目录
1、List<Map>使用map中每一个字符拼接字符串
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
Map m = new HashMap();
m.put("name", "樟树街");
Map m1 = new HashMap();
m1.put("name", "樟树街1");
Map m2 = new HashMap();
m2.put("name", "樟树街1");
list.add(m);
list.add(m2);
list.add(m1);
String s= list.stream().map(p->p.get("name")).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
List<SysInfoItem> sysInfoItems = sysFeignClient.getInfoItemsBySetId('');
// 【启用】状态的字段名称,以读好分隔
String items = sysInfoItems.stream().map(sysInfoItem -> sysInfoItem.getItemId()).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
2、取出list集合对象中某一个属性,生成新的list
List<TrnRequirement> list = this.list();
List<String> requirementIdList = list.stream().map(TrnRequirement::getId).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
3、list集合的排序
①List(Bean)
//排序 项目状态(已结束的在最后面),累计项目效能,部门,项目经理
resultList = resultList.stream()
.sorted(
Comparator.comparing(StatisticsProjectEfficacyVO::getProjectStatus)
.thenComparing(StatisticsProjectEfficacyVO::getEfficacyTotal)
.thenComparing(StatisticsProjectEfficacyVO::getDeptId)
.thenComparing(StatisticsProjectEfficacyVO::getProjectManageName)
).collect(Collectors.toList());
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
Integer id;
Integer age;
Integer type;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<>();
persons.add(new Person(7, 10, 1));
persons.add(new Person(2, 10, 1));
persons.add(new Person(5, 10, 1));
persons.add(new Person(3, 26, 2));
persons.add(new Person(4, 35, 2));
persons.add(new Person(6, 23, 2));
persons.add(new Person(10, 23, 3));
persons.add(new Person(11, 24, 3));
persons.add(new Person(11, 23, 3));
persons = persons.stream()
.sorted(
Comparator.comparing(Person::getType).reversed()
.thenComparing(Person::getId)
.thenComparing(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed())
).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(persons));
}
}
上面的代码,先对 type 降序, 再对 id 升序,最后对 age 降序
②List (Map):方式①
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("name", "ZK");
map.put("age", 13);
Map<String, Object> map2 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map2.put("name", "ZA");
map2.put("age", 15);
Map<String, Object> map3 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map3.put("name", "CX");
map3.put("age", 20);
Map<String, Object> map4 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map4.put("name", "CX");
map4.put("age", 18);
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();
list.add(map);
list.add(map2);
list.add(map3);
list.add(map4);
// 排序代码如下
List<Map<String, Object>> collect = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Test::comparingByName)
.thenComparing(Comparator.comparing(Test::comparingByAge).reversed()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private static String comparingByName(Map<String, Object> map){
return (String) map.get("name");
}
private static Integer comparingByAge(Map<String, Object> map){
return (Integer) map.get("age");
}
③List (Map):方式2
public static void main(String[] args) {
testListMapSort();
}
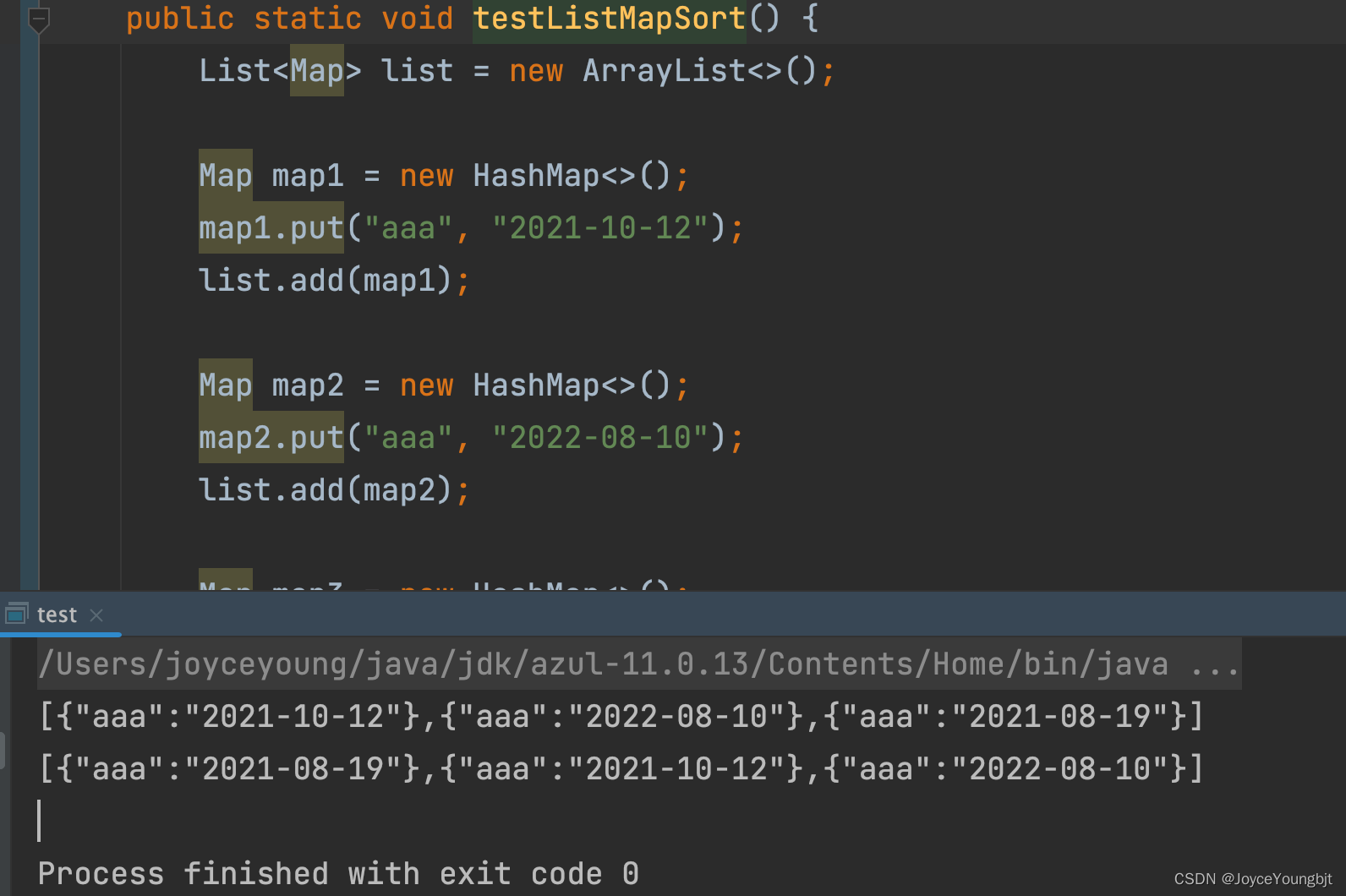
