UDP报文
UDP 报文也被称为用户数据报,与 ICMP协议一样,由报文首部与数据区域组成。在UDP 协议中, 它只是简单将应用层的数据进行封装(添加一个 UDP 报文首部), 然后传递到 IP 层, 再通过网卡发送出去, 因此, UDP 数据也是经过两次封装, 具体见图
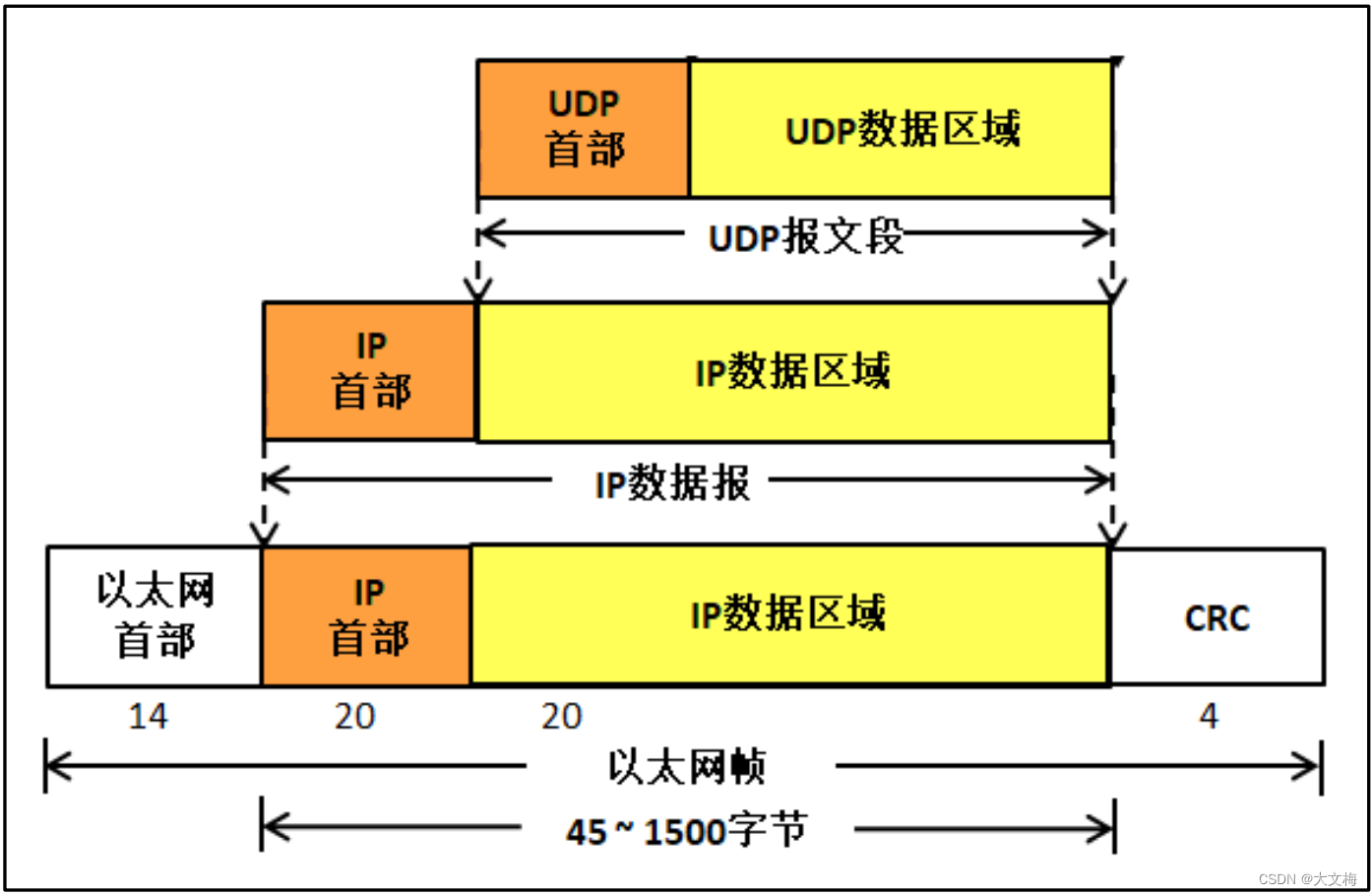
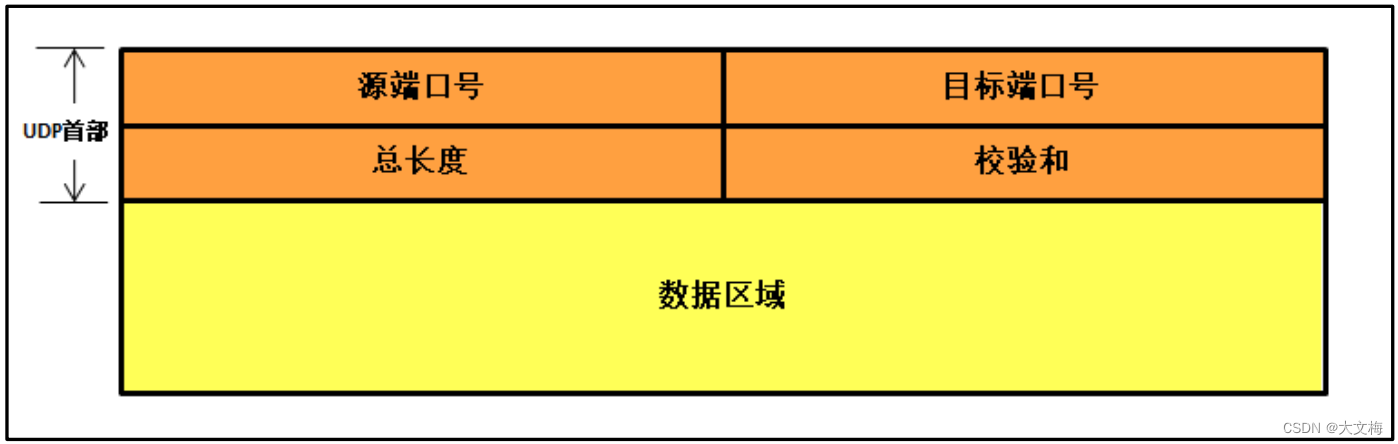
关于源端口号、目标端口号与校验和字段的作用与 TCP 报文段一样,端口号的取值在0~65535 之间; 16bit 的总长度用于记录 UDP 报文的总长度,包括 8 字节的首部长度与数据区域。
UDP报文的数据结构
LwIP 定义了一个 UDP 报文首部数据结构
PACK_STRUCT_BEGIN
struct udp_hdr {
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t src);
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t dest); /* src/dest UDP ports */
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t len);
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t chksum);
} PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT;
PACK_STRUCT_END
为了更好管理 UDP 报文, LwIP 定义了一个 UDP 控制块,记录与UDP 通信的所有信息,如源端口号、目标端口号、源 IP 地址、目标 IP 地址以及收到数据时候的回调函数等等,系统会为每一个基于 UDP 协议的应用线程创建一个 UDP 控制块,并且将其与对应的端口绑定,这样子就能进行 UDP 通信了。
#define IP_PCB \
/* ip addresses in network byte order */ \
/* 本地 ip 地址与远端 IP 地址 */ \
ip_addr_t local_ip; \
ip_addr_t remote_ip; \
/* Bound netif index 网卡 id*/ \
u8_t netif_idx; \
/* Socket options Socket 选项 */ \
