前言
上一篇博客中我们完成了 Lab0,使用双端队列实现了一个字节流类 ByteStream,可以向字节流中写入数据并按写入顺序读出数据。由于网络环境的变化,发送端滑动窗口内的数据包到达接收端时可能失序,所以接收端收到数据之后不能直接写入 ByteStream 中,而是应该缓存下来并按照序号重组成正确的数据。这篇博客所介绍的 Lab1 将实现一个字节流重组器 StreamReassambler 来完成上述任务。
实验要求
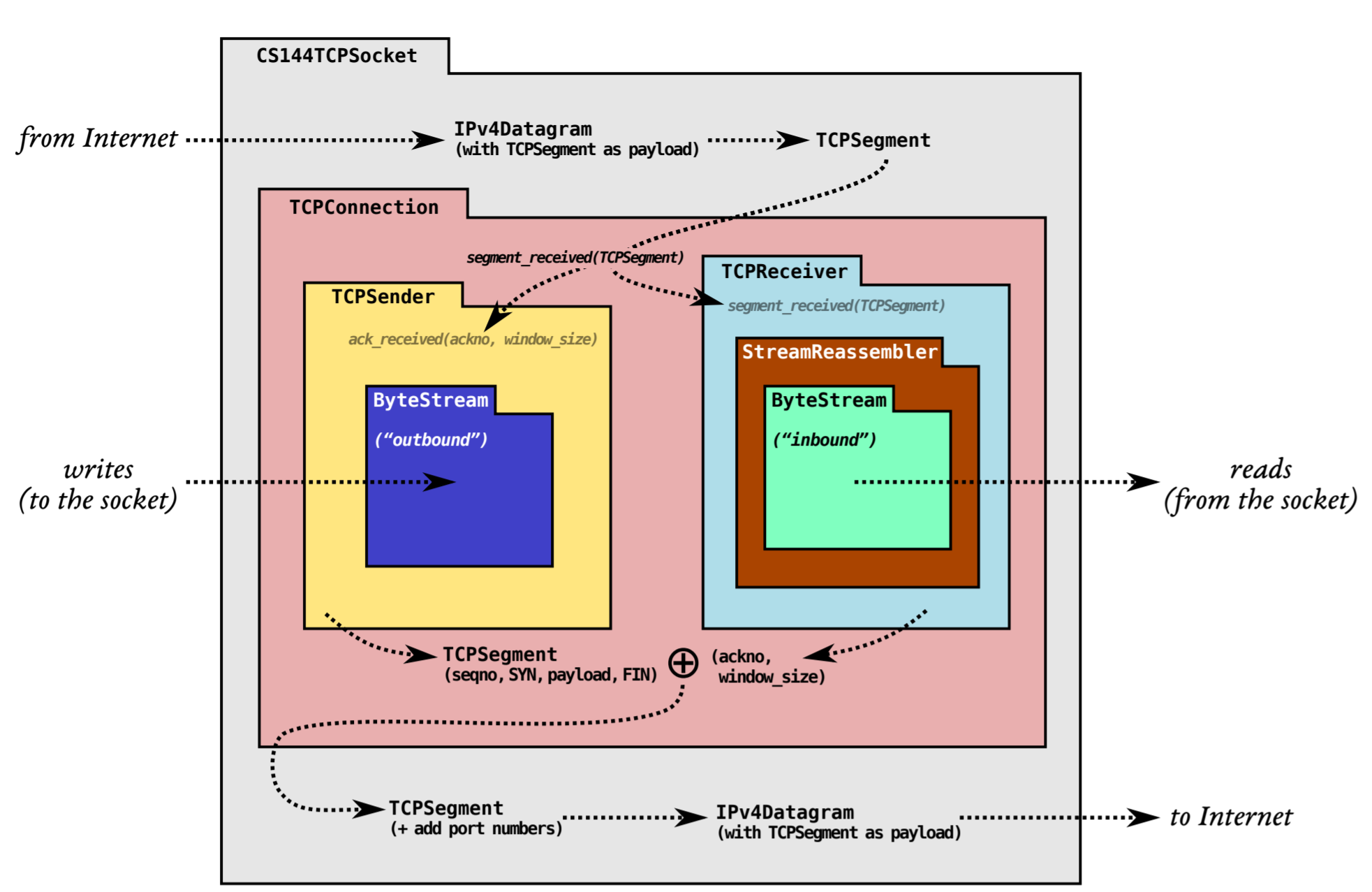
接收方的数据情况如下图所示,蓝色部分表示已消费的数据,绿色表示已正确重组但是还没消费的数据,红色则是失序到达且还没重组的数据:
由于接收端缓冲区大小 capacity 有限,超出容量的数据(first unacceptable 之后的数据)将被丢弃,这些被丢弃的数据包将起到流量控制的作用,可以限制发送端滑动窗口的大小。
流重组器的接口如下所示:
复制StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity);
//! \brief Receives a substring and writes any newly contiguous bytes into the stream.
