一、二叉树的遍历
1.二叉树的数据结构定义
public class TreeNode {
private TreeNode leftNode;
private TreeNode rightNode;
private int value;
public TreeNode(TreeNode leftNode, TreeNode rightNode, int value) {
this.leftNode = leftNode;
this.rightNode = rightNode;
this.value = value;
}
}2.二叉树的添加数据方法(这里是以二叉排序树的方式添加,左子树<根结点<右子树)
public void insert(int value){
TreeNode tn = this;
TreeNode tn1 = new TreeNode(null, null, value);
while (value<tn.value && tn.leftNode!=null){
tn = tn.leftNode;
}
while (value>tn.value && tn.rightNode!=null){
tn = tn.rightNode;
}
if (value<tn.value) {
tn.setLeftNode(tn1);
}else if (value>tn.value){
tn.setRightNode(tn1);
}
}3.二叉树的先序遍历方法
//先序遍历
public static void preOrder(TreeNode tn){
if (tn!=null) {
System.out.print(tn.getValue()+" ");
preOrder(tn.leftNode);
preOrder(tn.rightNode);
}
}4.二叉树的中序遍历方法
//中序遍历
public static void inOrder(TreeNode tn){
if (tn!=null) {
inOrder(tn.leftNode);
System.out.print(tn.getValue()+" ");
inOrder(tn.rightNode);
}
}5.二叉树的后续遍历方法
//后序遍历
public static void postOrder(TreeNode tn){
if (tn!=null) {
postOrder(tn.leftNode);
postOrder(tn.rightNode);
System.out.print(tn.getValue()+" ");
}
}6.二叉树的添加、遍历测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
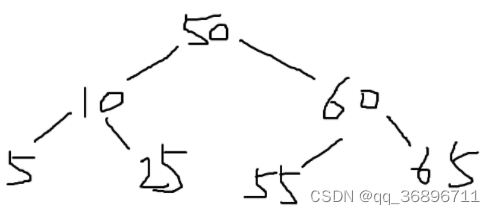
TreeNode tn = new TreeNode(null,null,50);
tn.insert(10);
tn.insert(60);
tn.insert(25);
tn.insert(5);
tn.insert(55);
tn.insert(65);
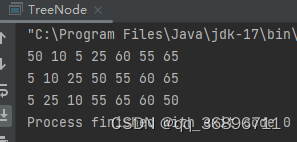
preOrder(tn);
System.out.println();
inOrder(tn);
System.out.println();
postOrder(tn);
} 
二、Map的性能分析
1.List和Map查找的区别,以arr = {10,11,22,13,4,5,16,17,48,69}为例,
(1)List是list.get(0)==17? -> list.get(1)==17? ->...->list.get(i)==17,时间复杂度为O(n)
(2)Map是17%10=7 -> arr[7],时间复杂度为O(1);
map的两种常用操作get和set,get(17) -> {return arr[17%10];} set(17) -> {arr[17%10]}=17;}
如果要继续put,数字27 -> arr[27%10]=27就会与17发生碰撞
2.Map的碰撞
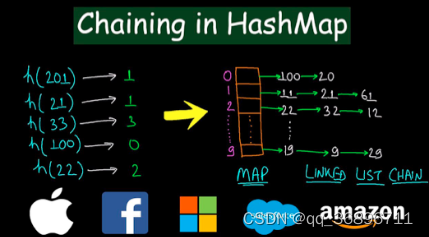
如果发生太多碰撞,map就会退化成链表
3.Map的树化
链表长度大于8时会进行树化,变为红黑树来维持平衡,小于6时链化,树化之后,时间复杂度也不会太高O(logN)
4.Map与List双重for循环的对比,测试代码如下
public static void test1(){
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
list1.add(i);
}
for (int i = 9999; i < 209999; i++) {
list2.add(i);
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < list2.size(); j++) {
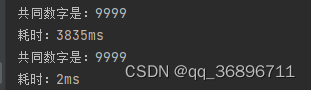
if (list1.get(i).equals(list2.get(j))) {
System.out.println("共同数字是:"+list1.get(i));
}
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
public static void test2(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
for (int i = 9999; i < 209999; i++) {
map.put(i,1);
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (map.get(list.get(i))!=null) {
System.out.println("共同数字是:"+list.get(i));
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
5.Map的缺陷
Map相比List,只支持put,get,remove等少量操作,不支持求最大值、最小值、排序等操作。





















 1468
1468











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








