一、问题描述
有向无环图中的 LCA。给定一幅有向无环图和两个顶点 v 和 w,找出 v 和 w 的 LCA( Lowest Common Ancestor, 最近共同祖先)。
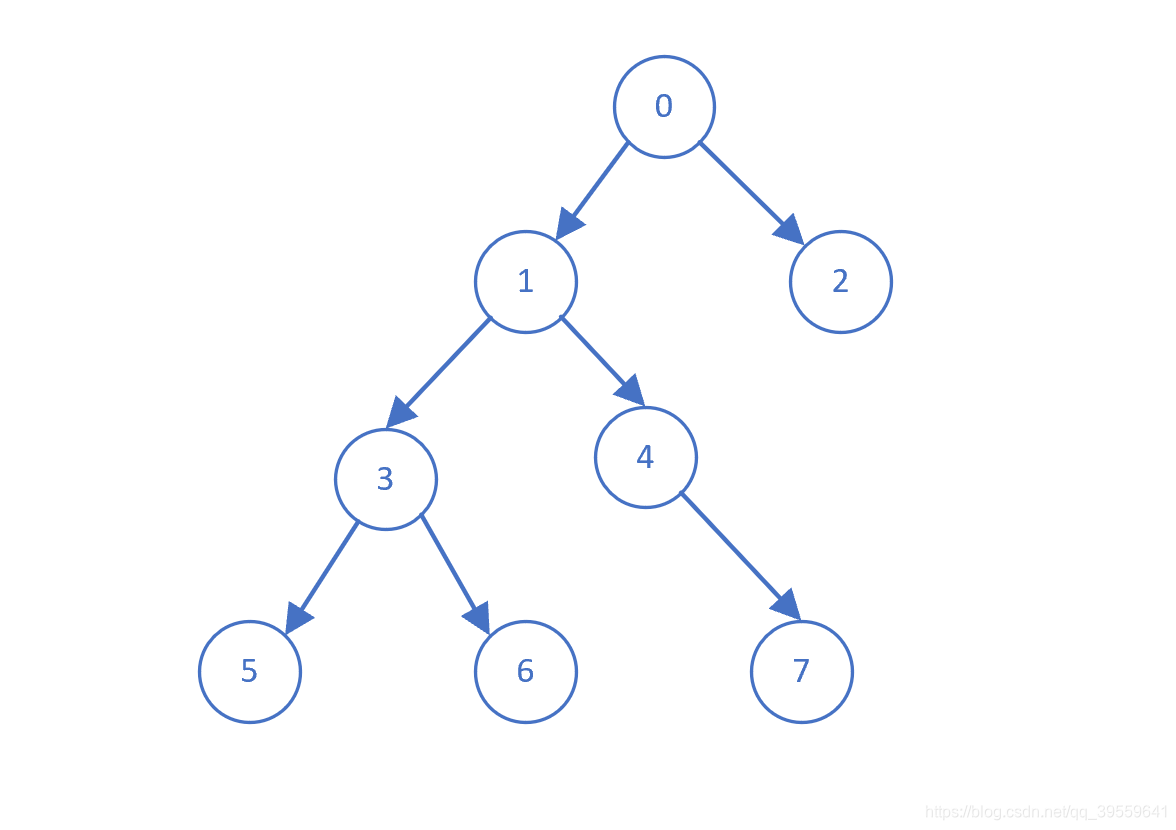
如上图所示:LCA(5,6) = 3、LCA(5,7) = 1、LCA(5,1) = 1。
二、Tarjan算法
Tarjan是根据深度优先搜索和并查集实现的,Tarjan 算法的基本思路:
- 任选一个节点为根节点,从根节点开始
- 遍历该点 v 的所有子节点 w ,并标记 w 已经被访问过
- 若 w 还有子节点,返回步骤2 ,否则下一步
- 合并 w 到 v 所在集合
- 寻找与当前点 w 有询问关系的点 p
- 若 p 已经被访问过,则可以确定 w、p 的最近公共祖先为 p所在集合的根节点
伪代码如下:
Tarjan(v) //union和find为并查集合并函数和查找函数
{
for each(v,w) //访问所有v子节点w
{
Tarjan(w); //继续往下遍历
union(v,w); //合并w到v上
标记w被访问过;
}
for each(w,p) //访问所有和w有询问关系的p
{
如果p被访问过;
w,p的最近公共祖先为find(p);
}
}三、代码实现
package graph.directed.practise;
import graph.directed.DirectedGraph;
import java.util.*;
/**
* LCA(最近共同祖先)
* @author hh
* @date 2021/2/11 14:56
*/
public class LowestCommonAncestor {
/**
* 有向图
*/
private DirectedGraph directedGraph;
/**
* 标记顶点是否被访问
*/
private boolean[] marked;
/**
* 保存当前点的祖先节点
*/
private int[] ancestor;
/**
* 记录每个连通分量数的大小
*/
private int[] size;
/**
* 保存查询节点
*/
private Set<Integer>[] query;
public LowestCommonAncestor(DirectedGraph directedGraph) {
this.directedGraph = directedGraph;
this.marked = new boolean[directedGraph.getVertices()];
Arrays.fill(marked,Boolean.FALSE);
this.ancestor = new int[directedGraph.getVertices()];
this.query = new HashSet[directedGraph.getVertices()];
this.size = new int[directedGraph.getVertices()];
for(int i = 0; i < directedGraph.getVertices(); i++){
this.ancestor[i] = i;
this.size[i] = 1;
this.query[i] = new HashSet<>();
}
}
/**
* 添加节点v和w的LCA查询
*
* @param v : 节点v
* @param w : 节点w
*/
public void addQuery(int v,int w){
query[v].add(w);
query[w].add(v);
}
public void doQuery(int v){
marked[v] = true;
