文章目录
一、MapReduce架构体系
一个完整的mapreduce程序在分布式运行时有三类实例进程:
1、MRAppMaster: 负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调
2、MapTask:负责map阶段的整个数据处理流程
3、ReduceTask:负责reduce阶段的额整个数据处理流程
- MapReduce分布式的运算程序需要分成2个阶段,分别是Map阶段和Reduce阶段。Map阶段对应的是MapTask并发实例,完全并行运行。Reduce阶段对应的是ReduceTask并发实例,数据依赖于上一个阶段所有MapTask并发实例的数据输出结果。
- MapReduce编程模型只能包含一个Map阶段和一个Reduce阶段,如果用户的业务逻辑非常复杂,那就只能多个MapReduce程序,串行运行。
- 用户编写的程序分成三个部分:Mapper,Reducer,Driver(提交运行mr程序的客户端驱动)。
- 用户自定义的Mapper和Reducer都要继承各自的父类。Mapper中的业务逻辑写在map()方法中,Reducer的业务逻辑写在reduce()方法中。整个程序需要一个Driver来进行提交,提交的是一个描述了各种必要信息的job对象。
- 整个MapReduce程序中,数据都是以kv键值对的形式流转的。
二、MapReduce的分区
2.1 MR框架图
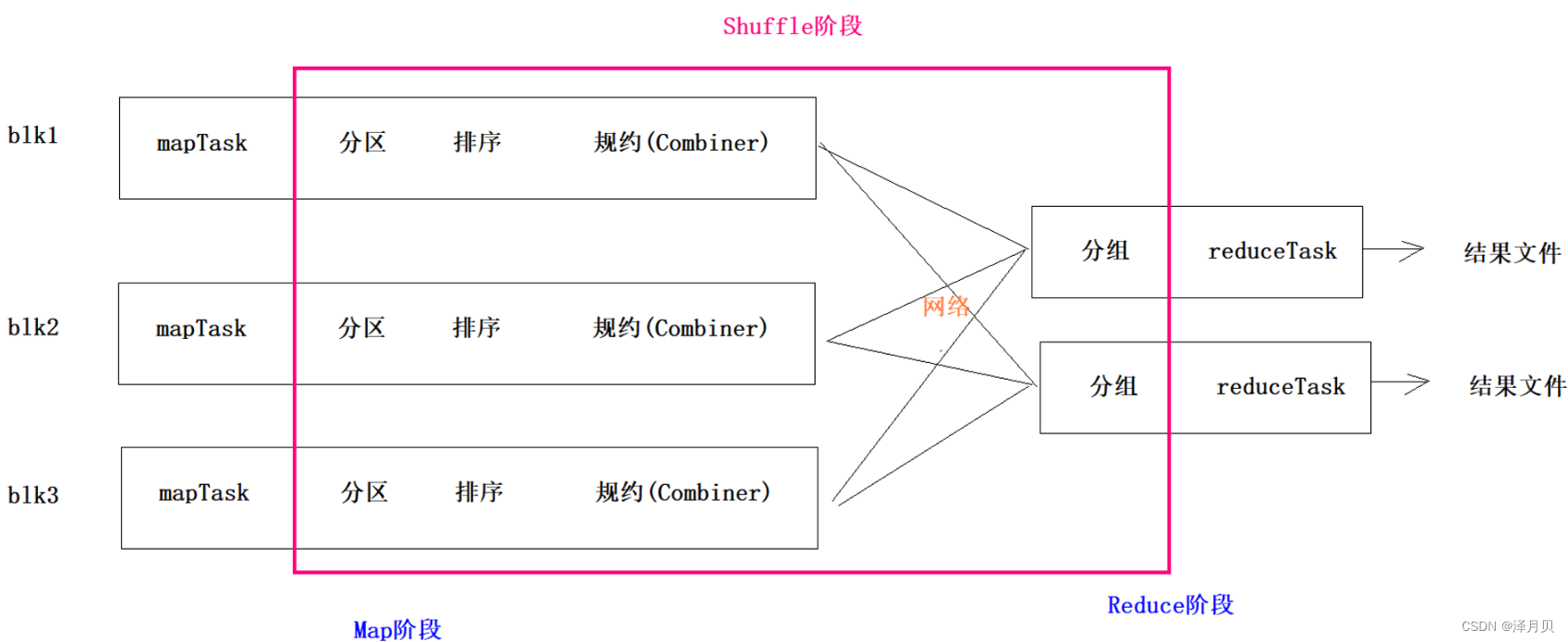
2.2 分区的意义
1、为了增加MR数据聚合的并行度,有时候需要增加Reduce的个数
2、增加Reduce之后,就要面临一个问题,哪些键值对由那个Reduce来聚合,需要定义一套规则,这套规则就是分区。
3、分区就是对每一个K2和V2键值对打标记,标记相同的键值对就会跑到同一个Reduce
4、如果你定义分区,系统有默认的分区机制
5、MR的默认分区是按照键K2进行分区
2.3 分区代码示例
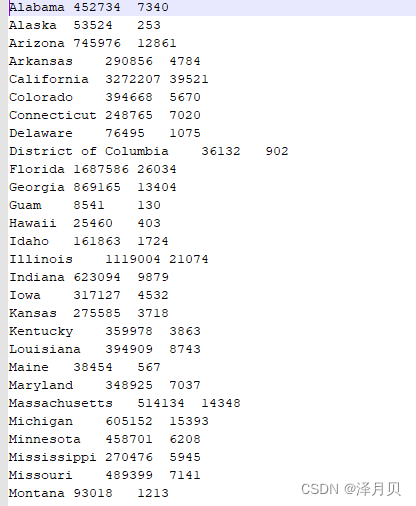
数据示例如下:
时间 县名 州名, 县编码 确诊人数 死亡人数
2021-01-28,Autauga,Alabama,01001,5554,69
2021-01-28,Baldwin,Alabama,01003,17779,225
2021-01-28,Barbour,Alabama,01005,1920,40
