拒绝策略采用函数式接口参数传入,策略模式
@FunctionalInterface
public interface RejectPolicy<T> {
void reject(BlockingQueue<T> queue, T task);
}package com.xkj.thread.pool;
import com.aspose.words.Run;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
public class ThreadPool {
//任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
//线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
//核心线程数
private int coreSize;
//获取任务的超时时间
private long timeout;
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy;
public ThreadPool(int coreSize,
int queueCapcity,
long timeout,
TimeUnit timeUnit,
RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapcity);
this.rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy;
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1.当task不为空执行任务
// 2.当task执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行...{}", task);
task.run();
}catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}
//执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
synchronized (workers) {
if(workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增worker{},{}", worker, task);
// 当任务数没有超过coreSize时,直接交给worker对象执行
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
// 当任务数超过coreSize时,加入任务队列暂存
// 1) 死等
// taskQueue.put(task);
// 2)超时等待
// 3)放弃任务执行
// 4)抛出异常
// 5)让调用者自己执行任务
taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy, task);
}
}
}
}
在原来的基础上添加了 带超时时间的阻塞添加方法,offer方法
package com.xkj.thread.pool;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.blockingQueue")
public class BlockingQueue<T> {
//1.任务队列
private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
//2.锁
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
//4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
//5.容量
private int capcity;
public BlockingQueue(int capcity) {
this.capcity = capcity;
}
/**
* 带超时的获取元素
* @param timeout
* @param unit
* @return
*/
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
//将timeout统一转化成纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) { //判断队列是否为空
try {
if(nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
//阻塞等待,当被唤醒后,队列不会空,不满足while条件,程序继续向下执行
