Laplacian matrix
Laplacian matrix是图论数学领域的一个概念,又名graph Laplacian, admittance matrix, Kirchhoff matrix或discrete Laplacian,是一个图的矩阵表示。
Definition
Laplacian matrix for simple graphs
给定一个有
n
n
n个节点的简单图
G
G
G,它的Laplacian矩阵
L
n
×
n
\bf{L}_{n\times n}
Ln×n可以定义为
L
=
D
−
A
,
{\bf L} = {\bf D} - {\bf A},
L=D−A,
其中,
D
\bf{D}
D是一个degree矩阵,
A
\bf{A}
A是一个adjacency矩阵。对于simple图,
A
\bf{A}
A是一个对角线上元素为0的二值矩阵。
对于directed图,indegree或outdegree都可能用到,完全取决于应用。
L
\bf{L}
L元素为
L
i
,
j
:
=
{
deg
(
v
i
)
if
i
=
j
−
1
if
i
≠
j
and
v
i
∼
v
j
0
otherwise
,
{\bf L}_{i,j} := \left \{ \begin{aligned}\deg(v_i) ~~~ & \text{if} ~ i = j\\-1 ~~~ & \text{if} ~ i \neq j ~\text{and}~ v_i \sim v_j \\0 ~~~ & \text{otherwise}\end{aligned}\right.,
Li,j:=⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧deg(vi) −1 0 if i=jif i=j and vi∼vjotherwise,
其中,
∼
\sim
∼表示
v
i
v_i
vi与
v
j
v_j
vj邻接。
Symmetric normalized Laplacian
对称归一化Laplacian矩阵被定义为
L
sys
:
=
D
−
1
2
L
D
−
1
2
=
I
−
D
−
1
2
A
D
−
1
2
.
{\bf L}^{\text{sys}} := {\bf D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} {\bf L} {\bf D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} = {\bf I} - {\bf D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} {\bf A} {\bf D}^{-\frac{1}{2}}.
Lsys:=D−21LD−21=I−D−21AD−21.
L
sys
{\bf L}^{\text{sys}}
Lsys元素为
L
i
,
j
sys
:
=
{
1
if
i
=
j
and
deg
(
v
i
)
≠
0
−
1
deg
(
v
i
)
deg
(
v
j
)
if
i
≠
j
and
v
i
∼
v
j
0
otherwise
.
{\bf L}_{i,j}^{\text{sys}} := \left \{ \begin{aligned}1 ~~~ & \text{if} ~ i = j ~ \text{and} \deg(v_i) \neq 0\\-\frac{1}{\sqrt{\deg(v_i) \deg(v_j)}} ~~~ & \text{if} ~ i \neq j ~\text{and}~ v_i \sim v_j \\0 ~~~ & \text{otherwise}\end{aligned}\right..
Li,jsys:=⎩⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎧1 −deg(vi)deg(vj)1 0 if i=j anddeg(vi)=0if i=j and vi∼vjotherwise.
Random walk normalized Laplacian
随机游走归一化Laplacian矩阵定义为
L
rw
:
=
D
−
1
L
=
I
−
D
−
1
A
.
{\bf L}^{\text{rw}} := {\bf D}^{-1} {\bf L} = {\bf I} - {\bf D}^{-1} {\bf A}.
Lrw:=D−1L=I−D−1A.
r
w
sys
{\bf rw}^{\text{sys}}
rwsys元素为
L
i
,
j
rw
:
=
{
1
if
i
=
j
and
deg
(
v
i
)
≠
0
−
1
deg
(
v
i
)
if
i
≠
j
and
v
i
∼
v
j
0
otherwise
.
{\bf L}_{i,j}^{\text{rw}} := \left \{ \begin{aligned}1 ~~~ & \text{if} ~ i = j ~ \text{and} \deg(v_i) \neq 0\\-\frac{1}{\sqrt{\deg(v_i)}} ~~~ & \text{if} ~ i \neq j ~\text{and}~ v_i \sim v_j \\0 ~~~ & \text{otherwise}\end{aligned}\right..
Li,jrw:=⎩⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎧1 −deg(vi)1 0 if i=j anddeg(vi)=0if i=j and vi∼vjotherwise.
