pytorch损失函数踩坑记:Hinge Embedding Loss并不是HingeLoss
0.前言
今天学习HingeLoss损失函数,看了下其他的博客示例代码,运行得到一个负数的损失函数。百思不得期解,于是仔细的分析了下错误原因。原来是Hinge Embedding Loss和HingeLoss混淆了。
1 Hinge Loss与HingeEmbeddingLoss介绍
1.1 Hinge Loss(合页损失)
Hinge Loss(合页损失)通常用于支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,SVM)等模型中,特别是在二分类问题中。它的目标是使正确类别的分数与错误类别的最高分之间的差异达到一个固定的边界,从而促使模型学会产生更大的间隔。Hinge Loss的损失函数:
l
i
=
{
m
a
x
(
0
,
1
−
x
)
i
f
y
=
1
m
a
x
(
0
,
1
+
x
)
i
f
y
i
=
−
1
l_i=\begin{cases} max(0,1-x) & if \quad y = 1\\ max(0, 1+x) & if \quad y_i = -1 \\ \end{cases}
li={max(0,1−x)max(0,1+x)ify=1ifyi=−1
函数形状如下图所示:

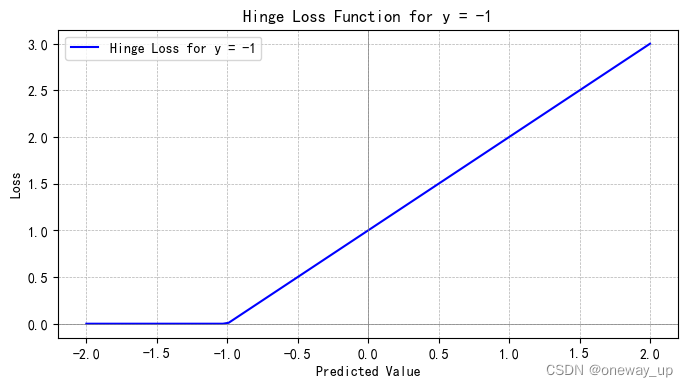
1.2 HingeEmbeddingLoss
用于判断两个向量是否相似,输入
x
x
x是两个向量之间的距离。 常用于非线性词向量学习以及半监督学习。
x
x
x是两个向量之间的距离!!! 所以
x
⩾
0
x\geqslant 0
x⩾0。
对于包含
N
N
N个样本的batch数据
D
(
x
,
y
)
D(x,y)
D(x,y)。
x
x
x代表两个向量的距离,
y
y
y代表真实的标签,
y
y
y中元素的值属于
{
1
,
−
1
}
\{1,-1\}
{1,−1},分别表示相似与不相似。 第
i
i
i个样本对应的loss
l
i
l_i
li如下:
l
i
=
{
x
i
i
f
y
i
=
1
m
a
x
(
0
,
m
a
r
g
i
n
−
x
)
i
f
y
i
=
−
1
l_i=\begin{cases} x_i & if \quad y_i = 1\\ max(0,margin -x) & if \quad y_i = -1 \\ \end{cases}
li={ximax(0,margin−x)ifyi=1ifyi=−1
函数如图所示:
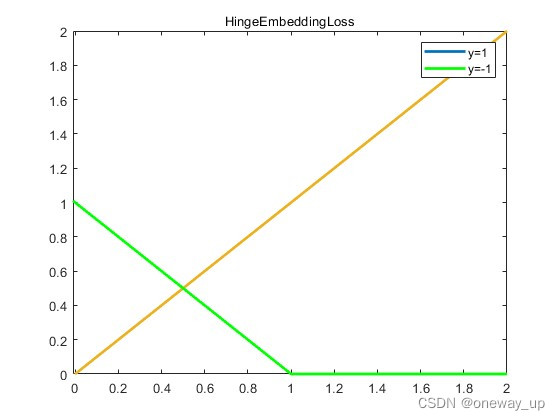
从图中可以看出HingeEmbeddingLoss和Hinge Loss并不相同。
参考链接: loss函数HingeEmbeddingLoss
2 pytorch中的实现
2.1 Hinge Loss错误实现示例
先看有问题的代码,原文链接: 【损失函数】Hinge Loss 合页损失
这篇文章介绍了Hinge Loss 合页损失,但在举例子的时候把Hinge Loss 和HingeEmbeddingLoss损失混淆了。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 示例数据
y_true = torch.tensor([-1, 1, -1], dtype=torch.float32)
y_pred_scores = torch.tensor([0.8, -0.5, 2.0], dtype=torch.float32)
# 定义 Hinge Loss 函数,设置 margin 和 reduce 参数
criterion = nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1.0, size_average=None, reduce=None)
# 计算损失
loss = criterion(y_pred_scores, y_true)
print(f'Hinge Loss: {loss.item()}')
运行结果:
t
e
n
s
o
r
(
−
0.1000
)
tensor(-0.1000)
tensor(−0.1000)
x = [ 0.8 , − 0.5 , 2.0 ] y = [ − 1 , 1 , − 1 ] x=[0.8, -0.5, 2.0] \quad y=[-1, 1, -1] x=[0.8,−0.5,2.0]y=[−1,1,−1],按Hinge Loss损失函数的公式计算,得到一个负数的损失函数-0.1,想了半天不明白为什么Hinge Loss损失函数是负数。后来才知道这个是HingeEmbeddingLoss损失。
nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1.0, size_average=None, reduce=None)
margin设置为1。