u8_t so_options; \
/* Type Of Service 服务类型*/ \
u8_t tos; \
/* Time To Live 生存时间 */ \
u8_t ttl \
/* link layer address resolution hint */ \
IP_PCB_NETIFHINT
/** the UDP protocol control block UDP 控制块 */
struct udp_pcb {
/** Common members of all PCB types */
IP_PCB;
/* Protocol specific PCB members */
struct udp_pcb *next; //指向下一个控制块
u8_t flags; //控制块状态
/** ports are in host byte order */
u16_t local_port, remote_port; /** 本地端口号与远端端口号 */
/** receive callback function */
udp_recv_fn recv; /** 接收回调函数 */
/** user-supplied argument for the recv callback */
void *recv_arg; /** 回调函数参数 */
};
//udp_recv_fn 函数原型
typedef void (*udp_recv_fn)(void *arg,
struct udp_pcb *pcb,
struct pbuf *p,
const ip_addr_t *addr,
u16_t port);
UDP 控制块会使用 IP 层的一个宏定义 IP_PCB, 里面包括 IP 层需要使用的信息, 如本地 IP 地址与目标 IP 地址(或者称为远端 IP 地址),服务类型、网卡、生存时间等,此外UDP 控制块还要本地端口号与目标(远端)端口号,这两个字段很重要, UDP 协议就是根据这些端口号识别应用线程,当 UDP 收到一个报文的时候,会遍历链表上的所有控制块,根据报文的目标端口号找到与本地端口号相匹配的 UDP 控制块,然后递交数据到上层应用,而如果找不到对应的端口号,那么就会返回一个端口不可达 ICMP 差错控制报文。
一般来说, 我们使用 NETCONN API 或者是 Socket API 编程, 是不需要我们自己去注册回调函数 recv_udp(), 因为这个函数 LwIP 内核会自动给我们注册,具体见代码清单。
void