Generalized Laplacian
广义Laplacian被定义为
Q
i
,
j
rw
:
=
{
<
0
if
i
=
j
and
deg
(
v
i
)
≠
0
=
0
if
i
≠
j
and
v
i
∼
v
j
any number
otherwise
.
{\bf Q}_{i,j}^{\text{rw}} := \left \{ \begin{aligned}< 0 ~~~ & \text{if} ~ i = j ~ \text{and} \deg(v_i) \neq 0\\= 0 ~~~ & \text{if} ~ i \neq j ~\text{and}~ v_i \sim v_j \\\text{any number} ~~~ & \text{otherwise}\end{aligned}\right..
Qi,jrw:=⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧<0 =0 any number if i=j anddeg(vi)=0if i=j and vi∼vjotherwise.
Notice the ordinary Laplacian is a generalized Laplacian.
Example
Labelled graph
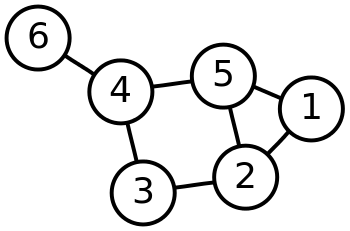
Degree matrix
( 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 ) \left (\begin{matrix}2 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 3 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 2 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 3 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 3 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\\\end{matrix}\right ) ⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛200000030000002000000300000030000001⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞
Adjacency matrix
( 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 3 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 ) \left (\begin{matrix}0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\\1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0\\0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 1\\1 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 3 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\\end{matrix}\right ) ⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛010010101010010100001011110130000100⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞
Laplacian matrix
( 2 − 1 0 0 − 1 0 − 1 3 − 1 0 − 1 0 0 − 1 2 − 1 0 0 0 0 − 1 3 − 1 − 1 − 1 − 1 0 − 1 3 0 0 0 0 − 1 0 1 ) \left (\begin{matrix}2 & -1 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\-1 & 3 & -1 & 0 & -1 & 0\\0 & -1 & 2 & -1 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & -1 & 3 & -1 & -1\\-1 & -1 & 0 & -1 & 3 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 1\\\end{matrix}\right ) ⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛2−100−10−13−10−100−12−10000−13−1−1−1−10−130000−101⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞
Properties
对于无向图 G G G,其Laplacian矩阵为 L {\bf L} L, L {\bf L} L特征值为 λ 0 ≤ λ 1 ≤ ⋯ λ n − 1 \lambda_0 \leq \lambda_1 \leq \cdots \lambda_{n - 1} λ0≤λ1≤⋯λn−1,则有:
-
L {\bf L} L是对称的;
-
L {\bf L} L是正定的( λ i ≥ 0 , ∀ i \lambda_i \geq 0, \forall i λi≥0,∀i);
-
∑ i = 0 n − 1 L i , j = ∑ j = 0 n − 1 L i , j = 1 \sum_{i = 0}^{n - 1} {\bf L}_{i,j} = \sum_{j = 0}^{n - 1} {\bf L}_{i,j} = 1 ∑i=0n−1Li,j=∑j=0n−1Li,j=1;
-
λ 0 = 0 , v 0 = ( 1 , 1 , ⋯ , 1 ) \lambda_0 = 0,~ \pmb{v}_0 = (1, 1, \cdots, 1) λ0=0, vvv0=(1,1,⋯,1);
-
Laplacian是 n n n维向量空间上的函数算子 f : V → R f:{ V}\rightarrow\mathbb{R} f:V→R;
L f ( v i ) = ∑ v j ∼ v i w i , j ( f ( v i ) − f ( v j ) {\bf L} f(v_i) = \sum_{v_j \sim v_i} w_{i,j} (f(v_i) - f(v_j) Lf(vi)=vj∼vi∑wi,j(f(vi)−f(vj)
-
二次型:
f T L f ( v i ) = 1 2 ∑ e i , j w i , j ( f ( v i ) − f ( v j ) {f^T {\bf L} f}(v_i) = \frac{1}{2}\sum_{e_{i,j}} w_{i,j} (f(v_i) - f(v_j) fTLf(vi)=21ei,j∑wi,j(f(vi)−f(vj)
-
……
Incidence matrix
Incidence matrix刻画了两类对象之间的关系,在graph theory中有广泛的应用。
Undirected and directed graphs
对于图 G = ( V , E ) G=(V,E) G=(V,E), n n n个顶点, m m m条边($|V| \times |E| = m \times n $),有两种incidence矩阵:
-
Unoriented incidence matrix
- 对于无向图
B i , j : = { 1 v i − e j 0 otherwise . {\bf B}_{i,j} := \left \{ \begin{aligned} 1 ~~~ &v_i - e_j\\ 0 ~~~ &\text{otherwise} \end{aligned} \right. . Bi,j:={1 0 vi−ejotherwise.