public static void testListMapSort() {
List<Map> list = new ArrayList<>();
Map map1 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("aaa", "2021-10-12");
list.add(map1);
Map map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put("aaa", "2022-08-10");
list.add(map2);
Map map3 = new HashMap<>();
map3.put("aaa", "2021-08-19");
list.add(map3);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(list));
list.sort(Comparator.comparing(map -> (String) map.get("aaa")));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(list));
}
}
4、list集合分组
①Collectors.groupingBy
注意:key不能为空
Map<String, List<SiFundBaseManage>> baseManageMap =
baseManageList.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(SiFundBaseManage::getPersonId)
);
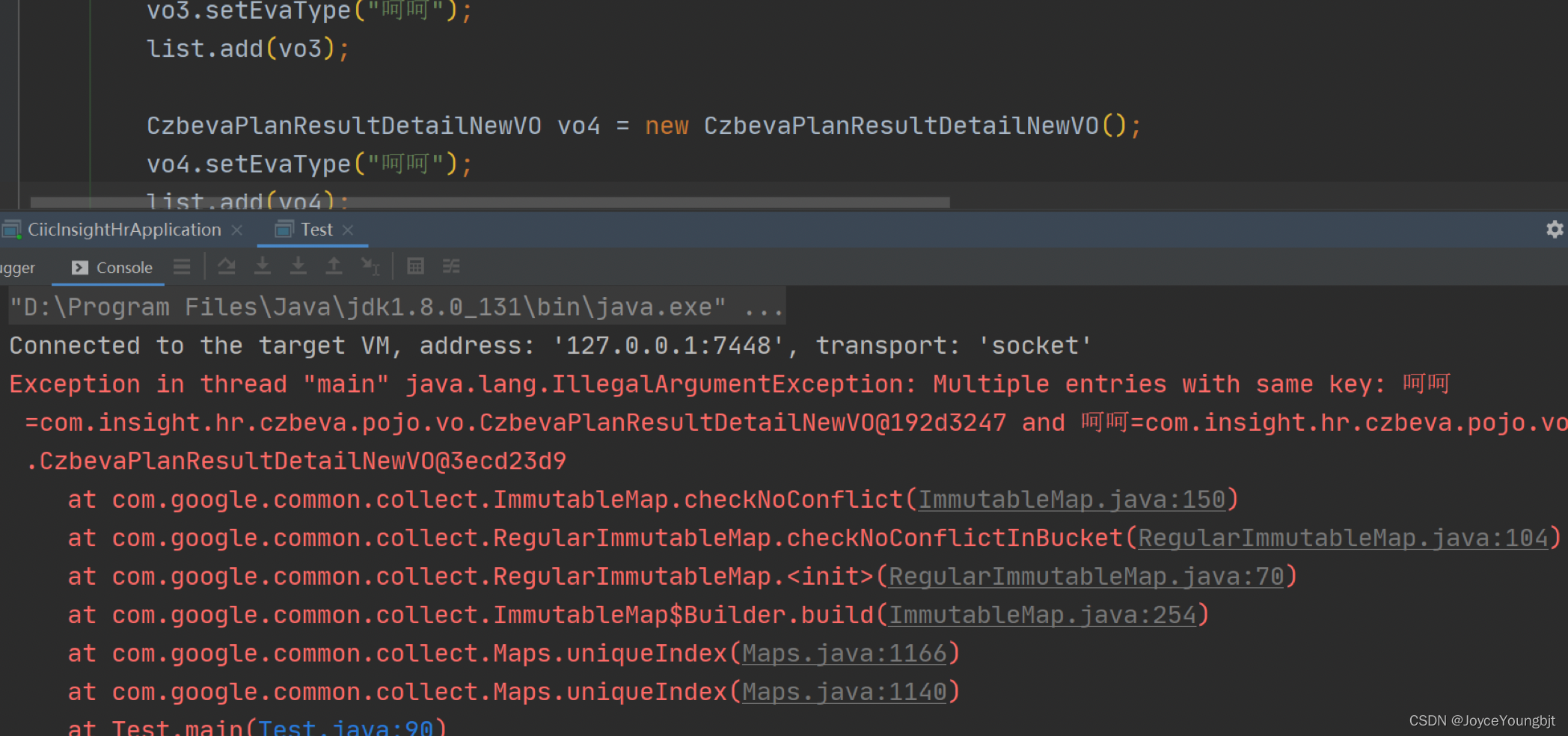
②Maps.uniqueIndex
//若name对应了多条记录,会报错
Map<String, Fruit> map = Maps.uniqueIndex(
fruitList, Fruit::getName);
5、List中Map 根据key去重
public List<Map<String, String>> getAttrActions(String ns, String category, String ci) {
String sql = "SELECT ID AS value,NAME AS label FROM IES.CMDB_META_ACTION " +
"WHERE NS = '" + ns + "' AND CATEGORY = '" + category + "' AND CI = '" + ci + "'";
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = runner.executeSQL(sql);
List<Map<String, Object>> attrActionsList = new ArrayList<>();
DMMetaEnum.MetaAttrActions[] attrActions = DMMetaEnum.MetaAttrActions.values();
for (DMMetaEnum.MetaAttrActions attrAction : attrActions) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(1);
map.put(VALUE, attrAction.getValue());
map.put(LABEL, attrAction.getLabel());
attrActionsList.add(map);
}
//合并
mapList.addAll(attrActionsList);
List<Map<String, String>> newList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Map<String, Object> map : mapList) {
Map<String, String> newMap = new HashMap<>();
newMap.put(VALUE, map.get(VALUE).toString());
newMap.put(LABEL, map.get(LABEL).toString());
newList.add(newMap);
}
//去重(map中的key和value都是String类型)
newList = newList.stream().collect(
Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toCollection(
() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(m -> m.get(VALUE)))), ArrayList::new));
return newList;
}
newList = newList.stream().collect(
Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toCollection(
() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(m -> m.get(VALUE)))), ArrayList::new));
6、list的filter过滤
① java8的方式
List<ActAtndLeave> approveInfoList_tmp =
JacksonUtils.fromJson(JacksonUtils.toJson(approveInfoList), ArrayList.class,
ActAtndLeave.class);
List<ActAtndLeave> atndLeaveList_date = approveInfoList_tmp.stream().filter(
(ActAtndLeave leave) ->
(leave.getStartTime().compareTo(fullWorkTime) >= 0 && leave.getStartTime().compareTo(fullOffWorkTime) <= 0)
|| (leave.getEndTime().compareTo(fullWorkTime) >= 0 && leave.getEndTime().compareTo(fullOffWorkTime) <= 0)
|| (fullWorkTime.compareTo(leave.getStartTime()) >= 0 && fullWorkTime.compareTo(leave.getEndTime()) <= 0)
|| (fullOffWorkTime.compareTo(leave.getStartTime()) >= 0 && fullOffWorkTime.compareTo(leave.getEndTime()) <= 0)
).collect(Collectors.toList());