udp_recv(struct udp_pcb *pcb, udp_recv_fn recv, void *recv_arg)
{
LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED();
LWIP_ERROR("udp_recv: invalid pcb", pcb != NULL, return);
/* remember recv() callback and user data */
pcb->recv = recv;
pcb->recv_arg = recv_arg;
}
static void
pcb_new(struct api_msg *msg)
{
enum lwip_ip_addr_type iptype = IPADDR_TYPE_V4;
LWIP_ASSERT("pcb_new: pcb already allocated", msg->conn->pcb.tcp == NULL);
/* Allocate a PCB for this connection */
switch (NETCONNTYPE_GROUP(msg->conn->type)) {
#if LWIP_UDP
case NETCONN_UDP:
msg->conn->pcb.udp = udp_new_ip_type(iptype);
if (msg->conn->pcb.udp != NULL) {
if (NETCONNTYPE_ISUDPNOCHKSUM(msg->conn->type)) {
udp_setflags(msg->conn->pcb.udp, UDP_FLAGS_NOCHKSUM);
}
udp_recv(msg->conn->pcb.udp, recv_udp, msg->conn); //注册recv_udp函数到udp控制块
}
break;
#endif /* LWIP_UDP */
default:
/* Unsupported netconn type, e.g. protocol disabled */
msg->err = ERR_VAL;
return;
}
if (msg->conn->pcb.ip == NULL) {
msg->err = ERR_MEM;
}
}
/**
* Receive callback function for UDP netconns.
* Posts the packet to conn->recvmbox or deletes it on memory error.
