DDP 和 FSDP的区别
DDP:每个GPU都有一套完整的模型(模型权重,优化器,梯度),只是所有的GPU均分了Batchsize数量的训练数据。
FSDP:每个GPU仅仅有一套完整模型(模型权重,优化器,梯度)的一部分。分担了GPU显存和计算压力。相当于zero3。
怎么使用
参考代码对自己的代码进行修改即可。
参考文档
Doc url https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/FSDP_tutorial.html
Based on: https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/master/mnist/main.py
API:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/fsdp.html#torch.distributed.fsdp.FullyShardedDataParallel
Introduction
Training AI models at a large scale is a challenging task that requires a lot of compute power and resources. It also comes with considerable engineering complexity to handle the training of these very large models. PyTorch FSDP, released in PyTorch 1.11 makes this easier.
In this tutorial, we show how to use FSDP APIs, for simple MNIST models that can be extended to other larger models such as HuggingFace BERT models, GPT 3 models up to 1T parameters . The sample DDP MNIST code has been borrowed from here.
How FSDP works
In DistributedDataParallel, (DDP) training, each process/ worker owns a replica of the model and processes a batch of data, finally it uses all-reduce to sum up gradients over different workers. In DDP the model weights and optimizer states are replicated across all workers. FSDP is a type of data parallelism that shards model parameters, optimizer states and gradients across DDP ranks.
When training with FSDP, the GPU memory footprint is smaller than when training with DDP across all workers. This makes the training of some very large models feasible by allowing larger models or batch sizes to fit on device. This comes with the cost of increased communication volume. The communication overhead is reduced by internal optimizations like overlapping communication and computation.

