JDK1.7版本的HashMap
1、HashMap是一个集合类,主要是帮我们做数据存储,那么他是如何存储的呢?


HashMap是用一个table来做存储,这个table只是一个基于K,V的Entry数组。
2、hashmap的put()方法解析
调用put方法的时候,首先对key值进行hash算法,int hash = hash(key); index=hash%length。通过hash取抹的方式找到数组的下标,通过这个下标将数据存到对应的位置,但是两个不同的hash值可能取到相同的下标,这个时候在对应的数组的位置就会形成一个链表。可以从上图源码中看出,它是做了一个for循环,首先判断hash值相同的前提下,如果key值或者equals值相同,那么就判定key值一样,新值就会覆盖旧值,然后返回旧值;如果没有覆盖,就会进入addEntry方法中

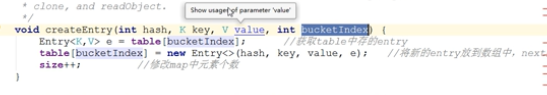
通过addEntry方法把值插入到链表的头部。
如果数组已经存满,需要扩容,怎么办?首先我们要知道hashmap的初始长度,看源码


通过this的方法将值做处理

可见,hashmap的初始长度就是16*0.75=12;当链表到达一定的长度的时候,hashmap为了减缓链表过长,查询缓慢的压力,它就会进行扩容,通过resize方法,创建一个新的数组,长度是原数组长度的2倍,然后将旧数组里面的元素从新hash取值,放到新的数组里面去。
JDK1.8版本的HashMap
源码的可读性是非常差的
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
1.8和1.7版本的主要区别在1.8版本的hashmap中,当链表的长度达到8的时候,链表转化为红黑树,至于为什么是8,可能是jdk权衡查询和存储的性能,觉得8是最好的选择吧。
为什么说hashmap是线程不安全的呢?
因为里面抛去其他地方可能会存在原子性问题,1.7源码的modCount++和1.8版本的++modCount一定是会存在原子性问题的。所以hashmap一定是线程不安全的。
JDK1.7版本的ConcurrentHashMap
HashMap是基于table的存储,table就是一个entry数组。
ConcurrentHashMap是基于Segment的存储,Segment其实就是一个特殊的版本的hashtable,它继承了ReentrantLock,采用分段锁的方式保证线程安全。
ConcurrentHashMap就是把多份的hashtable放入到数组中,每一个hashtable都是线程安全的,put的时候,计算hash2次,第一次根据下标决定放到哪一个Segment,第二次是决定放到hashtable的哪一个位置。Segment的length决定了ConcurrentHashMap的并发度,这个值在初始化ConcurrentHashMap的时候就已经确定了,不能发生改变,因此它的扩容不会发生Segment,只会发生在hashtable,因为在进入hashtable之前,它是加了同步锁的,所以它不会发生原子性问题。
JDK1.8版本的ConcurrentHashMap
相对1.7版本的,1.8版本的ConcurrentHashMap就会高端很多
源码如下
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
1.8版本的concurrentHashMap放弃了segment,因为segment是一个复杂的数据结构,锁的粒度太大,不能方便的扩容,而1.8版本的是采用了Node,保存key,value及key的hash值的数据结构。其中value和next都用volatile修饰,保证并发的可见性。
总体来说:
1.7 是基于segment加锁的方式,保证线程安全
1.8 是基于数组+链表+红黑树,采用cas+synchronized的方式保证线程安全,它只对链表中元素加锁,将锁的粒度变小,提高了并发度。红黑树是为了提高查询效率,参照hashmap就可以知道。






















 135
135











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