//!
//! If accepting all the data would overflow the `capacity` of this
//! `StreamReassembler`, then only the part of the data that fits will be
//! accepted. If the substring is only partially accepted, then the `eof`
//! will be disregarded.
//!
//! \param data the string being added
//! \param index the index of the first byte in `data`
//! \param eof whether or not this segment ends with the end of the stream
void push_substring(const std::string &data, const uint64_t index, const bool eof);
//! Access the reassembled byte stream
const ByteStream &stream_out() const { return _output; }
ByteStream &stream_out() { return _output; }
//! The number of bytes in the substrings stored but not yet reassembled
size_t unassembled_bytes() const;
//! Is the internal state empty (other than the output stream)?
bool empty() const;
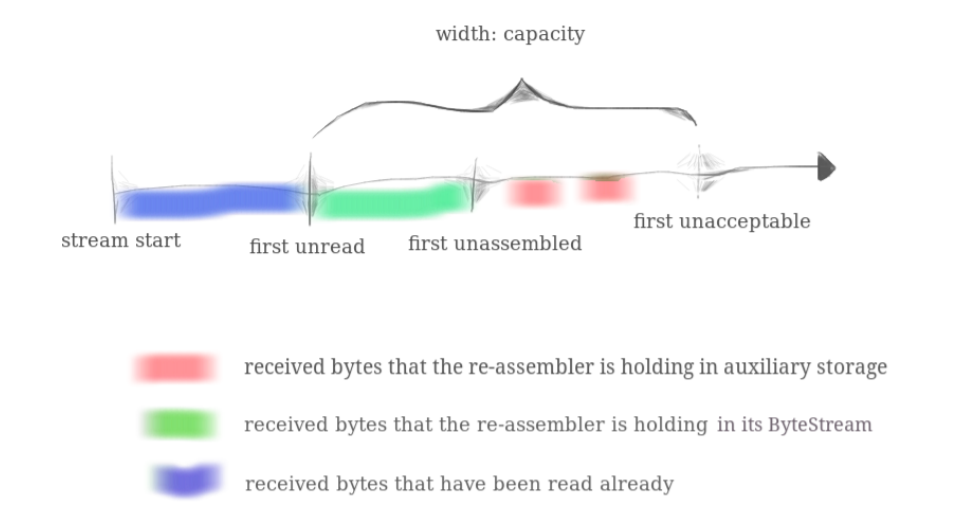
其中最重要的函数就是 StreamReassambler::push_substring(),接收方收到数据之后就会调用此函数将数据保存起来。此函数接受三个参数:
data: 接收到的数据index: 数据的第一个字节的索引,由于原始数据可能很大,超过了 TCPSegment 的容量,所以会将原始数据切分成多个片段,每个片段的第一个字节的索引就是index,最小值为 0。请注意,这个index是流索引,不是报文段包头上的那个序列号,二者的关系将在 Lab2 中指出。eof:是不是最后一个数据包
三个参数中,最耐人寻味的就是 index 参数,如果只是单纯的失序到达,数据之间没有发生重叠,Lab1 就比较好做了,但是实验指导书中明确指出
May substrings overlap? Yes
这就比较难搞了,因为重叠分成两种:
实际上由于 data 的末尾可能超出 first unacceptable,需要对超出部分进行截断,这可能导致 eof 标志失效,但是问题不大,发送方之后会重新发送这个数据包。
代码实现
为了处理上述重叠情况,需要一个 _next_index 成员代表 first unassembled 索引,一个 _unassembles 双端队列代表 first unassembled 到 first unacceptable 之间的数据,由于里面可能只有一部分数据是有效的,所以用一个遮罩 _unassembled_mask 指出哪些数据是有效但是还没重组的。
复制class StreamReassembler {
private:
ByteStream _output; //!< The reassembled in-order byte stream
size_t _capacity; //!< The maximum number of bytes
std::deque<char> _unassembles{};
std::deque<bool> _unassemble_mask{};
size_t _unassambled_bytes{0};
uint64_t _next_index{0};
bool _is_eof{false};
/** @brief 将数据写入未重组队列中
* @param data 将被写入的字符串
* @param dstart 字符串开始写入的位置
* @param len 写入的长度
* @param astart 队列中开始写入的位置
*/
void write_unassamble(const std::string &data, size_t dstart, size_t len, size_t astart);
/** @brief 重组数据
*/
void assemble();
public:
StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity);
//! \brief Receives a substring and writes any newly contiguous bytes into the stream.
