SkipList 原理及构造过程
SkipList 是受多层链表的启发而设计出来的。实际上,最理想的情况是上面每一层链表的节点个数,是下面一层的节点个数的一半,这样查找过程就非常类似于一个二分查找,使得查找的时间复杂度可以降低到 O(log n)。但是,这种方法在插入数据的时候有很大的问题。新插入一个节点之后,就会打乱上下相邻两层链表上节点个数严格的 2:1 的对应关系。如果要维持这种对应关系,就必须把新插入的节点后面的所有节点(也包括新插入的节点)重新进行调整,这会让时间复杂度重新退化成 O(n)。
SkipList 为了避免这一问题,它不要求上下相邻两层链表之间的节点个数有严格的对应关系,而是为每个节点随机出一个层数。比如,一个节点随机出的层数是 3,那么就把它链入到第 1 层到第 3 层这三层链表中。为了表达清楚,下图展示了如何通过一步步的插入操作从而形成一个 SkipList 的过程(图片源自网络):
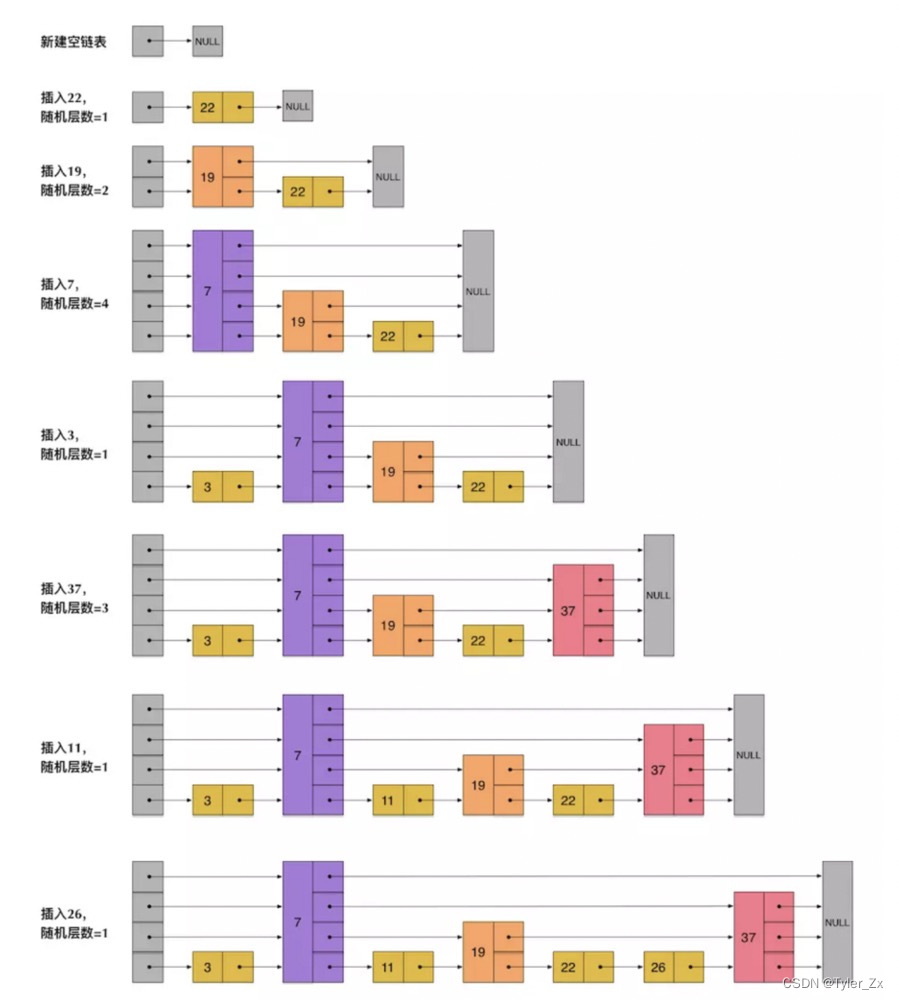
从上面 SkipList 的创建和插入过程可以看出,每一个节点的层数是随机出来的,而且新插入一个节点不会影响其它节点的层数。因此,插入操作只需要修改插入节点前的指针,而不需要对很多节点都进行调整。这就降低了插入操作的复杂度。
SkipList 优缺点
缺点:从上述 SkipList 构造的过程中可以发现,它并不处于一种严格的平衡状态,相比平衡二叉树而言,虽然两者的查询时间复杂度理论上都是 O(log n),但是平衡二叉树的查询效率应该更好。
优点:平衡树的插入和删除操作可能引发子树的调整,逻辑复杂,而 SkipList 的插入和删除只需要修改相邻节点的指针,操作简单又快速。如果插入一个节点引起了树的不平衡,AVL 都是最多只需要 2 次旋转操作,即时间复杂度为 O(1);但是在删除节点引起树的不平衡时,最坏情况下,AVL 需要维护从被删节点到 root 这条路径上所有节点的平衡性,因此需要旋转的量级 O(logn)。
SkipList 在做范围查询时比平衡二叉树更有优势,因为二叉树需要通过中序遍历获得结果,而 SkipList 最底层是一个有序链表。
folly::ConcurrentSkipList 源码详解
多线程环境下的 SkipList,读操作(count, find, skipper)都是 lock free 的,写操作(remove, add, insert)也只是小范围的加了锁。
Accessor 的读操作接口:
iterator find(const key_type& value) {
return iterator(sl_->find(value));
}
const_iterator find(const key_type& value) const {
return iterator(sl_->find(value));
}
size_type count(const key_type& data) const { return contains(data); }
bool contains(const key_type& data) const { return sl_->find(data); }Accessor 的写操作接口:
size_t erase(const key_type& data) { return remove(data); }
std::pair<key_type*, bool> addOrGetData(const key_type& data) {
auto ret = sl_->addOrGetData(data);
return std::make_pair(&ret.first->data(), ret.second);
}
bool add(const key_type& data) { return sl_->addOrGetData(data).second; }
bool remove(const key_type& data) { return sl_->remove(data); }如果存的数据不是基础类型,比如是一个 std::pair<int, int>,则需要实现一个比较函数。如下所示:
struct Less {
const bool operator()(const T& lhs, const T& rhs) {
return lhs.first < rhs.first;
}
};
using List = folly::ConcurrentSkipList<T, Less>;
List list_;简单的使用方法:
constexpr int init_height = 5;