②java版本低于8的方式
如果java版本低于8,那么可以用下面ListUtils这个工具类
package com.icitic.hrms.util;
/**
* @author YangYQ
* @since 2019-11-01 14:49
**/
public interface ListUtilsHook<T> {
public boolean test(T t);
}
package com.icitic.hrms.util;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author YangYQ
* @since 2019-11-01 14:49
**/
public class ListUtils {
public static <T> List<T> filter(List<T> list, ListUtilsHook<T> hook) {
ArrayList<T> r = new ArrayList<T>();
for (T t : list) {
if (hook.test(t)) {
r.add(t);
}
}
r.trimToSize();
return r;
}
}
使用方式
List clockList_dateMonth = this.jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql_exception_new);//期间内的打卡记录
List<KqClockRecordBO> clockRecordBOList = JacksonUtils.fromJson(JacksonUtils.toJson(clockList_dateMonth),
ArrayList.class, KqClockRecordBO.class);
// 1、当月缺卡信息查询
List<KqClockRecordBO> clockRecordBOList_this_MC = ListUtils.filter(clockRecordBOList,
new ListUtilsHook<KqClockRecordBO>() {
@Override
public boolean test(KqClockRecordBO bo) {
return bo.getSIGN_IN_STATUS().equals(KqConstants.KQ_CLOCK_TYPE_MISSINGCARD);
}
});
7、java8 stream做统计(分组后取最大最小,排序)
package com.lagou.multiThread.Test.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class User2 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1220193146286930256L;
private String id;
private String name;
private String groupId;
private int num;
private int age;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGroupId() {
return groupId;
}
public void setGroupId(String groupId) {
this.groupId = groupId;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public User2(String id, String name, String groupId, int num, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.groupId = groupId;
this.num = num;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", groupId='" + groupId + '\'' +
", num=" + num +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
private static <T> Predicate<T> distinctByKey(Function<? super T, ?> keyExtractor) {
Map<Object, Boolean> seen = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
return t -> seen.putIfAbsent(keyExtractor.apply(t), Boolean.TRUE) == null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<User2> list = new ArrayList<>(10);
list.add(new User2("1", "1号", "A", 10, 10));
list.add(new User2("2", "2号", "A", 20, 10));
list.add(new User2("3", "3号", "E", 50, 12));
list.add(new User2("4", "4号", "B", 60, 20));
list.add(new User2("5", "5号", "C", 80, 40));
list.add(new User2("6", "6号", "B", 220, 20));
list.add(new User2("7", "7号", "A", 110, 2));
list.add(new User2("8", "8号", "D", 110, 68));
//去重复获取组
System.out.println("----------去重复获取组-------------------");
list.stream().filter(distinctByKey(User2::getGroupId)).map(User2::getGroupId).forEach(s -> {
System.out.println(s);
});
//从第2个开始(下标)
System.out.println("-------------从第2个开始----------------");
list.stream().skip(2).forEach(s -> {
System.out.println(s);
});
//取10以内的
System.out.println("-------------取10以内的----------------");
list.stream().filter(user -> user.getAge() <= 10).forEach(s -> {
System.out.println(s);
});
//取最大