*
* @see udp.h (struct udp_pcb.recv) for parameters
*/
static void
recv_udp(void *arg, struct udp_pcb *pcb, struct pbuf *p,
const ip_addr_t *addr, u16_t port)
{
struct netbuf *buf;
struct netconn *conn;
u16_t len;
conn = (struct netconn *)arg; //获取当前UDP控制卡的连接结构
if (conn == NULL) {
pbuf_free(p);
return;
}
pbuf_free(p);
return;
}
buf = (struct netbuf *)memp_malloc(MEMP_NETBUF);
if (buf == NULL) {
pbuf_free(p);
return;
} else {
buf->p = p;
buf->ptr = p;
ip_addr_set(&buf->addr, addr);
buf->port = port;
}
len = p->tot_len;
if (sys_mbox_trypost(&conn->recvmbox, buf) != ERR_OK) { //投递邮箱,告知线程接受
netbuf_delete(buf);
return;
} else {
#if LWIP_SO_RCVBUF
SYS_ARCH_INC(conn->recv_avail, len);
#endif /* LWIP_SO_RCVBUF */
/* Register event with callback */
API_EVENT(conn, NETCONN_EVT_RCVPLUS, len);
}
}
UDP报文发送
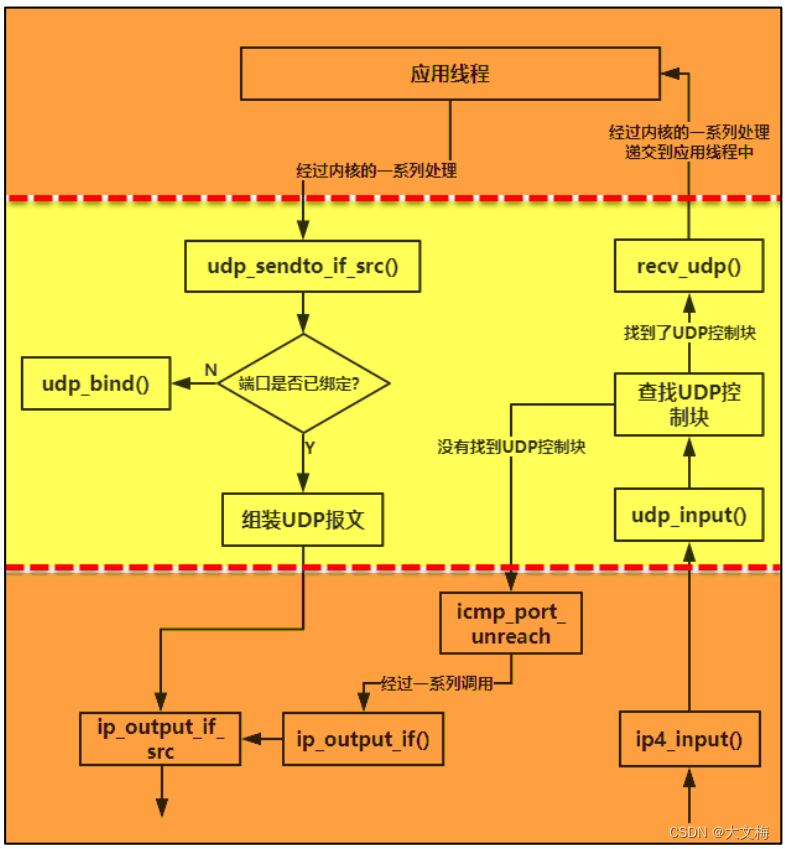
UDP 协议是传输层,所以需要从上层应用线程中得到数据,我们使用 NETCONN API或者是 Socket API 编程,那么传输的数据经过内核的层层处理,最后调用udp_sendto_if_src()函数进行发送 UDP 报文,具体见代码清单
/** @ingroup udp_raw
* Same as @ref udp_sendto_if, but with source address */
err_t
udp_sendto_if_src(struct udp_pcb *pcb, struct pbuf *p,
const ip_addr_t *dst_ip, u16_t dst_port, struct netif *netif, const ip_addr_t *src_ip)
{
struct udp_hdr *udphdr;
err_t err;
struct pbuf *q; /* q will be sent down the stack */
u8_t ip_proto;
u8_t ttl;
LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED();
if (!IP_ADDR_PCB_VERSION_MATCH(pcb, src_ip) ||
!IP_ADDR_PCB_VERSION_MATCH(pcb, dst_ip)) {
return ERR_VAL;
}
/* if the PCB is not yet bound to a port, bind it here */
/* 如果 UDP 控制块尚未绑定到端口,请将其绑定到这里 */
if (pcb->local_port == 0) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("udp_send: not yet bound to a port, binding now\n"));
err = udp_bind(pcb, &pcb->local_ip, pcb->local_port);
if (err != ERR_OK) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE | LWIP_DBG_LEVEL_SERIOUS, ("udp_send: forced port bind failed\n"));
return err;
}
}
/* packet too large to add a UDP header without causing an overflow? */
/* 数据包太大,无法添加 UDP 首部 */
if ((u16_t)(p->tot_len + UDP_HLEN) < p->tot_len) {
return ERR_MEM;
}
/* not enough space to add an UDP header to first pbuf in given p chain? */
/* 没有足够的空间将 UDP 首部添加到给定的 pbuf 中 */
if (pbuf_add_header(p, UDP_HLEN)) {
/* allocate header in a separate new pbuf */
/* 在一个单独的新 pbuf 中分配标头 */
q = pbuf_alloc(PBUF_IP, UDP_HLEN, PBUF_RAM);
/* new header pbuf could not be allocated? */
