一、在 struts2中,对常用的数据类型已经自动进行了类型转换工作。
DefaultTypeConverter里面已经处理了String向其他基本类型的转化工作。
/**
* Default type conversion. Converts among numeric types and also strings. Contains the basic
* type mapping code from OGNL.
*
* @author Luke Blanshard (blanshlu@netscape.net)
* @author Drew Davidson (drew@ognl.org)
*/
public abstract class DefaultTypeConverter implements TypeConverter {
protected static String MILLISECOND_FORMAT = ".SSS";
private static final String NULL_STRING = "null";
private static final Map<Class, Object> primitiveDefaults;
private Container container;
static {
Map<Class, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(Boolean.TYPE, Boolean.FALSE);
map.put(Byte.TYPE, Byte.valueOf((byte) 0));
map.put(Short.TYPE, Short.valueOf((short) 0));
map.put(Character.TYPE, new Character((char) 0));
map.put(Integer.TYPE, Integer.valueOf(0));
map.put(Long.TYPE, Long.valueOf(0L));
map.put(Float.TYPE, new Float(0.0f));
map.put(Double.TYPE, new Double(0.0));
map.put(BigInteger.class, new BigInteger("0"));
map.put(BigDecimal.class, new BigDecimal(0.0));
primitiveDefaults = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
}
@Inject
public void setContainer(Container container) {
this.container = container;
}
public Object convertValue(Map<String, Object> context, Object value, Class toType) {
return convertValue(value, toType);
}
public Object convertValue(Map<String, Object> context, Object target, Member member,
String propertyName, Object value, Class toType) {
return convertValue(context, value, toType);
}
public TypeConverter getTypeConverter( Map<String, Object> context )
{
Object obj = context.get(TypeConverter.TYPE_CONVERTER_CONTEXT_KEY);
if (obj instanceof TypeConverter) {
return (TypeConverter) obj;
// for backwards-compatibility
} else if (obj instanceof ognl.TypeConverter) {
return new XWorkTypeConverterWrapper((ognl.TypeConverter) obj);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the value converted numerically to the given class type
*
* This method also detects when arrays are being converted and converts the
* components of one array to the type of the other.
*
* @param value
* an object to be converted to the given type
* @param toType
* class type to be converted to
* @return converted value of the type given, or value if the value cannot
* be converted to the given type.
*/
public Object convertValue(Object value, Class toType) {
Object result = null;
if (value != null) {
/* If array -> array then convert components of array individually */
if (value.getClass().isArray() && toType.isArray()) {
Class componentType = toType.getComponentType();
result = Array.newInstance(componentType, Array
.getLength(value));
for (int i = 0, icount = Array.getLength(value); i < icount; i++) {
Array.set(result, i, convertValue(Array.get(value, i),
componentType));
}
} else {
if ((toType == Integer.class) || (toType == Integer.TYPE))
result = (int) longValue(value);
if ((toType == Double.class) || (toType == Double.TYPE))
result = doubleValue(value);
if ((toType == Boolean.class) || (toType == Boolean.TYPE))
result = booleanValue(value) ? Boolean.TRUE : Boolean.FALSE;
if ((toType == Byte.class) || (toType == Byte.TYPE))
result = (byte) longValue(value);
if ((toType == Character.class) || (toType == Character.TYPE))
result = (char) longValue(value);
if ((toType == Short.class) || (toType == Short.TYPE))
result = (short) longValue(value);
if ((toType == Long.class) || (toType == Long.TYPE))
result = longValue(value);
if ((toType == Float.class) || (toType == Float.TYPE))
result = new Float(doubleValue(value));
if (toType == BigInteger.class)
result = bigIntValue(value);
if (toType == BigDecimal.class)
result = bigDecValue(value);
if (toType == String.class)
result = stringValue(value);
if (Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(toType))
result = enumValue(toType, value);
}
} else {
if (toType.isPrimitive()) {
result = primitiveDefaults.get(toType);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* Evaluates the given object as a boolean: if it is a Boolean object, it's
* easy; if it's a Number or a Character, returns true for non-zero objects;
* and otherwise returns true for non-null objects.
