Rikka with Travels
Problem Description
To enjoy their summer vacations, R i k k a Rikka Rikka and Y u t a Yuta Yuta decide to go travels. According to past experiences, contradictions always arose when they were planning for the same trip. This time, they decide to make plans dividually and will go travel twice.
Coincidentally, they choose the same country Fantasy as the destination, which is a small island country on the Pacific. There are n cities in Fantasy and they are connected with n − 1 n−1 n−1 two-way roads. It is guaranteed that any two cities can reach each other by the road system.
Though R i k k a Rikka Rikka and Y u t a Yuta Yuta love travels, visiting the same city more than once is still boring for them. Therefore, both R i k k a Rikka Rikka and Y u t a Yuta Yuta choose a simple path (i.e., a path without visiting any city more than once) as her/his plan. Moreover, they want to ensure the two paths do not intersect on any city.
Suppose R i k k a Rikka Rikka chooses the path from a to b, Y u t a Yuta Yuta chooses the path from c c c to d d d (both a = b a=b a=b and c = d c=d c=d are allowed), they define the feature of the plan is an ordered pair ( L ( a , b ) , L ( c , d ) ) (L(a,b),L(c,d)) (L(a,b),L(c,d)), where L ( x , y ) L(x,y) L(x,y) represents the number of cities on the path from x x x to y y y.
Now, Rikka wants to count the number of different features, i.e., the number of different integer pairs ( l 1 , l 2 ) (l_1,l_2) (l1,l2) which satisfies there exists a valid travel plan ( a , b , c , d ) (a,b,c,d) (a,b,c,d) meets L ( a , b ) = l 1 , L ( c , d ) = l 2 L(a,b)=l_1,L(c,d)=l_2 L(a,b)=l1,L(c,d)=l2. Since Rikka and Yuta are busy with planning their trip, R i k k a Rikka Rikka asks you to help her calculate the answer.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer T ( 1 ≤ T ≤ 300 ) T(1\leq T\leq 300) T(1≤T≤300), the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains a single integer n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 ) n(1\leq n\leq 10^5) n(1≤n≤105), the number of cities in Fantasy.
Then n − 1 n−1 n−1 lines follow. Each line contains two integers u i , v i ( 1 ≤ u i , v i ≤ n ) u_i,v_i(1\leq u_i,v_i\leq n) ui,vi(1≤ui,vi≤n) which represents a two-way road ( u i , v i ) (u_i,v_i) (ui,vi) in the road system.
The input guarantees that there are no more than 5 5 5 test cases with n > 500 n>500 n>500.
Output
For each test case, output a single line with a single integer, the answer.
Hint
In the first test case, the possible features are ( 1 , 1 ) , ( 1 , 2 ) , ( 1 , 3 ) , ( 2 , 1 ) , ( 3 , 1 ) (1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(2,1),(3,1) (1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(2,1),(3,1). Therefore the answer is 5 5 5.
In the second test case, the possible features are ( 1 , 1 ) , ( 1 , 2 ) , ( 1 , 3 ) , ( 1 , 4 ) , ( 2 , 1 ) , ( 2 , 2 ) , ( 2 , 3 ) , ( 3 , 1 ) , ( 3 , 2 ) , ( 4 , 1 ) (1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(2,1),(2,2),(2,3),(3,1),(3,2),(4,1) (1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(2,1),(2,2),(2,3),(3,1),(3,2),(4,1). Therefore the answer is 10. 10. 10.
Sample Input
2
4
1 2
1 3
1 4
5
1 2
2 3
3 4
3 5
Sample Output
5
10
题意
- 就是问你有多少有序整数对 ( l 1 , l 2 ) (l_1,l_2) (l1,l2),使得存在两条没有公共节点的两条路径,使得他们的长度分别为 l 1 l_1 l1与 l 2 l_2 l2
题解
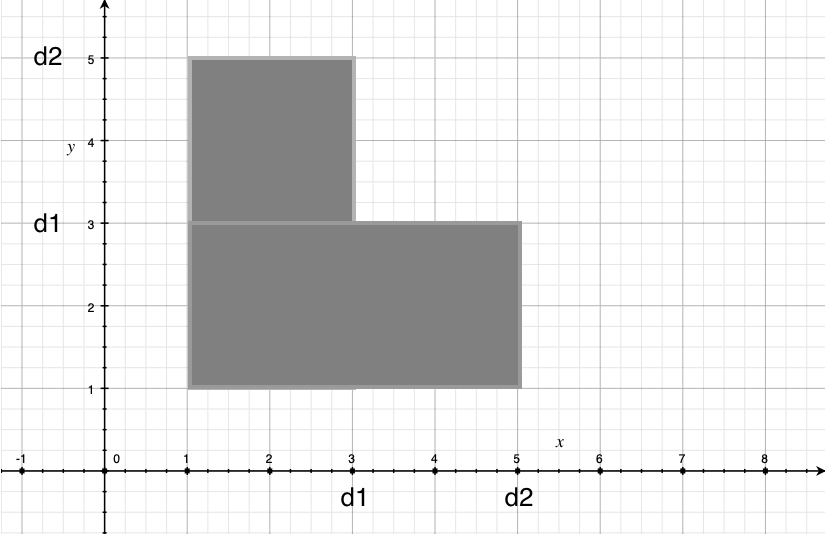
