【课程1.3】 Numpy通用函数
基本操作
1.数组形状:.T/.reshape()/.resize()
ar1 = np.arange(10)
ar2 = np.ones((5,2))
print(ar1,'\n',ar1.T)
print(ar2,'\n',ar2.T)
print('------')
# .T方法:转置,例如原shape为(3,4)/(2,3,4),转置结果为(4,3)/(4,3,2) → 所以一维数组转置后结果不变
ar3 = ar1.reshape(2,5) # 用法1:直接将已有数组改变形状
ar4 = np.zeros((4,6)).reshape(3,8) # 用法2:生成数组后直接改变形状
ar5 = np.reshape(np.arange(12),(3,4)) # 用法3:参数内添加数组,目标形状
print(ar1,'\n',ar3)
print(ar4)
print(ar5)
print('------')
# numpy.reshape(a, newshape, order='C'):为数组提供新形状,而不更改其数据,所以元素数量需要一致!!
ar6 = np.resize(np.arange(5),(3,4))
print(ar6)
# numpy.resize(a, new_shape):返回具有指定形状的新数组,如有必要可重复填充所需数量的元素。
# 注意了:.T/.reshape()/.resize()都是生成新的数组!!!
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[[ 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1.]]
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
------
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[[0 1 2 3 4]
[5 6 7 8 9]]
[[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
------
[[0 1 2 3]
[4 0 1 2]
[3 4 0 1]]
2.数组的复制
ar1 = np.arange(10)
ar2 = ar1
print(ar2 is ar1)
ar1[2] = 9
print(ar1,ar2)
# 回忆python的赋值逻辑:指向内存中生成的一个值 → 这里ar1和ar2指向同一个值,所以ar1改变,ar2一起改变
ar3 = ar1.copy()
print(ar3 is ar1)
ar1[0] = 9
print(ar1,ar3)
# copy方法生成数组及其数据的完整拷贝
# 再次提醒:.T/.reshape()/.resize()都是生成新的数组!!!
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
True
[0 1 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [0 1 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
False
[9 1 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] [0 1 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
3.数组类型转换:.astype()
ar1 = np.arange(10,dtype=float)
print(ar1,ar1.dtype)
print('-----')
# 可以在参数位置设置数组类型
ar2 = ar1.astype(np.int32)
print(ar2,ar2.dtype)
print(ar1,ar1.dtype)
# a.astype():转换数组类型
# 注意:养成好习惯,数组类型用np.int32,而不是直接int32
-----------------------------------------------------------------------[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.] float64
-----
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] int32
[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.] float64
4.数组堆叠
a = np.arange(5) # a为一维数组,5个元素
b = np.arange(5,9) # b为一维数组,4个元素
ar1 = np.hstack((a,b)) # 注意:((a,b)),这里形状可以不一样
print(a,a.shape)
print(b,b.shape)
print(ar1,ar1.shape)
a = np.array([[1],[2],[3]]) # a为二维数组,3行1列
b = np.array([['a'],['b'],['c']]) # b为二维数组,3行1列
ar2 = np.hstack((a,b)) # 注意:((a,b)),这里形状必须一样
print(a,a.shape)
print(b,b.shape)
print(ar2,ar2.shape)
print('-----')
# numpy.hstack(tup):水平(按列顺序)堆叠数组
a = np.arange(5)
b = np.arange(5,10)
ar1 = np.vstack((a,b))
print(a,a.shape)
print(b,b.shape)
print(ar1,ar1.shape)
a = np.array([[1],[2],[3]])
b = np.array([['a'],['b'],['c'],['d']])
ar2 = np.vstack((a,b)) # 这里形状可以不一样
print(a,a.shape)
print(b,b.shape)
print(ar2,ar2.shape)
print('-----')
# numpy.vstack(tup):垂直(按列顺序)堆叠数组
a = np.arange(5)