*
* @param value
* an object to interpret as a boolean
* @return the boolean value implied by the given object
*/
public static boolean booleanValue(Object value) {
if (value == null)
return false;
Class c = value.getClass();
if (c == Boolean.class)
return (Boolean) value;
// if ( c == String.class )
// return ((String)value).length() > 0;
if (c == Character.class)
return (Character) value != 0;
if (value instanceof Number)
return ((Number) value).doubleValue() != 0;
return true; // non-null
}
public Enum<?> enumValue(Class toClass, Object o) {
Enum<?> result = null;
if (o == null) {
result = null;
} else if (o instanceof String[]) {
result = Enum.valueOf(toClass, ((String[]) o)[0]);
} else if (o instanceof String) {
result = Enum.valueOf(toClass, (String) o);
}
return result;
}
/**
* Evaluates the given object as a long integer.
*
* @param value
* an object to interpret as a long integer
* @return the long integer value implied by the given object
* @throws NumberFormatException
* if the given object can't be understood as a long integer
*/
public static long longValue(Object value) throws NumberFormatException {
if (value == null)
return 0L;
Class c = value.getClass();
if (c.getSuperclass() == Number.class)
return ((Number) value).longValue();
if (c == Boolean.class)
return (Boolean) value ? 1 : 0;
if (c == Character.class)
return (Character) value;
return Long.parseLong(stringValue(value, true));
}
/**
* Evaluates the given object as a double-precision floating-point number.
*
* @param value
* an object to interpret as a double
* @return the double value implied by the given object
* @throws NumberFormatException
* if the given object can't be understood as a double
*/
public static double doubleValue(Object value) throws NumberFormatException {
if (value == null)
return 0.0;
Class c = value.getClass();
if (c.getSuperclass() == Number.class)
return ((Number) value).doubleValue();
if (c == Boolean.class)
return (Boolean) value ? 1 : 0;
if (c == Character.class)
return (Character) value;
String s = stringValue(value, true);
return (s.length() == 0) ? 0.0 : Double.parseDouble(s);
/*
* For 1.1 parseDouble() is not available
*/
// return Double.valueOf( value.toString() ).doubleValue();
}
/**
* Evaluates the given object as a BigInteger.
*
* @param value
* an object to interpret as a BigInteger
* @return the BigInteger value implied by the given object
* @throws NumberFormatException
* if the given object can't be understood as a BigInteger
*/
public static BigInteger bigIntValue(Object value)
throws NumberFormatException {
if (value == null)
return BigInteger.valueOf(0L);
Class c = value.getClass();
if (c == BigInteger.class)
return (BigInteger) value;
if (c == BigDecimal.class)
return ((BigDecimal) value).toBigInteger();
if (c.getSuperclass() == Number.class)
return BigInteger.valueOf(((Number) value).longValue());
if (c == Boolean.class)
return BigInteger.valueOf((Boolean) value ? 1 : 0);
if (c == Character.class)
return BigInteger.valueOf(((Character) value).charValue());
return new BigInteger(stringValue(value, true));
}
/**
* Evaluates the given object as a BigDecimal.
*
* @param value
* an object to interpret as a BigDecimal
* @return the BigDecimal value implied by the given object
* @throws NumberFormatException
* if the given object can't be understood as a BigDecimal
*/
public static BigDecimal bigDecValue(Object value)
throws NumberFormatException {
if (value == null)
return BigDecimal.valueOf(0L);
Class c = value.getClass();
if (c == BigDecimal.class)
return (BigDecimal) value;
if (c == BigInteger.class)
return new BigDecimal((BigInteger) value);
if (c.getSuperclass() == Number.class)
return new BigDecimal(((Number) value).doubleValue());
if (c == Boolean.class)
return BigDecimal.valueOf((Boolean) value ? 1 : 0);
if (c == Character.class)
return BigDecimal.valueOf(((Character) value).charValue());
return new BigDecimal(stringValue(value, true));
}
/**
* Evaluates the given object as a String and trims it if the trim flag is
* true.
*
* @param value
* an object to interpret as a String
* @param trim
* trims the result if true
* @return the String value implied by the given object as returned by the
* toString() method, or "null" if the object is null.
*/
public static String stringValue(Object value, boolean trim) {
String result;
if (value == null) {
result = NULL_STRING;
} else {
result = value.toString();
if (trim) {
result = result.trim();
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* Evaluates the given object as a String.
*
* @param value
* an object to interpret as a String
* @return the String value implied by the given object as returned by the
* toString() method, or "null" if the object is null.