if (q == NULL) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE | LWIP_DBG_LEVEL_SERIOUS, ("udp_send: could not allocate header\n"));
return ERR_MEM;
}
if (p->tot_len != 0) {
/* chain header q in front of given pbuf p (only if p contains data) */
/* 把首部 pbuf 和数据 pbuf 连接到一个 pbuf 链表上 */
pbuf_chain(q, p);
}
/* first pbuf q points to header pbuf */
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG,
("udp_send: added header pbuf %p before given pbuf %p\n", (void *)q, (void *)p));
} else {
/* adding space for header within p succeeded */
/* first pbuf q equals given pbuf */
q = p;
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG, ("udp_send: added header in given pbuf %p\n", (void *)p));
}
LWIP_ASSERT("check that first pbuf can hold struct udp_hdr",
(q->len >= sizeof(struct udp_hdr)));
/* q now represents the packet to be sent */
/* 填写 UDP 首部各个字段 */
udphdr = (struct udp_hdr *)q->payload;
udphdr->src = lwip_htons(pcb->local_port);
udphdr->dest = lwip_htons(dst_port);
/* in UDP, 0 checksum means 'no checksum' */
udphdr->chksum = 0x0000;
{ /* UDP */
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG, ("udp_send: UDP packet length %"U16_F"\n", q->tot_len));
udphdr->len = lwip_htons(q->tot_len);
/* calculate checksum */
ip_proto = IP_PROTO_UDP;
}
ttl = pcb->ttl;
#endif /* LWIP_MULTICAST_TX_OPTIONS */
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG, ("udp_send: UDP checksum 0x%04"X16_F"\n", udphdr->chksum));
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG, ("udp_send: ip_output_if (,,,,0x%02"X16_F",)\n", (u16_t)ip_proto));
/* output to IP */
NETIF_SET_HINTS(netif, &(pcb->netif_hints));
err = ip_output_if_src(q, src_ip, dst_ip, ttl, pcb->tos, ip_proto, netif); //发送到IP层
NETIF_RESET_HINTS(netif);
/* @todo: must this be increased even if error occurred? */
MIB2_STATS_INC(mib2.udpoutdatagrams);
/* did we chain a separate header pbuf earlier? */
if (q != p) {
/* free the header pbuf */
pbuf_free(q);
q = NULL;
/* p is still referenced by the caller, and will live on */
}
UDP_STATS_INC(udp.xmit);
return err;
}
UDP报文接收
当有一个 UDP 报文被 IP 层接收的时候, IP 层会调用udp_input()函数将报文传递到传输层, LwIP 就会去处理这个 UDP 报文, UDP 协议会对报文进行一些合法性的检测,如果确认了这个报文是合法的,那么就遍历 UDP 控制块链表,在这些控制块中找到对应的端口,然后递交到应用层,首先要判断本地端口号、本地 IP 地址与报文中的目标端口号、目标 IP 地址是否匹配,如果匹配就说明这个报文是给我们的,然后调用用户的回调函数 recv_udp()将受到的数据传递给上层应用。而如果找不到对应的端口,那么将返回一个端口不可达 ICMP 差错控制报文到源主机,当然, 如果 LwIP 接收到这个端口不可达 ICMP 报文,也是不会去处理它的, udp_input()函数源码具体见。
/**
* Process an incoming UDP datagram.