- 考虑枚举分开两条路径的边,然后除去这条边后,一棵树被分成两棵树,他们的直径分别为 d 1 , d 2 d_1,d_2 d1,d2那么显然此时对答案的贡献是:如果以这条边分割,整数对第一个数可以取到 [ 1 , d 1 ] [1,d_1] [1,d1],对应的第二个数可以取到 [ 1 , d 2 ] [1,d_2] [1,d2],或者将 d 1 d_1 d1和 d 2 d_2 d2反过来,然后考虑怎么统计答案,实际上你会发现实际上每次选定一条割边后,是给一个大小为 d 1 × d 2 d_1\times d_2 d1×d2的矩阵内填 1 1 1【注意不是加 1 1 1,即每个点的最大值为 1 1 1】考虑用一颗线段树维护单点最大值就行了,最后每个点的最大值加起来就是答案
- 对与枚举边找到两棵树的直径当然是上换根
d
p
dp
dp喽
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+10;
int mark[maxn<<2];
void build(int id,int l,int r)
{
mark[id]=0;
if(l==r) return;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(id<<1,l,mid);build(id<<1|1,mid+1,r);
}
void down(int id)
{
mark[id<<1]=max(mark[id<<1],mark[id]);
mark[id<<1|1]=max(mark[id<<1|1],mark[id]);
}
void update(int id,int L,int R,int l,int r,int val)
{
if(L>=l&&R<=r) {
mark[id]=max(mark[id],val);
return;
}
int mid=(L+R)>>1;
if(l<=L) update(id<<1,L,mid,l,r,val);
if(r>mid) update(id<<1|1,mid+1,R,l,r,val);
}
int query(int id,int L,int R,int pos)
{
if(L==R) return mark[id];
int mid=(L+R)>>1;
if(mark[id]) down(id);
if(pos<=mid) return query(id<<1,L,mid,pos);
else return query(id<<1|1,mid+1,R,pos);
}
vector<int> vec[maxn];
int n,dp1[2][maxn],dp2[2][maxn];
//dp1[1][i]:除去节点i为子树的以fa[i]为终点的最长链
//dp1[0][i]:以节点i为子树的且以i为终点的最长链
//dp2[1][i]:除去节点i为子树的树直径
//dp2[0][i]:以节点i为子树的树直径
void update(int &fir,int &sec,int val) //插入val维护最大次大值
{
if(val>=fir) {sec=fir;fir=val;}
else if(val>sec) {sec=val;}
}
int get(int &fir,int &sec,int val) //查询除去值val的情况下的最大值
{
if(val==fir) return sec;
else return fir;
}
void update(int &fir,int &sec,int &thi,int val) //插入val维护最大的三个值
{
if(val>=fir) {thi=sec;sec=fir;fir=val;}
else if(val>=sec) {thi=sec;sec=val;}
else if(val>thi) {thi=val;}
}
int get(int &fir,int &sec,int &thi,int val) //查询除去值val的情况下的最大值与次大值之和
{
if(val==fir) return sec+thi;
else if(val==sec) return fir+thi;
else return fir+sec;
}
void dfs1(int cur,int fa)
{
dp1[0][cur]=1;dp2[0][cur]=1;
for(int i=0;i<vec[cur].size();i++) if(vec[cur][i]!=fa) dfs1(vec[cur][i],cur);
int firr=0,secc=0;
for(int i=0;i<vec[cur].size();i++) if(vec[cur][i]!=fa) {
dp1[0][cur]=max(dp1[0][cur],dp1[0][vec[cur][i]]+1);
dp2[0][cur]=max(dp2[0][cur],dp2[0][vec[cur][i]]);
update(firr,secc,dp1[0][vec[cur][i]]);
}
dp2[0][cur]=max(dp2[0][cur],firr+secc+1);
}
void dfs2(int cur,int fa)
{
int sonlen=dp2[0][cur],falen=dp2[1][cur];
if(sonlen&&falen) {
update(1,1,n,1,sonlen,falen);
update(1,1,n,1,falen,sonlen);
}
//更新dp1[1]
int fir=dp1[1][cur],sec=0,thi=0;
for(int i=0;i<vec[cur].size();i++) if(vec[cur][i]!=fa) {
update(fir,sec,thi,dp1[0][vec[cur][i]]);
}
for(int i=0;i<vec[cur].size();i++) if(vec[cur][i]!=fa) {
dp1[1][vec[cur][i]]=get(fir,sec,dp1[0][vec[cur][i]])+1;
dp2[1][vec[cur][i]]=get(fir,sec,thi,dp1[0][vec[cur][i]])+1;
}
//更新dp2[1]
fir=dp2[1][cur],sec=0;
for(int i=0;i<vec[cur].size();i++) if(vec[cur][i]!=fa) {
update(fir,sec,dp2[0][vec[cur][i]]);
}
for(int i=0;i<vec[cur].size();i++) if(vec[cur][i]!=fa) {
dp2[1][vec[cur][i]]=max(dp2[1][vec[cur][i]],get(fir,sec,dp2[0][vec[cur][i]]));
}
for(int i=0;i<vec[cur].size();i++) if(vec[cur][i]!=fa) dfs2(vec[cur][i],cur);
}
int main()
{
int t;scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--) {
scanf("%d",&n);
build(1,1,n);
for(int i=1,u,v;i<n;i++) {
scanf("%d %d",&u,&v);
vec[u].push_back(v);
vec[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs1(1,0);dfs2(1,0);
long long ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) ans+=query(1,1,n,i);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) vec[i].clear();
}
}
























 235
235











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