*/
public static String stringValue(Object value) {
return stringValue(value, false);
}
protected Locale getLocale(Map<String, Object> context) {
Locale locale = null;
if (context != null) {
locale = (Locale) context.get(ActionContext.LOCALE);
}
if (locale == null) {
LocaleProviderFactory localeProviderFactory = container.getInstance(LocaleProviderFactory.class);
locale = localeProviderFactory.createLocaleProvider().getLocale();
}
return locale;
}
}
但是我们还可以生成更加复杂的对象,比如Collection或者Map的实例。
input.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK" language="java" errorPage="" %>
<%@taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>直接封装成Map</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>直接封装成Map</h3>
<s:form action="login">
<s:textfield name="users['one'].name" label="第one个用户名"/>
<s:textfield name="users['one'].pass" label="第one个密码"/>
<s:textfield name="users['two'].name" label="第two个用户名"/>
<s:textfield name="users['two'].pass" label="第two个密码"/>
<tr>
<td colspan="2"><s:submit value="转换" theme="simple"/>
<s:reset value="重填" theme="simple"/></td>
</tr>
</s:form>
</body>
</html>
welcome.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK" language="java" errorPage="" %>
<%@taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>转换结果</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:actionmessage/>
key为one的用户名为:<s:property value="users['one'].name"/><br/>
key为one的密码为:<s:property value="users['one'].pass"/><br/>
key为two的用户名为:<s:property value="users['two'].name"/><br/>
key为two的密码为:<s:property value="users['two'].pass"/><br/>
</body>
</html>
struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd">
<struts>
<!-- 乱码解决 默认utf-8 是i18n(1 2 3 的1 internationalization中间18个单词) 不是il8n -->
<constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="GBK"></constant>
<package name="lee" extends="struts-default">
<action name="login" class="org.crazyit.app.action.LoginAction">
<result>/WEB-INF/content/welcome.jsp</result>
<result name="error">/WEB-INF/content/welcome.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="*">
<result>/WEB-INF/content/{1}.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>Action处理类
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import java.util.Map;
import org.crazyit.app.domain.*;
public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport{
// Action类里包含一个Map类型的成员变量
// Map的value类型为User类型
private Map<String , User> users;
// users的setter和getter方法
public void setUsers(Map<String , User> users){
this.users = users;
}
public Map<String , User> getUsers(){
return this.users;
}
public String execute() throws Exception{
// 在控制台输出Struts 2封装产生的Map对象
System.out.println(getUsers());
// 根据Map集合中key为one的User实例来决定控制逻辑
if (getUsers().get("one").getName().equals("张三")
&& getUsers().get("one").getPass().equals("123456") )
{
addActionMessage("登录成功!");
return SUCCESS;
}
addActionMessage("登录失败!!");
return ERROR;
}
}public class User{
private String name;
private String pass;
// name的setter和getter方法
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
// pass的setter和getter方法
public void setPass(String pass){
this.pass = pass;
}
public String getPass(){
return this.pass;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [name=" + name + ", pass=" + pass + "]";
}
}


上面生成了一个Map对象,程序必须使用泛型,同样的如果想把Map改成List<User>,只需要把上面的users['one'].name改成users[下标].name 即可。
如果我不用泛型要怎么办,这个时候就可以指定集合元素类型。
只需要一个局部类型转换文件即可,下面用List来演示。
局部类型转换文件:
命名:ActionName-conversion.properties ActionName时需要Action的类名,后面的固定。
位置:和Action类文件相同的位置。
配置文件写法:
Element_<ListPropName>=<ElementType> <ListPropName>替换成Listj集合属性的名称,<ElementType> 替换成集合元素类型。
LoginAction-conversion.properties
Element_users=org.crazyit.app.domain.UserMap集合需要写两个:
1)指定key
Key_<MapPropName>=<keyType> <MapPropName>时Map类型的属性,<keyType>Map key值的全限定类名。
2)指定value
Element_<MapPropName>=<ValueType> <MapPropName>时Map类型的属性,<ValueType>Map ValueType值的全限定类名。
比如
Key_users=java.lang.String
Element_users=org.crazyit.app.domain.User
struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd">
<struts>
<!-- 乱码解决 默认utf-8 是i18n(1 2 3 的1 internationalization中间18个单词) 不是il8n -->
<constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="GBK"></constant>
<package name="lee" extends="struts-default">
<action name="login" class="org.crazyit.app.action.LoginAction">
<result>/WEB-INF/content/welcome.jsp</result>
<result name="error">/WEB-INF/content/welcome.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="*">
<result>/WEB-INF/content/{1}.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>Action类
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import java.util.List;
import org.crazyit.app.domain.*;
public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport{
// Action类里包含一个不带泛型的List类型的成员变量
private List users;
// users的setter和getter方法
public void setUsers(List users){
this.users = users;
}
public List getUsers(){
return this.users;
}
public String execute() throws Exception{
// 在控制台输出Struts 2封装产生的List对象
System.out.println(getUsers());
// 因为没有使用泛型,所以要进行强制类型转换
User firstUser = (User)getUsers().get(0);
// users属性的第一个User实例来决定控制逻辑
if (firstUser.getName().equals("张三")
&& firstUser.getPass().equals("123456") )
{
addActionMessage("登录成功!");
return SUCCESS;
}
addActionMessage("登录失败!!");
return ERROR;
}
}public class User{
private String name;
private String pass;
//name属性的setter和getter方法
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
//pass属性的setter和getter方法
public void setPass(String pass){
this.pass = pass;
}
public String getPass(){
return this.pass;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [name=" + name + ", pass=" + pass + "]";
}
}input.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK" language="java" errorPage="" %>
<%@taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>直接封装成List</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>直接封装成List</h3>
<s:form action="login">
<s:textfield name="users[0].name" label="第一个用户名"/>
<s:textfield name="users[0].pass" label="第一个密码"/>
<s:textfield name="users[1].name" label="第二个用户名"/>
<s:textfield name="users[1].pass" label="第二个密码"/>
<tr>
<td colspan="2"><s:submit value="转换" theme="simple"/>
<s:reset value="重填" theme="simple"/></td>
</tr>
</s:form>
</body>
</html>welcome.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK" language="java" errorPage="" %>
<%@taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>转换结果</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:actionmessage/>
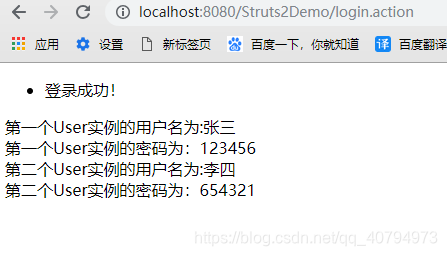
第一个User实例的用户名为:<s:property value="users[0].name"/><br/>
第一个User实例的密码为:<s:property value="users[0].pass"/><br/>
第二个User实例的用户名为:<s:property value="users[1].name"/><br/>
第二个User实例的密码为:<s:property value="users[1].pass"/><br/>
</body>
</html>

甚至可以处理Set集合,但是需要注意的是Set集合里的元素必须有一个唯一标识。
Action类
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.*;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Set;
public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport{
private Set users;
private Date birth;
// users的setter和getter方法
public void setUsers(Set users){
this.users = users;
}
public Set getUsers(){
return this.users;
}
// birth的setter和getter方法
public void setBirth(Date birth){
this.birth = birth;
}
public Date getBirth(){
return this.birth;
}
// 没有提供execute()方法,
// 将直接使用ActionSupport的execute()方法
}类型转换器
import java.util.*;
import org.apache.struts2.util.StrutsTypeConverter;
import org.crazyit.app.domain.*;
public class UserConverter extends StrutsTypeConverter{
public Object convertFromString(Map context, String[] values, Class toClass){
Set result = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length ; i++ ){
// 创建一个User实例
User user = new User();
// 只处理请求参数数组第一个数组元素,
// 并将该字符串以英文逗号分割成两个字符串
String[] userValues = values[i].split(",");
// 为User实例的属性赋值
user.setName(userValues[0]);
user.setPass(userValues[1]);
// 将User实例添加到Set集合中
result.add(user);
}
return result;
}
