hadoop103:8088/proxy/application_1612577921195_0001/
RPC Port : 34756
AM Host : hadoop104
Diagnostics :
5.5.4 yarn container查看容器
(1)列出所有Container
yarn container -list
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn container -list appattempt_1612577921195_0001_000001
2021-02-06 10:28:41,396 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Total number of containers :0
Container-Id Start Time Finish Time State Host Node Http Address
(2)打印Container状态
yarn container -status
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn container -status container_1612577921195_0001_01_000001
2021-02-06 10:29:58,554 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Container with id 'container_1612577921195_0001_01_000001' doesn't exist in RM or Timeline Server.
注:只有在任务跑的途中才能看到container的状态==
5.5.5 yarn node查看节点状态
列出所有节点:
yarn node -list -all
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn node -list -all
2021-02-06 10:31:36,962 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Total Nodes:3
Node-Id Node-State Node-Http-Address Number-of-Running-Containers
hadoop103:38168 RUNNING hadoop103:8042 0
hadoop102:42012 RUNNING hadoop102:8042 0
hadoop104:39702 RUNNING hadoop104:8042 0
5.5.6 yarn rmadmin更新配置
加载队列配置:yarn rmadmin -refreshQueues
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn rmadmin -refreshQueues
2021-02-06 10:32:03,331 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8033
5.5.7 yarn queue查看队列
打印队列信息:yarn queue -status
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn queue -status default
2021-02-06 10:32:33,403 INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at hadoop103/192.168.10.103:8032
Queue Information :
Queue Name : default
State : RUNNING
Capacity : 100.0%
Current Capacity : .0%
Maximum Capacity : 100.0%
Default Node Label expression : <DEFAULT_PARTITION>
Accessible Node Labels : *
Preemption : disabled
Intra-queue Preemption : disabled
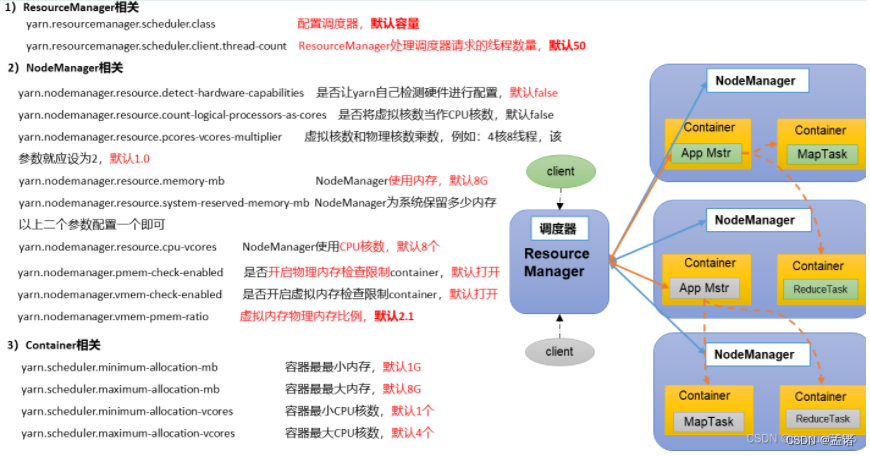
5.6 Yarn生产环境核心参数
5.7 Yarn 案例实操
5.7.1 Yarn生产环境核心参数配置案例
1)需求:从1G数据中,统计每个单词出现次数。服务器3台,每台配置4G内存,4核CPU,4线程。
2)需求分析:
1G / 128m = 8个MapTask;1个ReduceTask;1个mrAppMaster
平均每个节点运行10个 / 3台 ≈ 3个任务(4 3 3)
3)修改yarn-site.xml配置参数如下:
<!-- 选择调度器,默认容量 -->
<property>
<description>The class to use as the resource scheduler.</description>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.class</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.capacity.CapacityScheduler</value>
</property>
<!-- ResourceManager处理调度器请求的线程数量,默认50;如果提交的任务数大于50,可以增加该值,但是不能超过3台 * 4线程 = 12线程(去除其他应用程序实际不能超过8) -->
<property>
<description>Number of threads to handle scheduler interface.</description>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.client.thread-count</name>
<value>8</value>
</property>
<!-- 是否让yarn自动检测硬件进行配置,默认是false,如果该节点有很多其他应用程序,建议手动配置。如果该节点没有其他应用程序,可以采用自动 -->
<property>
<description>Enable auto-detection of node capabilities such as
memory and CPU.
</description>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<!-- 是否将虚拟核数当作CPU核数,默认是false,采用物理CPU核数 -->
<property>
<description>Flag to determine if logical processors(such as
hyperthreads) should be counted as cores. Only applicable on Linux
when yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores is set to -1 and
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities is true.