*
* Given an incoming UDP datagram (as a chain of pbufs) this function
* finds a corresponding UDP PCB and hands over the pbuf to the pcbs
* recv function. If no pcb is found or the datagram is incorrect, the
* pbuf is freed.
*
* @param p pbuf to be demultiplexed to a UDP PCB (p->payload pointing to the UDP header)
* @param inp network interface on which the datagram was received.
*
*/
void
udp_input(struct pbuf *p, struct netif *inp)
{
struct udp_hdr *udphdr;
struct udp_pcb *pcb, *prev;
struct udp_pcb *uncon_pcb;
u16_t src, dest;
u8_t broadcast;
u8_t for_us = 0;
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(inp);
LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED();
PERF_START;
UDP_STATS_INC(udp.recv);
/* Check minimum length (UDP header) */
if (p->len < UDP_HLEN) { //检查最小长度
/* drop short packets */
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG,
("udp_input: short UDP datagram (%"U16_F" bytes) discarded\n", p->tot_len));
UDP_STATS_INC(udp.lenerr);
UDP_STATS_INC(udp.drop);
MIB2_STATS_INC(mib2.udpinerrors);
pbuf_free(p);
goto end;
}
//指向 UDP 报文首部,并且强制转换成 udp_hdr 类型,方便操作
udphdr = (struct udp_hdr *)p->payload;
/* is broadcast packet ? *//* 判断一下是不是广播包 */
broadcast = ip_addr_isbroadcast(ip_current_dest_addr(), ip_current_netif());
/* convert src and dest ports to host byte order */
/* 得到 UDP 首部中的源主机和目标主机端口号 */
src = lwip_ntohs(udphdr->src);
dest = lwip_ntohs(udphdr->dest);
udp_debug_print(udphdr);
pcb = NULL;
prev = NULL;
uncon_pcb = NULL;
/* Iterate through the UDP pcb list for a matching pcb.
* 'Perfect match' pcbs (connected to the remote port & ip address) are
* preferred. If no perfect match is found, the first unconnected pcb that
* matches the local port and ip address gets the datagram. */
//遍历 UDP 链表,找到对应的端口号,如果找不到,
//那就用链表的第一个未使用的 UDP 控制块
for (pcb = udp_pcbs; pcb != NULL; pcb = pcb->next) {
/* compare PCB local addr+port to UDP destination addr+port */
/* 将 UDP 控制块本地地址+端口与 UDP 目标地址+端口进行比较 */
if ((pcb->local_port == dest) &&
(udp_input_local_match(pcb, inp, broadcast) != 0)) {
if ((pcb->flags & UDP_FLAGS_CONNECTED) == 0) {
if (uncon_pcb == NULL) {
/* the first unconnected matching PCB *//* 如果未找到使用第一个 UDP 控制块 */
uncon_pcb = pcb;
#if LWIP_IPV4
} else if (broadcast && ip4_current_dest_addr()->addr == IPADDR_BROADCAST) {
/* global broadcast address (only valid for IPv4; match was checked before) */
if (!IP_IS_V4_VAL(uncon_pcb->local_ip) || !ip4_addr_cmp(ip_2_ip4(&uncon_pcb->local_ip), netif_ip4_addr(inp))) {
/* uncon_pcb does not match the input netif, check this pcb */
if (IP_IS_V4_VAL(pcb->local_ip) && ip4_addr_cmp(ip_2_ip4(&pcb->local_ip), netif_ip4_addr(inp))) {
/* better match */
uncon_pcb = pcb;
}
}
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
}
}
