JAVA多线程并发——创建线程
第一章:线程的创建与实现
一、继承Thread类
代码示例:
public class ExtendThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new MyThread(1);
Thread thread2 = new MyThread(2);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
public static class MyThread extends Thread {
int num;
public MyThread(int num){
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程"+ num);
}
}
}
运行结果:
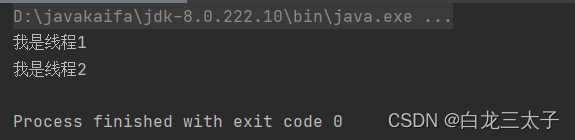
二、实现runnable接口
代码示例:
/**
* 通过实现Runnable接口创建线程
* 线程无返回值
*/
public class implementRunnable {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable1 = new MyRunnable(1);
Runnable runnable2 = new MyRunnable(2);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable2);
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread2.start();
}
public static class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
int num;
public MyRunnable(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程" + num);
}
}
}
运行结果:
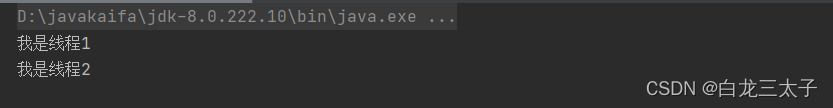
三、简单匿名内部类写法
代码示例:
public class innerRunnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("我是原线程");
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是新线程");
}
});
thread.start();
}
}
运行结果:
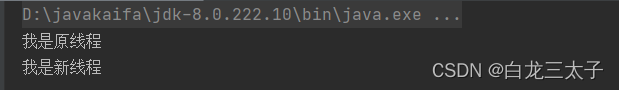
四、实现Callable接口
该方式创建线程可以获取新线程的返回值,上面的方法均无返回值
示例代码:
/**
* 通过实现Callable接口实现
* 线程有返回值
*/
public class implementCallable {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyCallable myCallable1 = new MyCallable(1);
FutureTask<String> futureTask1 = new FutureTask<>(myCallable1);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(futureTask1);
thread1.start();
String str1 = futureTask1.get();
System.out.println("线程返回值:" + str1);
MyCallable myCallable2 = new MyCallable(2);
FutureTask<String> futureTask2 = new FutureTask<>(myCallable2);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(futureTask2);
thread2.start();
String str2 = futureTask2.get();
System.out.println("线程返回值: " + str2);
}
public static class MyCallable implements Callable<String>{
int num;
public MyCallable(int num){
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("新线程" + num + "开始执行");
return "创建了线程" + num;
}
}
}
运行结果:

五、线程池
推荐使用最后一种,new ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) ;
/**
* 通过Executor的几个默认的线程池配置
*/
public class ByExecutor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//createCachedThreadPool();
//createFixThreadPool();
//createScheduledThreadPool();
//createSingleThreadPool();
createByThreadPoolExecutor();
}
/**
* newCachedThreadPool
* 核心线程数无限大
* 会重复利用之前的线程
* 没有旧线程会创建新线程
*/
private static void createCachedThreadPool() {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
while (true) {
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* newFixedThreadPool
* 固定线程数
* 当前没有可用线程则会等待
* 不会创建新线程
*/
private static void createFixThreadPool() {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
while (true) {
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是线程 " + Thread.currentThread());
}
});
}
}
/**
* newScheduledThreadPool
* 支持延时执行
* 固定线程数
*/
private static void createScheduledThreadPool() {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
long delay = 5;
System.out.println(new Date().getSeconds());
while (true) {
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是定时线程:" + Thread.currentThread() + new Date().getSeconds());
}
}, delay, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
/**
* newSingleThreadPool
* 单线程
*/
private static void createSingleThreadPool() {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
while (true) {
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是single线程 " + Thread.currentThread());
}
});
}
}
/**
* 推荐的使用线程池的方式,通过构造方法创建
*/
private static void createByThreadPoolExecutor() {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
2,
3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(2),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//创建任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
// 将任务交给线程池管理
threadPoolExecutor.execute(runnable);
}
}
}























 9580
9580











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