</description>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.count-logical-processors-as-cores</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<!-- 虚拟核数和物理核数乘数,默认是1.0 -->
<property>
<description>Multiplier to determine how to convert phyiscal cores to
vcores. This value is used if yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores
is set to -1(which implies auto-calculate vcores) and
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities is set to true. The number of vcores will be calculated as number of CPUs * multiplier.
</description>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.pcores-vcores-multiplier</name>
<value>1.0</value>
</property>
<!-- NodeManager使用内存数,默认8G,修改为4G内存 -->
<property>
<description>Amount of physical memory, in MB, that can be allocated
for containers. If set to -1 and
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities is true, it is
automatically calculated(in case of Windows and Linux).
In other cases, the default is 8192MB.
</description>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb</name>
<value>4096</value>
</property>
<!-- nodemanager的CPU核数,不按照硬件环境自动设定时默认是8个,修改为4个 -->
<property>
<description>Number of vcores that can be allocated
for containers. This is used by the RM scheduler when allocating
resources for containers. This is not used to limit the number of
CPUs used by YARN containers. If it is set to -1 and
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities is true, it is
automatically determined from the hardware in case of Windows and Linux.
In other cases, number of vcores is 8 by default.</description>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores</name>
<value>4</value>
</property>
<!-- 容器最小内存,默认1G -->
<property>
<description>The minimum allocation for every container request at the RM in MBs. Memory requests lower than this will be set to the value of this property. Additionally, a node manager that is configured to have less memory than this value will be shut down by the resource manager.
</description>
<name>yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb</name>
<value>1024</value>
</property>
<!-- 容器最大内存,默认8G,修改为2G -->
<property>
<description>The maximum allocation for every container request at the RM in MBs. Memory requests higher than this will throw an InvalidResourceRequestException.
</description>
<name>yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb</name>
<value>2048</value>
</property>
<!-- 容器最小CPU核数,默认1个 -->
<property>
<description>The minimum allocation for every container request at the RM in terms of virtual CPU cores. Requests lower than this will be set to the value of this property. Additionally, a node manager that is configured to have fewer virtual cores than this value will be shut down by the resource manager.
</description>
<name>yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-vcores</name>
<value>1</value>
</property>
<!-- 容器最大CPU核数,默认4个,修改为2个 -->
<property>
<description>The maximum allocation for every container request at the RM in terms of virtual CPU cores. Requests higher than this will throw an
InvalidResourceRequestException.</description>
<name>yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-vcores</name>
<value>2</value>
</property>
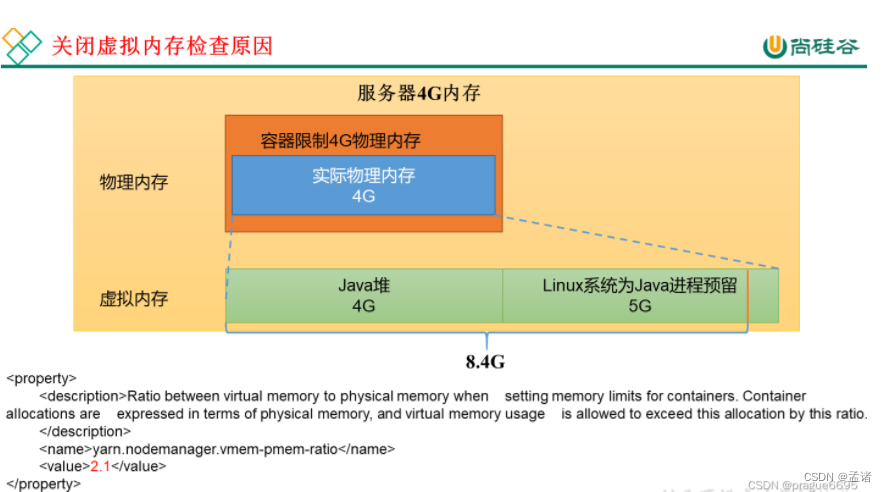
<!-- 虚拟内存检查,默认打开,修改为关闭 -->
<property>
<description>Whether virtual memory limits will be enforced for
containers.</description>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.vmem-check-enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<!-- 虚拟内存和物理内存设置比例,默认2.1 -->
<property>
<description>Ratio between virtual memory to physical memory when setting memory limits for containers. Container allocations are expressed in terms of physical memory, and virtual memory usage is allowed to exceed this allocation by this ratio.