void push_substring(const std::string &data, const uint64_t index, const bool eof);
//! \name Access the reassembled byte stream
const ByteStream &stream_out() const { return _output; }
ByteStream &stream_out() { return _output; }
//! The number of bytes in the substrings stored but not yet reassembled
size_t unassembled_bytes() const;
bool empty() const;
};
收到数据时,先将不重叠的数据写入 _unassembles 队列中,之后调用 StreamReassabler::assemble() 函数重组队列中的连续数据,并更新 _next_index:
复制StreamReassembler::StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity)
: _output(capacity), _capacity(capacity), _unassembles(capacity, '\0'), _unassemble_mask(capacity, false) {}
//! \details This function accepts a substring (aka a segment) of bytes,
//! possibly out-of-order, from the logical stream, and assembles any newly
//! contiguous substrings and writes them into the output stream in order.
void StreamReassembler::push_substring(const string &data, const size_t index, const bool eof) {
if (index > _next_index + _capacity)
return;
if (eof)
_is_eof = true;
if (_is_eof && empty() && data.empty()) {
_output.end_input();
return;
}
auto end_index = data.size() + index;
// 新数据在后面
if (index >= _next_index) {
auto astart = index - _next_index;
auto len = min(_output.remaining_capacity() - astart, data.size());
if (len < data.size())
_is_eof = false;