2021-01-28,Coffee,Alabama,01031,4795,72
2021-01-28,Colbert,Alabama,01033,5686,104
2021-01-28,Conecuh,Alabama,01035,999,23
2021-01-28,Coosa,Alabama,01037,670,19
2021-01-28,Covington,Alabama,01039,3504,87
2021-01-28,Crenshaw,Alabama,01041,1279,47
2021-01-28,Cullman,Alabama,01043,8466,145
2021-01-28,Dale,Alabama,01045,4235,92
2021-01-28,Dallas,Alabama,01047,3181,108
2021-01-28,Madison,Alabama,01089,29098,248
2021-01-28,Marengo,Alabama,01091,2152,34
2021-01-28,Petersburg Borough,Alaska,02195,43,0
2021-01-28,Prince of Wales-Hyder Census Area,Alaska,02198,69,1
2021-01-28,Sitka City and Borough,Alaska,02220,294,0
2021-01-28,Skagway Municipality,Alaska,02230,15,0
2021-01-28,Southeast Fairbanks Census Area,Alaska,02240,425,3
2021-01-28,Unknown,Alaska,,379,1
2021-01-28,Valdez-Cordova Census Area,Alaska,02261,433,2
2021-01-28,Wrangell City and Borough,Alaska,02275,24,0
2021-01-28,Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area,Alaska,02290,265,4
2021-01-28,Apache,Arizona,04001,9472,307
2021-01-28,Cochise,Arizona,04003,10324,220
...
...
...