typedef ConcurrentSkipList<int> SkipList;
shared_ptr<SkipList> skiplist(SkipList::createInstance(init_height));
{
// Accessor 提供了访问 skip list 的接口,我们不能直接使用 skip list 对象来访问数据
SkipList::Accessor accessor(skiplist);
accessor.insert(23); // 增加节点
accessor.erase(2); // 删除节点
for (auto &elem : accessor) {
// use elem to access data
}
... ...
}
还有一种访问方式是 skipper,主要是用来跳过一部分数据,例如
{
SkipList::Accessor accessor(sl);
SkipList::Skipper skipper(accessor);
skipper.to(30); // 跳到比30大的第一个节点
if (skipper) {
CHECK_LE(30, *skipper);
}
... ...
// GC may happen when the accessor get sdestructed.
}SkipList 查找
typedef detail::SkipListNode<T> NodeType;
typedef detail::csl_iterator<value_type, NodeType> iterator;
// 利用 boostiterator_facade 生成的iterator
Accessor 提供的访问接口
iterator find(const key_type& value) { return iterator(sl_->find(value)); }
// Returns the node if found, nullptr otherwise.
NodeType* find(const value_type& data) {
auto ret = findNode(data);
if (ret.second && !ret.first->markedForRemoval()) {
return ret.first;
}
return nullptr;
}
// Find node for access. Returns a paired values:
// pair.first = the first node that no-less than data value
// pair.second = 1 when the data value is founded, or 0 otherwise.
// This is like lower_bound, but not exact: we could have the node marked for
// removal so still need to check that.
std::pair<NodeType*, int> findNode(const value_type& data) const {
return findNodeDownRight(data);
}调用 SkipList 的 find 方法,会调用 findNode 方法,如果找到节点并且该节点没有被标记删除的话就返回,否则返回 nullptr。 调用 findNodeDownRight(查找时先向下遍历,然后再向右遍历)方法。其实这里还实现了一个 findNodeRightDown(查找时先向右遍历,然后再向下遍历)方法。来看下 findNodeDownRight 方法是怎么实现的:
static bool greater(const value_type& data, const NodeType* node) {
return node && Comp()(node->data(), data);
}
static bool less(const value_type& data, const NodeType* node) {
return (node == nullptr) || Comp()(data, node->data());
}
// Find node by first stepping down then stepping right. Based on benchmark
// results, this is slightly faster than findNodeRightDown for better
// localality on the skipping pointers.