/* compare PCB remote addr+port to UDP source addr+port */
/* 将 UDP 控制块的目标地址+端口与 UDP 控制块源地址+端口进行比较 */
if ((pcb->remote_port == src) &&
(ip_addr_isany_val(pcb->remote_ip) ||
ip_addr_cmp(&pcb->remote_ip, ip_current_src_addr()))) {
/* the first fully matching PCB *//* 第一个完全匹配的 UDP 控制块 */
if (prev != NULL) {
/* move the pcb to the front of udp_pcbs so that is
found faster next time */
/* 将 UDP 控制块移动到 udp_pcbs 的前面,这样就可以在下次查找的时候处理速度更快 */
prev->next = pcb->next;
pcb->next = udp_pcbs;
udp_pcbs = pcb;
} else {
UDP_STATS_INC(udp.cachehit);
}
break;
}
}
prev = pcb;
}
/* no fully matching pcb found? then look for an unconnected pcb */
/* 找不到完全匹配的 UDP 控制块? 将第一个未使用的 UDP 控制块作为匹配结果 */
if (pcb == NULL) {
pcb = uncon_pcb;
}
/* Check checksum if this is a match or if it was directed at us. */
/* 检查校验和是否匹配或是否匹配。 */
if (pcb != NULL) {
for_us = 1;
} else {
#if LWIP_IPV4
if (!ip_current_is_v6()) {
for_us = ip4_addr_cmp(netif_ip4_addr(inp), ip4_current_dest_addr());
}
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
}
if (for_us) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("udp_input: calculating checksum\n"));
if (pbuf_remove_header(p, UDP_HLEN)) { //调整报文的数据区域指针
/* Can we cope with this failing? Just assert for now */
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_remove_header failed\n", 0);
UDP_STATS_INC(udp.drop);
MIB2_STATS_INC(mib2.udpinerrors);
pbuf_free(p);
goto end;
}
if (pcb != NULL) { //如果找到对应的控制块
MIB2_STATS_INC(mib2.udpindatagrams);
/* callback */
if (pcb->recv != NULL) { /* 回调函数,将数据递交给上层应用 */
/* now the recv function is responsible for freeing p */
pcb->recv(pcb->recv_arg, pcb, p, ip_current_src_addr(), src); //调用recv_udp()
} else {
/* no recv function registered? then we have to free the pbuf! */
pbuf_free(p);
goto end;
}
} else { /* 没有找到匹配的控制块,返回端口不可达 ICMP 报文 */
LWIP_DEBUGF(UDP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("udp_input: not for us.\n"));
#if LWIP_ICMP || LWIP_ICMP6
/* No match was found, send ICMP destination port unreachable unless
destination address was broadcast/multicast. */
if (!broadcast && !ip_addr_ismulticast(ip_current_dest_addr())) {
/* move payload pointer back to ip header */
pbuf_header_force(p, (s16_t)(ip_current_header_tot_len() + UDP_HLEN));
icmp_port_unreach(ip_current_is_v6(), p);
}
#endif /* LWIP_ICMP || LWIP_ICMP6 */
UDP_STATS_INC(udp.proterr);
UDP_STATS_INC(udp.drop);
MIB2_STATS_INC(mib2.udpnoports);
pbuf_free(p);
}
} else {
pbuf_free(p);
}
end:
PERF_STOP("udp_input");
return;
}
虽然 udp_input()函数看起来很长,但是其实是非常简单的处理,主要就是遍历 UDP 控制块链表 udp_pcbs 找到对应的 UDP 控制块, 然后将去掉 UDP 控制块首部信息, 提取 UDP报文数据递交给应用程序, 而递交的函数就是在 UDP 控制块初始化时注册的回调函数, 即recv_udp(),而这个函数会让应用能读取到数据,然后做对应的处理。






















 3462
3462











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