代码示例如下:
--------------------Mapper-------------------
public class CovidMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 1.获取K2
// 1.1 对V1按照空格进行切割,获取的每个单词就是K2
String[] splitArray = value.toString().split(",");
if (splitArray.length!=6){
return;
}
context.write(new Text(splitArray[2]), value);
}
}
-------------------------Reducer--------------------------
public class CovidReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//1:获取K3-遍历 [V2],每个元素就是K3
//2:获取V3,就是NullWritable
for (Text k3 : values) {
//3:将K3和V3写入上下文中
context.write(k3, NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
---------------------------Partitioner(分区代码)---------------------
public class CovidPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, Text> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text k2, Text value, int i) {
return (k2.toString().hashCode() & 2147483647) % i;
}
}
-------------------------Driver(MRAppMaster)--------------------
public class CovidDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1:创建Job任务对象
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration, "covid_partitioner");
//2、设置置作业驱动类
job.setJarByClass(CovidDriver.class);
//3、设置文件读取输入类的名字和文件的读取路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("file:///D:\\input\\covid"));
//4:设置你自定义的Mapper类信息、设置K2类型、设置V2类型
job.setMapperClass(CovidMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//5.1 设置你的定义分区类
job.setPartitionerClass(CovidPartitioner.class);
//5.2 设置Reduce个数
//每一个reduce能够聚合的数据量是1G:hive.exec.reducers.bytes.per.reducer
job.setNumReduceTasks(56);
//6:设置你自定义的Reducer类信息、设置K3类型、设置V3类型
job.setReducerClass(CovidReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
//7、设置文件读取输出类的名字和文件的写入路径
//7.1 如果目标目录存在,则删除
String fsType = "file:";
String outputPath = "file:D:\\output\\covid";
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI(fsType), configuration);
boolean flag = fileSystem.exists(new Path(outputPath));
if (flag){
fileSystem.delete(new Path(outputPath));
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(outputPath));
//8、将设置好的job交给Yarn集群去执行
// 提交作业并等待执行完成
boolean completion = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(completion ? 0 : 1);
}
}
三、MapReduce的自定义案例
3.1 案例分析
数据同MapReduce分区案例数据
- 思路:
1、将州名作为K2,将确诊人数 死亡人数作为V2
2、可以将V2封装成一个Java类,如果一个自定义类出现在MapReduce中,必须保证该类能够被序列化和反序列化
自定义类,必须根据条件实现Writable/WritableComparable
- Writable
#应用场景:JavaBean类对象不作为K2,不需要能够被排序
public class CovidBean implements Writable {
//实现序列化
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
}
//实现反序列化
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
}
}
- WritableComparable
#应用场景:JavaBean类对象作为K2,需要能够被排序
public class CovidBean implements WritableComparable<CovidBean> {
//定义类对象排序的比较规则
@Override
public int compareTo(CovidBean o) {
return 0;
}
//实现序列化
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
}
//实现反序列化
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
}
}
3.2 代码示例
- 自定义类
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CovidBean implements Writable {
private int cases; //确诊人数
private int deaths; //死亡人数
public CovidBean(int cases, int deaths) {
this.cases = cases;
this.deaths = deaths;
}
public CovidBean() {
}
public int getCases() {
return cases;
}
public void setCases(int cases) {
this.cases = cases;
}
public int getDeaths() {
return deaths;
}
public void setDeaths(int deaths) {
this.deaths = deaths;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return + cases + "\t" + deaths;
}
//实现序列化:写
@Override
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeInt(cases);
dataOutput.writeInt(deaths);
}
//实现反序列化:读
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
this.cases = dataInput.readInt();
this.deaths = dataInput.readInt();
}
}
- Mapper
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CovidMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, CovidBean> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, CovidBean>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] arrays = value.toString().split(",");