std::pair<NodeType*, int> findNodeDownRight(const value_type& data) const {
NodeType* pred = head_.load(std::memory_order_consume);
int ht = pred->height();
NodeType* node = nullptr;
bool found = false;
while (!found) {
// stepping down,直到找到一个节点 pred 的数据比 data 大
for (; ht > 0 && less(data, node = pred->skip(ht - 1)); --ht) {
}
if (ht == 0) {
return std::make_pair(node, 0); // not found
}
// node <= data now, but we need to fix up ht
--ht;
// stepping right,继续接近 data
while (greater(data, node)) {
pred = node;
node = node->skip(ht);
}
found = !less(data, node);
}
return std::make_pair(node, found);
}SkipList 增加
Accessor 接口
template <
typename U,
typename =
typename std::enable_if<std::is_convertible<U, T>::value>::type>
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(U&& data) {
auto ret = sl_->addOrGetData(std::forward<U>(data));
return std::make_pair(iterator(ret.first), ret.second);
}
std::pair<key_type*, bool> addOrGetData(const key_type& data) {
auto ret = sl_->addOrGetData(data);
return std::make_pair(&ret.first->data(), ret.second);
}上面调用 SkipList 的 addOrGetData 方法如下所示:
// Returns a paired value:
// pair.first always stores the pointer to the node with the same input key.
// It could be either the newly added data, or the existed data in the
// list with the same key.
// pair.second stores whether the data is added successfully:
// 0 means not added, otherwise reutrns the new size.
template <typename U>
std::pair<NodeType*, size_t> addOrGetData(U&& data) {
NodeType *preds[MAX_HEIGHT], *succs[MAX_HEIGHT];
NodeType* newNode;
size_t newSize;
while (true) {
int max_layer = 0;
// 找到 data 对应的节点,以及它的前继和后继,max_layer 返回当前 skip list 的最大层级
// 返回值 layer 是 data 对应的节点备找到时的 layer
int layer = findInsertionPointGetMaxLayer(data, preds, succs, &max_layer);
if (layer >= 0) {// 如果找到
NodeType* nodeFound = succs[layer];
DCHECK(nodeFound != nullptr);
if (nodeFound->markedForRemoval()) {
continue; // if it's getting deleted retry finding node.
}
// wait until fully linked. 可能节点被其他线程加入了,暂时还没有 fully linked
// 等待完成后再返回给用户完整的节点
while (UNLIKELY(!nodeFound->fullyLinked())) {
}
return std::make_pair(nodeFound, 0);
}
// need to capped at the original height -- the real height may have grown
// 按概率生成新的节点高度,新节点的高度上限设为 max_layer+1
// 值得注意的是选取概率是 1/e
int nodeHeight =
detail::SkipListRandomHeight::instance()->getHeight(max_layer + 1);
ScopedLocker guards[MAX_HEIGHT];
// 把前继全部加上锁
if (!lockNodesForChange(nodeHeight, guards, preds, succs)) {
continue; // give up the locks and retry until all valid
}
// locks acquired and all valid, need to modify the links under the locks.
// 按照生成的高度建立新的节点
newNode = NodeType::create(
recycler_.alloc(), nodeHeight, std::forward<U>(data));
// 把新的节点联入 skip list 中
for (int k = 0; k < nodeHeight; ++k) {
newNode->setSkip(k, succs[k]);
preds[k]->setSkip(k, newNode);
}
// 标记 fully linked
newNode->setFullyLinked();
newSize = incrementSize(1);
break;
}
int hgt = height();
size_t sizeLimit =
detail::SkipListRandomHeight::instance()->getSizeLimit(hgt);
// 检查是否需要增加 skip list 节点的高度
if (hgt < MAX_HEIGHT && newSize > sizeLimit) {
growHeight(hgt + 1);
}
CHECK_GT(newSize, 0);
return std::make_pair(newNode, newSize);
}这个函数中调用的几个方法:
findInsertionPointGetMaxLayer:首先它返回 skiplist 的高度,然后按照 right down 的方式查找节点,不同的是在查找过程中会保留前继指针 preds[] 和后继指针 succs[]。
// find node for insertion/deleting
int findInsertionPointGetMaxLayer(
const value_type& data,
NodeType* preds[],
NodeType* succs[],
int* max_layer) const {
*max_layer = maxLayer();
return findInsertionPoint(
head_.load(std::memory_order_consume), *max_layer, data, preds, succs);
}
static int findInsertionPoint(
NodeType* cur,
int cur_layer,
const value_type& data,
NodeType* preds[],
NodeType* succs[]) {
int foundLayer = -1;
NodeType* pred = cur;
NodeType* foundNode = nullptr;
for (int layer = cur_layer; layer >= 0; --layer) {
NodeType* node = pred->skip(layer);
while (greater(data, node)) {
pred = node;
node = node->skip(layer);
}
if (foundLayer == -1 && !less(data, node)) { // the two keys equal
foundLayer = layer;
foundNode = node;
}
preds[layer] = pred;
// if found, succs[0..foundLayer] need to point to the cached foundNode,
// as foundNode might be deleted at the same time thus pred->skip() can
// return nullptr or another node.