//返回的是timeout - 已经等待的时间 = 剩余的时间
//防止虚假唤醒
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取队列头部的元素返回,获取元素后应该从队列中移除
T t = queue.removeFirst();
//唤醒生产者,继续添加元素
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取元素
* @return
*/
public T take() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) { //判断队列是否为空
try {
//阻塞等待,当被唤醒后,队列不会空,不满足while条件,程序继续向下执行
emptyWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取队列头部的元素返回,获取元素后应该从队列中移除
T t = queue.removeFirst();
//唤醒生产者,继续添加元素
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 添加元素
* @param element
*/
public void put(T element) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capcity){
try {
log.debug("等待加入任务队列{}...", element);
fullWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列{}", element);
queue.addLast(element);
//唤醒消费者,继续获取任务
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 带超时时间的阻塞添加
* @param element 任务
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
* @return
*/
public boolean offer(T element, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeout);
while(queue.size() == capcity) {
try {
log.debug("等待加入任务队列{}...", element);
if(nanos < 0) {
return false;
}
nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列{}", element);
queue.addLast(element);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
return true;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取大小
* @return
*/
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void tryPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy, T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
if(queue.size() == capcity) { //队列已满
rejectPolicy.reject(this, task);
}else { //队列有空闲
log.debug("加入任务队列{}", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
场景一:拒绝策略死等
package com.xkj.thread.pool;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(
1,
1,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
(queue, task) -> {
// 1.死等
queue.put(task);
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
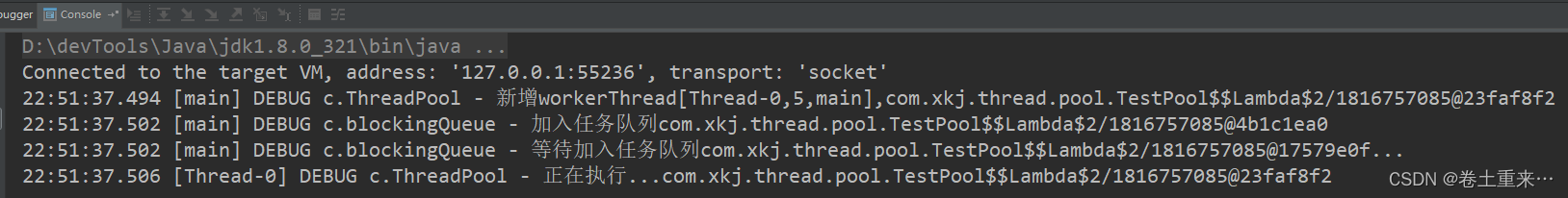
场景二:带超时等待
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(
1,