先回答这个-0.1是怎么得到的
第一个x=0.8,y=-1, 代入HingeEmbeddingLoss损失公式,值为:
l
o
s
s
=
m
a
x
(
0
,
1
−
0.8
)
=
0.2
loss = max(0,1-0.8) =0.2
loss=max(0,1−0.8)=0.2
第二个 x=-0.5,y=1 代入HingeEmbeddingLoss损失公式,值为:
l
o
s
s
=
x
=
−
0.5
loss = x =-0.5
loss=x=−0.5
第三个x=2,y=-1 代入HingeEmbeddingLoss损失公式,值为:
l
o
s
s
=
m
a
x
(
0
,
1
−
2
)
=
0
loss = max(0,1-2)=0
loss=max(0,1−2)=0
最后HingeEmbeddingLoss默认取平均值:
l
o
s
s
=
(
0.2
+
(
−
0.5
)
+
0
)
/
3
=
−
0.1
loss =(0.2+(-0.5)+0)/3=-0.1
loss=(0.2+(−0.5)+0)/3=−0.1
损失函数是负数明显有问题,这里是因为对于HingeEmbeddingLoss,x取值要大于等于0,x是向量之间的距离。上面第二个数据x=-0.5是错误的数据。
2.2 HingeEmbeddingLoss使用示例
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.manual_seed(20)
hinge_loss = nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=0.2)
a = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
b = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
x = 1 - torch.cosine_similarity(a, b)
# 定义a与b之间的距离为x
print(x.size())
y = 2 * torch.empty(100).random_(2) - 1
output = hinge_loss(x, y)
print(output.item())
hinge_loss = nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=0.2, reduction="none")
output = hinge_loss(x, y)
print(output)
2.3 HingeLoss的实现
输入 x = [ 0.8 , − 0.5 , 2.0 ] y = [ − 1 , 1 , − 1 ] x=[0.8, -0.5, 2.0] \quad y=[-1, 1, -1] x=[0.8,−0.5,2.0]y=[−1,1,−1],运行以下代码HingeLoss 为2.1,与预期结果相似。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class HingeLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(HingeLoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, y_pred, y_true):
# 计算Hinge Loss
loss = F.relu(1 - y_true * y_pred)
# 计算平均Hinge Loss
mean_loss = torch.mean(loss)
return mean_loss
# 创建HingeLoss实例
hinge_criterion = HingeLoss()
y_true = torch.tensor([-1, 1, -1], dtype=torch.float32)
# print(y_true)
y_pred_scores = torch.tensor([0.8, -0.5, 2.0], dtype=torch.float32)
# 计算Hinge Loss
loss = hinge_criterion(y_pred_scores, y_true)
print("Mean Hinge Loss:", loss)







 文章讲述了在PyTorch中HingeLoss与HingeEmbeddingLoss的混淆,解释了两者在二分类和向量相似度判断中的作用,并提供了代码示例以展示正确的HingeLoss实现。
文章讲述了在PyTorch中HingeLoss与HingeEmbeddingLoss的混淆,解释了两者在二分类和向量相似度判断中的作用,并提供了代码示例以展示正确的HingeLoss实现。
















 1359
1359

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








