这个以前的时候,采取的是把要显示的图片copy到一张大图片上去~ 这个也忒麻烦了点
然后 在 http://download.csdn.net/detail/zhazhiqiang2010/3614993#comment 这里发现一个好用的代码。。。。
感谢上传者,记录在这里只为了以后方便使用~~~
#include <cv.h>
#include <highgui.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#pragma comment(lib, "cv.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "cxcore.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "highgui.lib")
void cvShowManyImages(char* title, int nArgs, ...)
{
// img - Used for getting the arguments
IplImage *img;
// DispImage - the image in which input images are to be copied
IplImage *DispImage;
int size;
int i;
int m, n;
int x, y;
// w - Maximum number of images in a row
// h - Maximum number of images in a column
int w, h;
// scale - How much we have to resize the image
float scale;
int max;
// If the number of arguments is lesser than 0 or greater than 12
// return without displaying
if(nArgs <= 0)
{
printf("Number of arguments too small....\n");
return;
}
else if(nArgs > 12)
{
printf("Number of arguments too large....\n");
return;
}
// Determine the size of the image, and the number of rows/cols from number of arguments
else if (nArgs == 1)
{
w = h = 1;
size = 300;
}
else if (nArgs == 2)
{
w = 2; h = 1;
size = 300;
}
else if (nArgs == 3 || nArgs == 4)
{
w = 2; h = 2;
size = 300;
}
else if (nArgs == 5 || nArgs == 6) {
w = 3; h = 2;
size = 200;
}
else if (nArgs == 7 || nArgs == 8)
{
w = 4; h = 2;
size = 200;
}
else
{
w = 4; h = 3;
size = 150;
}
// Create a new 3 channel image0
DispImage = cvCreateImage( cvSize( 100+ size*w, 60 + size*h), 8, 3 );
// Used to get the arguments passed
va_list args;
va_start(args, nArgs);
// Loop for nArgs number of arguments
for (i = 0, m = 20, n = 20; i < nArgs; i++, m += (20 + size))
{
// Get the Pointer to the IplImage
img = va_arg(args, IplImage*);
// Check whether it is NULL or not
// If it is NULL, release the image, and return
if(img == 0)
{
printf("Invalid arguments");
cvReleaseImage(&DispImage);
return;
}
// Find the width and height of the image
x = img->width;
y = img->height;
// Find whether height or width is greater in order to resize the image
max = (x > y)? x: y;
// Find the scaling factor to resize the image
scale = (float) ( (float) max / size );
// Used to Align the images
if( i % w == 0 && m!= 20)
{
m = 20;
n+= 0 + size;
}
// Set the image ROI to display the current image
//cvSetImageROI(DispImage, cvRect(m, n, (int)( x/scale ), (int)( y/scale )));
cvSetImageROI(DispImage, cvRect(m, n, (int)( x/scale ), (int)( y/scale )));
// cout<<"x="<<m<<"y="<<n<<endl;
// Resize the input image and copy the it to the Single Big Image
cvResize(img, DispImage);
// Reset the ROI in order to display the next image