System.out.println("----------------取最大-------------");
User2 user = list.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(User2::getNum)).get();
System.out.println(user);
//分组求合
System.out.println("---------------分组求合--------------");
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User2::getGroupId, Collectors.summingInt(User2::getNum))).forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println("K:" + k + "-V:" + v);
});
//分组取组内最大
System.out.println("--------------分组取组内最大---------------");
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User2::getGroupId, Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparingInt(User2::getNum)))).forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println("K:" + k + "-V:" + v.get());
});
//分组取组内最小
System.out.println("------------分组取组内最小-----------------");
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User2::getGroupId, Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparingInt(User2::getNum)))).forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println("K:" + k + "-V:" + v.get());
});
//分组聚合多列
System.out.println("---------------分组聚合多列计算--------------");
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User2::getGroupId, Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), users -> {
Double[] ints = new Double[2];
Double asDouble1 = users.stream().mapToInt(User2::getNum).average().getAsDouble();
Double asDouble2 = users.stream().mapToInt(User2::getAge).average().getAsDouble();
ints[0] = asDouble1;
ints[1] = asDouble2;
return ints;
}))).forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println("K:" + k + "-V:" + v[0] + "," + v[1]);
});
//分组后组内排序
System.out.println("---------------分组后组内排序--------------");
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User2::getGroupId, Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), users -> {
users.sort(Comparator.comparing(User2::getNum));
return users;
}))).forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println("k:" + k);
System.out.println("v----->:");
v.forEach(s -> {
System.out.println(s);
});
});
}
}
8、先用groupingBy分组,再使用joining将某个字段进行拼接
public class User {
private String name;
private String age;
private String groupId;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGroupId() {
return groupId;
}
public void setGroupId(String groupId) {
this.groupId = groupId;
}
public User(String name, String age, String groupId) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.groupId = groupId;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user1 = new User("测试1", "21", "1");
User user2 = new User("测试2", "22", "1");
User user3 = new User("测试3", "23", "2");
User user4 = new User("测试4", "24", "1");
User user5 = new User("测试5", "25", "3");
User user6 = new User("测试6", "26", "2");
User user7 = new User("测试7", "27", "1");
User user8 = new User("测试8", "28", "5");
User user9 = new User("测试9", "29", "1");
User user10 = new User("测试10", "30", "5");
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(user1);
list.add(user2);
list.add(user3);
list.add(user4);
list.add(user5);
list.add(user6);
list.add(user7);