if (arrays.length!=6){
return;
}
//得到k2
String k2 = arrays[2];
//得到v2
CovidBean v2 = new CovidBean(Integer.parseInt(arrays[4]), Integer.parseInt(arrays[5]));
//将k2,v2写入上下文
context.write(new Text(k2),v2);
}
}
- Reduce
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CovidReducer extends Reducer<Text, CovidBean, Text, CovidBean> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<CovidBean> values, Reducer<Text, CovidBean, Text, CovidBean>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
/*
K2 [V2]
Alabama {Covid(18919,234),Covid(383883,119)}
*/
//1:得到K3,K2就是K3,
//2:得到V3
int casesCount = 0;
int deathsCount = 0;
for (CovidBean value : values) {
casesCount += value.getCases(); //累加确诊病例
deathsCount += value.getDeaths(); //累加死亡病例
}
CovidBean covidBean = new CovidBean(casesCount, deathsCount);
//3:将K3和V3写入上下文中
context.write(key,covidBean);
}
}
- Driver
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
public class CovidDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1:创建Job任务对象
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration, "covid_bean_demo");
//2、设置置作业驱动类
job.setJarByClass(CovidDriver.class);
//3、设置文件读取输入类的名字和文件的读取路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
//4:设置你自定义的Mapper类信息、设置K2类型、设置V2类型
job.setMapperClass(CovidMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(CovidBean.class);
//5:设置分区、排序,规约、分组(保留)
//6:设置你自定义的Reducer类信息、设置K3类型、设置V3类型
job.setReducerClass(CovidReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(CovidBean.class);
//7.1 如果目标目录存在,则删除
String fsType = "file:///";
String outputPath = args[1];
URI uri = new URI(fsType);
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(uri, configuration);
boolean exists = fileSystem.exists(new Path(outputPath));
if (exists) {
fileSystem.delete(new Path(outputPath),true);
}
//8、设置文件输出路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(outputPath));
//8、将设置好的job交给Yarn集群去执行
// 提交作业并等待执行完成
boolean resultFlag = job.waitForCompletion(true);
//程序退出
System.exit(resultFlag ? 0 :1);
}
}
运行结果
四、排序
4.1 思路
1、MR的排序只能按照K2排序,哪个字段要参与排序,则哪个字段就应该包含在K2中
2、如果你自定义类作为K2,则必须指定排序规则,实现WritableComparable接口,重写compareTo方法,其他的地方不需要再做任何的设置
4.2 示例代码
与自定义类案例不同的是自定义类实现了WritableComparable,包含排序方法,排序方法会被自动调用,Mapper、Reducer、Driver类都没什么差别
- 自定义类
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CovidSortBean implements WritableComparable<CovidSortBean> {
private String state; //州名
private int cases; //确诊人数
private int deaths; //死亡人数
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public int getCases() {
return cases;
}
public void setCases(int cases) {
this.cases = cases;
}
public int getDeaths() {
return deaths;
}
public void setDeaths(int deaths) {
this.deaths = deaths;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return state + "\t" + cases + "\t"+deaths ;
}
//定义你的JavaBean对象的排序规则
/*
Alabama 452734 7340
Alaska 53524 253
Arizona 745976 12861
基于以上数据对确诊病例数进行降序排序,如果确诊病例数相同 ,则按照死亡病例数升序排序
select * from A order by cases desc , deaths asc;
我 > 他 返回大于0的值
我 < 他 返回小于0的值
我 = 他 返回等于0的值
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(CovidSortBean o) {
int result = this.cases - o.cases;
if(result == 0){
return this.deaths - o.deaths;
}
return result * -1;
}
//实现序列化
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(state);
out.writeInt(cases);
out.writeInt(deaths);
}
//实现反序列化
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.state = in.readUTF();
this.cases = in.readInt();
this.deaths = in.readInt();
}
}
五、MapReduce的串联
5.1 介绍
当我们在使用MapReduce进行大数据分析时,很多时候使用一个MR并不能完成分析任务,需要使用多个MR进行串联时,我们可以使用MR提供的Job控制器来实现多个MR的依赖串联执行

5.2 代码示例
将多个MR串联,Driver类发生了变化
- Driver
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.jobcontrol.ControlledJob;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.jobcontrol.JobControl;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.net.URI;
