匿名管道

#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
功能:创建一个匿名管道,用来进程间通信。
参数:int pipefd[2] 这个数组是一个传出参数。
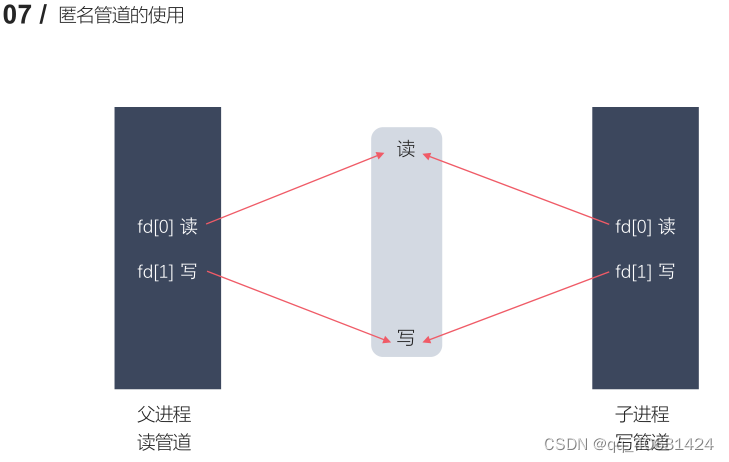
pipefd[0] 对应的是管道的读端
pipefd[1] 对应的是管道的写端
返回值:
成功 0
失败 -1
管道默认是阻塞的:如果管道中没有数据,read阻塞,如果管道满了,write阻塞
注意:匿名管道只能用于具有关系的进程之间的通信(父子进程,兄弟进程)
*/
// 子进程发送数据给父进程,父进程读取到数据输出
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
// 在fork之前创建管道
int pipefd[2];
int ret = pipe(pipefd);
if(ret == -1) {
perror("pipe");
exit(0);
}
// 创建子进程
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid > 0) {
// 父进程
printf("i am parent process, pid : %d\n", getpid());
// 关闭写端
close(pipefd[1]);
// 从管道的读取端读取数据
char buf[1024] = {0};
while(1) {
int len = read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("parent recv : %s, pid : %d\n", buf, getpid());
// 向管道中写入数据
//char * str = "hello,i am parent";
//write(pipefd[1], str, strlen(str));
//sleep(1);
}
} else if(pid == 0){
// 子进程
printf("i am child process, pid : %d\n", getpid());
// 关闭读端
close(pipefd[0]);
char buf[1024] = {0};
while(1) {
// 向管道中写入数据
char * str = "hello,i am child";
write(pipefd[1], str, strlen(str));
//sleep(1);
// int len = read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf));
// printf("child recv : %s, pid : %d\n", buf, getpid());
// bzero(buf, 1024);
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
int pipefd[2];
int ret = pipe(pipefd);
//获取管道的大小
long size = fpathconf(pipefd[1],_PC_PIPE_BUF);
printf("pipe size : %ld\n", size);
return 0;
}
实现 ps aux | grep xxx 父子进程间通信
子进程: ps aux, 子进程结束后,将数据发送给父进程
父进程:获取到数据,过滤
pipe()
execlp()
子进程将标准输出 stdout_fileno 重定向到管道的写端。 dup2
*/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <wait.h>
int main() {
// 创建一个管道
int fd[2];
int ret = pipe(fd);
if(ret == -1) {
perror("pipe");
exit(0);
}
// 创建子进程
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid > 0) {
// 父进程
// 关闭写端
close(fd[1]);
// 从管道中读取
char buf[1024] = {0};
int len = -1;
while((len = read(fd[0], buf, sizeof(buf) - 1)) > 0) {
// 过滤数据输出
printf("%s", buf);
memset(buf, 0, 1024);
}
wait(NULL);
} else if(pid == 0) {
// 子进程
// 关闭读端
close(fd[0]);
// 文件描述符的重定向 stdout_fileno -> fd[1]
dup2(fd[1], STDOUT_FILENO);
// 执行 ps aux
execlp("ps", "ps", "aux", NULL);
perror("execlp");
exit(0);
} else {
perror("fork");
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}






















 94
94











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