b = np.arange(5,10)
ar1 = np.stack((a,b))
ar2 = np.stack((a,b),axis = 1)
print(a,a.shape)
print(b,b.shape)
print(ar1,ar1.shape)
print(ar2,ar2.shape)
# numpy.stack(arrays, axis=0):沿着新轴连接数组的序列,形状必须一样!
# 重点解释axis参数的意思,假设两个数组[1 2 3]和[4 5 6],shape均为(3,0)
# axis=0:[[1 2 3] [4 5 6]],shape为(2,3)
# axis=1:[[1 4] [2 5] [3 6]],shape为(3,2)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------[0 1 2 3 4] (5,)
[5 6 7 8] (4,)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8] (9,)
[[1]
[2]
[3]] (3, 1)
[['a']
['b']
['c']] (3, 1)
[['1' 'a']
['2' 'b']
['3' 'c']] (3, 2)
-----
[0 1 2 3 4] (5,)
[5 6 7 8 9] (5,)
[[0 1 2 3 4]
[5 6 7 8 9]] (2, 5)
[[1]
[2]
[3]] (3, 1)
[['a']
['b']
['c']
['d']] (4, 1)
[['1']
['2']
['3']
['a']
['b']
['c']
['d']] (7, 1)
-----
[0 1 2 3 4] (5,)
[5 6 7 8 9] (5,)
[[0 1 2 3 4]
[5 6 7 8 9]] (2, 5)
[[0 5]
[1 6]
[2 7]
[3 8]
[4 9]] (5, 2)
5.数组拆分
ar = np.arange(16).reshape(4,4)
ar1 = np.hsplit(ar,2)
print(ar)
print(ar1,type(ar1))
# numpy.hsplit(ary, indices_or_sections):将数组水平(逐列)拆分为多个子数组 → 按列拆分
# 输出结果为列表,列表中元素为数组
ar2 = np.vsplit(ar,4)
print(ar2,type(ar2))
# numpy.vsplit(ary, indices_or_sections)::将数组垂直(行方向)拆分为多个子数组 → 按行拆
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15]]
[array([[ 0, 1],
[ 4, 5],
[ 8, 9],
[12, 13]]), array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11],
[14, 15]])] <class 'list'>
[array([[0, 1, 2, 3]]), array([[4, 5, 6, 7]]), array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11]]), array([[12, 13, 14, 15]])] <class 'list'>
6.数组简单运算
ar = np.arange(6).reshape(2,3)
print(ar + 10) # 加法
print(ar * 2) # 乘法
print(1 / (ar+1)) # 除法
print(ar ** 0.5) # 幂
# 与标量的运算
print(ar.mean()) # 求平均值
print(ar.max()) # 求最大值
print(ar.min()) # 求最小值
print(ar.std()) # 求标准差
print(ar.var()) # 求方差
print(ar.sum(), np.sum(ar,axis = 0)) # 求和,np.sum() → axis为0,按列求和;axis为1,按行求和
print(np.sort(np.array([1,4,3,2,5,6]))) # 排序
# 常用函数
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
[[10 11 12]
[13 14 15]]
[[ 0 2 4]
[ 6 8 10]]
[[ 1. 0.5 0.33333333]
[ 0.25 0.2 0.16666667]]
[[ 0. 1. 1.41421356]
[ 1.73205081 2. 2.23606798]]
2.5
5
0
1.70782512766
2.91666666667
15 [3 5 7]
[1 2 3 4 5 6]
【课程1.3 Numpy通用函数】 课程作业
作业1:创建一个20个元素的数组,分别改变成两个形状:(4,5),(5,6) (提示:超出范围用resize)

ar = np.arange(20)
print(ar.reshape(4,5), '\n-------')
print(np.resize(ar,(5,6)), '\n-------')
作业2:创建一个(4,4)的数组,把其元素类型改为字符型
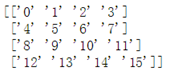
ar = np.arange(16).reshape(4,4)
print(ar.astype(np.str))
作业3:根据要求创建数组,运用数组的运算方法得到结果:result = ar * 10 +100,并求出result的均值及求和
ar = np.arange(16).reshape(4,4)
print('创建数组为:\n', ar, '\n-------')
result = ar * 10 +100
print('计算后的数组为:\n', result, '\n-------')
print('result的均值为:\n', result.mean(), '\n-------')
print('result求和为:\n', result.sum(), '\n-------')






















 569
569











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