write_unassamble(data, 0, len, astart);
}
// 新数据与已重组的数据部分重叠
else if (end_index > _next_index) {
auto dstart = _next_index - index;
auto len = min(_output.remaining_capacity(), data.size() - dstart);
if (len < data.size() - dstart)
_is_eof = false;
write_unassamble(data, dstart, len, 0);
}
// 最后合并数据
assemble();
if (_is_eof && empty())
_output.end_input();
}
void StreamReassembler::write_unassamble(const string &data, size_t dstart, size_t len, size_t astart) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if (_unassemble_mask[i + astart])
continue;
_unassembles[i + astart] = data[dstart + i];
_unassemble_mask[i + astart] = true;
_unassambled_bytes++;
}
}
void StreamReassembler::assemble() {
string s;
while (_unassemble_mask.front()) {
s.push_back(_unassembles.front());
_unassembles.pop_front();
_unassemble_mask.pop_front();
_unassembles.push_back('\0');
_unassemble_mask.push_back(false);
}
if (s.empty())
return;
_output.write(s);
_next_index += s.size();
_unassambled_bytes -= s.size();
}
size_t StreamReassembler::unassembled_bytes() const { return _unassambled_bytes; }
bool StreamReassembler::empty() const { return _unassambled_bytes == 0; }
在命令行中输入:
复制cd build
make -j8
make check_lab1
可以看到测试用例也全部通过了:
调试代码
由于使用代码编辑器的是 VSCode,所以这里给出在 VSCode 中调试项目代码的方式。
tasks.json
首先在项目目录下创建 .vscode 文件夹,并新建一个 tasks.json 文件,在里面写入下述内容:
复制{
"tasks": [