public String convertToString(Map context, Object o){
// 如果待转换对象的类型是Set
if (o.getClass() == Set.class){
Set users = (Set)o;
String result = "[";
for (Object obj : users ){
User user = (User)obj;
result += "<" + user.getName()
+ "," + user.getPass() + ">";
}
return result + "]";
}else{
return "";
}
}
}
上面代码实现了字符串数组和List结合的转换处理,还需要让struts2明白Set集合元素的标识属性,指定Struts2根据该标识属性来存取Set集合元素。
User类:
public class User{
private String name;
private String pass;
// name的setter和getter方法
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName()
{
return this.name;
}
// pass的setter和getter方法
public void setPass(String pass){
this.pass = pass;
}
public String getPass(){
return this.pass;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
// 如果待比较的两个对象是同一个对象,直接返回true
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
// 只有当obj是User对象
if (obj != null && obj.getClass() == User.class){
User user = (User)obj;
// 两个对象的name属性相等即认为二者相等
return this.getName().equals(user.getName());
}
return false;
}
// 根据name计算hashCode
public int hashCode(){
return name.hashCode();
}
}该User重写了 equals 和 hashCode,该User类的标识属性是name,当两个User的name相同时认为它们相同。
使用局部类型转换文件来指定Set元素的标识属性
写法:
KeyProperty_<SetPropName>=<KeyPropName> SetPropName替换成属性名 KeyPropName替换成元素的标识属性。
#指定users属性的类型转换器是UserConverter
users= org.crazyit.app.converter.UserConverter
# 指定users集合属性里集合元素的索引属性是name
KeyProperty_users=name
在jsp页面直接通过索引来访问Set元素
welcome.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=GBK"%>
<%@taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>转换结果</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:actionmessage/>
<s:property value="users"/>
<!-- 访问users集合属性里索引属性值为crazyit.org的元素的name属性-->
用户crazyit.org的用户名为:<s:property value="users('crazyit.org').name"/><br/>
<!-- 访问users集合属性里索引属性值为crazyit.org的元素的pass属性-->
用户crazyit.org的密码为:<s:property value="users('crazyit.org').pass"/><br/>
<!-- 访问users集合属性里索引属性值为fkit的元素的name属性-->
用户fkit的用户名为:<s:property value="users('fkit').name"/><br/>
<!-- 访问users集合属性里索引属性值为fkit的元素的pass属性-->
用户fkit的密码为:<s:property value="users('fkit').pass"/><br/>
生日为:<s:property value="birth"/><br/>
</body>
</html>访问Set元素用的是圆括号,而不是方括号。对于数组,List和Map属性,则通过方括号来访问指定集合元素。
input.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK" language="java" errorPage="" %>
<%@taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Set属性的类型转换</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Set属性的类型转换</h3>
<s:form action="login">
<s:textfield name="users" label="第一个用户信息"/>
<s:textfield name="users" label="第二个用户信息"/>
<s:textfield name="birth" label="用户生日"/>
<tr>
<td colspan="2"><s:submit value="转换" theme="simple"/>
<s:reset value="重填" theme="simple"/></td>
</tr>
</s:form>
</body>
</html>struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd">
<struts>
<constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="gbk"></constant>
<!-- 配置国际化资源文件 -->
<constant name="struts.custom.i18n.resources" value="GBK"/>
<package name="lee" extends="struts-default">
<!-- 定义处理用户请求的Action -->
<action name="login" class="org.crazyit.app.action.LoginAction">
<!-- 配置名为input的逻辑视图,当转换失败后转入该逻辑视图 -->
<result name="input">/WEB-INF/content/input.jsp</result>
<!-- 配置名为success的逻辑视图 -->
<result>/WEB-INF/content/welcome.jsp</result>
<result name="error">/WEB-INF/content/welcome.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="*">
<result>/WEB-INF/content/{1}.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts> 


二、但是对于自定义类型struts2没法去做类型转换工作。需要自定义类型转换器来实现类型的转换。
我想要实现一个点的输入比如(1,2)
输入页面
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="add.action" method="post">
坐标点::<input type="text" name="point">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>point类
public class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "toString方法: toString("+this.x+","+this.y+")";
}
}
Action处理类
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action;
import cn.sxt.vo.Point;
public class PointAction {
private Point point;
public Point getPoint() {
