Image stitch
学号:23020201153794
系别:计算机科学系
课程名称:计算机视觉
一、问题分析
1.问题描述
图像拼接技术就是将数张有重叠部分的图像(可能是不同时间、不同视角或者不同传感器获得的)拼成一幅无缝的全景图或高分辨率图像的技术。在医学成像、计算机视觉、卫星数据、军事目标自动识别等领域具有重要意义。图像拼接的输出是两个输入图像的并集。
2.实验数据分析
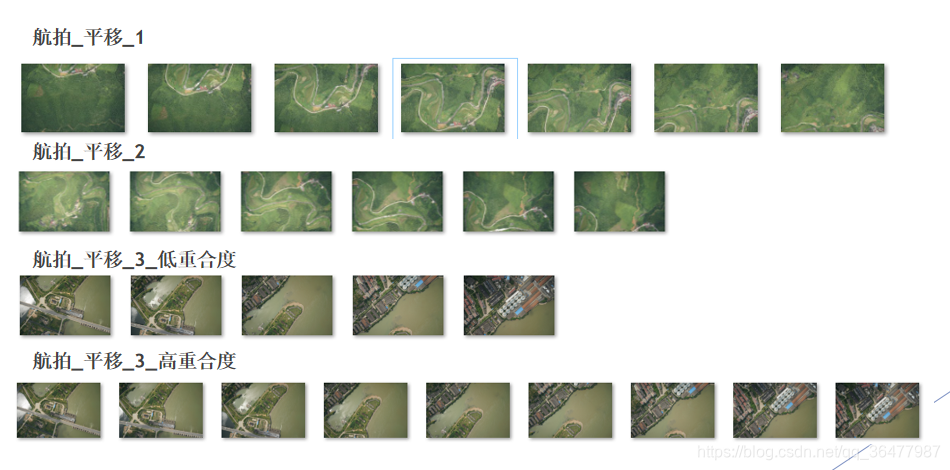
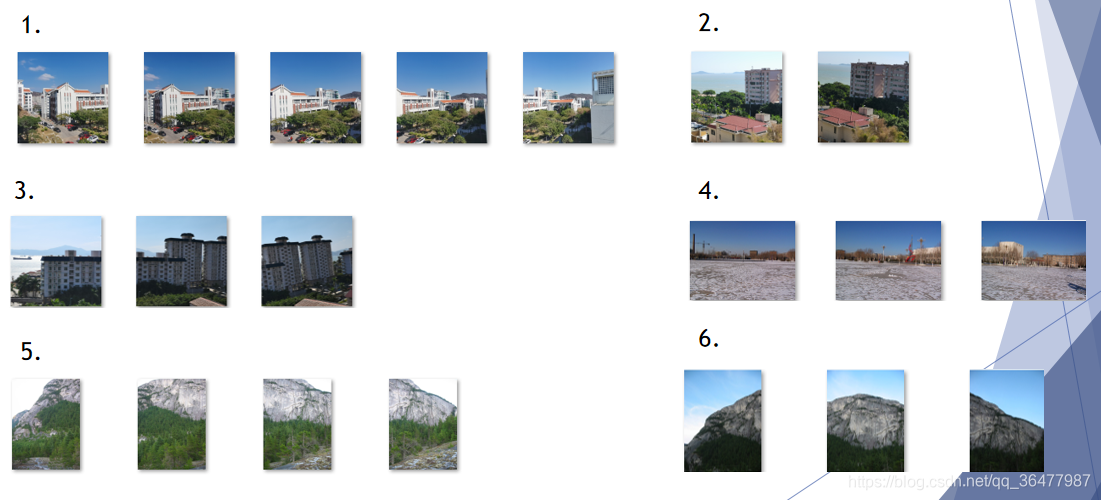
数据集一共提供了一共10组数据,已经按照拍摄顺序排列好,每组图片进行拼接得到一幅全景图。根据观察,实验给出航拍图4组,各图像拍摄角度近似平行。旋转或缩放图6组。
航拍图如下:

旋转缩放图如下:

二、实验原理
1.SURF 加速稳健特征
SURF是一种稳健的局部特征点检测和描述算法。它是对SIFT算法的改进,提升了算法的执行效率,为算法在实时计算机视觉系统中应用提供了可能。
SURF算法的基本流程可以分为三大部分:局部特征点的提取、特征点的描述、特征点的匹配。
SURF在执行效率上有两大制胜法宝——一个是积分图在Hessian(黑塞矩阵)上的使用,一个是降维的特征描述子的使用。
Surf算法特征检测的基本步骤:
(1)尺度空间的极值检测:搜索所有尺度空间上的图像,通过Hessian来对空间极值点进行检测。
(2)特征点过滤并进行精确定位。
(3)特征方向赋值:统计特征点圆形邻域内的Harr小波特征。即在60度扇形内,每次将60度扇形区域旋转0.2弧度进行统计,将值最大的那个扇形的方向作为该特征点的主方向。
(4)特征点描述:沿着特征点主方向周围的邻域内,取4×4个矩形小区域,统计每个小区域的Haar特征,然后每个区域得到一个4维的特征向量。一个特征点共有64维的特征向量作为SURF特征的描述子。
2.RANSAC 随机一致性采样
RANSAC是用来找到正确模型来拟合带有噪声数据的迭代方法。给定一个模型,例如点集之间的单应性矩阵,RANSAC 基本的思想是,数据中包含正确的点和噪声点,合理的模型应该能够在描述正确数据点的同时摒弃噪声点。
RANSAC步骤:
(1)随机从数据集中随机抽出4个样本数据 (此4个样本之间不能共线),计算出变换矩阵H,记为模型M;
(2) 计算数据集中所有数据与模型M的投影误差,若误差小于阈值,加入内点集 I ;
(3)如果当前内点集 I 元素个数大于最优内点集 I_best , 则更新 I_best = I,同时更新迭代次数k ;
(4)如果迭代次数大于k,则退出 ; 否则迭代次数加1,并重复上述步骤;
三、实验流程
1.算法流程
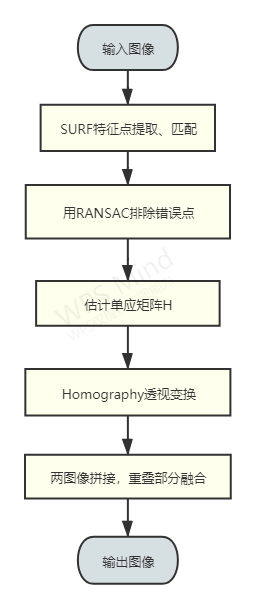
算法流程主要分为以下几个部分:
(1)特征提取:SURF提取特征点,计算不变特征描述符,进行特征点匹配
(2)RANSAC(随机一致性采样)算法进行特征点对的筛选,排除错误点。筛选后的特征点基本能够一一对应
(3)估计单应矩阵(homography matrix);
(4)通过单应矩阵来对图像进行仿射变换;
(5)两图像拼接,重叠部分融合;
2.实验代码
实验在matlabR2018a上进行。
%main.m
%% Script to run function (homog.m) that returns the projective transformation (i.e., homography) between each image and the reference image (i.e., first image) and registers and composes images into a single panoramic image
%Clear screen and command window
clear;
clc;
%Read images from selected dataset
folder_name = 'datasets/2/';
d = dir(strcat(folder_name, '*.jpg'));
image_list = cell(length(d),1);
for i=1:length(d)
image_list{i} = strcat(folder_name, d(i).name);
end
%Obtain projective transformations
tic
[Homog] = homog(image_list);
toc
%Determine image corners in image 1 reference coordinate frame
world_pts_x = zeros(length(image_list), 4);
world_pts_y = zeros(length(image_list), 4);
for i=1:length(image_list)
im = imread(image_list{i});
[rows, cols, ~] = size(im);
corners = [1 cols cols 1; 1 1 rows rows; ones(1, 4)];
wrld_corners = Homog{i, 1} * corners;
world_pts_x(i, :) = wrld_corners(1, :)./wrld_corners(3, :);
world_pts_y(i, :) = wrld_corners(2, :)./wrld_corners(3, :);
end
%Calculate mosaic dimensions