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "cmake",
"command": "cd build && cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug",
"detail": "CMake 生成 Makefile",
"args": [],
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
},
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "build",
"command": "cd build && make -j8",
"detail": "编译项目",
"args": [],
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
},
],
"version": "2.0.0"
}
这里主要配置了两个任务,一个调用 CMake 生成 Makefile,一个编译 Makefile。在 VSCode 中按下 Alt + T + R,就能在任务列表中看到这两个任务,点击之后就能执行。
launch.json
在 .vscode 文件夹中新建 launch.json,并写入下述内容:
复制{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "debug lab test",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/build/tests/${fileBasenameNoExtension}",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"miDebuggerPath": "/usr/bin/gdb"
},
{
"name": "debug current file",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "C/C++: g++ build active file",
"miDebuggerPath": "/usr/bin/gdb"
}
]
}
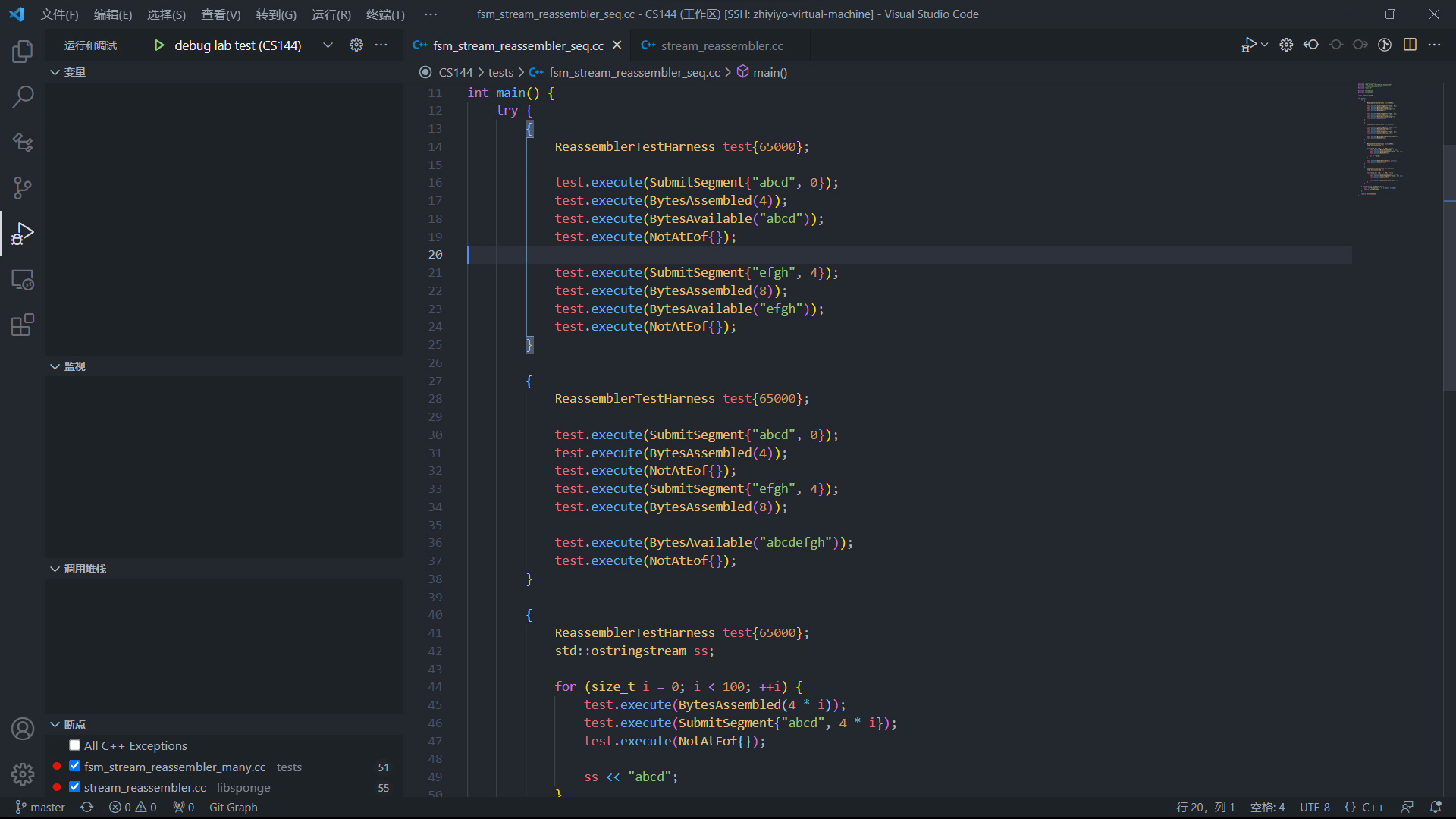
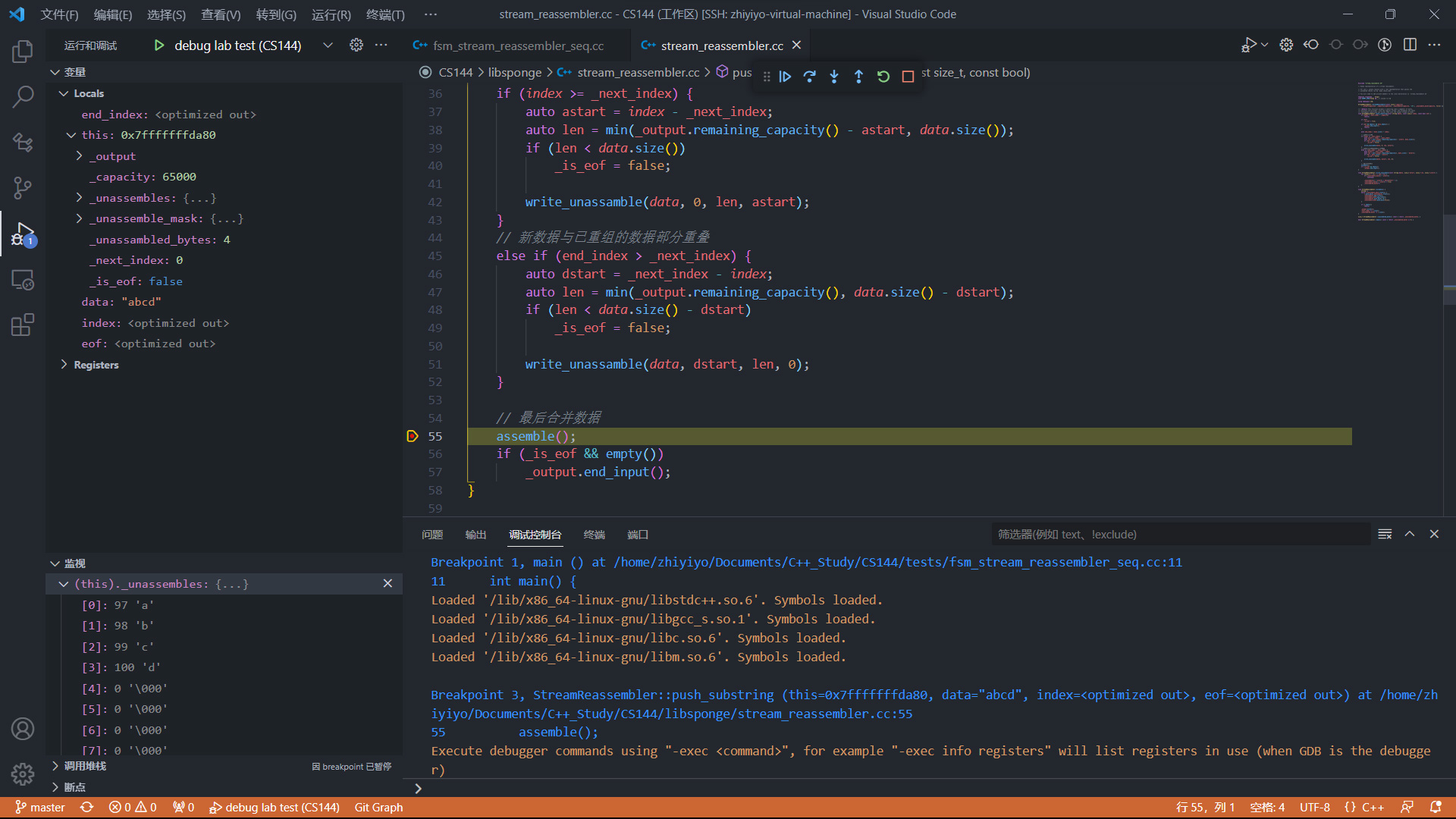
之后打开一个测试用例,比如 tests/fsm_stream_reassembler_seq.cc,转到 debug 标签页,在代码中打下断点, 点击绿色按钮就能开始调试了:
调试效果如下图所示:
后记
通过这次实验,可以加深对接收端数据重组和分组序号的了解,期待后面的几个实验,以上~~























 888
888











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










