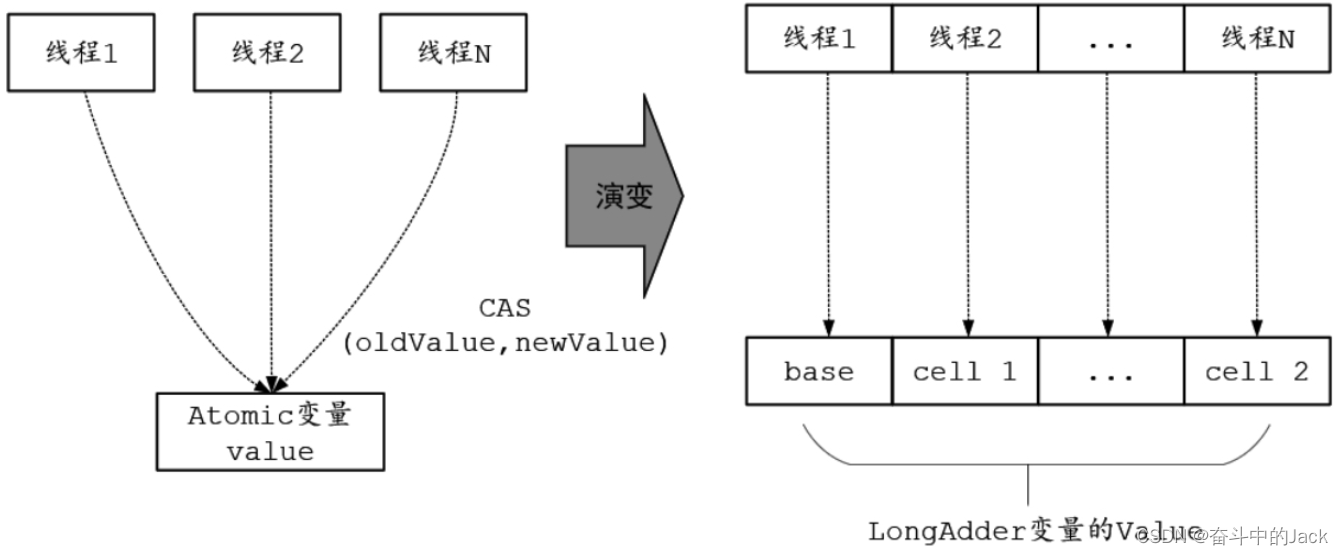
LongAdder 的核心思想是热点分离,与 ConcurrentHashMap 的设计思想类似:将value值分离成一个数组,当多线程访问时,通过Hash算法将线程映射到数组的一个元素进行操作;而获取最终的value结果时,则将数组的元素求和。最终,通过 LongAdder 将内部操作对象从单个value值“演变”成一系列的数组元素,从而减小了内部竞争的粒度。
package cn.jaa.cas;
import cn.jaa.util.Print;
import cn.jaa.util.ThreadUtil;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
/**
* @Author: Jaa
* @Description: LongAdder 和 AtomicLong 的对比测试
* @Date 2024/4/13
*/
public class LongAdderVSAtomicLongTest {
// 每条线程的执行轮数
final int TURNS = 1000000000;
/**
* 使用 AtomicLong 完成 10个线程 每个线程累加1000次
*/
@Test
public void testAtomicLong() {
// 并发任务数
final int TASK_AMOUNT = 10;
// 线程池,获取CPU密集型任务线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = ThreadUtil.getCpuIntenseTargetThreadPool();
// 定义一个原子对象
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
// 线程同步倒数闩
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(TASK_AMOUNT);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < TASK_AMOUNT; i++) {
// 提交任务
pool.submit(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 0; j < TURNS; j++) {
// 执行累加操作
atomicLong.incrementAndGet();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 线程执行完毕,倒数闩减一
latch.countDown();
});
}
try {
// 等待所有线程执行完毕,倒数闩完成所有的倒数操作
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
float time = (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000F;
// 输出统计结果
Print.tcfo("运行的时长为:" + time);
Print.tcfo("累加结果为:" + atomicLong.get());
// [main|LongAdderVSAtomicLongTest.testAtomicLong]:运行的时长为:17.283
// [main|LongAdderVSAtomicLongTest.testAtomicLong]:累加结果为:1000000000
}
/**
* 使用 LongAdder 完成 10个线程累加1000万次
*/
@Test
public void testLongAdder() {
// 并发任务数
final int TASK_AMOUNT = 10;
// 线程池,获取CPU密集型任务线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = ThreadUtil.getCpuIntenseTargetThreadPool();
// 定义一个 LongAdder 对象
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
// 线程同步倒数闩
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(TASK_AMOUNT);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < TASK_AMOUNT; i++) {
// 提交任务
pool.submit(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 0; j < TURNS; j++) {
// 执行累加操作
longAdder.add(1);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 线程执行完毕,倒数闩减一
latch.countDown();
});
}
// 等待所有线程执行完毕,倒数闩完成所有的倒数操作
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
float time = (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000F;
// 输出统计结果
Print.tcfo("运行的时长为:" + time);
Print.tcfo("累加结果为:" + longAdder.longValue());
// [main|LongAdderVSAtomicLongTest.testLongAdder]:运行的时长为:1.191
// [main|LongAdderVSAtomicLongTest.testLongAdder]:累加结果为:1000000000
}
}
为了进行速度的对比,可以多次运行以上用例多次,每一次运行可以修改 TASK_AMOUNT(次数常量)的值。测试5次,TASK_AMOUNT的值从1000到1?000?000?000,对比出来的速度倍数值如下图(参考,测试时间与计算机配置有关系)
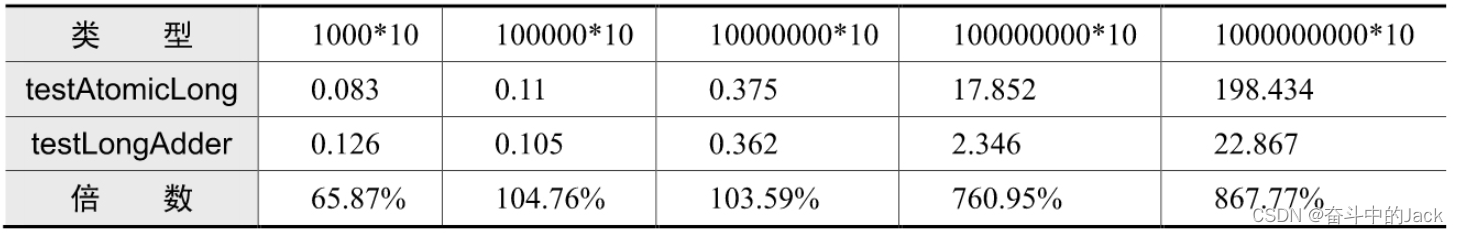
通过对比实验可以看到:当有10个线程总计累加10?000次的时候,AtomicLong的性能更好。随着累加次数的增加,CAS操作的次数急剧增多,AtomicLong的性能急剧下降。从对比实验的结果可以看出,在CAS争用最为激烈的场景下,LongAdder的性能是AtomicLong的8倍。





















 397
397











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