for(int w : directedGraph.adj(v)){
if(!marked[w]){
doQuery(w);
this.ancestor[w] = v;
}
}
for(int q : this.query[v]){
//如果查询节点q已经访问过,则输出LCA(q,v)
if(marked[q]){
System.out.println("LCA("+q+","+v+")="+find(q));
}
}
}
/**
* 查找节点p的连通分量标识
*
* @param p :节点编号
* @return
*/
public int find(int p){
while(p != ancestor[p]){
p = ancestor[p];
}
return p;
}
/**
* 连接节点p和q
*
* @param p: 节点编号
* @param q:节点编号
*/
public void union(int p,int q){
if(connected(p,q)){
return;
}
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
//把连通分量小的树连接到大树中,相应节点数量也想加
if(size[rootP] > size[rootQ]){
ancestor[rootQ] = rootP;
size[rootP] += size[rootQ];
}else{
ancestor[rootP] = rootQ;
size[rootQ] += size[rootP];
}
}
/**
* 判断两节点是否在同一连通分量上
*
* @param p :节点编号
* @param q :节点编号
* @return
*/
public boolean connected(int p,int q){
return ancestor[p] == ancestor[q];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String fileName = "D:\\Desktop\\graph\\directed\\graph6.txt";
DirectedGraph directedGraph = new DirectedGraph();
directedGraph.createGraphByFile(fileName);
LowestCommonAncestor lowestCommonAncestor = new LowestCommonAncestor(directedGraph);
lowestCommonAncestor.addQuery(5,6);
lowestCommonAncestor.addQuery(5,7);
lowestCommonAncestor.addQuery(5,1);
lowestCommonAncestor.doQuery(0);
}
} 执行结果如下图所示: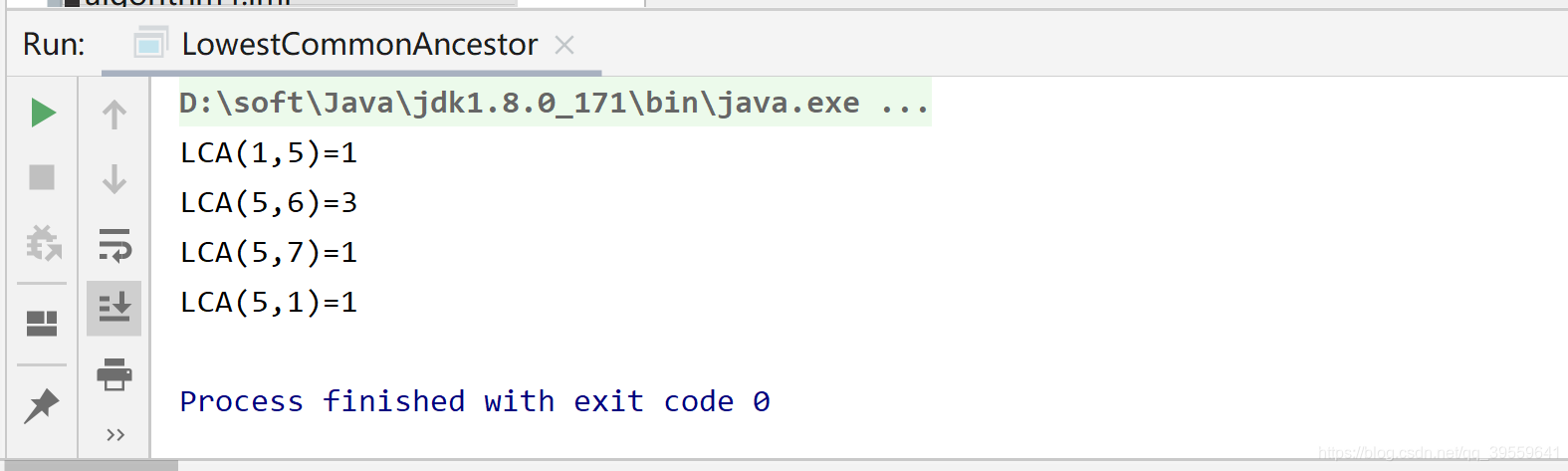





 本文详细介绍了如何使用Tarjan算法解决有向无环图中的最近共同祖先(LCA)问题。通过深度优先搜索和并查集,展示了如何在给定向图中找到任意两点的最近公共祖先。提供了代码实现和示例,适用于数据结构和图论学习者。
本文详细介绍了如何使用Tarjan算法解决有向无环图中的最近共同祖先(LCA)问题。通过深度优先搜索和并查集,展示了如何在给定向图中找到任意两点的最近公共祖先。提供了代码实现和示例,适用于数据结构和图论学习者。
















 456
456

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