1,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
(queue, task) -> {
// 1.死等
// queue.put(task);
// 2.带超时时间的等待
queue.offer(task, 500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}注意:ThreadPool的区别,取任务也要调用超时的poll方法
package com.xkj.thread.pool;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
public class ThreadPool {
//任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
//线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
//核心线程数
private int coreSize;
//获取任务的超时时间
private long timeout;
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy;
public ThreadPool(int coreSize,
int queueCapcity,
long timeout,
TimeUnit timeUnit,
RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapcity);
this.rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy;
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行任务
// 1.当task不为空执行任务
// 2.当task执行完毕,再接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
while(task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, timeUnit)) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行...{}", task);
task.run();
}catch (Exception e) {
}finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("worker 被移除{}", this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}
//执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
synchronized (workers) {
if(workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增worker{},{}", worker, task);
// 当任务数没有超过coreSize时,直接交给worker对象执行
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
// 当任务数超过coreSize时,加入任务队列暂存
// 1) 死等
// taskQueue.put(task);
// 2)超时等待
// 3)放弃任务执行
// 4)抛出异常
// 5)让调用者自己执行任务
taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy, task);
}
}
}
}
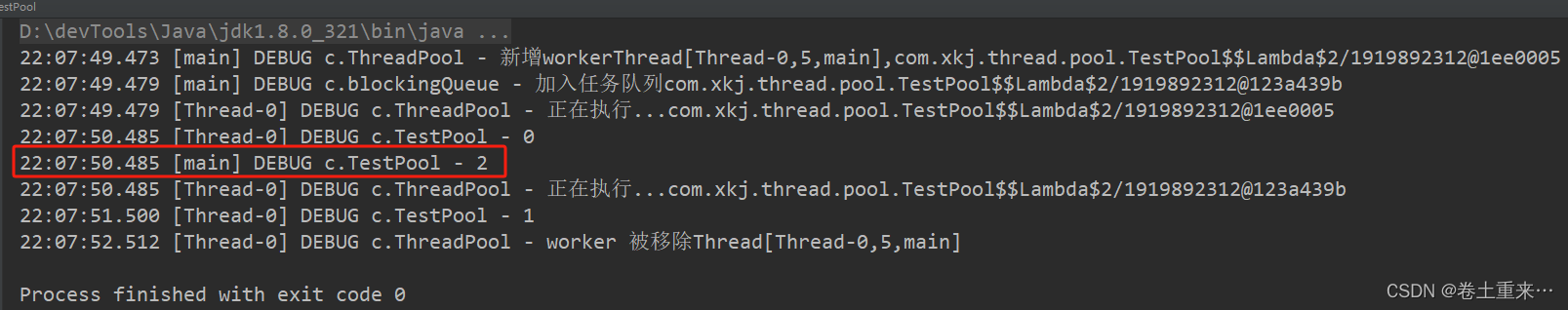
流程分析
一共三个任务,一个核心线程,队列的容量为1。
第一个任务占用核心线程
第二个任务进入队列
因为队列已满,第三个任务无法放入队列中,只有等待,等待超时时间为500ms
第一个任务执行完成需要1s
1s后才会执行队列中的任务
但是,第三个任务等待500ms就会超时,就不会等待了,也就是不会添加到队列中了。第三个任务也不会被执行了。
这个时候还没有结束,取任务的也会超时,超时时间为1s,所以取任务等了1s后队列中没有新的任务所以也会超时。超时后,核心线程会被移除。
结果
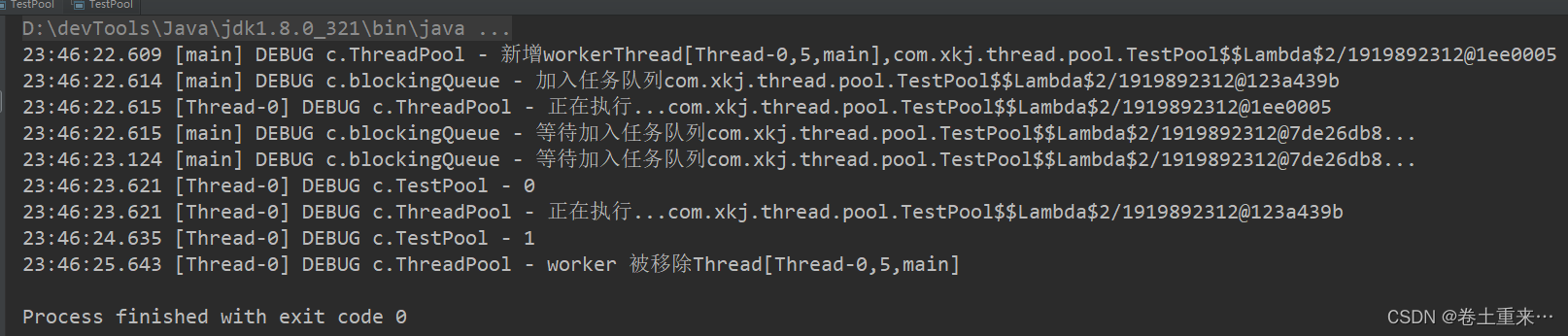
如果第三个任务等待的超时时间变大,设置为1500ms,那么当第一个线程执行完毕花费1s时间,然后从队列中取出第二个线程执行,此时队列为空,第三个线程添加到队列还未超时,成功添加到队列中,等待执行。所以三个线程都可以得到执行。