return point;
}
public void setPoint(Point point) {
this.point = point;
}
//获取页面提交的坐标点
public String execute() {
System.out.println("x="+point.getX()+"\ty="+point.getY());
return Action.SUCCESS;
}
}
struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
<package name="default" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="add" class="cn.sxt.action.PointAction">
<result >/sucess.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>就这样去输入提交的话会报错的(空指针异常),应为struts2无法处理。
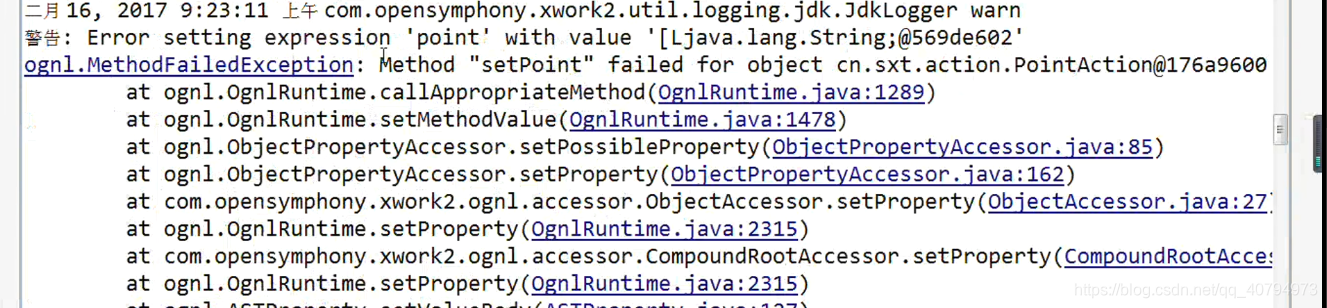

自定义类型转换器就是解决这种问题的。
2、类型转换的实现步骤
a)新建一个类型转换器类继承 StrutsTypeconverter类(实现两个抽象方法),继承DefaultTypeConverter也可以(只需要实现一个抽象方法)
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.struts2.util.StrutsTypeConverter;
import cn.sxt.vo.Point;
/**
* 之定义类型转换器
* @author yuanyu
*
*/
/*
* 使用类型转换的步骤:
a) 编写类型转换器--继承 StrutsTypeConverter 类
b) 编写 xwork-conversion.properties 的配置文件,放于 src 下;内容为 要转换的类型=类型转换器
*/
//DefaultTypeConverter
//static {
// Map<Class, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// map.put(Boolean.TYPE, Boolean.FALSE);
// map.put(Byte.TYPE, Byte.valueOf((byte) 0));
// map.put(Short.TYPE, Short.valueOf((short) 0));
// map.put(Character.TYPE, new Character((char) 0));
// map.put(Integer.TYPE, Integer.valueOf(0));
// map.put(Long.TYPE, Long.valueOf(0L));
// map.put(Float.TYPE, new Float(0.0f));
// map.put(Double.TYPE, new Double(0.0));
// map.put(BigInteger.class, new BigInteger("0"));
// map.put(BigDecimal.class, new BigDecimal(0.0));
// primitiveDefaults = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);
//}
//
//public abstract class StrutsTypeConverter extends DefaultTypeConverter {
// public Object convertValue(Map context, Object o, Class toClass) {
// if (toClass.equals(String.class)) {
// return convertToString(context, o);//对象转换为String
// } else if (o instanceof String[]) {
// return convertFromString(context, (String[]) o, toClass); //string 转换为对象
// } else if (o instanceof String) {
// return convertFromString(context, new String[]{(String) o}, toClass);
// } else {
// return performFallbackConversion(context, o, toClass);
// }
// }
public class PointConverter extends StrutsTypeConverter /**继承DefaultTypeConverter(默认类型转换器),也可以*/ {
/**
* 表达提交的数据在这个方法中被转换 将String 转换为指定的类型
* Converts one or more String values to the specified class.
*
* @param context the action context
* @param values the String values to be converted, such as those submitted from an HTML form 从表达上提交的字符串
* @param toClass the class to convert to 转换为这种类型
* @return the converted object
*/
@Override
public Object convertFromString(Map context, String[] values, Class toClass) {
System.out.println("PointConverter.convertFromString()");
String value = values[0];
Point point = new Point();
point.setX(Integer.parseInt(value.substring(1, value.indexOf(","))));//(1,2)
point.setY(Integer.parseInt(value.substring(value.indexOf(",")+1, value.lastIndexOf(")"))));
return point;
}
/**
*将指定的类型转换为Strig
*使用ognl表达式获取值时会调用该方法 EL表达式获取的时候不会调用
* Converts the specified object to a String.
*
* @param context the action context
* @param o the object to be converted
* @return the converted String
*/
@Override
public String convertToString(Map context, Object o) {
System.out.println("PointConverter.convertToString()");
Point p = (Point)o;
return "("+p.getX()+","+p.getY()+")";
}
}
b)在src下创建xwork-conversion.properties配置文件(全局类型转换器 用什么类型转换器去转换它)。当默认的类型转换器没有时它会去找自己定义的类型转换器。
#be converted type=converter
cn.sxt.vo.Point=cn.sxt.converter.PointConverter显示页面
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>(${point.x},${point.y})</h1>
<h1>EL表达式获取:${point}</h1>
<h1>ognl表达式或:<s:property value="point"/></h1>
</body>


需要重新point的toStrin()方法,不然后面打印出来的是地址。
使用ognl表达式获取值时才会调用convertToString()方法,数据的赋值就是通过ognl表达式和类型转换器,由于数据被放在了请求域里面,我可以直接用el表达式去获取,el表达式是不会用convertToString()方法的,struts2是推荐用ognl表达式获取值的。
























 634
634

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