At a high level FSDP works as follow:
In constructor
-
Shard model parameters and each rank only keeps its own shard
In forward path
-
Run all_gather to collect all shards from all ranks to recover the full parameter in this FSDP unit
-
Run forward computation
-
Discard parameter shards it has just collected
In backward path
-
Run all_gather to collect all shards from all ranks to recover the full parameter in this FSDP unit
-
Run backward computation
-
Run reduce_scatter to sync gradients
-
Discard parameters.
One way to view FSDP’s sharding is to decompose the DDP gradient all-reduce into reduce-scatter and all-gather. Specifically, during the backward pass, FSDP reduces and scatters gradients, ensuring that each rank possesses a shard of the gradients. Then it updates the corresponding shard of the parameters in the optimizer step. Finally, in the subsequent forward pass, it performs an all-gather operation to collect and combine the updated parameter shards.
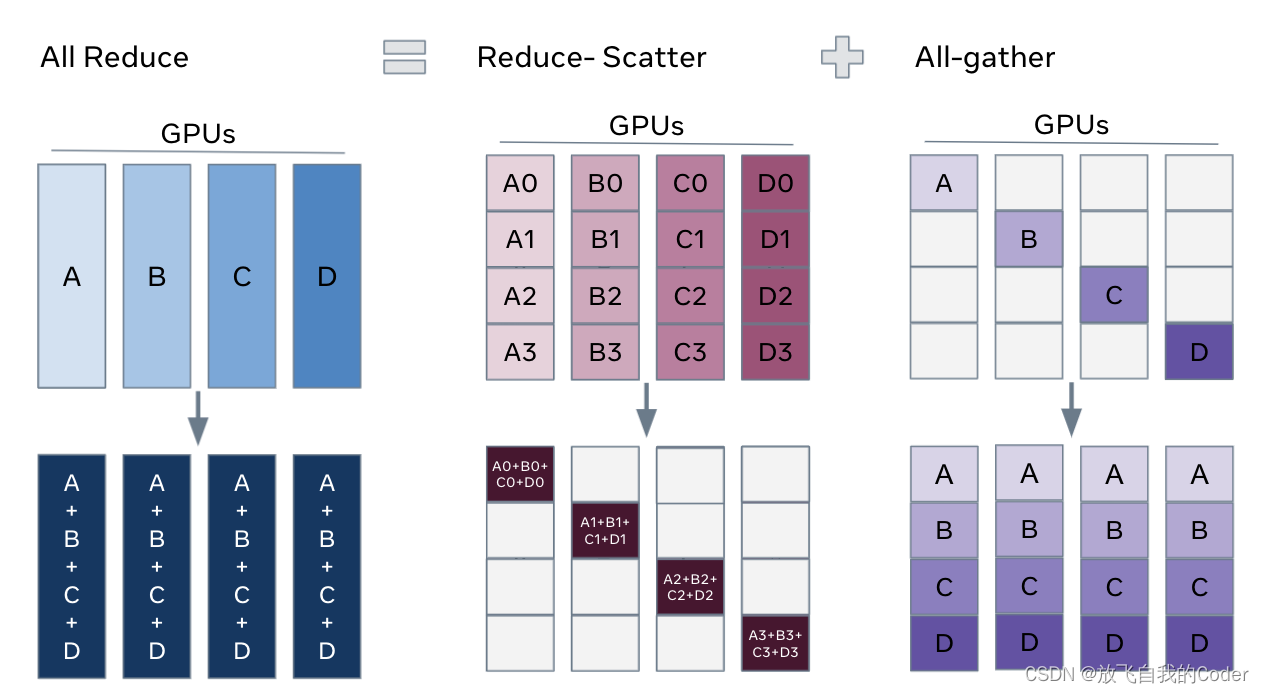
How to use FSDP
Here we use a toy model to run training on the MNIST dataset for demonstration purposes. The APIs and logic can be applied to training larger models as well.
Setup
1.1 Install PyTorch along with Torchvision
pip3 install --pre torch torchvision torchaudio -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu113/torch_nightly.html
We add the following code snippets to a python script “FSDP_mnist.py”.
完整的代码
"""
@Create time : 2024/1/31
@Functions :
@Author : LX
"""
# doc url: https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/FSDP_tutorial.html
# Based on: https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/master/mnist/main.py
import os
import argparse
import functools
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel as DDP
from torch.utils.data.distributed import DistributedSampler
from torch.distributed.fsdp import FullyShardedDataParallel as FSDP
from torch.distributed.fsdp.fully_sharded_data_parallel import (
CPUOffload,
BackwardPrefetch,
)
from torch.distributed.fsdp.wrap import (
size_based_auto_wrap_policy,
enable_wrap,
wrap,
)
def setup(rank, world_size):
os.environ['MASTER_ADDR'] = 'localhost'
os.environ['MASTER_PORT'] = '12355'
# initialize the process group
dist.init_process_group("nccl", rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
def cleanup():
dist.destroy_process_group()
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(0.25)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
def train(args, model, rank, world_size, train_loader, optimizer, epoch, sampler=None):
model.train()
ddp_loss = torch.zeros(2).to(rank)
if sampler:
sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, target = data.to(rank), target.to(rank)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum') # !!
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
ddp_loss[0] += loss.item()
ddp_loss[1] += len(data)
dist.all_reduce(ddp_loss, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)
if rank == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} \tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(epoch, ddp_loss[0] / ddp_loss[1]))
def test(model, rank, world_size, test_loader):
model.eval()
correct = 0
ddp_loss = torch.zeros(3).to(rank)
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(rank), target.to(rank)
output = model(data)
ddp_loss[0] += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability
ddp_loss[1] += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
ddp_loss[2] += len(data)
dist.all_reduce(ddp_loss, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)
if rank == 0:
test_loss = ddp_loss[0] / ddp_loss[2]
print('Test set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.2f}%)\n'.format(
test_loss, int(ddp_loss[1]), int(ddp_loss[2]),
100. * ddp_loss[1] / ddp_loss[2]))
def fsdp_main(rank, world_size, args):
setup(rank, world_size)
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])
dataset1 = datasets.MNIST('../data', train=True, download=True,
transform=transform)
dataset2 = datasets.MNIST('../data', train=False,
transform=transform)
sampler1 = DistributedSampler(dataset1, rank=rank, num_replicas=world_size, shuffle=True)
sampler2 = DistributedSampler(dataset2, rank=rank, num_replicas=world_size)
train_kwargs = {'batch_size': args.batch_size, 'sampler': sampler1}
test_kwargs = {'batch_size': args.test_batch_size, 'sampler': sampler2}
cuda_kwargs = {'num_workers': 2,
'pin_memory': True,
'shuffle': False}
train_kwargs.update(cuda_kwargs)
test_kwargs.update(cuda_kwargs)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset1, **train_kwargs)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset2, **test_kwargs)
my_auto_wrap_policy = functools.partial(
size_based_auto_wrap_policy, min_num_params=100
)
torch.cuda.set_device(rank)
init_start_event = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
init_end_event = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
model = Net().to(rank)
model = FSDP(model)
optimizer = optim.Adadelta(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr)
scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=1, gamma=args.gamma)
init_start_event.record()
for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1):
train(args, model, rank, world_size, train_loader, optimizer, epoch, sampler=sampler1)
test(model, rank, world_size, test_loader)
scheduler.step()
init_end_event.record()
if rank == 0:
print(f"CUDA event elapsed time: {init_start_event.elapsed_time(init_end_event) / 1000}sec")
print(f"{model}")
if args.save_model:
# use a barrier to make sure training is done on all ranks
dist.barrier()
states = model.state_dict()
if rank == 0:
torch.save(states, "mnist_cnn.pt")
cleanup()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Training settings
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch MNIST Example')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=1000, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
help='number of epochs to train (default: 14)')
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=1.0, metavar='LR',
help='learning rate (default: 1.0)')
parser.add_argument('--gamma', type=float, default=0.7, metavar='M',
help='Learning rate step gamma (default: 0.7)')
parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
help='disables CUDA training')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S',
help='random seed (default: 1)')
parser.add_argument('--save-model', action='store_true', default=False,
help='For Saving the current Model')
args = parser.parse_args()
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
WORLD_SIZE = torch.cuda.device_count()
mp.spawn(fsdp_main,
args=(WORLD_SIZE, args),
nprocs=WORLD_SIZE,
join=True)
# python FSDP_mnist.py























 548
548

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