minx = min(world_pts_x(:));
miny = min(world_pts_y(:));
maxx = max(world_pts_x(:));
maxy = max(world_pts_y(:));
%Build mosaic
mosaic = zeros([fix(maxy-miny+1) fix(maxx-minx+1) 3]);%fix(x)是向0取整,可以理解为中间取整,即向最靠近0的整数取整。
mosaic2 = mosaic;%ones白色矩阵,zeros黑色矩阵
imshow(uint8(mosaic));
%imshow((mosaic./mosaic2)/255);
res=mosaic2;
for i = 1:length(image_list)
im2 = imread(image_list{i});
imshow(im2);
imshow(uint8(im2));
imshow(uint8(mosaic));
tt = projective2d(Homog{i,1}');
%将几何tt变换应用于图像,im3c1:1 im3c:0~255
im3c1 = imwarp(uint8(ones(size(im2))),tt,'OutputView',imref2d([size(mosaic,1) size(mosaic,2)],[minx maxx],[miny maxy]));%黑
im3c = imwarp(im2,tt,'OutputView',imref2d([size(mosaic,1) size(mosaic,2)],[minx maxx],[miny maxy]));%原
%imshow(im3c1)
%imshow(im3c)
mosaic = (mosaic + double(im3c));%原
mosaic2 = mosaic2 + double(im3c1);%黑
imshow(uint8(mosaic));
imshow((mosaic./mosaic2)/255);
imwrite(((mosaic./mosaic2)/255), 'res.png');
end
%homog.m
%Function that returns the projective transformation (i.e., homography) between each image and the reference image (i.e., first image)
function [H] = homog(image_list)
%applies projective transformation
function [H] = projective_transf(num_points)
%Repeate each value of u1 and v1 twice
u1_2 = [u1'; u1'];
u1_2 = u1_2(:);
v1_2 = [v1'; v1'];
v1_2 = v1_2(:);
%Preparing columns 7 and 8 of I1 matrix
col_7 = (u1_2.*I2)*(-1);
col_8 = (v1_2.*I2)*(-1);
I1_3 = [col_7' ; col_8'];
I1_3_odd = I1_3(:,1:2:end); %all rows, odd cols
I1_3_even = I1_3(:,2:2:end); %all rows, even cols
%Prepare I1 matrix
I1_1 = [u1'; v1'; ones(1, num_points)];
I1_2 = repmat(zeros(1,num_points), [3 1]);
I1 = [I1_1; I1_2; I1_3_odd; I1_2; I1_1; I1_3_even];
I1 = reshape(I1, [8, 2*num_points])';
%GET Projective H model with DLT
warning('off')
H = (I1'*I1)\(I1'*I2);
warning('on')
H(9) = 1;
H = reshape(H, [3,3])';
end
%load first image
num_images = numel(image_list);
%num_images=numel(image_list,1==1);
im1 = imread(image_list{1});
%prepare output variables
H = cell(num_images);
H{1,1} = eye(3);
% Setup RANSAC (determine number of iterations)
threshold = 49; %set threshold (|r_i|<epsilon) - inlier criteria
%p表示一些迭代过程中从数据集内随机选取出的点均为局内点的概率
bigP = 0.99; %probability of success after k tries
%smallP表示每次从数据集中选取一个局内点的概率,smallP = 局内点的数目 / 数据集的数目
smallP = 0.28; %fraction of matches that are inliers - pessimistic assumption
K = ceil(log(1-bigP)/log(1-smallP^(4))); %number of iterations: formula from slides
%loop for each sequential pair of images