cvResetImageROI(DispImage);
}
// Create a new window, and show the Single Big Image
//cvNamedWindow( title, 1 );
cvShowImage( title, DispImage);
/*cvWaitKey(0);*/
//cvDestroyWindow(title);
// End the number of arguments
va_end(args);
// Release the Image Memory
cvReleaseImage(&DispImage);
}
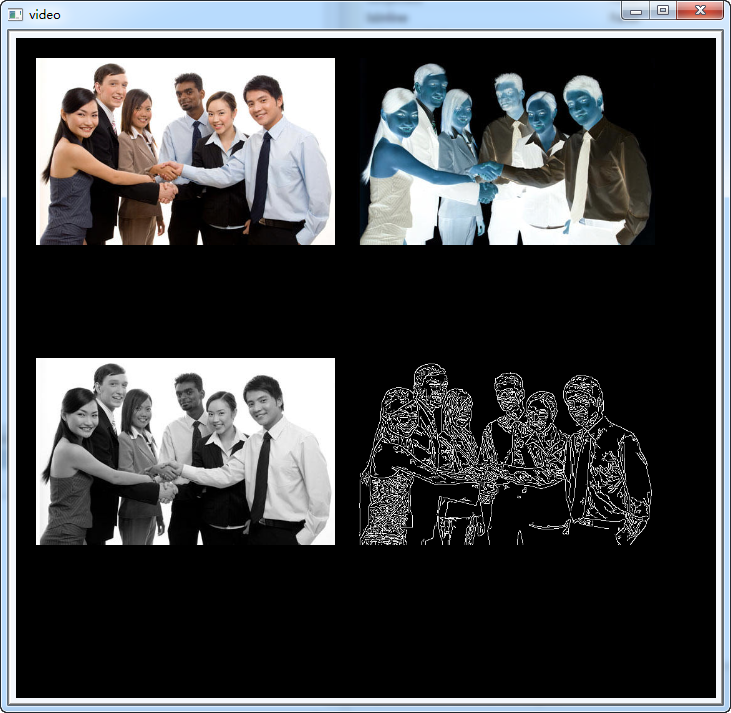
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
/* CvCapture *capture;*/
int i=0;
IplImage *frame=cvLoadImage(".\\test.png");
cvNamedWindow("video",1);
cvResizeWindow("video",700,660);
IplImage *frame_not=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(frame),frame->depth,frame->nChannels);
cvNot(frame,frame_not);
IplImage *frame_gray=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(frame),frame->depth,1);
IplImage *frame1=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(frame),frame->depth,frame->nChannels);
IplImage *frame_canny=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(frame),frame->depth,1);
IplImage *frame2=cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(frame),frame->depth,frame->nChannels);
cvCvtColor(frame,frame_gray,CV_RGB2GRAY);
cvCvtColor(frame_gray,frame1,CV_GRAY2BGR);
cvCanny(frame_gray,frame_canny,20,75,3);
cvCvtColor(frame_canny,frame2,CV_GRAY2BGR);
cvShowManyImages("video",4,frame,frame_not,frame1,frame2);
cvWaitKey();
cvReleaseImage(&frame_not);
cvReleaseImage(&frame1);
cvReleaseImage(&frame_gray);
cvReleaseImage(&frame2);
cvReleaseImage(&frame_canny);
cvDestroyWindow("video");
return 0;
}
【Note:】
注意 这个函数显示的图像是 nChannels = 3 的。
你看见 cvShowManyImages 函数中的
- // Create a new 3 channel image0
- DispImage = cvCreateImage( cvSize( 100+ size*w, 60 + size*h), 8, 3 );
了么~~~吼吼, 如果想要 显示 单通道 的,把 3 改为 1 就OK了~~
==============================================================================
【起初我 cvLoadImage( "tutu"); 读入了之前
【cvLoadImage( ,0) 读入了一张图像,然后用 cvSaveImage(); 保存图像】
得到的一张图像
】 这样是可以显示的。 然后就误导了我以为 可以显示灰度图。。。。。。
后来,发现 cvLoadImage( ,0) 读入的 灰度图 老是 出错。。。。。。
后来发现 【cvLoadImage( ,0) 读入了一张图像,然后用 cvSaveImage(); 保存图像】 之后的图像 nChanels = 3 !
才发现:
cvSaveImage()保存的 图像只能为深度为8U的1通道或者3通道(RGB)的图像。
也就是说 nChanels = 3 , R=G=B 的 3 通道的 灰度图
总之,函数只显示 通道为3 的 图像!
=========================================================================================================================================
从文件中读入一幅图像可以使用imread函数来读取图像,
Mat img=imread(filename);
该语句将filename所指定路径的指定文件读取到img数组中,该函数读取的是默认的三通道图像,读取的顺序默认情况下是BGR顺序,如果想得到单通道(灰度级的)图像,则可以使用下面的方式:
Mat img=imread(filename,0);
另一个版本:
来自: CSDN yang_xian521 'S blog
http://blog.csdn.net/yang_xian521/article/details/7915396
希望作者不要介意,拿来方便使用哈
/************************************************************************
* Copyright(c) 2012 Yang Xian
* All rights reserved.