succs[layer] = foundNode ? foundNode : node;
}
return foundLayer;
}SkipListRandomHeight::getHeight 和 SkipListRandomHeight::getSizeLimit
在 SkipListRandomHeight 构造的时候会初始化两张表:lookupTable_ 是高度的概率表,sizeLimitTable_ 是 SkipList 的高度对应的最大的 list size。
getHeight 方法用随机函数生成一个 0~1 之间的 double 值 p,然后在 lookupTable 中找比 p 大的值对应的表索引 i,找到后获得的高度就是 i+1。getSizeLimit 方法也类似,以参数 height 为 sizeLimitTable 的索引,返回对应高度的 sizeLimit。
lockNodesForChange 的实现:
// lock all the necessary nodes for changing (adding or removing) the list.
// returns true if all the lock acquried successfully and the related nodes
// are all validate (not in certain pending states), false otherwise.
bool lockNodesForChange(
int nodeHeight,
ScopedLocker guards[MAX_HEIGHT],
NodeType* preds[MAX_HEIGHT], // 插入或删除节点的前继
NodeType* succs[MAX_HEIGHT], // 插入或删除节点的后继
bool adding = true) {
// adding 为 true 表明该函数是在 add 里被调用,否则是在 remove 里被调用
NodeType *pred, *succ, *prevPred = nullptr;
bool valid = true;
for (int layer = 0; valid && layer < nodeHeight; ++layer) {
pred = preds[layer];
DCHECK(pred != nullptr) << "layer=" << layer << " height=" << height()
<< " nodeheight=" << nodeHeight;
succ = succs[layer];
if (pred != prevPred) {
// 可能连续多层的前继指针都是一个节点,这里可以避免多次上锁
guards[layer] = pred->acquireGuard();
prevPred = pred;
}
// 对于 remove 来说只要判断前继没有被删除并且前继的后继是后继节点即可
valid = !pred->markedForRemoval() &&
pred->skip(layer) == succ; // check again after locking
// 对于 adding 来说还需要判断后继节点没有被删除
if (adding) { // when adding a node, the succ shouldn't be going away
valid = valid && (succ == nullptr || !succ->markedForRemoval());
}
}
return valid;
}growHeight 的实现:
void growHeight(int height) {
NodeType* oldHead = head_.load(std::memory_order_consume);
if (oldHead->height() >= height) { // someone else already did this
return;
}
// 生成新的 head 节点,height 参数就是在原来的 heigth 基础上加1
NodeType* newHead =
NodeType::create(recycler_.alloc(), height, value_type(), true);
{ // need to guard the head node in case others are adding/removing
// nodes linked to the head.
ScopedLocker g = oldHead->acquireGuard();
// 从 oldHead 中把数据拷贝过来,类似拷贝构造函数
newHead->copyHead(oldHead);
NodeType* expected = oldHead;
// 原子替换 head_ 指针指向 newHead
if (!head_.compare_exchange_strong(
expected, newHead, std::memory_order_release)) {
// if someone has already done the swap, just return.