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(
1,
1,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
(queue, task) -> {
// 1.死等
// queue.put(task);
// 2.带超时时间的等待
queue.offer(task, 1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
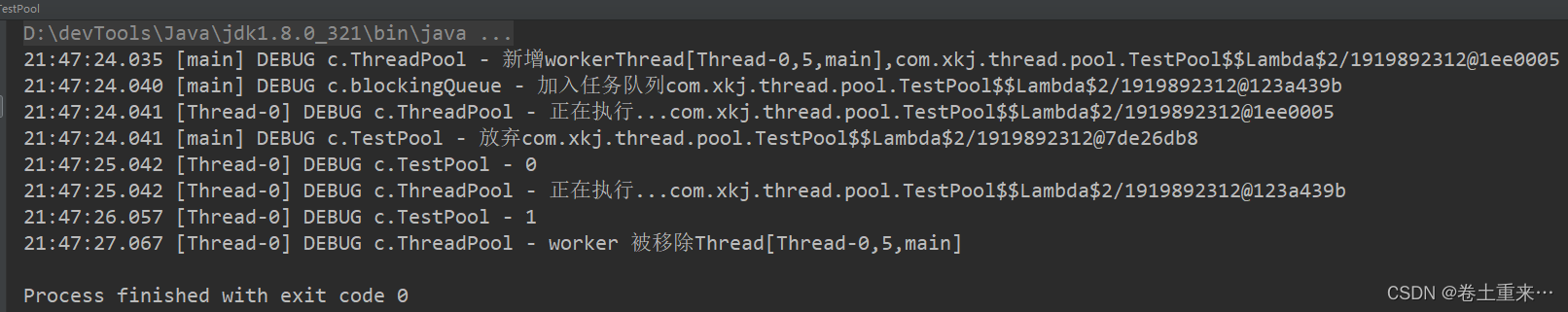
场景三:放弃任务的执行
队列满了,不做任何的操作,任务就不会加入到队列中,就等于放弃任务的执行。
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(
1,
1,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
(queue, task) -> {
// 1.死等
// queue.put(task);
// 2.带超时时间的等待
// queue.offer(task, 1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 3.让调用者放弃任务执行(不要添加任务到队列就是放弃)
log.debug("放弃{}", task);
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
场景四:让调用者抛出异常
package com.xkj.thread.pool;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(
1,
1,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
(queue, task) -> {
// 1.死等
// queue.put(task);
// 2.带超时时间的等待
// queue.offer(task, 1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 3.让调用者放弃任务执行(不要添加任务到队列就是放弃)
// log.debug("放弃{}", task);
// 4.让调用者抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败" + task);
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
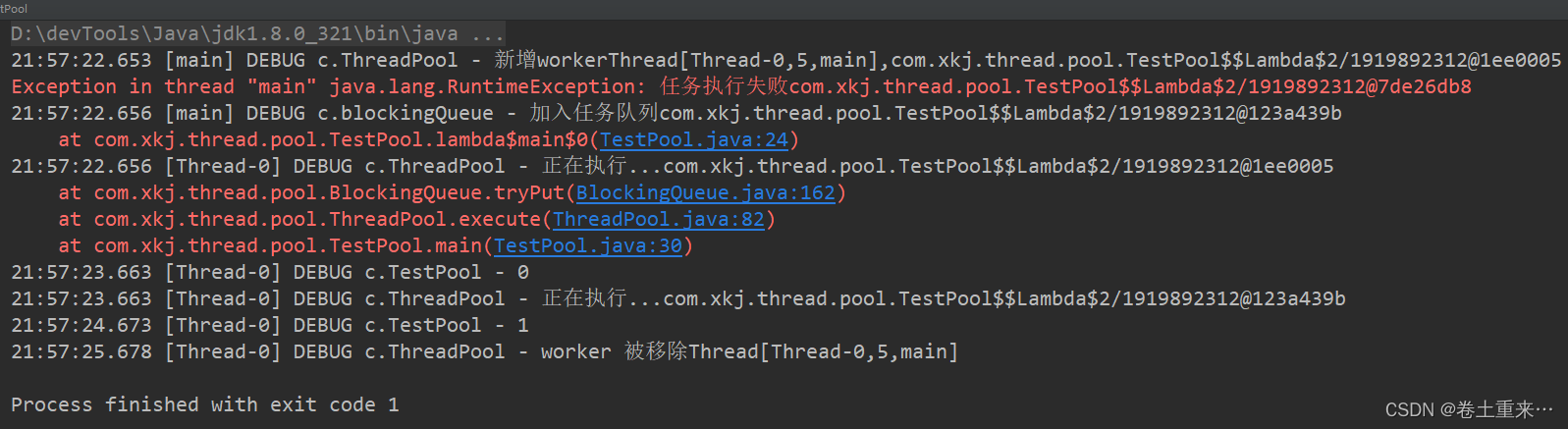
第三个任务抛出异常后,如果后面还有任务也不会再执行了。
场景五:让调用者自己执行任务
package com.xkj.thread.pool;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestPool")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(
1,
1,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
(queue, task) -> {
// 1.死等
// queue.put(task);
// 2.带超时时间的等待
// queue.offer(task, 1500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 3.让调用者放弃任务执行(不要添加任务到队列就是放弃)
// log.debug("放弃{}", task);
// 4.让调用者抛出异常
// throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败" + task);
// 5.让调用者自己执行任务
task.run();
});
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}








 本文探讨了线程池的拒绝策略,包括死等、带超时等待、放弃任务执行、调用者抛出异常和调用者自执行任务等场景。通过实例分析了不同策略下任务的执行流程和结果,揭示了线程池在处理任务饱和时的行为。
本文探讨了线程池的拒绝策略,包括死等、带超时等待、放弃任务执行、调用者抛出异常和调用者自执行任务等场景。通过实例分析了不同策略下任务的执行流程和结果,揭示了线程池在处理任务饱和时的行为。















 4986
4986

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