</description>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.vmem-pmem-ratio</name>
<value>2.1</value>
</property>
5.7.2 容量调度器多队列提交案例
1)在生产环境怎么创建队列?
(1)调度器默认就1个default队列,不能满足生产要求。
(2)按照框架:hive /spark/ flink 每个框架的任务放入指定的队列(企业用的不是特别多)
(3)按照业务模块:登录注册、购物车、下单、业务部门1、业务部门2
2)创建多队列的好处?
(1)因为担心员工不小心,写递归死循环代码,把所有资源全部耗尽。
(2)实现任务的降级使用,特殊时期保证重要的任务队列资源充足。11.11 6.18
业务部门1(重要)=》业务部门2(比较重要)=》下单(一般)=》购物车(一般)=》登录注册(次要)
需求:
- 需求1:default队列占总内存的40%,最大资源容量占总资源60%,hive队列占总内存的60%,最大资源容量占总资源80%。
- 需求2:配置队列优先级
5.7.2.1 配置多队列的容量调度器
1)在capacity-scheduler.xml中配置如下:
(1)修改如下配置
<!-- 指定多队列,增加hive队列 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.queues</name>
<value>default,hive</value>
<description>
The queues at the this level (root is the root queue).
</description>
</property>
<!-- 降低default队列资源额定容量为40%,默认100% -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.capacity</name>
<value>40</value>
</property>
<!-- 降低default队列资源最大容量为60%,默认100% -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-capacity</name>
<value>60</value>
</property>
(2)为新加队列添加必要属性:
<!-- 指定hive队列的资源额定容量 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.capacity</name>
<value>60</value>
</property>
<!-- 用户最多可以使用队列多少资源,1表示 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.user-limit-factor</name>
<value>1</value>
</property>
<!-- 指定hive队列的资源最大容量 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.maximum-capacity</name>
<value>80</value>
</property>
<!-- 启动hive队列 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.state</name>
<value>RUNNING</value>
</property>
<!-- 哪些用户有权向队列提交作业 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_submit_applications</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<!-- 哪些用户有权操作队列,管理员权限(查看/杀死) -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_administer_queue</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<!-- 哪些用户有权配置提交任务优先级 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_application_max_priority</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<!-- 任务的超时时间设置:yarn application -appId appId -updateLifetime Timeout
参考资料:https://blog.cloudera.com/enforcing-application-lifetime-slas-yarn/ -->
<!-- 如果application指定了超时时间,则提交到该队列的application能够指定的最大超时时间不能超过该值。
-->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.maximum-application-lifetime</name>
<value>-1</value>
</property>
<!-- 如果application没指定超时时间,则用default-application-lifetime作为默认值 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.default-application-lifetime</name>
<value>-1</value>
</property>
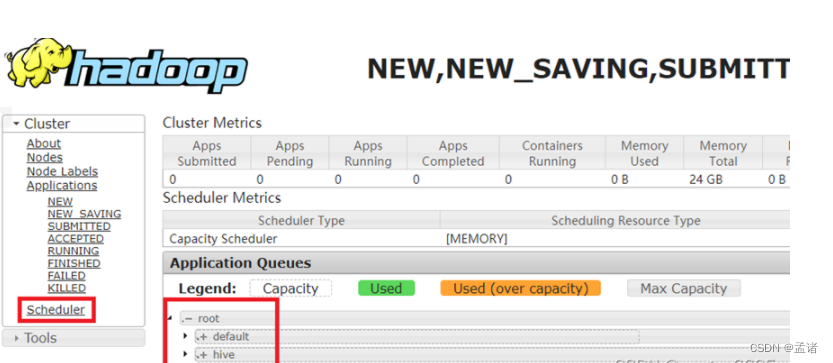
2)分发配置文件
3)重启Yarn或者执行yarn rmadmin -refreshQueues刷新队列,就可以看到两条队列:
5.7.2.2 向Hive队列提交任务
1)hadoop jar的方式
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar wordcount -D mapreduce.job.queuename=hive /input /output
2)打jar包的方式
默认的任务提交都是提交到default队列的。如果希望向其他队列提交任务,需要在Driver中声明:
public class WcDrvier {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("mapreduce.job.queuename","hive");
//1. 获取一个Job实例
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
。。。 。。。
//6. 提交Job
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
}
}
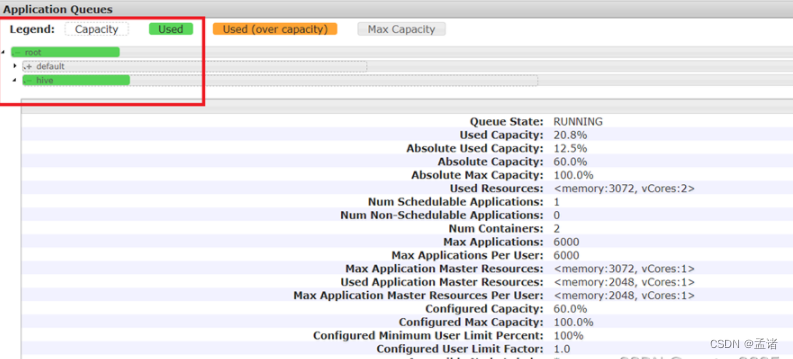
这样,这个任务在集群提交时,就会提交到hive队列:
5.7.2.3 任务优先级
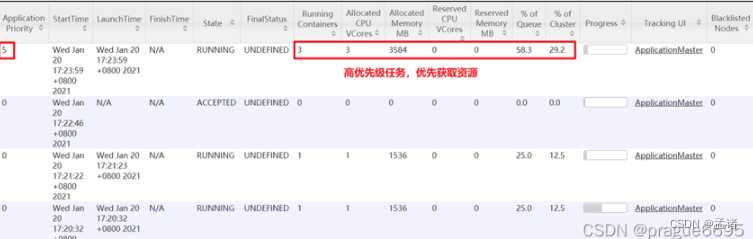
容量调度器,支持任务优先级的配置,在资源紧张时,优先级高的任务将优先获取资源。默认情况,Yarn将所有任务的优先级限制为0,若想使用任务的优先级功能,须开放该限制。
1)修改yarn-site.xml文件,增加以下参数
<property>
<name>yarn.cluster.max-application-priority</name>