public class MapReduceSeriesJob {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1:创建Job任务对象
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
Job job1 = Job.getInstance(configuration, "covid_bean_demo");
//2、设置置作业驱动类
job1.setJarByClass(CovidDriver.class);
//3、设置文件读取输入类的名字和文件的读取路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job1, new Path(args[0]));
//4:设置你自定义的Mapper类信息、设置K2类型、设置V2类型
job1.setMapperClass(CovidMapper.class);
job1.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); //设置K2类型
job1.setMapOutputValueClass(CovidBean.class); //设置V2类型
//5:设置分区、排序,规约、分组(保留)
//6:设置你自定义的Reducer类信息、设置K3类型、设置V3类型
job1.setReducerClass(CovidReducer.class);
job1.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); //设置K3类型
job1.setOutputValueClass(CovidBean.class); //设置V3类型
//7、设置文件读取输出类的名字和文件的写入路径
//7.1 如果目标目录存在,则删除
String fsType = "file:///";
String outputPath = args[1];
URI uri = new URI(fsType);
FileSystem fileSystem =
FileSystem.get(uri, configuration);
boolean flag = fileSystem.exists(new Path(outputPath));
if(flag == true){
fileSystem.delete(new Path(outputPath),true);
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job1, new Path(outputPath));
//todo 将普通的作用包装成受控作业
ControlledJob cj1 = new ControlledJob(configuration);
cj1.setJob(job1);
//1:创建Job2任务对象
//configuration.set("参数名字","参数值");
Job job2 = Job.getInstance(configuration, "covid_sort_demo");
//2、设置置作业驱动类
job2.setJarByClass(CovidSortDriver.class);
//3、设置文件读取输入类的名字和文件的读取路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job2, new Path(args[1]));
//4:设置你自定义的Mapper类信息、设置K2类型、设置V2类型
job2.setMapperClass(CovidSortMapper.class);
job2.setMapOutputKeyClass(CovidSortBean.class); //设置K2类型
job2.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); //设置V2类型
//5:设置分区、排序,规约、分组(保留)
//6:设置你自定义的Reducer类信息、设置K3类型、设置V3类型
job2.setReducerClass(CovidSortReducer.class);
job2.setOutputKeyClass(CovidSortBean.class); //设置K3类型
job2.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); //设置V3类型
//7、设置文件读取输出类的名字和文件的写入路径
//7.1 如果目标目录存在,则删除
String fsType2 = "file:///";
String outputPath2 = args[2];
URI uri2 = new URI(fsType);
FileSystem fileSystem2 =
FileSystem.get(uri2, configuration);
boolean flag2 = fileSystem.exists(new Path(outputPath2));
if(flag2 == true){
fileSystem2.delete(new Path(outputPath2),true);
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job2, new Path(outputPath2));
//todo 将普通的作用包装成受控作业
ControlledJob cj2 = new ControlledJob(configuration);
cj2.setJob(job2);
//todo 设置作业之间的依赖关系
cj2.addDependingJob(cj1);
//todo 创建主控制器 控制上面两个作业 一起提交
JobControl jc = new JobControl("myctrl");
jc.addJob(cj1);
jc.addJob(cj2);
//使用线程启动JobControl
Thread t = new Thread(jc);
t.start();
while (true){
if(jc.allFinished()){
System.out.println(jc.getSuccessfulJobList());
jc.stop();
break;
}
}
}
}
六、MapReduce的分组
- 需求
找出美国每个州state的确诊案例数最多的县county是哪一个。 - 思路
1、写类继承 WritableComparator,重写Compare方法。
2、Driver类中job.setGroupingComparatorClass(xxxx.class); - 代码示例
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
//1:自定义类去继承WritableComparator类
public class MyGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator {
//2:编写无参构造,将你的自定义类传给父类
/*
参1:表示传给父类的JavaBean类型
参2:表示允许父类通过反射造子类对象
*/
public MyGroupingComparator() {
super(GroupingBean.class,true);
}
//3:在方法中指定分组的规则:两个GroupingBean对象只要你们的state(州)是一样的,就应该分到同一组
//这个方法会被自动调用,只要该方法返回0,则两个GroupingBean对象就分到同一组
@Override // GroupingBean GroupingBean
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
GroupingBean g1 = (GroupingBean) a;
GroupingBean g2 = (GroupingBean) b;
//如果g1和g2的州state同,则应该return 0,则这两个对象就会被分到同一组
//if(g1.getState().equals(g2.getState())) {
// return 0;
//}else{
// return 1;
//}
return g1.getState().compareTo(g2.getState());
}
}
总结
MapReduce 就是氛围三块,map拆分,reduce聚合,还有一个主类,然后根据需求加上自定义分区、规约、分组、排序。





















 342
342











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