list.add(user8);
list.add(user9);
list.add(user10);
Map<String, String> collect = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getGroupId, Collectors.mapping(User::getName, Collectors.joining(","))));
for (String groupId : collect.keySet()) {
String names = collect.get(groupId);
System.out.println(groupId + ":" + names);
}
}
}
Map<Integer, List<String>> map2 = list.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getAge, Collectors.mapping(Person::getName, Collectors.toList())));
允许结果:
1:测试1,测试2,测试4,测试7,测试9
2:测试3,测试6
3:测试5
5:测试8,测试10
9、java8 两个List集合取交集、并集、差集
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<String>();
list1.add("1");
list1.add("2");
list1.add("3");
list1.add("5");
list1.add("6");
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<String>();
list2.add("2");
list2.add("3");
list2.add("7");
list2.add("8");
// 交集
List<String> intersection = list1.stream().filter(item -> list2.contains(item)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("---交集 intersection---");
intersection.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::println);
// 差集 (list1 - list2)
List<String> reduce1 = list1.stream().filter(item -> !list2.contains(item)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("---差集 reduce1 (list1 - list2)---");
reduce1.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::println);
// 并集
List<String> listAll = list1.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> listAll2 = list2.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.toList());
listAll.addAll(listAll2);
System.out.println("---并集 listAll---");
listAll.parallelStream().forEachOrdered(System.out::println);
// 去重并集
List<String> listAllDistinct = listAll.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("---得到去重并集 listAllDistinct---");
listAllDistinct.parallelStream().forEachOrdered(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---原来的List1---");
list1.parallelStream().forEachOrdered(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---原来的List2---");
list2.parallelStream().forEachOrdered(System.out::println);
}
}
10、java8 List里面,某一个字段取最大最小值
答案来源:百度AI
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Bean> list = // 初始化你的列表
// 获取最大值
Optional<Bean> maxValue = list.stream()
.max(Comparator.comparing(Bean::getField));
if (maxValue.isPresent()) {
System.out.println("最大值为: " + maxValue.get().getField());
}
// 获取最小值
Optional<Bean> minValue = list.stream()
.min(Comparator.comparing(Bean::getField));
if (minValue.isPresent()) {
System.out.println("最小值为: " + minValue.get().getField());
}
}
}
11、比较List中的时间段,与固定的时间段有没有重合的部分
// 比较时间段是否有重合部分
List<Bean> overlappingBeans = beanList.stream()
.filter(bean -> isOverlap(bean.getStart(), bean.getEnd(), fixedStart, fixedEnd)
).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 检查两个时间段是否有重合部分的方法
private static boolean isOverlap(LocalDateTime start1, LocalDateTime end1, LocalDateTime start2, LocalDateTime end2) {
return !(start1.isAfter(end2) || end1.isBefore(start2));
}





















 9802
9802











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