<value>5</value>
</property>
2)分发配置,并重启Yarn
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop]$ xsync yarn-site.xml
[atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-3.1.3]$ sbin/stop-yarn.sh
[atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-3.1.3]$ sbin/start-yarn.sh
3)模拟资源紧张环境,可连续提交以下任务,直到新提交的任务申请不到资源为止。
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar pi 5 2000000
4)再次重新提交优先级高的任务
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar pi -D mapreduce.job.priority=5 5 2000000
5)也可以通过以下命令修改正在执行的任务的优先级。
yarn application -appID -updatePriority 优先级
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn application -appID application_1611133087930_0009 -updatePriority 5
5.7.3 公平调度器案例
需求:
创建两个队列,分别是test和atguigu(以用户所属组命名)。期望实现以下效果:若用户提交任务时指定队列,则任务提交到指定队列运行;若未指定队列,test用户提交的任务到root.group.test队列运行,atguigu提交的任务到root.group.atguigu队列运行(注:group为用户所属组)。
公平调度器的配置涉及到两个文件,一个是yarn-site.xml,另一个是公平调度器队列分配文件fair-scheduler.xml(文件名可自定义)。
(1)配置文件参考资料:
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r3.1.3/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/FairScheduler.html
(2)任务队列放置规则参考资料:
https://blog.cloudera.com/untangling-apache-hadoop-yarn-part-4-fair-scheduler-queue-basics/
5.7.3.1 配置多队列的公平调度器
1)修改yarn-site.xml文件,加入以下参数
<property>
<name>yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.class</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.fair.FairScheduler</value>
<description>配置使用公平调度器</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.fair.allocation.file</name>
<value>/opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/etc/hadoop/fair-scheduler.xml</value>
<description>指明公平调度器队列分配配置文件</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.fair.preemption</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>禁止队列间资源抢占</description>
</property>
2)配置fair-scheduler.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<allocations>
<!-- 单个队列中Application Master占用资源的最大比例,取值0-1 ,企业一般配置0.1 -->
<queueMaxAMShareDefault>0.5</queueMaxAMShareDefault>
<!-- 单个队列最大资源的默认值 test atguigu default -->
<queueMaxResourcesDefault>4096mb,4vcores</queueMaxResourcesDefault>
<!-- 增加一个队列test -->
<queue name="test">
<!-- 队列最小资源 -->
<minResources>2048mb,2vcores</minResources>
<!-- 队列最大资源 -->
<maxResources>4096mb,4vcores</maxResources>
<!-- 队列中最多同时运行的应用数,默认50,根据线程数配置 -->
<maxRunningApps>4</maxRunningApps>
<!-- 队列中Application Master占用资源的最大比例 -->
<maxAMShare>0.5</maxAMShare>
<!-- 该队列资源权重,默认值为1.0 -->
<weight>1.0</weight>
<!-- 队列内部的资源分配策略 -->
<schedulingPolicy>fair</schedulingPolicy>
</queue>
<!-- 增加一个队列atguigu -->
<queue name="atguigu" type="parent">
<!-- 队列最小资源 -->
<minResources>2048mb,2vcores</minResources>
<!-- 队列最大资源 -->
<maxResources>4096mb,4vcores</maxResources>
<!-- 队列中最多同时运行的应用数,默认50,根据线程数配置 -->
<maxRunningApps>4</maxRunningApps>
<!-- 队列中Application Master占用资源的最大比例 -->
<maxAMShare>0.5</maxAMShare>
<!-- 该队列资源权重,默认值为1.0 -->
<weight>1.0</weight>
<!-- 队列内部的资源分配策略 -->
<schedulingPolicy>fair</schedulingPolicy>
</queue>
<!-- 任务队列分配策略,可配置多层规则,从第一个规则开始匹配,直到匹配成功 -->
<queuePlacementPolicy>
<!-- 提交任务时指定队列,如未指定提交队列,则继续匹配下一个规则; false表示:如果指定队列不存在,不允许自动创建-->
<rule name="specified" create="false"/>
<!-- 提交到root.group.username队列,若root.group不存在,不允许自动创建;若root.group.user不存在,允许自动创建 -->
<rule name="nestedUserQueue" create="true">
<rule name="primaryGroup" create="false"/>
</rule>
<!-- 最后一个规则必须为reject或者default。Reject表示拒绝创建提交失败,default表示把任务提交到default队列 -->