NodeType::destroy(recycler_.alloc(), newHead);
return;
}
oldHead->setMarkedForRemoval();
}
recycle(oldHead);
}SkipList 删除
Accessor 的接口
bool remove(const key_type& data) { return sl_->remove(data); }
size_t erase(const key_type& data) { return remove(data); }
具体调用
bool remove(const value_type& data) {
NodeType* nodeToDelete = nullptr;
ScopedLocker nodeGuard;
bool isMarked = false;
int nodeHeight = 0;
NodeType *preds[MAX_HEIGHT], *succs[MAX_HEIGHT];
while (true) {
int max_layer = 0;
int layer = findInsertionPointGetMaxLayer(data, preds, succs, &max_layer);
if (!isMarked && (layer < 0 || !okToDelete(succs[layer], layer))) {
return false;
}
if (!isMarked) {
nodeToDelete = succs[layer];
nodeHeight = nodeToDelete->height();
nodeGuard = nodeToDelete->acquireGuard();
if (nodeToDelete->markedForRemoval()) {
return false;
}
nodeToDelete->setMarkedForRemoval();
isMarked = true;
}
// acquire pred locks from bottom layer up
ScopedLocker guards[MAX_HEIGHT];
if (!lockNodesForChange(nodeHeight, guards, preds, succs, false)) {
continue; // this will unlock all the locks
}
for (int k = nodeHeight - 1; k >= 0; --k) {
preds[k]->setSkip(k, nodeToDelete->skip(k));
}
incrementSize(-1);
break;
}
recycle(nodeToDelete);
return true;
}注意:recycler 负责回收被删除的节点,但其实它只是把节点加入一个 vector 中,然后在 recycler 对象析构或者显示调用 release 方法时才会去释放这些节点。
void recycle(NodeType* node) { recycler_.add(node); }
detail::NodeRecycler<NodeType, NodeAlloc> recycler_;
template <typename NodeType, typename NodeAlloc>
class NodeRecycler<
NodeType,
NodeAlloc,
typename std::enable_if<
!NodeType::template DestroyIsNoOp<NodeAlloc>::value>::type> {
public:
explicit NodeRecycler(const NodeAlloc& alloc)
: refs_(0), dirty_(false), alloc_(alloc) {
lock_.init();
}
explicit NodeRecycler() : refs_(0), dirty_(false) { lock_.init(); }
~NodeRecycler() {
CHECK_EQ(refs(), 0);
if (nodes_) {
for (auto& node : *nodes_) {
NodeType::destroy(alloc_, node);
}
}
}
void add(NodeType* node) {
std::lock_guard<MicroSpinLock> g(lock_);
if (nodes_.get() == nullptr) {
nodes_ = std::make_unique<std::vector<NodeType*>>(1, node);
} else {
nodes_->push_back(node);
}
DCHECK_GT(refs(), 0);
dirty_.store(true, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
int addRef() { return refs_.fetch_add(1, std::memory_order_relaxed); }
int releaseRef() {
// We don't expect to clean the recycler immediately everytime it is OK
// to do so. Here, it is possible that multiple accessors all release at
// the same time but nobody would clean the recycler here. If this
// happens, the recycler will usually still get cleaned when
// such a race doesn't happen. The worst case is the recycler will
// eventually get deleted along with the skiplist.
if (LIKELY(!dirty_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) || refs() > 1)) {
return refs_.fetch_add(-1, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
std::unique_ptr<std::vector<NodeType*>> newNodes;
{
std::lock_guard<MicroSpinLock> g(lock_);
if (nodes_.get() == nullptr || refs() > 1) {
return refs_.fetch_add(-1, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
// once refs_ reaches 1 and there is no other accessor, it is safe to
// remove all the current nodes in the recycler, as we already acquired
// the lock here so no more new nodes can be added, even though new
// accessors may be added after that.
newNodes.swap(nodes_);
dirty_.store(false, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
// TODO(xliu) should we spawn a thread to do this when there are large
// number of nodes in the recycler?
for (auto& node : *newNodes) {
NodeType::destroy(alloc_, node);
}
// decrease the ref count at the very end, to minimize the
// chance of other threads acquiring lock_ to clear the deleted
// nodes again.
return refs_.fetch_add(-1, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
NodeAlloc& alloc() { return alloc_; }
private:
int refs() const { return refs_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); }
std::unique_ptr<std::vector<NodeType*>> nodes_;
std::atomic<int32_t> refs_; // current number of visitors to the list
std::atomic<bool> dirty_; // whether *nodes_ is non-empty
MicroSpinLock lock_; // protects access to *nodes_
NodeAlloc alloc_;
};

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










