在学习傅里叶变换的过程中,我发现了JohnHany大神的这篇博客:
opencv实现基于傅里叶变换的旋转文本校正,所以在学习完傅里叶变换以后,我迫不及待的想要去尝试一下,在此记录一下。在搜索的过程中,我发现网上并没有用python实现的,希望看了这篇文章,能对学习python的小伙伴有帮助。转载请注明出处,原创不易 ---zyh 2018-5-31
傅里叶变换的原理,可以看下我的上一篇博客:
傅里叶变换。
直接开始正题:
第一步、读取文件,灰度化
#1、读取文件,灰度化
img = cv.imread(
'img/imageTextR.png')
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv.imshow(
'gray', gray)
第二步、图像延扩
h, w = img.shape[:2] new_h = cv.getOptimalDFTSize(h) new_w = cv.getOptimalDFTSize(w) right = new_w - w bottom = new_h - h nimg = cv.copyMakeBorder(gray, 0, bottom, 0, right, borderType=cv.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=0) cv.imshow('new image', nimg)
OpenCV中的DFT采用的是快速算法,这种算法要求图像的尺寸是2的、3和5的倍数是处理速度最快。所以需要用getOptimalDFTSize()找到最合适的尺寸,然后用copyMakeBorder()填充多余的部分。这里是让原图像和扩大的图像左上角对齐。填充的颜色如果是纯色,对变换结果的影响不会很大,后面寻找倾斜线的过程又会完全忽略这一点影响。
第三步、执行傅里叶变换,并过得频域图像
f = np.fft.fft2(nimg) fshift = np.fft.fftshift(f) magnitude = np.log(np.abs(fshift)) magnitude_uint = magnitude.astype(np.uint8)
我们用np.fft.fft2()将图像从空间域转到频域,然后用np.fft.fftshift()将低频分量移动到中心,我们得到的结果是复数形式,所以用abs()得到实数,取对数是为了将数据变换到0-255,相当与实现了归一化。
第四步、二值化,进行Houge直线检测
#二值化 magnitude_uint = magnitude.astype(np.uint8) ret, thresh = cv.threshold(magnitude_uint, 11, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY) print(ret) cv.imshow('thresh', thresh) print(thresh.dtype) #霍夫直线变换 lines = cv.HoughLinesP(thresh, 2, np.pi/180, 30, minLineLength=40, maxLineGap=100) print(len(lines))
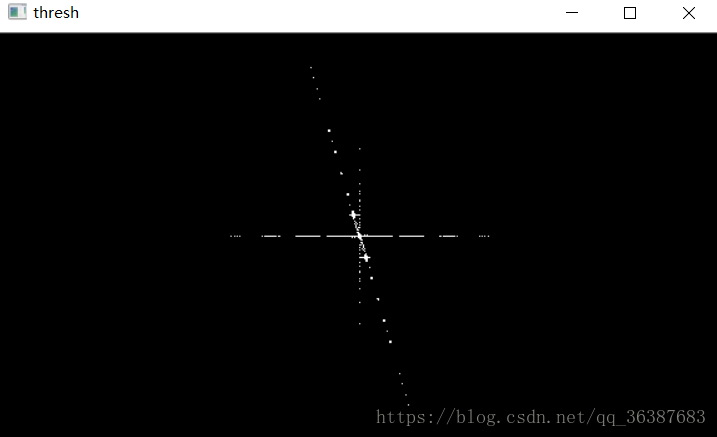
因为HougnLinesP()函数要求
输入图像必须为8位单通道图像,所以我们用astype()函数把图像数据转成uint8类型,接下来执行二值化操作。在操作过程中参数要自己根据情况设定。
第五步、创建一个新图像,标注直线,找出偏移弧度
#创建一个新图像,标注直线 lineimg = np.ones(nimg.shape,dtype=np.uint8) lineimg = lineimg * 255 piThresh = np.pi/180 pi2 = np.pi/2 print(piThresh) for line in lines: x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0] cv.line(lineimg, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2) if x2 - x1 == 0: continue else: theta = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) if abs(theta) < piThresh or abs(theta - pi2) < piThresh: continue else: print(theta)
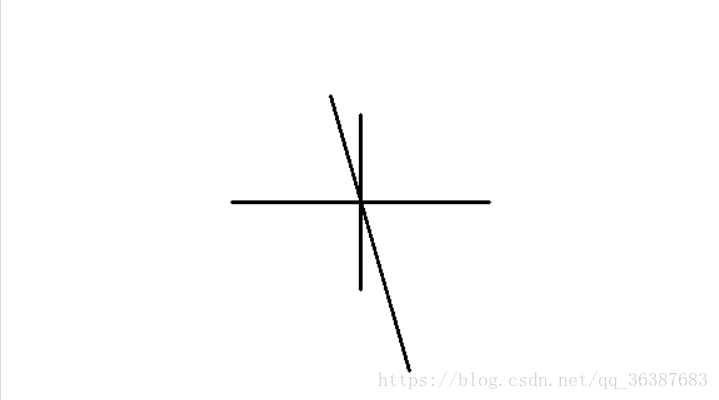
上面得到三个角度,一个是0度,一个是90度,另一个就是我们需要的倾斜角。我们要把这个角找出来,并且要考虑判断条件。
第六步、计算倾斜角,将弧度转换成角度,并注意误差
angle = math.atan(theta) print(angle) angle = angle * (180 / np.pi) print(angle) angle = (angle - 90)/(w/h) print(angle)
由于DFT的特点,只有输出图像是正方形时,检测到的角才是文本真正旋转的角度。但是我们的输入图像不一定是正方形的,所以要根据图像的长宽比改变这个角度。