<rule name="reject" />
</queuePlacementPolicy>
</allocations>
3)分发配置并重启Yarn
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop]$ xsync yarn-site.xml
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop]$ xsync fair-scheduler.xml
[atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-3.1.3]$ sbin/stop-yarn.sh
[atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-3.1.3]$ sbin/start-yarn.sh
5.7.3.2 测试提交任务
1)提交任务时指定队列,按照配置规则,任务会到指定的root.test队列
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar pi -Dmapreduce.job.queuename=root.test 1 1
2)提交任务时不指定队列,按照配置规则,任务会到root.atguigu.atguigu队列
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar pi 1 1
5.7.4 Yarn 的 Tool 接口案例
回顾:
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar wc.jar com.atguigu.mapreduce.wordcount2.WordCountDriver /input /output1
期望可以动态传参,结果报错,误认为是第一个输入参数。
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar wc.jar com.atguigu.mapreduce.wordcount2.WordCountDriver -Dmapreduce.job.queuename=root.test /input /output1
1)需求:自己写的程序也可以动态修改参数。编写Yarn的Tool接口。
2)具体步骤:
(1)新建Maven项目YarnDemo,pom如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.atguigu.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>yarn_tool_test</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>3.1.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
(2)新建com.atguigu.yarn报名
(3)创建类WordCount并实现Tool接口:
package com.atguigu.yarn;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCount implements Tool {
private Configuration conf;
// run方法有driver驱动类来调用(conf需要传入)
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
}
@Override
public void setConf(Configuration conf) {
this.conf = conf;
}
@Override
public Configuration getConf() {
return conf;
}
public static class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private Text outK = new Text();
private IntWritable outV = new IntWritable(1);
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] words = line.split(" ");
for (String word : words) {
outK.set(word);
context.write(outK, outV);
}
}
}
public static class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private IntWritable outV = new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
sum += value.get();
}
outV.set(sum);
context.write(key, outV);
}
}
}
(4)新建WordCountDriver
package com.atguigu.yarn;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class WordCountDriver {
private static Tool tool;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 创建配置文件
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 2. 判断是否有tool接口
switch (args[0]){
case "wordcount":
tool = new WordCount();
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException(" No such tool: "+ args[0] );
}
// 3. 用Tool执行程序
// Arrays.copyOfRange 将老数组的元素放到新数组里面
int run = ToolRunner.run(conf, tool, Arrays.copyOfRange(args, 1, args.length));
System.exit(run);
}
}
3)在HDFS上准备输入文件,假设为/input目录,向集群提交该Jar包
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn jar YarnDemo.jar com.atguigu.yarn.WordCountDriver wordcount /input /output
注意此时提交的3个参数,第一个用于生成特定的Tool,第二个和第三个为输入输出目录。此时如果我们希望加入设置参数,可以在wordcount后面添加参数,例如:
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn jar YarnDemo.jar com.atguigu.yarn.WordCountDriver wordcount -Dmapreduce.job.queuename=root.test /input /output1






















 3582
3582











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