for i = 2:num_images
%load next image
im2 = imread(image_list{i});
%--------%
% SURF %
%--------%
% Automatically select points based on SURF features
[f1, vp1] = extractFeatures(rgb2gray(im1), detectSURFFeatures(rgb2gray(im1)));
[f2, vp2] = extractFeatures(rgb2gray(im2), detectSURFFeatures(rgb2gray(im2)));
[idxPairs, ~] = matchFeatures(f1, f2);
p1 = double(vp1(idxPairs(:,1),:).Location); % [u1 v1]
p2 = double(vp2(idxPairs(:,2),:).Location); % [u2 v2]
%---------%
% RANSAC %
%---------%
% Prepare variables
num_SURF_matches = length(p1(:, 1));
max_inliers = 0;
SURF_pts = [p1'; p2'];
% Loop for RANSAC
for k = 1:K
%Randomly pick 4 points
comb = randperm(num_SURF_matches, 4);
pickedPts = SURF_pts(:, comb(:))';
u1 = full(pickedPts(:, 1));
v1 = full(pickedPts(:, 2));
u2 = full(pickedPts(:, 3));
v2 = full(pickedPts(:, 4));
%Prepare I2 vector and apply projective transformation
I2 = [u2' ; v2'];
I2 = I2(:);
[H_model] = projective_transf(4);
%Pass all points through the H_model transform
pts1 = [p1'; ones(1, size(p1', 2))];
pts2 = p2';
pts2_ = full(H_model)*pts1; %pts1 has all image points [w1_2_; w2_2_;w3_2_ ] = H_model*[x1; y1; 1]
pts2_ = [pts2_(1, :)./pts2_(3,:) ; pts2_(2, :)./pts2_(3,:)]; %[x2_ ; y2_]
%Get difference from image2 actual points
diff = pts2_ - pts2;
mod_diff = diag(diff'*diff); %diagonal values are norm^2
%Count inliers and update best model accordingly (model with more inliers)
num_inliers = sum(mod_diff < threshold); % - 4;
if num_inliers > max_inliers
max_inliers = num_inliers;
%Save inliers, exclude pickedPts as well
ransac_inliers = SURF_pts.*((mod_diff < threshold)'); %get only coordinates from inliers
ransac_inliers(:, all(~ransac_inliers, 1)) = []; %remove empty cols
end
end
%----------------------%
% Transformations %
%----------------------%
%Split inliers coordinates
u1 = ransac_inliers(1,:)';
v1 = ransac_inliers(2,:)';
u2 = ransac_inliers(3,:)';
v2 = ransac_inliers(4,:)';
%Get all inlier points
num_points = length(u1);
%Prepare I2 vector
I2 = [u2' ; v2'];
I2 = I2(:);
%Apply homography
[T_proj] = projective_transf(num_points);
%---------------%
% H transform %
%---------------%
H{i,i} = eye(3);
for k = 1:i-1
H{k,i} = T_proj*H{k,i-1};
H{i,k} = inv(H{k,i});
end
%Update image
im1 = im2;
end
end
四、实验结果:





五、分析总结
1.航拍平移图像拼接结果较好,同一组图像拍摄角度相差太大会导致后面图片被放缩的过大。
2.结果重合部分有亮度有差异,融合方法需要改进,例如使用拉普拉斯金字塔等方法。
3.融合顺序为从左到右,可以改进为从中间到两边。





















 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