在OpenCV中,
逆时针旋转,角度为正,所以我们要对角度进行处理。
第七步、校正图片
center = (w//
2, h//
2)
M = cv.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle,
1.0)
rotated = cv.warpAffine(img, M, (w, h),
flags=cv.INTER_CUBIC,
borderMode=cv.BORDER_REPLICATE)
cv.imshow(
'line image', lineimg)
cv.imshow(
'rotated', rotated)
先用getRotationMatrix2D()获得一个仿射变换矩阵,再把这个矩阵输入warpAffine(),做一个单纯的仿射变换。
校正的结果:

完整代码:
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np import math from matplotlib import pyplot as plt def fourier_demo(): #1、读取文件,灰度化 img = cv.imread('img/imageTextR.png') cv.imshow('original', img) gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) cv.imshow('gray', gray) #2、图像延扩 h, w = img.shape[:2] new_h = cv.getOptimalDFTSize(h) new_w = cv.getOptimalDFTSize(w) right = new_w - w bottom = new_h - h nimg = cv.copyMakeBorder(gray, 0, bottom, 0, right, borderType=cv.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=0) cv.imshow('new image', nimg) #3、执行傅里叶变换,并过得频域图像 f = np.fft.fft2(nimg) fshift = np.fft.fftshift(f) magnitude = np.log(np.abs(fshift)) #二值化 magnitude_uint = magnitude.astype(np.uint8) ret, thresh = cv.threshold(magnitude_uint, 11, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY) print(ret) cv.imshow('thresh', thresh) print(thresh.dtype) #霍夫直线变换 lines = cv.HoughLinesP(thresh, 2, np.pi/180, 30, minLineLength=40, maxLineGap=100) print(len(lines)) #创建一个新图像,标注直线 lineimg = np.ones(nimg.shape,dtype=np.uint8) lineimg = lineimg * 255 piThresh = np.pi/180 pi2 = np.pi/2 print(piThresh) for line in lines: x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0] cv.line(lineimg, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2) if x2 - x1 == 0: continue else: theta = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) if abs(theta) < piThresh or abs(theta - pi2) < piThresh: continue else: print(theta) angle = math.atan(theta) print(angle) angle = angle * (180 / np.pi) print(angle) angle = (angle - 90)/(w/h) print(angle) center = (w//2, h//2) M = cv.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0) rotated = cv.warpAffine(img, M, (w, h), flags=cv.INTER_CUBIC, borderMode=cv.BORDER_REPLICATE) cv.imshow('line image', lineimg) cv.imshow('rotated', rotated) fourier_demo() cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows()



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