- 对于有向图
B i , j : = { 1 v i → e j 1 v i ← e j 0 otherwise . {\bf B}_{i,j} := \left \{ \begin{aligned} 1 ~~~ &v_i \rightarrow e_j\\ 1 ~~~ &v_i \leftarrow e_j\\ 0 ~~~ &\text{otherwise} \end{aligned} \right. . Bi,j:=⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧1 1 0 vi→ejvi←ejotherwise.
-
Oriented incidence matrix
-
对于无向图:无向图的有向关联矩阵是图的任何方向的关联矩阵。
-
对于有向图
B i , j : = { 1 v i → e j − 1 v i ← e j 0 otherwise . {\bf B}_{i,j} := \left \{ \begin{aligned} 1 ~~~ &v_i \rightarrow e_j\\ -1 ~~~ &v_i \leftarrow e_j\\ 0 ~~~ &\text{otherwise} \end{aligned} \right. . Bi,j:=⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧1 −1 0 vi→ejvi←ejotherwise.
-
Boundary operator
图的boundary operator定义为:
ϑ
:
E
(
G
)
→
V
(
G
)
\vartheta:E(G) \rightarrow V(G)
ϑ:E(G)→V(G)
而图的co-boundary operator定义为:
π
:
V
(
G
)
→
E
(
G
)
\pi:V(G) \rightarrow E(G)
π:V(G)→E(G)
Discrete differential operator
-
f → B f f \rightarrow {\bf B} f f→Bf是一个co-boundary mapping;
-
特别地, ( B f ) ( e i , j ) f ( v j ) − f ( v i ) ({\bf B} f) (e_{i,j})f(v_j) - f(v_i) (Bf)(ei,j)f(vj)−f(vi)
-
Example:
( f ( 2 ) − f ( 1 ) f ( 1 ) − f ( 3 ) f ( 3 ) − f ( 2 ) f ( 4 ) − f ( 2 ) ) = ( − 1 1 0 0 1 0 − 1 0 0 − 1 1 0 0 − 1 0 1 ) ( f ( 1 ) f ( 2 ) f ( 3 ) f ( 4 ) ) \left (\begin{matrix}f(2) - f(1) \\f(1) - f(3) \\f(3) - f(2) \\f(4) - f(2)\end{matrix}\right )= \left (\begin{matrix}-1 & 1 & 0 & 0\\1 & 0 & -1 & 0\\0 & -1 & 1 & 0\\0 & -1 & 0 & 1\\\end{matrix} \right )\left (\begin{matrix}f(1) \\f(2) \\f(3) \\f(4)\end{matrix}\right ) ⎝⎜⎜⎛f(2)−f(1)f(1)−f(3)f(3)−f(2)f(4)−f(2)⎠⎟⎟⎞=⎝⎜⎜⎛−110010−1−10−1100001⎠⎟⎟⎞⎝⎜⎜⎛f(1)f(2)f(3)f(4)⎠⎟⎟⎞
Laplacian & incidence
L = B B T {\bf L} = {\bf B} {\bf B}^T L=BBT








 本文深入探讨了图论中拉普拉斯矩阵的概念,包括其定义、类型如对称归一化和随机游走归一化,以及在无向图中的性质。通过实例展示了矩阵的构造过程,解释了拉普拉斯矩阵与关联矩阵的关系。
本文深入探讨了图论中拉普拉斯矩阵的概念,包括其定义、类型如对称归一化和随机游走归一化,以及在无向图中的性质。通过实例展示了矩阵的构造过程,解释了拉普拉斯矩阵与关联矩阵的关系。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