*
* File: showManyImage.cpp
* Brief:
* Version: 1.0
* Author: Yang Xian
* Email: yang_xian521@163.com
* Date: 2012/08/28
* History:
************************************************************************/
#include"cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void imshowMany(const std::string& _winName, const vector<Mat>& _imgs);
int main(void)
{
vector<Mat> imgs(6);
imgs[0] = imread("cm.png");
imgs[1] = imread("wr.png");
imgs[2] = imread("lina.png");
imgs[3] = imread("dr.png");
imgs[4] = imread("pom.png");
imgs[5] = imread("qop.png");
imshowMany("DOTA2_Hero", imgs);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
void imshowMany(const std::string& _winName, const vector<Mat>& _imgs)
{
int nImg = (int)_imgs.size();
Mat dispImg;
int size;
int x, y;
// w - Maximum number of images in a row
// h - Maximum number of images in a column
int w, h;
// scale - How much we have to resize the image
float scale;
int max;
if (nImg <= 0)
{
printf("Number of arguments too small....\n");
return;
}
else if (nImg > 12)
{
printf("Number of arguments too large....\n");
return;
}
else if (nImg == 1)
{
w = h = 1;
size = 300;
}
else if (nImg == 2)
{
w = 2; h = 1;
size = 300;
}
else if (nImg == 3 || nImg == 4)
{
w = 2; h = 2;
size = 300;
}
else if (nImg == 5 || nImg == 6)
{
w = 3; h = 2;
size = 200;
}
else if (nImg == 7 || nImg == 8)
{
w = 4; h = 2;
size = 200;
}
else
{
w = 4; h = 3;
size = 150;
}
dispImg.create(Size(100 + size*w, 60 + size*h), CV_8UC3);
for (int i= 0, m=20, n=20; i<nImg; i++, m+=(20+size))
{
x = _imgs[i].cols;
y = _imgs[i].rows;
max = (x > y)? x: y;
scale = (float) ( (float) max / size );
if (i%w==0 && m!=20)
{
m = 20;
n += 20+size;
}
Mat imgROI = dispImg(Rect(m, n, (int)(x/scale), (int)(y/scale)));
resize(_imgs[i], imgROI, Size((int)(x/scale), (int)(y/scale)));
}
namedWindow(_winName);
imshow(_winName, dispImg);
}以下是整理成OpenCV 1,0后的代码版本:
/************************************************************************
* Copyright(c) 2012 Yang Xian
* All rights reserved.
*
* File: showManyImage.cpp
* Brief:
* Version: 1.0
* Author: Yang Xian
* Email: yang_xian521@163.com
* Date: 2012/08/28
* History:
************************************************************************/
#include <cv.h>
#include <highgui.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#pragma comment(lib, "cv.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "cxcore.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "highgui.lib")
void imshowMany(const std::string& _winName, const vector<IplImage*>& _imgs);
int main(void)
{
std::vector<IplImage*> imgs(6);
imgs[0] = cvLoadImage("test.png");
imgs[1] = cvLoadImage("test.png");
imgs[2] = cvLoadImage("test.png");
imgs[3] = cvLoadImage("test.png");
imgs[4] = cvLoadImage("test.png");
imgs[5] = cvLoadImage("test.png");
imshowMany("DOTA2_Hero", imgs);
cvWaitKey();
return 0;
}
void imshowMany(const std::string& _winName, const vector<IplImage*>& _imgs)
{
int nImg = (int)_imgs.size();
IplImage* dispImg;
int size;
int x, y;
// w - Maximum number of images in a row
// h - Maximum number of images in a column
int w, h;
// scale - How much we have to resize the image
float scale;
int max;
if (nImg <= 0)
{
printf("Number of arguments too small....\n");
return;
}
else if (nImg > 12)
{
printf("Number of arguments too large....\n");
return;
}
else if (nImg == 1)
{
w = h = 1;
size = 300;
}
else if (nImg == 2)
{
w = 2; h = 1;
size = 300;
}
else if (nImg == 3 || nImg == 4)
{
w = 2; h = 2;
size = 300;
}
else if (nImg == 5 || nImg == 6)
{
w = 3; h = 2;
size = 200;
}
else if (nImg == 7 || nImg == 8)
{
w = 4; h = 2;
size = 200;
}
else
{
w = 4; h = 3;
size = 150;
}
dispImg = cvCreateImage(cvSize(100 + size*w, 60 + size*h), IPL_DEPTH_8U, 3);
for (int i= 0, m=20, n=20; i<nImg; i++, m+=(20+size))
{
x = _imgs[i]->height;
y = _imgs[i]->width;
max = (x > y)? x: y;
scale = (float) ( (float) max / size );
if (i%w==0 && m!=20)
{
m = 20;
n += 20+size;
}
cvSetImageROI(dispImg,cvRect(m, n, (int)(x/scale), (int)(y/scale)));
cvResize(_imgs[i], dispImg);
cvResetImageROI(dispImg);
}
cvNamedWindow(_winName.c_str());
cvShowImage(_winName.c_str(), dispImg);
}
























 1223
1223

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








