
1、提交的代码,分治
class Solution {
map< pair<int,int>, vector<int> >hash;
public:
vector<int> ways(const string &input, int left, int right)
{
pair<int,int>curKey(left, right);
if(hash.find(curKey) != hash.end())
{
return hash[curKey];
}
vector<int> res;
for(int i = left; i < right; i++)
{
if(input[i] == '-' || input[i] == '+' || input[i] == '*')
{
vector<int>left_result = ways(input, left, i);
vector<int>right_result = ways(input, i+1, right);
for(auto l: left_result)
{
for(auto r:right_result)
{
res.push_back(cal(input[i], l, r));
}
}
}
}
if(res.size() == 0)
{
res.push_back(stoi(input.substr(left, right - left)));
}
hash[curKey] = res;
return res;
}
int cal(char ops, int a, int b)
{
int res;
switch(ops)
{
case '-': res = a - b; break;
case '+': res = a + b; break;
case '*': res = a * b; break;
}
return res;
}
vector<int> diffWaysToCompute(string input) {
return ways(input, 0, input.size());
}
};
2、在自己电脑上打印输出:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int num;
string exp;
Node(int n,string e):num(n),exp(e){}
};
class Solution {
map< pair<int,int>, vector<Node> >hash;
public:
vector<Node> ways(const string &input, int left, int right)
{
pair<int,int>curKey(left, right);
if(hash.find(curKey) != hash.end())
{
return hash[curKey];
}
vector<Node> res;
for(int i = left; i < right; i++)
{
if(input[i] == '-' || input[i] == '+' || input[i] == '*')
{
vector<Node>left_result = ways(input, left, i);
vector<Node>right_result = ways(input, i+1, right);
for(int ii = 0; ii < left_result.size(); ii++)
{
for(int jj = 0; jj < right_result.size(); jj++)
{
int num = cal(input[i], left_result[ii].num, right_result[jj].num);
string exp = "(" + left_result[ii].exp + " " + input[i] + " "+ right_result[jj].exp + ")";
res.push_back(Node(num, exp));
}
}
}
}
if(res.size() == 0)
{
int num = atoi(input.substr(left, right - left).c_str());
string exp = input.substr(left, right - left);
res.push_back(Node(num, exp));
}
hash[curKey] = res;
return res;
}
int cal(char ops, int a, int b)
{
int res;
switch(ops)
{
case '-': res = a - b; break;
case '+': res = a + b; break;
case '*': res = a * b; break;
}
return res;
}
vector<Node> diffWaysToCompute(string input) {
return ways(input, 0, input.size());
}
};
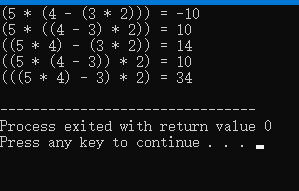
int main()
{
string input = "5*4-3*2";
Solution s;
vector<Node> res = s.diffWaysToCompute(input);
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++)
cout <<res[i].exp<<" = "<< res[i].num<<endl;
return 0;
}
























 2368
2368











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








